Difference Between Obstructive and Restrictive Lung Disease
- Obstructive lung diseases feature airway blockage while restrictive diseases feature a failure of lung expansion.
- In obstructive lung diseases, there is increased mucus formation while there’s none in restrictive diseases.
- Restrictive diseases are due to lung scarring while there is no scarring in obstructive diseases.
What is the prognosis for COPD?
Summary COPD is a heterogeneous disease without a simple prognostic trajectory. For ambulatory patients, age, degree of dyspnea, weight loss (BMI), functional status, and FEV1 are relevant prognostic factors for predicting 1-3 year survival. For hospitalized patients, the same factors are relevant.
Why is FEV1 FVC increased in restrictive lung disease?
In the restricted lung, the FVC is again smaller than normal, but the FEV1 is relatively large in comparison. i.e. the FEV1/FVC ratio can be higher than normal, for example 90% as opposed to 80%. This is because it is easy for a person with a restricted lung (e.g fibrosis) to breathe out quickly, because of the high elastic recoil of the stiff lungs.
What are the treatments for moderate-to-severe COPD?
Oral Medications. Roflumilast is an oral medication taken on a regular basis that can be used to treat severe COPD. It may decrease the incidence or severity of flare-ups. Even with medications, you may have symptoms like wheezing, coughing, trouble catching your breath, and feeling tired. This is when extra oxygen can help.
What to know about obstructive lung disease?
What to know about obstructive lung disease
- Obstructive vs. restrictive lung disease. ...
- Symptoms. Symptoms of obstructive lung disease include shortness of breath, low energy, and tightness in the chest.
- Causes and risk factors. ...
- Diagnosis. ...
- Treatment and remedies. ...
- Prevention. ...
- Outlook. ...

What are restrictive lung diseases?
What is restrictive lung disease? Restrictive lung disease, a decrease in the total volume of air that the lungs are able to hold, is often due to a decrease in the elasticity of the lungs themselves or caused by a problem related to the expansion of the chest wall during inhalation.
How do you determine obstructive and restrictive lung disease?
Common tests to diagnose obstructive and restrictive lung disease include:Forced vital capacity (FVC) testing. ... Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) testing. ... FVC to FEVI ratio testing. ... X-rays. ... Computed tomography (CT) scans. ... Bronchoscopy.
What is an obstructive lung disease?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or COPD, refers to a group of diseases that cause airflow blockage and breathing-related problems. It includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis. COPD makes breathing difficult for the 16 million Americans who have this disease.
Can a lung disease be both restrictive and obstructive?
This is measured with pulmonary function tests. However, it is possible to have both restrictive and obstructive lung diseases at the same time. People with both conditions have significantly more trouble breathing than those with only one.
Is COPD obstructive or restrictive?
While both types can cause shortness of breath, obstructive lung diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD), cause more difficulty with exhaling air, while restrictive lung diseases (such as pulmonary fibrosis) can cause problems by restricting a person's ability to inhale air.
Can restrictive lung disease be cured?
For most of these conditions, there is no cure, but a person can manage the symptoms with medication and physical therapy. It is crucial for a doctor to identify the root cause of any lung-related symptoms. In this article, we describe the types of restrictive lung disease and their symptoms.
What are the causes of restrictive lung disease?
Restrictive lung diseases may be caused by the destruction of distal lung parenchyma due to infiltrates from inflammation, toxins, and mechanisms yet to be elucidated (intrinsic conditions) as well as extra parenchymal conditions (extrinsic causes).
How is obstructive lung disease treated?
For most people with COPD, short-acting bronchodilator inhalers are the first treatment used. Bronchodilators are medicines that make breathing easier by relaxing and widening your airways. There are 2 types of short-acting bronchodilator inhaler: beta-2 agonist inhalers – such as salbutamol and terbutaline.
Is asthma an obstructive lung disease?
