
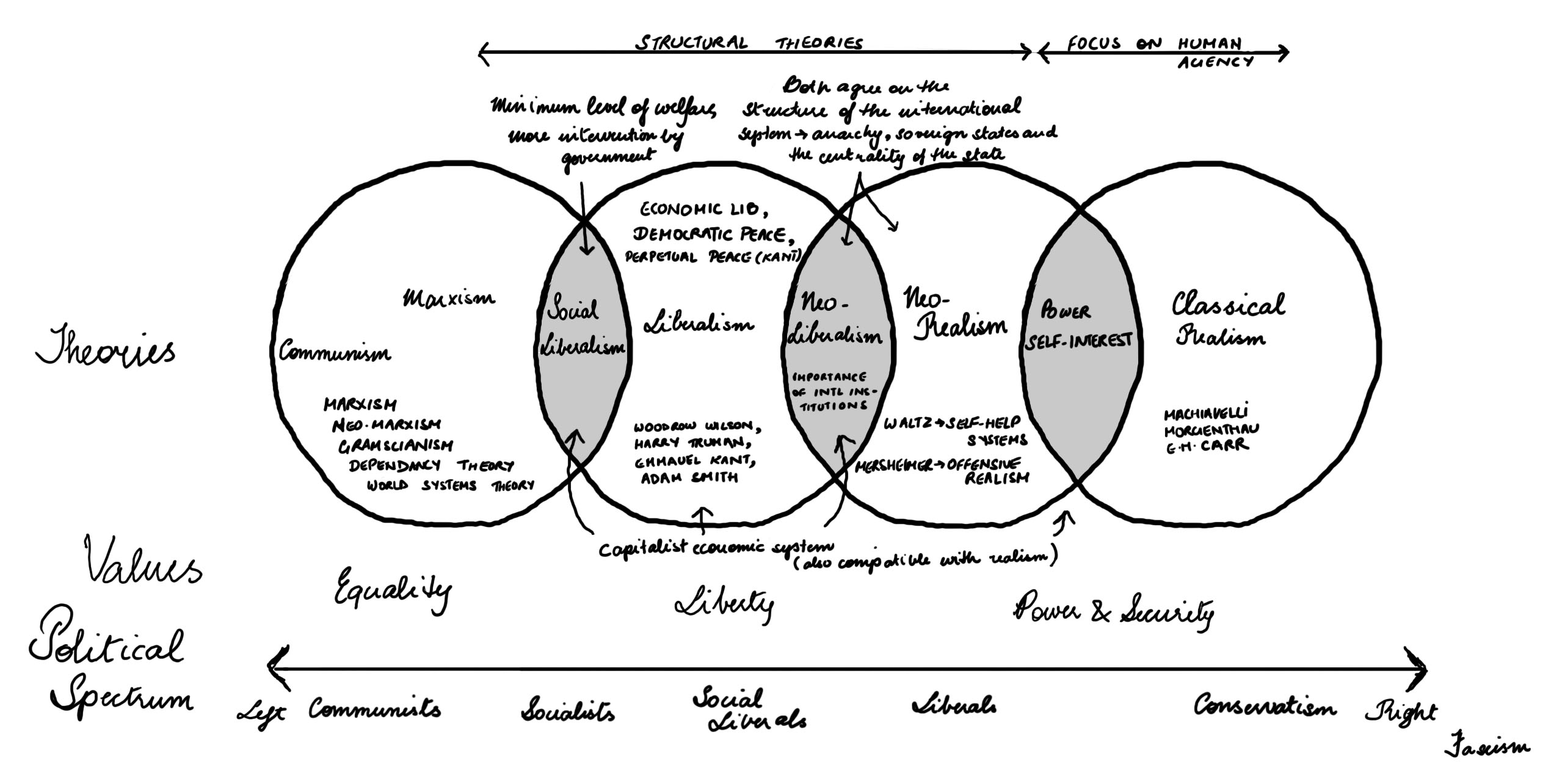
What is object-relationship theory?
In object relations theory, the word "object" refers to a person. The "object" played a major role in that person's life when they were an infant or small child, such as a parent. An approach based on object relations theory can benefit your current well-being. Wondering If Object-Relationship Therapy Can Help You Relationship? Get Answers.
