Full Answer
What is an oil and gas trap?
Oil and gas traps. Oil and gas traps, sometimes referred to as petroleum traps are below ground traps where a permeable reservoir rock is covered by some low permeability cap rock. This combination of rock can take several forms, but they all prevent the upward migration of oil and natural gas up through the reservoir rock.
What is a structural trap in geology?
Structural Traps. In these traps, the pores of the reservoir rock contain oil, gas, or water. Gas moves up in the trap as it is the lightest, with oil below it and water at the bottom. The cap rock prevents upward migration of these fluids .
How is a petroleum trap formed?
Petroleum trap. The most common type of structural trap is formed by an anticline, a structure with a concave (as viewed from below) roof caused by the local deformation of the reservoir rock and the impermeable cap rock. In this case, the intersection of the oil-water contact with the cap rock determines the edges of the reservoir.
What are two types of petroleum traps?
Two types of petroleum traps are; structural and stratigraphic. Structural traps are formed by deformation of reservoir rock, such as by folding or faulting. Stratigraphic traps are formed by deposition of reservoir rock, such as river channel or reef, or by erosion of reservoir rock, such as an angular unconformity

What is meant by oil trap?
Oil and gas traps, sometimes referred to as petroleum traps are below ground traps where a permeable reservoir rock is covered by some low permeability cap rock. This combination of rock can take several forms, but they all prevent the upward migration of oil and natural gas up through the reservoir rock.
How do oil traps work?
In the most basic terms, a grease trap works by slowing down the flow of warm/hot greasy water and allowing it to cool. As the water cools, the grease and oil in the water separate out and float to the top of the trap. The cooler water - minus the grease - continues to flow down the pipe to the sewer.
What are the 4 types of oil traps?
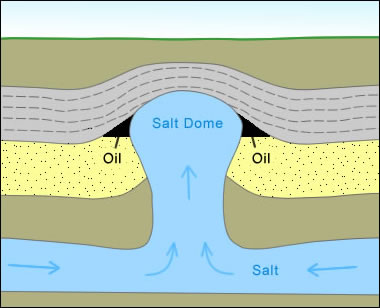
The three basic forms of structural traps are the anticline trap, the fault trap and the salt dome trap.
What is the most common type of oil trap?
Hydrodynamic Trap. the most common type of structural trap is formed by an anticline, a structure with a concave roof caused by the local deformation of the reservoir rock and the impermeable cap rock. In this case, the intersection of the oil-water contact with the cap rock determines the edges of the reservoir.
Which of the following are types of oil traps?
The four types of oil traps are salt domes, fault traps, anticlines, and stratigraphic traps. All four traps have a porous, permeable reservoir rock that yields the natural gas and an impermeable cap rock that keeps the gas from escaping at the surface.
How is oil trapped underground?
Oil doesn't exist in deep, black pools. In fact, an underground oil formation—called an “oil reservoir” —looks very much like any other rock formation. It looks a lot like...well, rock. Oil exists underground as tiny droplets trapped inside the open spaces, called “pores,” inside rocks.
What are the properties of a trap?
A trap consists of a geometric arrangement of permeable (reservoir) and less-permeable (seal) rocks which, when combined with the physical and chemical properties of subsurface fluids, can allow hydrocarbons to accumulate.
What is the most important part of a trap?
The most important element of your trap beat might just be your kick drum and 808 pattern. Your kick and 808 are what give your trap that heavy, trunk-rattling bass. Putting your kick or 808 on beat 1 is essential, but beyond that, you're on your own.
What is trap rock used for?
Because of its insensitivity to chemical influences, resistance to mechanical stress, high dry relative density, frost resistance, and sea water resistance, trap rock is used as ballast for railroad track bed and hydraulic engineering rock (riprap) in coast and bank protection for paving embankments.
What type of rock is oil found in?
Sedimentary rocksSedimentary rocks Petroleum may occur in any porous rock, but it is usually found in sedimentary rocks such as sandstone or limestone. Sedimentary rocks are grouped into three major classes: clastic, carbonate, and evaporitic.
What is spill point in geology?
1. n. [Geology] The structurally lowest point in a hydrocarbon trap that can retain hydrocarbons. Once a trap has been filled to its spill point, further storage or retention of hydrocarbons will not occur for lack of reservoir space within that trap.
Why is a trap necessary to create a conventional oil reserve?
Why is a trap necessary to create a conventional reserve? Without a trap, hydrocarbons would rise buoyantly and seep onto the Earth's surface.
How do oil traps keep oil from escaping?
