Odontogenic keratocysts (OKC), previously known as keratocystic odontogenic tumors (KCOT or KOT), are benign cystic lesions involving the mandible or maxilla and are believed to arise from dental lamina.
What is keratocystic odontogenic tumor?
An odontogenic keratocyst is a benign tumor of the jaw (that’s why the new name, keratocystic odontogenic tumor makes sense.) It is associated with an unerupted tooth about one-third of the time.
What are the treatment options for odontogenic keratocysts?
A 2015 Cochrane review found that there is currently no high quality evidence to suggest the effectiveness of specific treatments for the treatment of odontogenic keratocysts. Treatment depends on extent of multilocularity and cyst. Small multilocular and unilocular cysts can be treated more conservatively through enucleation and curretage.
What is the histologic appearance of odontogenic keratocysts?
Odontogenic keratocysts have a diagnostic histological appearance. Under the microscope, OKCs vaguely resemble keratinized squamous epithelium; however, they lack rete ridges and often have an artifactual separation from their basement membrane. The fibrous wall of the cyst is usually thin and uninflamed.
What are the signs and symptoms of odontogenic keratocysts?
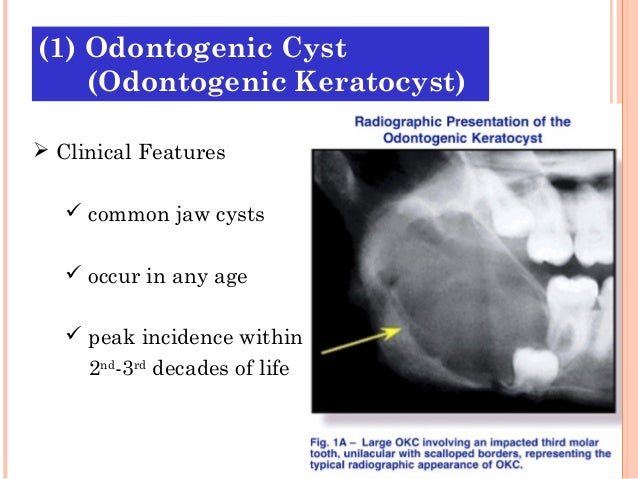
Occasional odontogenic keratocysts will be associated with pain or drainage, but even extremely large cysts may not cause any symptoms. On radiographic examination, a small odontogenic keratocyst usually presents as a well-circumscribed unilocular radiolucency that often demonstrates a sclerotic border (Fig. 10-8A ).

What is the cause of odontogenic keratocyst?
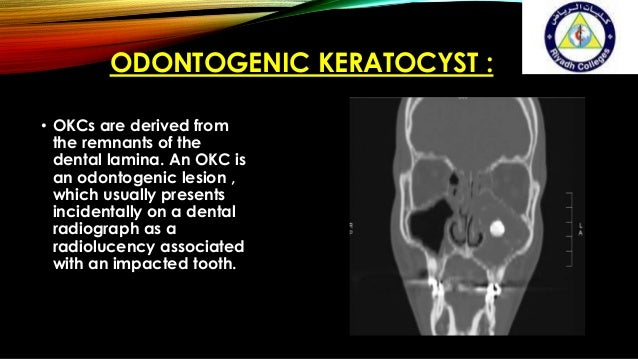
Odontogenic keratocysts (OKCs) are generally thought to be derived from remnants of the dental lamina (rests of Seres), traumatic implantation or down growth of the basal cell layer of the surface epithelium, or reduced enamel epithelium of the dental follicle.
How is odontogenic keratocyst treated?
Depending on other studies KCOT can be conservatively treated with enucleation and application of Carnoy's solution or cryotherapy. This can be used specially in the large lesions that when treated with resection, the continuity of the jaw will be interrupted.
Is an odontogenic keratocyst a tumor or a cyst?
The odontogenic keratocyst (OKC) is an enigmatic developmental cyst that deserves special attention. It has characteristic histopathological and clinical features; but, what makes this cyst special is its aggressive behavior and high recurrence rate.
Is Keratocyst a tumor?
The keratocystic odontogenic tumor (KCOT), formerly known as the odontogenic keratocyst (OKC), received its new designation in order to better convey its neoplastic nature [1]. It is a benign developmental odontogenic tumor with many distinguishing clinical and histologic features.
How common are jaw cysts?
Glandular odontogenic cysts are very rare, mostly slow-growing intraosseous lesions that generally tend to occur on average around the fifth decade of life and in the anterior mandible.
Which cyst has high recurrence rate?
Botryoid odontogenic cyst (BOC) is considered as a variant of the LPC, with different radiographic features and higher risk of recurrence (3-15).
Can dental cysts be cancerous?