What are object relations?
Objects refer to people, parts of people, or physical items that symbolically represent either a person or part of a person. Object relations, then, are our relationships to those people or items. We explore how you are affected and what your relationship with your mother may say about your future in relationships.
What is Klein's object relations theory?
Since Klein's theory focuses on connections between people and situations, the goal of object relations therapy is to help a person uncover early life experiences that may contribute to their current relationships.
Who is the founder of object relations theory?
Karl Abraham, Margaret Mahler, and Melanie Klein are among those credited with its origination and refinement. Object relations theory is sometimes used in the treatment of phobias, particularly those that focus on people, or our relationships with them.
What is object relations theory example?
The theory suggests that the way people relate to others and situations in their adult lives is shaped by family experiences during infancy. For example, an adult who experienced neglect or abuse in infancy would expect similar behavior from others who remind them of the neglectful or abusive parent from their past.
What are the four stages of object relations theory?
The separation-individuation process proper is broken down into four sub-phases: differentiation, practicing, rapprochement, and on the road to object constancy.
What are the goals of object relations theory?
Goals of Object Relations Therapy During Object Relations Therapy treatment consists of various techniques used so that the client holds a neutral position in how they view others. The goal is to see people and the world around them in a neutral manner instead of attaching their world to this behavioral object.
Why is it called object relations theory?
The term “object relations” refers to the dynamic internalized relationships between the self and significant others (objects). An object relation involves mental representations of: The object as perceived by the self.
What is object relations theory quizlet?
Object Relations Theory. Focuses on the reciprocal relationship between a Mother and her infant and its effect on the infants development of sense of self. Object Relations concepts. refers to the way a child's Ego becomes organized over the first 3 1/2 years of life.
What are the major constructs concepts of Klein's theory?
Klein's theory emphasized the idea of objects, which are related to human contact during infancy. The most important objects to a child are the mother and the mother's breast. According to Klein, infants are born with an unconscious fantasy life.
What is Margaret Mahler's theory?
In Mahler's theory, child development takes place in phases, each with several sub phases: Normal autistic phase – First few weeks of life. The infant is detached and self-absorbed. Spends most of his/her time sleeping. Mahler later abandoned this phase, based on new findings from her infant research.
What is splitting in object relations theory?
Splitting. Central to object relations theory is the notion of splitting, which can be described as the mental separation of objects into "good" and "bad" parts and the subsequent repression of the "bad," or anxiety-provoking, aspects (Klein, 1932; 1935).
What is object relations theory?
Object relations theory is centered on our internal relationships with others. According to this theory, our lifelong relationship skills are strongly rooted in our early attachments with our parents, especially our mothers.
What is an external object?
External and Internal Objects. An external object is an actual person or thing that someone invests in with emotional energy. A whole object is a person as she actually exists, with all of the positive and negative traits that she embodies.
What are the three things that a child experiences in relationship to the mother and father?
Father, mother, and infant, all three living together: The dynamics and interactions that the child experiences in relationship to the mother and father influence the child's experience and expectations of what family relationships will be like later in life. Holding: Actual physical affection and holding including cuddling, holding hands, ...
When do infants learn object constancy?
Infants begin to learn object constancy when their parents leave for a short time and then return. As children mature, they begin to spend longer periods of time away from their parents. Separation anxiety and fear of abandonment are common in people who have not successfully developed a sense of object constancy.
What is an object relation?
The term “object relations” refers to the dynamic internalized relationships between the self and significant others (objects). An object relation involves mental representations of: For example, an infant might think: "My mother is good because she feeds me when I am hungry" (representation of the object).
Why is object relations important?
Object relations theorists stress the importance of early family interactions, primarily the mother-infant relationship, in personality development. It is believed that infants form mental representations of themselves in relation to others and that these internal images significantly influence interpersonal relationships later in life. Since relationships are at the center of object relations theory, the person-therapist alliance is important to the success of therapy.
Who Practices Object Relations?
