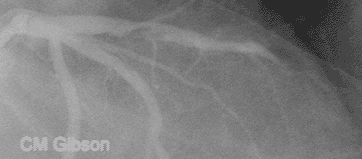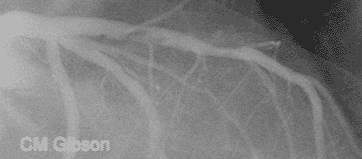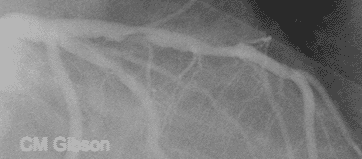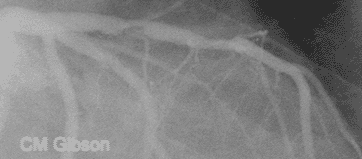
What is the difference in the treatment between a STEMI and NSTEMI?
A STEMI or ST-elevation myocardial infarction is caused by a sudden complete (100 percent) blockage of a heart artery (coronary artery). A non-STEMI is usually caused by a severely narrowed artery but the artery is usually not completely blocked. The diagnosis is initially made by an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG).
Is a NSTEMI the same thing as unstable angina?
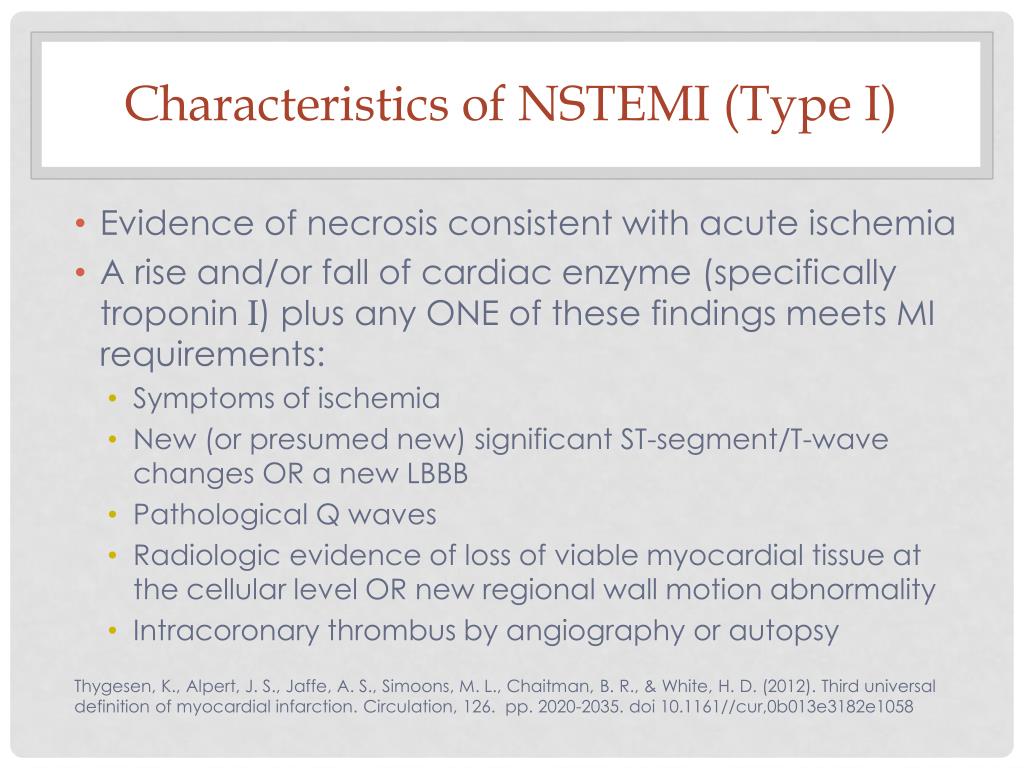
This underlines the importance of prompt diagnosis and intervention. NSTEMI and unstable angina are different in one fundamental aspect: NSTEMI is by definition an acute myocardial infarction, whereas unstable angina is not an infarction. Unstable angina is only diagnosed if there are no evidence of myocardial infarction (necrosis).