Your doctor or dentist may discover them during regular check-ups or x-rays. When they do cause symptoms, they usually look like a non-painful bump or lump. These cysts and tumors are often benign (not cancer), but all tumors in the head and neck must be examined by our surgeons as soon as possible.
What does odontogenic mean?
or capable of forming teethMedical Definition of odontogenic 1 : forming or capable of forming teeth odontogenic tissues. 2 : containing or arising from odontogenic tissues odontogenic tumors.
How do I get rid of a cyst on my gum?
The only way for a dentist to treat this cyst is to remove it surgically. The cyst may appear again and that's why dentists usually prescribe treatment after the surgery.
Do dental cysts go away?
Most oral cysts are benign and disappear without treatment, like cyst draining. Other oral cysts remain small or harmless. However, if a cyst becomes infected, it may turn into an abscess. An abscess can cause extreme pain, swelling, and discomfort and will need medical treatment to keep the infection from spreading.
Can keratocystic odontogenic tumor recur?
The Keratocystic Odontogenic Tumor (KCOT) is characterized by its high tendency to recur after surgical treatment. This is attributed to its infiltrative growth pattern and to the failure during surgery to remove the epithelial rests of the dental lamina or the daughter cysts [1-4].
How can we prevent the recurrence of odontogenic keratocysts?
The application of Carnoy's solution may be useful to minimize recurrence rate in those odontogenic keratocysts with an aggressive clinical behavior and secondly may be used for all the other lesions treated with simple enucleation that experienced relapse.
What is an odontogenic keratocyst?
Odontogenic keratocyst. Micrograph of an odontogenic keratocyst. H&E stain. An odontogenic keratocyst is a rare and benign but locally aggressive developmental cyst. It most often affects the posterior mandible and most commonly presents in the third decade of life. Odontogenic keratocysts make up around 19% of jaw cysts.
What is the protein content of odontogenic keratocysts?
Aspirational biopsy of odontogenic keratocysts contains a greasy fluid which is pale in colour and contains keratotic squames. Protein content of cyst fluid below 4g% is diagnostic of odontogenic keratocysts. Smaller and unilocular lesions resembling other types of cysts may require a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
What is the diagnosis of a keratocyst?
Diagnosis. Classic look of an odontogenic keratocyst of the right mandible in the place of a former wisdom tooth. Well defined, unilocular, radiolucent lesion within the bone. Diagnosis is usually radiological. However, definitive diagnosis is through biopsy.
What is a nevoid basal cell carcinoma?
Nevoid basal-cell carcinoma syndrome. Multiple odontogenic keratocysts are a feature, and major diagnostic criteria, of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS, also known as Gorlin-Goltz Syndrome). Almost all individuals with NBCCS have odontogenic keratocysts which require numerous treatments.
How many units are there in a keratocystic odontogenic tumour?
On a CT scan, the radiodensity of a keratocystic odontogenic tumour is about 30 Hounsfield units, which is about the same as ameloblastomas. However, ameloblastomas show more bone expansion and seldom show high density areas.
Why is odontogenic keratocyst no longer considered a neo?
Under The WHO/IARC classification, Odontogenic Keratocyst underwent the reclassification as it is no longer considered a neoplasm due to a lack of quality evidence regarding this hypothesis, especially with respect to clonality. Within the Head and Neck pathology community there is still controversy surrounding the reclassification, ...
Why do keratocysts grow?
However, bony expansion is uncommon as odontogenic keratocysts grow due to increased epithelial turnover rather than osmotic pressure. When symptoms are present they usually take the form of pain, swelling and discharge due to secondary infection.
What is Odontogenic Keratocyst
An odontogenic keratocyst is a benign but locally violent developmental cyst that is uncommon. It usually affects the posterior mandible and appears in the third decade of life. Odontogenic keratocysts account for about 19% of all jaw cysts.
What causes odontogenic cysts?
Cells and tissues involved in natural tooth growth give rise to odontogenic jaw tumors and cysts. Other cancers that involve the jaws can be nonodontogenic, which means they can arise from tissues within the jaws that are unrelated to the teeth.
How is odontogenic Keratocyst treated?
Decompression, marsupilization, enucleation with or without adjunct (Carnoy’s solution, cryotherapy), and resection were also implemented as surgical methods. keratocystic odontogenic tumour ( KCOT ) may be handled conservatively with enculation and Carnoy’s solution or cryotherapy, depending on other research.
Initial Diagnosis in his Hometown
The patient is a 24-year-old male from Karur in Tamil Nadu, India. Approximately two years ago, he began developing swelling in his anterior lower jaw. At first, he had neglected it, but it continued to grow. Alarmed at the increase in size, he presented to a local oral surgeon.