Bronchial asthma and COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease) are obstructive pulmonary diseases that affected millions of people all over the world. Asthma is a serious global health problem with an estimated 300 million affected individuals.
What is the difference between COPD and restrictive lung disease?
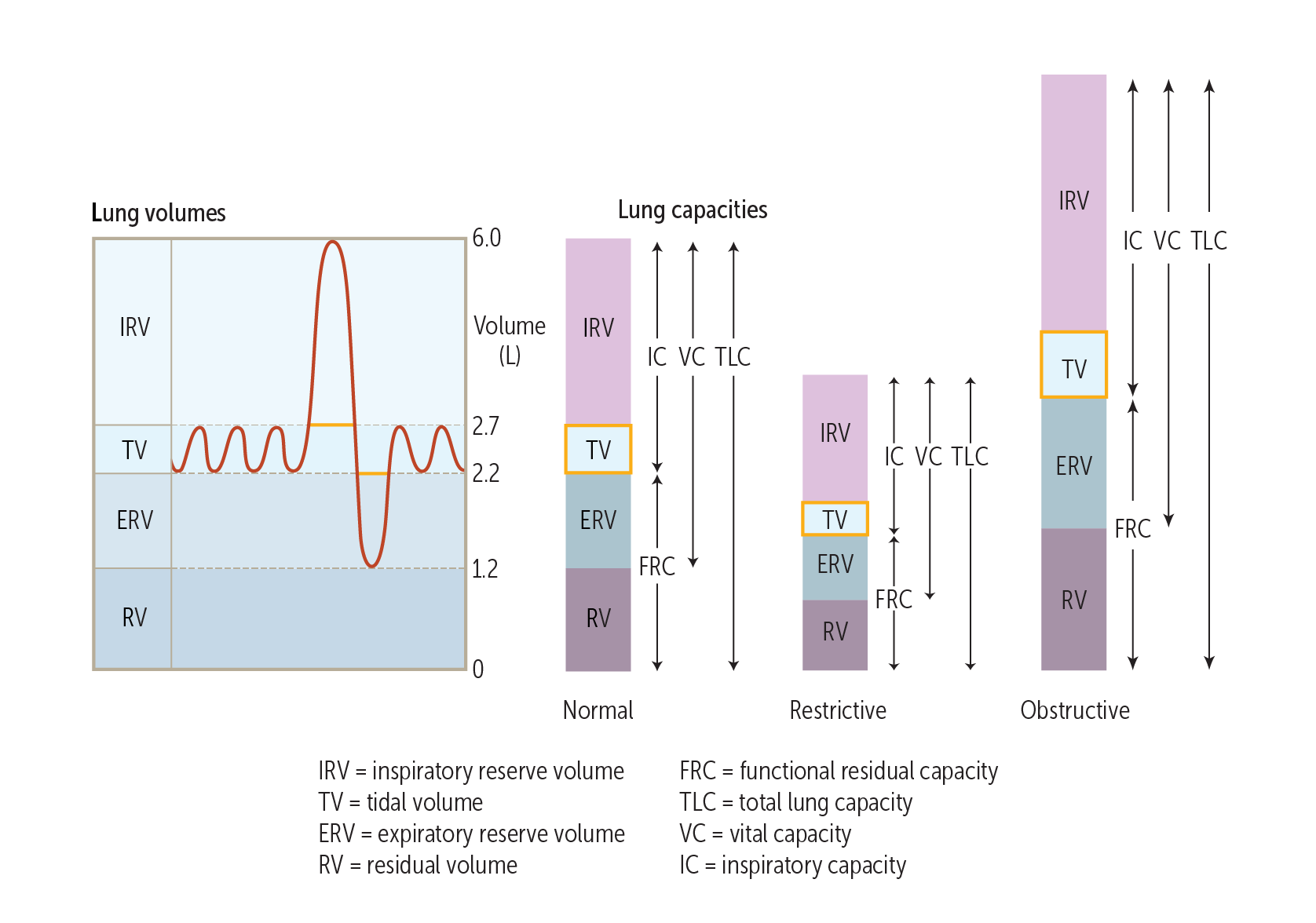
Unlike obstructive lung diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which show a normal or increased total lung capacity (TLC), restrictive disease are associated with a decreased TLC.