Why is the difference in treatment between STEMI and NSTEMI?
Treat them differently. Now, in terms of treatment between NSTEMI and STEMI, the difference in it lies on the pathophysiology. NSTEMI's are thought to be due to partial obstructions of the artery which causes the surface muscle to become ischaemia. Let's ponder this for a second.
Is a NSTEMI a heart attack?
Yes, NSTEMI is a type of heart attack that is relatively mild. It occurs when there is a partial obstruction of a major coronary artery or a complete blockage of a minor coronary artery.

Is NSTEMI heart attack?
A non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) is a type of heart attack that usually happens when your heart's need for oxygen can't be met. This condition gets its name because it doesn't have an easily identifiable electrical pattern (ST elevation) like the other main types of heart attacks.
What causes a NSTEMI?
The etiology of NSTEMI varies as there are several potential causes. These include tobacco abuse, lack of physical activity, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, and family history.
What is the difference between STEMI and NSTEMI?
STEMI results from complete and prolonged occlusion of an epicardial coronary blood vessel and is defined based on ECG criteria..NSTEMI usually results from severe coronary artery narrowing, transient occlusion, or microembolization of thrombus and/or atheromatous material.
How is NSTEMI treated?
Drug treatment is used for those who are low risk who've had an NSTEMI. Medications that may be given include anticoagulants, antiplatelets, beta-blockers, nitrates, statins, angiotensin-converting-enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
Can NSTEMI lead to death?
Deaths due to post resuscitation status and heart failure were more frequent in NSTEMI within 6 months after AMI.
Does NSTEMI mean heart failure?
A Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction is a type of heart attack, often referred to as NSTEMI or a non-STEMI. In medical terminology, a heart attack is a myocardial infarction. An NSTEMI is a less severe form of heart attack than the STEMI because it inflicts less damage to the heart.
How long can you live after a NSTEMI?
After adjusting for baseline differences in age, sex, length of stay, comorbidities, hospital clinical complications, and physiologic variables, patients with STEMI were significantly more likely to have survived at 3 months (OR 1.38; 95% CI 1.01–1.87), 1 year (OR 1.38; 95% CI 1.09–1.74), and 2 years (OR 1.53; 95% CI ...
What happens to the heart during NSTEMI?
Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) is a type of involving partial blockage of one of the coronary arteries, causing reduced flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle.
Is NSTEMI less serious?
An NSTEMI can be less serious than an STEMI because the supply of blood to the heart may be only partially, rather than completely, blocked. As a result, a smaller section of the heart may be damaged. However, an NSTEMI is still regarded as a serious medical emergency.
How long is a NSTEMI considered acute?
❖ Myocardial Infarction (MI) o Acute Myocardial Infarction: A new MI is considered acute from onset up to 4 weeks post MI.
What meds are given for NSTEMI?
Heparins, such as unfractionated heparin (UFH) and low-molecular weight heparins (LMWH) have been used in patients with NSTEMI for more than a decade. UFH is proven to reduce the rate of death and MI in multiple trials [65], especially when given in combination with aspirin, though with some increased risk of bleeding.
Does NSTEMI require surgery?
Heart attacks are often frightening. They can be fatal and cause long-term health consequences, including a reduced lifespan. This applies to an NSTEMI, even though it is a less severe type of heart attack than a STEMI. Medication and surgery may help treat an NSTEMI.
How long can you live after a NSTEMI?
After adjusting for baseline differences in age, sex, length of stay, comorbidities, hospital clinical complications, and physiologic variables, patients with STEMI were significantly more likely to have survived at 3 months (OR 1.38; 95% CI 1.01–1.87), 1 year (OR 1.38; 95% CI 1.09–1.74), and 2 years (OR 1.53; 95% CI ...
Is NSTEMI less serious?
An NSTEMI can be less serious than an STEMI because the supply of blood to the heart may be only partially, rather than completely, blocked. As a result, a smaller section of the heart may be damaged. However, an NSTEMI is still regarded as a serious medical emergency.