Referral to our Hospital for Management of His Jaw Lesion
He was advised to undergo jaw resection surgery at the earliest. A referral was made to our hospital as we are one of the leading oral surgical hospitals in India. Our hospital is a leading jaw reconstruction center in India. Patients with loss of bony tissue in the jaws are referred to us for corrective surgery.
Treatment Planning and Successful Surgical Rehabilitation
It was also explained to him that rib grafts would be used for jaw reconstruction surgery. Total rehabilitation would include the replacement of lost teeth with dental implants. He then consented to undergo surgery.
Placement of Dental Implants after Consolidation of Graft Bone
He returned six months later and imaging revealed a union of the graft with the jawbone. A flap was then raised and the titanium screws were removed. Premium dental implants were then fixed to the reconstructed jaw bone. This would undergo osseointegration with surrounding alveolar bone in 4-6 months.
What is an Odontogenic Keratocyst (OKC)?
The odontogenic keratocyst (OKC) is the most important of the tooth-derived cysts.
What is the treatment for odontogenic keratocysts?
JOMS 2005. The Treatment of Odontogenic Keratocysts by Excision of the Overlying, Attached Mucosa, Enucleation & Treatment of the Bony Defect With Carnoy Solution
What is an odontogenic keratocyst?
Odontogenic keratocysts (OKC), previously known as keratocystic odontogenic tumors (KCOT or KOT), are rare benign cystic lesions involving the mandible or maxilla and are believed to arise from dental lamina. Whether these lesions are developmental or neoplastic is controversial, with the 2017 WHO classification placing it ...
When was the first keratocyst discovered?
It was first described by H.P. Philipsen in 1956 as an odontogenic keratocyst.
What are the symptoms of a tumor on the jaw?
Commonly discovered incidentally. When symptomatic, jaw swelling and pain are common symptoms associated with these tumors 8. Less commonly, trismus and paresthesia may occur.
Where do keratinizing cells originate?
They originate from epithelial cell rests (stratified squamous keratinizing epithelium) found along the dental lamina and periodontal margin of the alveolus of the mandible 7 . Inflammation may impede histologic characterization.
Does ameloblastoma cause tooth resorption?
tendency for ameloblastoma to be more aggressiv e and cause more significant tooth resorption.
Overview
An odontogenic keratocyst is a rare and benign but locally aggressive developmental cyst. It most often affects the posterior mandible and most commonly presents in the third decade of life. Odontogenic keratocysts make up around 19% of jaw cysts.
In the WHO/IARC classification of head and neck pathology, this clinical entity …
Signs and symptoms
Odontogenic keratocysts can occur at any age, however they are more common in the third to sixth decades. The male to female ratio is approximately 2:1. The majority are found in the mandible, with half occurring at the angle of the mandible.
Early odontogenic keratocysts usually do not display symptoms. Typically, clin…
Odontogenic keratocysts can occur at any age, however they are more common in the third to sixth decades. The male to female ratio is approximately 2:1. The majority are found in the mandible, with half occurring at the angle of the mandible.
Early odontogenic keratocysts usually do not display symptoms. Typically, clin…
Pathogenesis
Odontogenic keratocysts originate from the odontogenic epithelium (dental lamina) in the alveolus left from tooth development stages. They are mainly thought to arise from rests of Serres.
Sporadic (non-syndromic) and syndromic OKCs are associated with mutations in the gene PTCH found on chromosome 9q, which is part of the Hedgehog signaling pathway. PTCH is a tumour su…
Nevoid basal-cell carcinoma syndrome
Multiple odontogenic keratocysts are a feature, and major diagnostic criteria, of nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome (NBCCS, also known as Gorlin-Goltz Syndrome). Almost all individuals with NBCCS have odontogenic keratocysts which require numerous treatments. Consideration of the syndrome needs to be taken into account if found in children or if multiple OKCs are present; diagnosis of multiple OKCs in a child necessitates referral for genetic evaluation. Histologically, …
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is usually radiological. However, definitive diagnosis is through biopsy. Aspirational biopsy of odontogenic keratocysts contains a greasy fluid which is pale in colour and contains keratotic squames. Protein content of cyst fluid below 4g% is diagnostic of odontogenic keratocysts. Smaller and unilocular lesions resembling other types of cysts may require a biopsy to confirm the di…
Treatment
As the condition is quite rare, opinions among experts about how to treat OKCs differ. A 2015 Cochrane review found that there is currently no high quality evidence to suggest the effectiveness of specific treatments for the treatment of odontogenic keratocysts. Treatment depends on extent of multilocularity and cyst. Small multilocular and unilocular cysts can be treated more conservativel…
See also
• Cysts of the jaws