Psychologists, psychotherapists, counselors, and social workers may earn certification in object relations therapy from one of several training institutions across the country. For example, the International Psychotherapy Institute (IPI), formerly the International Institute of Object Relations Theory, offers a two-year certificate program in Object Relations Theory and Practice for professionals involved in the mental health field. The Object Relations Institute for Psychotherapy and Psychoanalysis offers a one-year introductory certificate program in object relations theory and clinical technique, as well as a more advanced two-year program. The Ottawa Institute for Object Relations Therapy also certifies psychotherapists in Object Relations Therapy.
What can a therapist do to help people with childhood object relations?
A therapist can help people in therapy understand how childhood object relations impact current emotions, motivations, and relationships and contribute to any problems being faced.
Why do people engage in object relations therapy?
Once critical symptoms are dealt with, however, an individual may choose to engage in object relations therapy to determine how past relationships with significant others might contribute to present concerns.
What is the relationship between self and object?
For example, an infant might think: "My mother is good because she feeds me when I am hungry" (representation of the object). "The fact that she takes care of me must mean that I am good" (representation of the self in relation to the object).
Who are the three main authors of object relations?
Object relations theory is composed of the diverse and sometimes conflicting ideas of various theorists, mainly Melanie Klein, Ronald Fairbairn, and Donald Winnicott . Each of their theories place great emphasis on the mother-infant bond as a key factor in the development of a child’s psychic structure during the first three years of life.
What is object relations theory?
Object relations theory in psychoanalytic psychology is the process of developing a psyche in relation to others in the childhood environment. It designates theories or aspects of theories that are concerned with the exploration of relationships between real and external people as well as internal images and ...
Who wrote the object relation theory of personality?
Fairbairn, W. R. D. (1952). An Object-Relations Theory of the Personality. New York: Basic Books.
What is the effect of introjection on object relations?
The effect of introjection on object relations is equally important. The introjection of the good object, first of all the mother’s breast, is a precondition for normal development . . . It comes to form a focal point in the ego and makes for cohesiveness of the ego. . . .
Why is the introduction of the good object important?
Introjection of the good object is also used by the ego as a defense against anxiety. . . . The processes of splitting off parts of the self and projecting them into objects are thus of vital importance for normal development as well as for abnormal object-relation.
What is the conflict of loyalties between Klein and object relations theory?
Within the London psychoanalytic community, a conflict of loyalties took place between Klein and object relations theory (sometimes referred to as "id psychology"), [10] and Anna Freud and ego psychology. In America, Anna Freud heavily influenced American psychoanalysis in the 1940s, 1950s, and 1960s. American ego psychology was furthered in the ...
What is the first object in a person?
The first "object" in someone is usually an internalized image of one's mother. Internal objects are formed by the patterns in one's experience of being taken care of as a baby, which may or may not be accurate representations of the actual, external caretakers.
When does the child's central ego relate to the Ideal object?
The child's central ego relates to the Ideal object when the parent is supportive and nurturant.
What is object relations therapy?
The goal of object relations therapy is to help people improve relationships by improving the way they function internally. A therapist will review patients' childhood object relations to see how those interactions may influence their current relationships.
How does object relations therapy help with relationships?
You might feel like you are investing a lot of time into your relationships, but you might not use that time effectively if you are viewing your relationships through an incorrect lens. Most theorists believe that your earliest interactions as a child play a large part in how you view your current relationships. So if you are struggling now, it may be directly linked to the way you viewed relationships as a child. Object relations therapy can improve current relationships by addressing unhealthy patterns from the past.
What is Melanie Klein's theory of child psychics?
Melanie Klein is most often credited with founding object relations therapy. Her theory focuses on the first few months of a child's life.
Is object relations therapy a quick fix?
Object relations therapy is not a quick fix. The treatment is designed to deal with deep-seated issues. The approach tends to be non-directive; this therapy is not well suited for individuals who are looking for quick results.
What Are Object Relations?
Object relations is a theory that people have about how they relate to the things around them. It’s based on your own memories and experiences. If you have a good memory of your childhood blanket, you might feel attached to or drawn to blankets when you are an adult.
Conclusion
Object relations psychology explores how our early relationships with objects affect our adult lives. It can be used in psychotherapy when patients try to understand themselves better by exploring why they relate things back to specific times from their pasts.