Answer: A trap consists of an impervious stratum that overlies the reservoir rock thereby prohibiting hydrocarbons from escaping upward and laterally. This impervious stratum is called a roof rock; it intervenes to collect and hold hydrocarbons underground.
What type of rock is oil found in?
Sedimentary rocksSedimentary rocks Petroleum may occur in any porous rock, but it is usually found in sedimentary rocks such as sandstone or limestone. Sedimentary rocks are grouped into three major classes: clastic, carbonate, and evaporitic.
How is the organic material trapped in sedimentary rocks transformed into hydrocarbons?
Over the years, layers of silt, sand and other sediments settled over the buried organic matter. The increase of pressure and temperature slowly transformed the organic matter into hydrocarbons (kerogen, oil, gas).
What is the most important part of a trap?
The most important element of your trap beat might just be your kick drum and 808 pattern. Your kick and 808 are what give your trap that heavy, trunk-rattling bass. Putting your kick or 808 on beat 1 is essential, but beyond that, you're on your own.
What is a petroleum trap?
Full Article. Petroleum trap, underground rock formation that blocks the movement of petroleum and causes it to accumulate in a reservoir that can be exploited.
What is the part of the trap actually occupied by the oil and gas called?
That part of the trap actually occupied by the oil and gas is called the petroleum reservoir. Many systems have been proposed for the classification of traps; one simple system divides them into structural traps and stratigraphic traps.
What is the trap rock?
petroleum trap, underground rock formation that blocks the movement of petroleumand causes it to accumulate in a reservoir that can be exploited. The oil is accompanied always by water and often by natural gas; all are confined in a porous and permeable reservoir rock, which is usually composed of sedimentary rocksuch as sandstones, arkoses, and fissuredlimestonesand dolomites. The natural gas, being lightest, occupies the top of the trap and is underlain by the oil and then the water. A layer of impermeable rock, called the cap rock, prevents the upward or lateral escape of the petroleum. That part of the trap actually occupied by the oil and gas is called the petroleum reservoir.
What are structural traps?
Many systems have been proposed for the classification of traps; one simple system divides them into structural trapsand stratigraphic traps. The most common type of structural trap is formed by an anticline, a structure with a concave (as viewed from below) roof caused by the local deformation of the reservoir rock and the impermeable cap rock. In this case, the intersection of the oil-water contact with the cap rock determines the edges of the reservoir. Another kind of structural trap is the fault trap. Here, the fractureand slippage of rock along a faultline may bring an impermeable stratum in contact with a layer of permeable reservoir rock and thus forms a barrier to petroleum migration.
How are structural traps formed?
The most common type of structural trap is formed by an anticline, a structure with a concave (as viewed from below) roof caused by the local deformation of the reservoir rock and the impermeable cap rock. In this case, the intersection of the oil-water contact with the cap rock determines the edges of the reservoir.
What is the fundamental characteristic of a trap?
The fundamental characteristic of a trap is an... In a stratigraphic trap, variations within the rock strata themselves (e.g., a change in the local porosity and permeability of the reservoir rock, a change in the kinds of rocks laid down, or a termination of the reservoir rock) play the important role. The stratigraphic variations associated ...
Why does the pool rise to the top of the trap?
The oil and gas pool will rise to the top of the trap if the underlying water is stationary, and the resulting oil-water contact will be level . When the water is moving, however, the pool is displaced down the trap’s side in the direction of flow because of hydrodynamic pressure.
What are the two types of petroleum traps?
What are types of Petroleum Traps? Two types of petroleum traps are; structural and stratigraphic. Structural traps are formed by deformation of reservoir rock, such as by folding or faulting. Stratigraphic traps are formed by deposition of reservoir rock, such as river channel or reef, or by erosion of reservoir rock, ...
What is structural trap?
Structural trap is a type of geological trap that forms as a result of changes in the structure of the subsurface, due to tectonic, diapiric, gravitational and compactional processes. These changes block the upward migration of hydrocarbons and can lead to the formation of a petroleum reservoir.
How is a fault trap formed?
Fault Trap. This trap is formed by the movement of permeable and impermeable layers of rock along a fault line. The permeable reservoir rock faults such that it is now adjacent to an impermeable rock, preventing hydrocarbons from further migration.
What is anticline trap?
An anticline is an area of the subsurface where the strata have been pushed into forming a domed shape. If there is a layer of impermeable rock present in this dome shape, then hydrocarbons can accumulate at the crest until the anticline is filled to the spill point – the highest point where hydrocarbons can escape the anticline. This type of trap is by far the most significant to the hydrocarbon industry. Anticline traps are usually long oval domes of land that can often be seen by looking at a geological map or by flying over the land.
What are the three types of traps?