How Is A Nstemi Diagnosed?
In addition to signs such as chest pain, a heart attack is diagnosed mainly through 2 ways. Firstly is a blood test that shows elevated levels of c...
Treatment of Non St Segment Myocardial Infarction
Once NSTEMI has been suggested, a cardiologist who can help determine the risk and the treatment strategy will typically see a patient. An echocard...
Prognosis – Life After An Nstemi
A NSTEMI is a heart attack, so the treatment of that applies. Medicines are prescribed that have been proven to save lives in the long term for hea...
Why Does My Hospital Discharge Paperwork Say Nstemi but No-One Told Me About A Heart Attack?
Part of the way of diagnosing a NSTEMI is by a blood test called troponin that is indicative of heart damage. Although the troponin test is great i...
STEMI vs Nstemi – Which Is Worse?
The bottom line is that both are just as bad. STEMI is seen as more of an immediate emergency because there is a known total occlusion of a heart v...
What does NSTEMI stand for?
Overview. NSTEMI stands for non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction, which is a type of heart attack. Compared to the more common type of heart attack known as STEMI, an NSTEMI is typically less damaging to your heart.
How to diagnose NSTEMI?
Diagnosing an NSTEMI. NSTEMI is diagnosed through a blood test and an ECG. The blood test will show elevated levels of creatine kinase-myocardial band (CK-MB), troponin I, and troponin T. These markers are evidence of possible damage to the heart cells, and are typically mild compared with STEMI. However, blood tests alone can’t diagnose ...
What does STEMI mean in heart attack?
partial blockage of the coronary artery. A STEMI will show: elevated ST wave. progression to Q wave. full blockage of the coronary artery. Both types of heart attack are considered acute coronary syndromes, a term that describes any blockage of blood supply to the heart muscle. As a result, NSTEMI and STEMI can lead to damage of the heart tissue.
How to tell if you have NSTEMI?
Symptoms of NSTEMI include: shortness of breath. pressure, tightness, or discomfort in your chest. pain or discomfort in your jaw, neck, back, or stomach. dizziness. lightheadedness.
How to prevent NSTEMI?
Lowering your risk factors can help prevent NSTEMI. Lifestyle changes will have the biggest impact on your heart health. Focus on: eating a well-balanced, heart-healthy diet that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats. limiting intake of saturated and trans fats.
Is NSTEMI more likely to be acute?
You’re much more likely to experience acute coronary syndrome such as NSTEMI if you have the following risk factors:
What does NSTEMI stand for?
NSTEMI is a type of heart attack. NSTEMI stands for Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Sometimes an NSTEMI is known as a non-STEMI. A myocardial infarction is the medical term for a heart attack. ST refers to the ST segment, which is part of the EKG heart tracing used to diagnose a heart attack.
How to treat NSTEMI?
A NSTEMI is a heart attack, so the treatment of that applies. Medicines are prescribed that have been proven to save lives in the long term for heart attack sufferers. Depending on factors such as symptoms and heart function, a number of medicines may be prescribed. Lifestyle changes and modification of risk factors is key in preventing recurrence. It is important for smokers to stop smoking. Blood pressure controland control of diabetesare key. A post-heart attack exercise planshould be incorporated into a daily lifestyle if possible. Often NSTEMI patients will be sent to cardiac rehab to receive education on the important of exerciseand begin a program in a supervised environment.
How to diagnose NSTEMI?
Part of the way of diagnosing a NSTEMI is by a blood test called troponin that is indicative of heart damage. Although the troponin test is great in that it does not miss heart attacks, it is not specific for heart attacks alone. Basically, there are other problems that can cause an elevated troponin level. Many patients with critical illnesses, infections and kidney diseaseamong many other conditions can have an elevated troponin that is not related to heart blockage. In these cases, although sometimes it is labeled NSTEMI, there is no concern for underlying critical heart blockage.
What is the treatment for NSTEMI?
