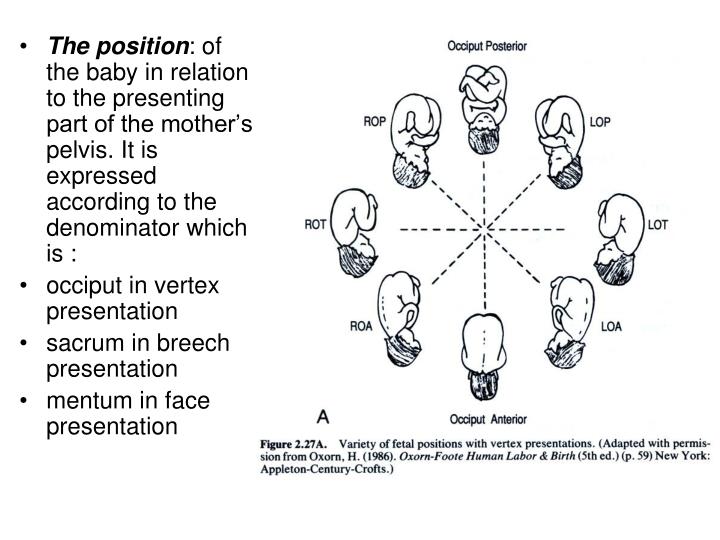
What is the op (occiput posterior fetal position)?
The OP position (occiput posterior fetal position) is when the back of the baby’s head is against the mother’s back. Here are drawings of an anterior and posterior presentation. When is Breech an Issue? Look at the above drawing. The posterior baby’s back is often extended straight or arched along the mother’s spine.
What is the op position?
The OP position (occiput posterior fetal position) is when the back of the baby’s head is against the mother’s back. Here are drawings of an anterior and posterior presentation. When is Breech an Issue? Look at the above drawing.
How is op position in pregnancy diagnosed?
The OP position could be diagnosed through an ultrasound scanning, and its management is done only if the fetal heart rate is reassuring. Operative vaginal delivery from the OP position: It could be done if there is sufficient room between the occiput and the sacrum, allowing the baby to turn.
When does the fetal head stay in the op position?
During the first stage of labor, the fetal head may stay in the OP position in 30% of the cases, but of these only 5-7% remains as such at time of delivery. The diagnosis of OP position in the second stage of l …

Can you deliver an op baby?
Occiput Posterior (OP) In occiput posterior position, your baby's head is down, but it is facing the mother's front instead of her back. It is safe to deliver a baby facing this way.
What does op in pregnancy mean?
INTRODUCTION. Occiput posterior (OP) position is the most common fetal malposition. It is important because it is associated with labor abnormalities that may lead to adverse maternal and neonatal consequences, particularly operative vaginal or cesarean birth.
How common is OP position?
Epidemiology. The prevalence of the OP position is 15 to 32% at the onset of labour [15-18], 10 to 20% early in the second stage of labour and 5 to 8% at delivery [2,17,19,20].
How do I get my baby out of the OP position?
3:3416:12Positions to Turn a Posterior Baby - Part 2 | Sarah Lavonne - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAlone is gonna just pull the baby's head off the tailbone a little bit off these structuresMoreAlone is gonna just pull the baby's head off the tailbone a little bit off these structures typically people that have an op baby baby's in that position in labor.
What causes OP position?
The occipitoposterior position in the main is caused by the adaptation of the head to a pelvis having a narrow fore pelvis and an ample anteroposterior diameter and therefore may be considered “physiologic.” 2.
How is Occipito posterior position diagnosed?
OCCIPUT POSTERIOR POSITION occurs when the fetal occiput is posterior in relation to the maternal pelvis (Fig S-13 and Fig S-14). On abdominal examination, the lower part of the abdomen is flattened, fetal limbs are palpable anteriorly and the fetal heart may be heard in the flank.
What causes Occipito posterior position?
A highest incidence of occipito-posterior fetal head position may depend by nulliparity, malnutrition with pelvic deformity, pelvic immaturity in the teenager and anterior placenta. Epidural analgesia is a risk factor for fetal head malposition.
What causes op babies?
Being born OP Some babies are born in the OP position either because they stay in that position, or because they rotate into that position during labour (from OA). You can watch the birth of a big OP baby in 'The Birth of Beau'.
Is posterior labour more painful?
Posterior labours have increased chances of: Producing more pain in the woman's back, rather than the front. Having a longer labour, as the baby rotates into the anterior position.
How can we avoid occiput posterior position?
How to Prevent a Posterior LaborAvoid all reclining positions. ... Keep knees below your pelvis at all times, back straight. ... Keep active, walk as much as possible.More items...
How long after baby's head is down does labor start?
This is known as dropping or lightening. Dropping is not a good predictor of when labor will begin. In first-time mothers, dropping usually occurs 2 to 4 weeks before delivery, but it can happen earlier. In women who have already had children, the baby may not drop until labor begins.
How can I turn my baby naturally?
Natural methodsBreech tilt, or pelvic tilt: Lie on the floor with your legs bent and your feet flat on the ground. ... Inversion: There are a few moves you can do that use gravity to turn the baby. ... Music: Certain sounds may appeal to your baby. ... Temperature: Like music, your baby may respond to temperature.More items...•
What causes op babies?