A Word From Mantra Care
Your mental health — your psychological, emotional, and social well-being — has an impact on every aspect of your life. Positive mental health essentially allows you to effectively deal with life’s everyday challenges.
Which theory of unconscious phantasy is linked to the conceptualisation of internal objects?
The conceptualisation of internal objects is linked to Klein’s theory of unconscious phantasy, and development from the paranoid-schizoid position to the depressive position
What is Klein's theory of the unconscious?
Klein’s (1921) theory of the unconscious focused on the relationship between the mother–infant rather than the father–infant one, and inspired the central concepts of the Object Relations School within psychoanalysis. Klein stressed the importance of the first 4 or 6 months after birth.
What is the theory of unconscious phantasy?
Developing a Theory of Unconscious Phantasy. Klein’s (1923) theory of the unconscious is based in the phantasy life of the infant from birth. Her ideas elucidated how infants processed their anxieties around feeding and relating to others as objects and part-objects.
Why was Klein rejected?
Psychoanalyst Jaqueline Rose (1993) has noted that, especially in the USA, Klein’s work has been rejected because of her violence and negativity. Klein herself wrote: ‘My method presupposes that I have been from the beginning willing to attract to myself the negative as well as the positive transference’.
What is the meaning of the phrase "the ego is incapable of splitting the object"?
Klein wrote that ‘The Ego is incapable of splitting the object – internal and external – without a corresponding splitting taking place within the Ego...

The Fundamentals of Object Relations Theory
- In object relations theory, therapists help people identify patterns in their lives that may be impacting their relationships with others. Therapists refer to significant others in a person’s life, particularly a person’s primary caregiver (mother, father, etc.) as the object in object relations theory. The focus of this kind of treatment centers around early attachment relationships betwe…
The Goal of Object Relations Therapy
- The key to object relations therapy is to help a person begin to develop insight into problematic patterns in their interpersonal life, and to help them better understand these issues and how to improve them. Helping shed light onto how very early attachment related concepts may have impacted their ability to function in their current relationships can help a person understand the…
Conditions Treated with Object Relations
- Object relations is a psychological theory that deals with helping a person safely uncover deeply repressed psychological patterns, which can be difficult for many people to be motivated to do, or to tolerate. This type of therapy has been successful in the treatment of addictions, personality disorders, and other cases where a person may be cravin...
Final Thoughts
- If you are someone who with patterns of feeling stuck in your relationships or has a history of highly conflictual relationships, mood swings, and addiction-related symptoms, a psychoanalytic approach like object relations could help you uncover some of the deep messages you have about yourself and others. These messages could then be changed to improve these parts of your life. …
Basic Concepts in Object Relations
Development and History of Object Relations
- Object relations theory is composed of the diverse and sometimes conflicting ideas of various theorists, mainly Melanie Klein, Ronald Fairbairn, and Donald Winnicott. Each of their theories place great emphasis on the mother-infant bond as a key factor in the development of a child’s psychic structure during the first three years of life. 1. Kleini...
Who Practices Object Relations?
- Psychologists, psychotherapists, counselors, and social workers may earn certification in object relations therapy from one of several training institutions across the country. For example, the International Psychotherapy Institute (IPI), formerly the International Institute of Object Relations Theory, offers a two-year certificate program in Object Relations Theory and Practice for profess…
Goals of Object Relations Therapy
- Object relations therapy focuses on helping individuals identify and address deficits in their interpersonal functioning and explore ways that relationships can be improved. A therapist can help people in therapy understand how childhood object relations impact current emotions, motivations, and relationships and contribute to any problems being faced. Aspects of the self t…
Object Relations Techniques
- Many of the techniques used in object relations therapy are similar to those employed in psychoanalytic and other psychodynamic therapies. The primary distinction lies in the therapist's way of thinking about what is happening in the therapeutic exchange. For example, in classical psychoanalysis, transferencetends to be carefully analyzed, as it is thought to provide valuable i…
Limitations of Object Relations Therapy
- Early object relations therapists were criticized for underestimating the biological basis of some conditions, such as autism, learning difficulties, and some forms of psychosis. The value of object relations therapy in treating such conditions has been debated by many experts. Modern object relation theorists generally recognize that therapy alone is not sufficient for treating certain issu…
Theory
- While object relations theory is based on psychodynamic theory, it modified it so that the role of biological drives in the formation of adult personality received less emphasis. The theory suggests that the way people relate to others and situations in their adult lives is shaped by family experiences during infancy. For example, an adult who expe...