Is Covid a restrictive lung disease?
Researchers have also found that patients who have recovered from COVID-19, especially those who had severe disease, can later develop restrictive lung disease. COVID-19 patients who require a ventilator may also have recovery rates similar to those who require a ventilator for other conditions.
What spirometry results indicate restrictive lung disease?
Restrictive spirometry pattern Typical spirometry findings in restrictive lung disease include: Reduced FEV1 (<80% of the predicted normal) Reduced FVC (<80% of the predicted normal) FEV1/FVC ratio normal (>0.7)
What spirometry results indicate restrictive lung disease?
Restrictive spirometry pattern Typical spirometry findings in restrictive lung disease include: Reduced FEV1 (<80% of the predicted normal) Reduced FVC (<80% of the predicted normal) FEV1/FVC ratio normal (>0.7)
Which respiratory measurement is useful in differentiating between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary dysfunction?
(1) Spirometry is used as a complementary tool for diagnosis of a disease. Therefore, spirometry helps make a diagnosis by differentiating between obstructive lung diseases, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and restrictive lung disorders, such as interstitial pneumonia.
What is the FEV1 FVC ratio in restrictive lung disease?
In the restricted lung, the FVC is again smaller than normal, but the FEV1 is relatively large in comparison. i.e. the FEV1/FVC ratio can be higher than normal, for example 90% as opposed to 80%.
What is a normal FEV1 FVC ratio and what does that mean?
The FEV1/FVC ratio is the ratio of the forced expiratory volume in the first one second to the forced vital capacity of the lungs. The normal value for this ratio is above 0.75-85, though this is age dependent. values less than 0.70 are suggestive of airflow limitation with an obstructive pattern.
What is restrictive lung disease?
Restrictive lung diseases are characterized by a reduced total lung capacity or the sum of residual volume combined with the forced vital capacity (the amount of air that can be exhaled forcefully after taking a deep breath). This occurs because of difficulty filling the lungs completely in the first place.
What are the symptoms of obstructive and restrictive lung disease?
2 . Symptoms shared by both obstructive and restrictive conditions include: Shortness of breath (dyspnea) Persistent cough.
What tests are needed to diagnose restrictive lung disease?
Making a diagnosis of either obstructive or restrictive lung disease begins with a careful history and physical exam, though pulmonary function tests and imaging tests are very important, especially when the diagnosis is unclear.
What is the first step in diagnosing lung disease?
Diagnosis. Treatment. One of the first steps in diagnosing lung diseases is differentiating between obstructive lung disease and restrictive lung disease. While both types can cause shortness of breath, obstructive lung diseases (such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder) cause more difficulty with exhaling air, ...
What are the different types of pulmonary function tests?
There are other types of pulmonary function tests that may be needed as well: 1 Lung plethysmography estimates the amount of air that is left in the lungs after expiration ( functional residual capacity ) and can be helpful when there is overlap with other pulmonary function tests. It estimates how much air is left in the lungs (residual capacity), which is a measure of the compliance of the lungs. With restrictive airway disease, the lungs are often "stiffer" or less compliant. 2 Diffusing capacity (DLCO) measures how well oxygen and carbon dioxide can diffuse between the tiny air sacs ( alveoli) and blood vessels ( capillaries) in the lungs. The number may be low in some restrictive lung diseases (for example, pulmonary fibrosis) because the membrane is thicker; it may be low in some obstructive diseases (for example, emphysema) because there is less surface area for this gas exchange to take place.
What is a lung obstruction?
Obstructive lung diseases are characterized by an obstruction in the air passages, with obstruction defined by exhalation that is slower and shallower than in someone without the disease.