An echocardiogrammay be ordered to look at the heart functioning. Initially, blood-thinning agentswill be given such as aspirinand the blood thinner heparin. These medicines have been proven to improve outcomes in patients with NSTEMI. There may be other medicines given such as a beta-blocker or nitrates.
Can Adderall cause NSTEMI?
look up Takatsubo Cardiomyopathy. Also, for young people, cocaine, meth and alcohol and some prescription drugs such as Adderall can precipitate a NSTEMI.
Is STEMI or NSTEMI the same?
In terms of long-term outcomes, they have equal health implications. Patients with NSTEMI often have other illnesses such as ongoing critical illness, diabetes, kidney disease, and other that means they have a generally high risk over the long term. Both STEMI and NSTEMI need aggressive treatment over the short and long term.
What is a NSTEMI?
NSTEMI or non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction is a type of heart attack. An NSTEMI differs from a STEMI, which is the most common type of heart attack, by causing less damage to a person’s heart. An electrocardiogram or ECG that displays each heartbeat as a waveform is used to determine if an NSTEMI or a STEMI has occurred in a person.
How to know if you have NSTEMI?
The following are symptoms of an NSTEMI: feeling short of breath. pressure, tightness, or discomfort in the chest. pain or tightness in the jaw, neck, back, or stomach. dizziness or a feeling of lightheadedness. experiencing nausea. excessive sweating.
How to reduce the risk of NSTEMI?
Steps people can take to reduce their risk of an NSTEMI include: having a healthy, nutritious, and balanced diet, including fruits, vegetables, healthy fats, and whole grains.
Is NSTEMI a heart attack?
Heart attacks are often frightening and are considered serious. This applies to an NSTEMI even though it is considered a less severe type of heart attack than a STEMI. Medication and, in some cases, surgery, may be required to treat an NSTEMI.
Why is NSTEMI called NSTEMI?
During a heart attack, the ST-segment is raised. As such, NSTEMI gets its name because there is no evidence of ST-segment elevation. Because NSTEMI causes damage to the heart muscle, doctors still consider it a heart attack (some might say a "mild" heart attack).
What is NSTEMI treatment?
Emergency Treatment. NSTEMI treatment is identical to that for unstable angina. If you have cardiac symptoms (chest tightness, clamminess of the skin, shooting pains in the left arm, etc.), the doctor will begin intensive therapy to stabilize the heart and prevent further damage.
What are the criteria for a TIMI score?
The TIMI score assesses whether the person has any of the following risk factors: 1 Age 65 years or older 2 Presence of at least three risk factors for coronary heart disease 3 Prior coronary blockage of greater than 50% 4 ST-segment deviation on the admission ECG 5 At least two angina episodes in the past 24 hours 6 Elevated cardiac enzymes 7 Use of aspirin within the past seven days
How to tell if a patient has NSTEMI or STEMI?
Doctors can differentiate STEMI from NSTEMI via readings on an electrocardiogram (ECG) in the so-called "ST -segment." Under normal conditions, the ST-segment is the flat line you see on an ECG between heartbeats.
What is a TIMI score?
Many cardiologists will use a TIMI (thro mbosis in myocard ial infarction) score to determine the likely outcome for the individual. The TIMI score assesses whether the person has any of the following risk factors: Age 65 years or older. Presence of at least three risk factors for coronary heart disease.
Can you use aspirin for a TIMI score of 0-2?
Elevated cardiac enzymes. Use of aspirin within the past seven days. If you have two risk factors or less (TIMI score 0-2), you may not need further intervention. If the score is higher, the cardiologist may want to perform a cardiac catheterization with angioplasty and stenting.
Does NSTEMI cause STEMI?
NSTEMI rarely leads to STEMI because they have different mechanisms of action. NSTEMI is more likely in people with diffuse coronary disease, who often have collateral vessel development. People with STEMI are less likely to have that sort of diffuse disease or collateral vessel development.
What is an NSTEMI?
A Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction is a type of heart attack, often referred to as NSTEMI or a non-STEMI. In medical terminology, a heart attack is a myocardial infarction. An NSTEMI is a less severe form of heart attack than the STEMI because it inflicts less damage to the heart. However, both are heart attacks and require immediate medical care.
How to diagnose NSTEMI?
Diagnosis. NSTEMI heart attacks are diagnosed through the combination of a blood test and an electrocardiogram (ECG). Doctors use the blood test to look for indications of NSTEMI, such as higher than usual levels of creatine kinase-myocardial band (CK-MB), troponin I, and troponin T.
How to tell if you have NSTEMI?
Symptoms of NSTEMI: Difficulty or trouble breathing. Heaviness or pressure in your chest. Tension or tightness in your che st. Discomfort in your che st. Pain or irritation in your neck. Pain or irritation in your stomach. Pain or irritation in your jaw. Pain or irritation in your back.
Is NSTEMI a heart attack?
NSTEMI produces several symptoms similar to other conditions. Any symptoms associated with a heart attack are serious. Anyone experiencing any of the NTEMI symptoms should contact 911 or visit an emergency room immediately, regardless of severity. With heart attacks, every minute counts.
Why does NSTEMI occur?
Finally, conditions relatively unrelated to the coronary arteries or myocardium itself such as hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, aortic stenosis, and pulmonary embolism lead to NSTEMI because the increased oxygen demand cannot be met. [4][5] History and Physical.
What are the outcomes of NSTEMI?
The outcomes of patients with NSTEMI depend on the severity of the myocardial injury, compliance with treatment and other comorbidities. Patients who do not change their risk factors for the coronary disease have a poor outcome. [15][16](Level V)
What causes ACS in STEMI?
While the cause of this mismatch in STEMI is nearly always coronary plaque rupture resulting in thrombosis formation occluding a coronary artery, there are several potential causes of this mismatch in NSTEMI. There may be a flow-limiting condition such as a stable plaque, vasospasm as in Prinzmetal angina, coronary embolism, or coronary arteritis. Non-coronary injury to the heart such as cardiac contusion, myocarditis, or presence of cardiotoxic substances can also produce NSTEMI. Finally, conditions relatively unrelated to the coronary arteries or myocardium itself such as hypotension, hypertension, tachycardia, aortic stenosis, and pulmonary embolism lead to NSTEMI because the increased oxygen demand cannot be met. [4][5]
What is the initial management strategy for ACS?
Initial management strategies aim to reduce cardiac ischemia and prevent death. Oxygen, aspirin, and nitrates are administered based on initial concern for ACS and prior to a definitive diagnosis. Subsequent treatment depends on confirmation of diagnosis or a high index of suspicion with or without a definitive diagnosis. [1][9][10][11][12]
Is ACS a ST-segment elevation?
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) can be divided into subgroups of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), and unstable angina. ACS carries significant morbidity and mortality and the prompt diagnosis, and appropriate treatment is essential. STEMI diagnosis and management are discussed elsewhere. NSTEMI and Unstable angina are very similar, with NSTEMI having positive cardiac biomarkers. The presentation, diagnosis, and management of NSTEMI are discussed below. [1][2][3]
When should beta blocker therapy be started for NSTEMI?
Beta-blocker therapy should be started within 24 hours after the presentation in patients who do not have a contraindication.
Is a physical exam for ACS or NSTEMI?
Physical Exam for ACS and NSTEMI is often nonspecific. Clues such as back pain with aortic dissection or pericardial friction rub with pericarditis may point to an alternative diagnosis for a patient’s chest pain, but no such exam finding exists that indicates ACS as the most likely diagnosis. Signs of heart failure should increase concern for ACS but are, again, nonspecific findings. [6][7][8]
How effective is aspirin for NSTEMI?