History
- The initial line of thought emerged in 1917 with Ferenczi and, early in the 1930s, Sullivan, coiner of the term "interpersonal". British psychologists Melanie Klein, Donald Winnicott, Harry Guntrip, Scott Stuart, and others extended object relations theory during the 1940s and 1950s. Ronald Fairbairn in 1952 independently formulated his theory of object relations. The term has been use…
Kleinian Object Relations Theory
- Unconscious phantasy
Klein termed the psychological aspect of instinct unconscious phantasy(deliberately spelled with 'ph' to distinguish it from the word 'fantasy'). Phantasy is a given of psychic life which moves outward towards the world. These image-potentials are given a priority with the drives and event… - Projective identification
As a specific term, projective identificationis introduced by Klein in “Notes on some schizoid mechanisms.” Ogdenidentifies four functions that projective identification may serve. As in the traditional Kleinian model, it serves as a defense. Projective identification serves as a mode of c…
Ronald Fairbairn's Model of Object Relations Theory
- Fairbairn was impressed with the work of Klein, particularly in her emphasis on internalized objects, but he objected to the notion that internalization of external objects was based on death instinct. The death instinct is a remnant of the Freudian model that was emphasized in Klein's model, and her model assumes that human behavior is motivated by a struggle between the inst…
Continuing Developments in The Theory
- Attachment theory, researched by John Bowlbyand others, has continued to deepen our understanding of early object relationships. While a different strain of psychoanalytic theory and research, the findings in attachment studies have continued to support the validity of the developmental progressions described in object relations. Recent decades in developmental psy…
Further Reading
- Fairbairn, W. R. D. (1952). An Object-Relations Theory of the Personality. New York: Basic Books.
- Gomez, L. (1997). An Introduction to Object Relations Theory. London: Free Association Press.
- Masterson, James F. (1988). The Search for the Real Self.
- Mitchell, S.A., & Black, M.J. (1995). Freud and beyond: A history of modern psycho analytic th…
- Fairbairn, W. R. D. (1952). An Object-Relations Theory of the Personality. New York: Basic Books.
- Gomez, L. (1997). An Introduction to Object Relations Theory. London: Free Association Press.
- Masterson, James F. (1988). The Search for the Real Self.
- Mitchell, S.A., & Black, M.J. (1995). Freud and beyond: A history of modern psycho analytic thought. Basic Books, New York.
External Links
Notes and References
- Book: Greenberg, Jay. Object Relations in Psychoanalytic Theory. Mitchell. Stephen. Harvard University Press. 1983. 0674629752. Cambridge, MA. 12.
- Book: Goldenberg, Herbert. Family Therapy: An Overview: An Overview. Goldenberg. Irene. Thomson Higher Education. 2008. 9780495097594. Belmont, CA. 160.
- Book: Andersen, Margaret. Sociology: Understanding a Diverse Society, Updated. Taylor. How…
- Book: Greenberg, Jay. Object Relations in Psychoanalytic Theory. Mitchell. Stephen. Harvard University Press. 1983. 0674629752. Cambridge, MA. 12.
- Book: Goldenberg, Herbert. Family Therapy: An Overview: An Overview. Goldenberg. Irene. Thomson Higher Education. 2008. 9780495097594. Belmont, CA. 160.
- Book: Andersen, Margaret. Sociology: Understanding a Diverse Society, Updated. Taylor. Howard. Thomson Wadsworth. 2008. 9780495007425. Belmont, CA. 93.
- Book: St. Clair, Michael . Object Relations and Self Psychology: An Introduction . 2000 . Brooks/Cole Counseling, an imprint of Wadsworth, a division of Thomson Learning . 978-0-534-36280-5 . 3rd ....