Can a lab test tell if a lung disease is restrictive?
Lab tests may give an indication of the severity of lung disease, but are not very helpful in determining if it is obstructive or restrictive in nature.
What Is Restrictive Lung Disease?
Individuals with restrictive lung disease can't fill their lungs fully with air due to their lungs being restricted from expanding fully. These individuals find it difficult to take a full breath. Frequently this occurs due to a condition that causes lung stiffness, muscle weakness, or physical restriction.
What is the procedure to check for obstructions in the lungs?
Sometimes, the physician will look at the patient's lungs with a flexible, thin lighted camera known as a bronchoscope. This procedure checks for obstructions and lung damage.
What is the pulmonary function test?
A pulmonary function test is performed to assist with the diagnosis of obstructive lung disease.
Why is it important to get a lung test?
Obtaining an official diagnosis is essential since the distinction between these two forms of disease will ensure the patient receives the right treatment.
Why does my lung expand?
This condition often results from disorders that cause lung stiffness. In other cases, weak muscles, stiffness of the chest wall or damaged nerves could be causing the lung expansion restriction.
Can environmental irritants cause obstructive lung disease?
Exposure to environmental lung irritants can also lead to obstructive lung disease.
Is restrictive lung disease progressive?
Many forms of restrictive lung diseases are progressive which means they'll become worse over time. However, there are available treatments based on the individual needs of the patient.
How are restrictive and obstructive lung diseases similar?
Also, both obstructive and restrictive disease will be diagnosed by using a careful medical history and a variety of pulmonary function tests.
What are some examples of obstructive lung disease?
Exhaling becomes slower and shallower than in a person with a healthy respiratory system. 1. Examples of obstructive lung disease include: 1. Asthma. COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), which includes emphysema and bronchitis. Bronchiectasis. Restrictive lung disease is a condition where the lungs don't function effectively.
What is the condition where the airflow into and out of the lungs is impeded?
Obstructive lung disease is a condition where the airflow into and out of the lungs is impeded. 1 This occurs when inflammation causes the airways to swell, making them narrower. Because of that, breathing well becomes harder and air often gets trapped in the lungs. This results in something known as hyperinflation of the lungs. Exhaling becomes slower and shallower than in a person with a healthy respiratory system. 1
What are some ways to treat restrictive disease?
They may also vary greatly, depending on the specific type of restrictive disease. Steroids and bronchodilators are sometimes used. Medications that suppress the immune system may also be helpful. 1 Other options might include supportive oxygen therapy and even lung transplants. 1.
How to keep asthma under control?
Changes in lifestyle may also be helpful. For example, with asthma, learning to avoid your triggers can help keep your asthma under control. 1. With restrictive lung disease, the treatment options are often more limited. They may also vary greatly, depending on the specific type of restrictive disease.
Is asthma obstructive or obstructive?
So prognosis and life expectancy can vary widely. It's easy to see that although there are similarities between both COPD and asthma (bo th obstructive), the outcomes can be quite different. Asthma, except for the severe persistent type, could be milder, less progressive and affect the quality of life much less than COPD does. 1
Is asthma a dry cough?
On the other hand, restrictive diseases tend to have more of a dry cough. However, asthma, which is obstructive, also tends more to a dry cough than a "wet" one. 1. Other symptoms typical for obstructive disease include: 1. Wheezing. Chest tightness.
What is the aim of treatment for obstructive lung disease?
The aim of treatment for obstructive lung disease is to open the airways. Treatment for obstructive lung disease typically involves opening the airways. Obstructive lung disease causes bronchospasms, which are spasms of the smooth muscles in the walls of the airways.
What is a type of lung disease that occurs due to blockages or obstructions in the airways?
Prevention. Outlook. Obstructive lung disease is a type of lung disease that occurs due to blockages or obstructions in the airways. Blockages damage the lungs and cause their airways to narrow. This damage leads to difficulty breathing.