Aspirin has an astonishing effect in NSTEMI and unstable angina: it reduces 30-days mortality by 50%. Aspirin is also effective in preventing re-infarction beyond 30-days and must never be discontinued without careful consideration. The optimal dose of aspirin is unknown but studies show that maintenance doses between 80 mg and 1500 mg are equally effective; hence, 80 mg is preferred as it minimizes the risk of gastrointestinal bleedings. Similarly, loading doses greater than 320 mg do not confer any additional benefit, which is why a loading dose of 320 mg is recommended.
How is unstable angina different from NSTEMI?
NSTEMI and unstable angina are different in one fundamental aspect: NSTEMI is by definition an acute myocardial infarction, whereas unstable angina is not an infarction. Unstable angina is only diagnosed if there are no evidence of myocardial infarction (necrosis). However, unstable angina is considered an acute coronary syndrome because it is an imminent precursor to myocardial infarction. Approximately 50% of patients with unstable angina progress to myocardial infarction within 30 days if left untreated. Moreover, the pathophysiology of NSTEMI and unstable angina is very similar: both are due to partial (incomplete) coronary artery occlusions, which implies that there remains residual blood flow in the artery. Moreover, management of NSTEMI and unstable angina is virtually equal and this explains why NSTEMI and unstable angina have traditionally been grouped together.
What causes ST segment depression?
NSTEMI and unstable angina typically cause ST segment depressions, which are frequently accompanied by negative (inverted) T-waves or flat T-waves. Importantly, leads which display ST depressions do not necessarily reflect the ischemic area. This implies that ST depressions in leads V3–V4 are not necessarily due to anterior wall ischemia. Similarly, ST depressions in leads II, aVF and III does not imply that the ischemia is located to the inferior wall. In other words, ST depressions do not localize the ischemic area and therefore the ECG cannot be used to determine the location of ischemia in patients with NSTEMI or unstable angina. This contrasts against ST elevations, which are indicative of the ischemia area (refer to Localization of Acute Myocardial Ischemia and Infarction for details).
What percentage of myocardial infarctions are caused by STEMI?
The incidence of STEMI has declined gradually since then. Currently, STEMI represents 25–40% of all cases of acute myocardial infarction. During the same period, NSTEMI increased from 50% to 60–75% of all infarctions. This is explained by the implementation of increasingly sensitive biomarker (troponin) assays for detection of myocardial necrosis (i.e infarction). In 2017 it was possible to detect myocardial infarctions 100 times smaller than what was possible in 2001. Hence, many patients who would have previously been diagnosed as unstable angina are nowadays classified as NSTEMI. It is expected that the proportion classified as unstable angina will continue to decline as troponin assays become more sensitive.
What is ischemia ST depression?
Ischemic ST depressions are characterized by a horizontal or downsloping ST segment. North American and European guidelines assert that the ST segment must be either downsloping or horizontal, otherwise ischemia is unlikely to be the cause ( Figure 5 ). An in-depth discussion on ST depressions are provided in the chapter ST Segment Depressions in Ischemia and Infarction.
What does RCA mean in a STEMI?
Figure 4. Acute, sub-acute and long-term complications of acute (STEMI) and myocardial infarction in general. RCA = Right Coronary Artery. Adapted from GW Reed et al, The Lancet (2017).
Can NSTE-ACS show normal ECG?
Most patients with normal ECG on arrival will develop some ECG changes during the process. Moreover, a normal ECG on arrival does not rule out myocardial ische mia/infarction ; some infarctions are too small to engender ECG changes and others may be dynamic over time and initially present without ECG changes.
What is a NSTEMI heart attack?
NSTEMI heart attack refers to non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction. NSTEMI heart attacks occur due to the complete blockage or closure of a minor coronary artery, or partial blockage or closure of a major artery that was previously affected by atherosclerosis. (for comparison, STEMI is the complete blockage of a major artery that could have been affected by atherosclerosis ).
Why is STEMI treated?
Emergency treatment is required in order to immediately restore blood flow to the heart. Initial treatment for a STEMI heart attack is aimed at fixing the cause. In the majority of cases, STEMI heart attack is due to a complete blockage of an artery, so unblocking the artery and restoring blood flow is the first course of treatment.