The three basic forms of structural traps are the anticline trap, the fault trap and the salt dome trap .
What are stratigraphic traps?
stratigraphic traps result from variations that developed after sedimentation, mainly because of diagenesis. These include variations due to porosity enhancement by dissolution or loss by cementation. Paleogeomorphic traps are controlled by buried landscape.
What are traps controlled by?
Paleogeomorphic traps are controlled by buried landscape. Some are associated with prominences (hills); others with depressions (valleys). Many are also partly controlled by unconformities so are also termed unconformity traps .
What is a trap?
Traps are the product of the interaction of many geologic elements and processes. The outcome of all the possible combinations of geologic elements makes each trap unique. Yet each trap generally shares enough similarities with other traps in the same basin or in other basins that traps may be classified. The classification chosen depends on one’s ...
What is trap classification?
Trap classification. Traps are the product of the interaction of many geologic elements and processes. The outcome of all the possible combinations of geologic elements makes each trap unique. Yet each trap generally shares enough similarities with other traps in the same basin or in other basins that traps may be classified.
What is the difference between formal and informal classification of traps?
An informal classification is descriptive; little knowledge is needed to classify a trap beyond learning how to describe it. A formal classification is more rigorous and requires knowing the structure of the scheme proposed in this chapter.
How are traps classified?
Most petroleum geologists classify traps according to the scheme proposed by Levorsen. Levorsen’s scheme breaks traps into three basic types: structural, stratigraphic, and combination. The trap classification scheme proposed here uses Levorsen’s scheme as a foundation and adds new trap types discovered since 1954. The proposed scheme attempts to formalize the schemes of Levorsen and others (Rittenhouse, North, Melton and Bertram, and Biddle and Weilchowsky) by developing a more systematic and rigorous approach. It uses elements critical to petroleum exploration to group traps into levels. The method is similar to the one used by biologists to classify plants and animals.
How to determine the trap system?
Determine the trap system: structural, stratigraphic, or fluidic. If More than one element controls the trap Go to step 2. If Only one element controls the trap Go to step 3. Determine the primary, secondary, and (if necessary) tertiary trap system. Determine the trap regime.
What is a combination trap?
The common occurrence of combination traps, which involve many different types and varieties of trapping elements, requires a scheme that allows for such variations. Consequently, a classification scheme such as that used to organize a stamp or coin collection might be more useful, especially one in which a variety of flexible methods of organization can be used.
Can trap classification change?
As more data become available, the trap classification can change or be modified. Different explorationists may classify a particular trap in completely different categories, depending on their particular viewpoints. Traps can be classified formally or informally.
What is Trap Rock?
Trap rock is a name used in the construction industry for any dark-colored igneous rock that is used to produce crushed stone. Basalt, gabbro, diabase, and peridotite are the most common rock types referred to as trap rock.
Where did the name "trap rock" come from?
Origin of the Name. The name "trap rock" is from the Swedish word "trappa" which means "stair step.". This refers to the step-like landscape that is present in geographic areas where stacked basalt flows and shallow intrusions outcrop to form a landscape of steep cliffs and narrow ledges.
How much trap rock was produced in 2014?
During calendar year 2014, about 7% of the crushed stone produced in the United States was trap rock [1]. That is a total of about 88 million tons of trap rock. The pie chart on this page shows which states were important producers of trap rock in 2012 [2]. In construction projects, trap rock has an excellent freeze-thaw resistance ...
How many states produce trap rock?
Trap rock is only produced in the United States in those small areas where suitable dark-colored igneous rocks are present at the surface. Ten states account for approximately 85% of the United States trap rock production. These are shown in the pie diagram on this page.
What is the rock used in New Jersey?
About 60% of the crushed stone used in New Jersey is trap rock from the Palisades Sill. Nearly 90% of the crushed stone used in Hawaii is trap rock because the entire island chain is underlain by basalt flows [2].
Is trap rock a good abrasion?
In construction projects, trap rock has an excellent free ze-thaw resistance and a good abrasion resistance. It can substitute for limestone as a road base material, as a concrete aggregate, and as an asphalt aggregate. It is superior to limestone when it is used in soils or water where acid resistance is important. More Rocks.
What is stratigraphic trap?
In a stratigraphic trap, variations within the rock strata themselves (e.g., a change in the local porosity and permeability of the reservoir rock, a change in the kinds of rocks laid down, or a termination of the reservoir rock) play the important role.
What is the second class of traps?
In petroleum: Stratigraphic traps. A second major class of petroleum traps is the stratigraphic trap. It is related to sediment deposition or erosion and is bounded on one or more sides by zones of low permeability.