What test is performed to diagnose obstructive lung disease?
A doctor will usually perform a pulmonary function test to help diagnose obstructive lung disease.
What causes obstructive air flow?
Common factors that obstruct airflow include: swelling and inflammation in the airways. thick mucus in the airways. damage to the walls of the air sacs.
What happens when you breathe in a healthy lungs?
Share on Pinterest. When a person with healthy lungs breathes, gas exchange occurs in air sacs called alveoli. When a person breathes, air travels down the windpipe through a series of tubes called bronchi, which gradually get smaller. At the end of these tubes are bunches of air sacs called alveoli. In healthy lungs, the alveoli fill up ...
Can exposure to other irritants through the environment cause obstructive lung disease?
Exposure to other lung irritants through the environment can also cause obstructive lung disease.
Can obstructive lung disease cause shortness of breath?
Shortness of breath is the main symptom of obstructive lung disease. At first, this may only occur with physical activity. However, as the disease progresses, it can occur at any time, including when a person is resting.
What is restrictive lung disease?
Treatment. Restrictive lung diseases are chronic lung conditions that limit the ability of a person’s lungs to expand during inhalation. Most cases of restrictive lung diseases are not curable, but they are often manageable with medication and exercise regimes.
What causes extrinsic restrictive lung disease?
Extrinsic restrictive lung disease is caused by complications with tissues or structures outside of the lungs, including neurological conditions. External factors that cause an extrinsic restrictive lung disease are often associated with weakened muscles, damaged nerves, or the stiffening of the chest wall tissues.
What is mixed lung disease?
Mixed lung disease most commonly occurs in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), who also have congestive heart failure. In cases of obstructive lung diseases, such as asthma, bronchiectasis, COPD, and emphysema, the lungs are unable to expel air properly during exhalation. Restrictive lung diseases, on the other hand, mean ...
Why is FEV1 lower in restrictive disease?
In restrictive disease, because the FVC is usually reduced, the FEV1 will be lower, proportionally. FEVI to FVC ratio test, which compares the amount of air expelled during the first second of exhalation (FEV1) to the total amount of air exhaled during an FVC test.
What is the third category of lung disease?
These categories are either obstructive or restrictive. A third category, called mixed lung disease , is smaller and has characteristics of both obstructive and restrictive lung diseases.
What are some examples of obstructive pulmonary disease?
Obstructive lung diseases account for around 80% of lung-related syndromes. Some examples include asthma, bronchiectasis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, known as COPD, and emphysema.
How to reduce restrictive disease symptoms?
Doing at-home exercises and making some lifestyle changes have been shown to reduce the severity of restrictive disease symptoms. Commonly recommended methods include: breath conditioning, often pursed lip breathing, slow-deep breathing, or diaphragmatic breathing.
What is restrictive lung disease?
Restrictive lung disease, a decrease in the total volume of air that the lungs are able to hold, is often due to a decrease in the elasticity of the lungs themselves or caused by a problem related to the expansion of the chest wall during inhalation. Examples of restrictive lung diseases include asbestosis, sarcoidosis and pulmonary fibrosis.
What are the factors that determine the treatment of lung disease?
As with diagnostic testing, treatment of lung disease depends on many factors, such as the type and stage of disease, family history, patient’s medical history and the health and age of the patient. Any of the following may be used for treating lung disease:

Defining Obstructive vs Restrictive
How Obstructive and Restrictive Lung Diseases Are Similar
How They Differ
Treatment Options For Obstructive vs Restrictive Lung Disease
in Summary
- Obstructive lung disease is a condition where the airflow into and out of the lungs is impeded.1 This occurs when inflammation causes the airways to swell, making them narrower. Because of that, breathing well becomes harder and air often gets trapped in the lungs. This results in something known as hyperinflation of the lungs. Exhaling becomes slower and shallower than i…