Being born OP Some babies are born in the OP position either because they stay in that position, or because they rotate into that position during labour (from OA). You can watch the birth of a big OP baby in 'The Birth of Beau'.
How long is a closed cervix?
The length of a normal adult non-pregnant cervix is approximately 25 mm, with an anteroposterior diameter ranging between 20 and 25 mm and a transverse diameter of 25–30 mm, although considerable variations occur due to age, parity and stage of menstrual cycle [3], [4], [5].
What can I do to help my cervix open?
Nonpharmacologic Cervical RipeningHERBAL SUPPLEMENTS.CASTOR OIL, HOT BATHS, AND ENEMAS.SEXUAL INTERCOURSE.BREAST STIMULATION.ACUPUNCTURE/TRANSCUTANEOUS NERVE STIMULATION.MECHANICAL MODALITIES.SURGICAL METHODS.Stripping of the Membranes.More items...•
What are the types of delivery?
Some of the most common are:Vaginal Birth.Natural Birth.Scheduled Cesarean.Unplanned Cesarean.Vaginal Birth after C-Section (VBAC)Scheduled Induction.
What is the position of the baby's head?
The back of the baby’s head is to the mother’s left or right (Occiput Transverse position) in about half (48.9%) of babies. Jean Sutton re-introduced attention to the shape of the human uterus. It is higher on the right than the left, making the right wall steeper and the left wall rounder.
How much back pain does an OP baby have?
As a doula of women with and without epidural pain relief, many without, I have noted that OP back pain, when it does come, often comes between 4 and 6 cm.
How many babies are OP when they are born?
The point I’m making is, that just because most OP babies rotate to OA (about 87%, according to Gardberg), we shouldn’t ignore the 15% (Lieberman) who are OP when they are born, either vaginally or via cesarean.
What is an android pelvis?
A pelvic shape which is triangularly called an android pelvis can make it hard for a larger, posterior baby to fit through. A woman with a smaller than average android pelvis will need to, in my observations, eat carefully to get good protein and vegetables without a lot of sweets and white bread. She will have to work on her baby’s position in the 2nd trimester, especially if she is a first-time mom. That way she can avoid the scenario I have often seen of being 8 months pregnant and trying to get a large OP baby to turn around and get settled in the brim facing the back right SI joint.
Why don't midwives pay attention to head down babies?
Sometimes a midwife or doctor will say they don’t pay much attention to a head-down baby’s position in late pregnancy because some posterior babies come out vaginally. Spinning Babies ® is concerned about the 15-30% of OP babies that need more help than strong labor and the hands-and-knees position.
Does fetal position change during labor?
A 2005 study by Ellice Lieberman and her research group in Boston busted some of the myths about posterior labors. Unfortunately, people reading the study could also conclude that fetal position changes at random throughout the course of labor. Yet, in reading the data carefully, we find several consistencies with previous research on the posterior fetal presentation and its effects on labor.
Can ultrasound tell the position of a baby?
Ultrasound can tell the baby’s position. Funny we rely so wholeheartedly on technology. We are looking through dark water to see a 3-D person displayed on a 2-D computer screen. There can be blurred pictures of the crucial landmarks of the baby’s head or the viewer can make a mistake.
What is the best way to deliver a baby from the OP position?
Operative vaginal delivery from the OP position: It could be done if there is sufficient room between the occiput and the sacrum, allowing the baby to turn. Forceps or a vacuum extractor may be used to bring the baby out (8).
How does an OP position complicate labor?
An OP position might complicate the labor by prolonging it. Timely diagnosis and management could help minimize the implications.
How To Prevent An Occiput Posterior Position?
Following the below postures and exercises might help keep the fetus in an appropriate position and facilitate delivery (9).
What Could Be The Complications Of A Posterior Labor?
Here are the possible complications for the mother and the baby in the case of posterior labor (3) (4):
What causes an occiput posterior baby?
Some factors that could lead to an occiput posterior baby are (6): The shape of the pelvis: Anthropoid and android-shaped pelvis es could lead to OP. Women with a heart-shaped pelvis (android) may have the baby in this position because of the narrower front.
What happens to babies in occiput posterior position?
Here is what could happen in the case of posterior labor: Most babies, who are in the occiput posterior position before labor, tend to rotate to the occiput anterior (OA) position after the labor sets in.
Why does the fetal back fit into the curve?
Maternal kyphosis: The mother’s kyphosis or hunchback (excessive curvature of the spinal cord) could make the fetal back fit into the curve. Multiple pregnancies (twins or more) may also be a reason for this position. These causes might increase the chances of OP during delivery if you belong to the high-risk group.
What is the care of OP position?
Usual care in the case of diagnosis of OP position is expectant management. Previous studies report that 72-90% of fetuses will spontaneously rotate to an anterior position during the first or second stage of labour [ 1, 3 ]. Digital rotation of OP to anterior position has been described for the management during the second stage of labour. Although, it has the potential to successfully rotate the fetus and reduce the need for caesarean section, instrumental delivery, and other complications associated with OP position, it may also be traumatic for the fetal head and perineum.
What position should a woman in labor be placed in?
A pillow should be placed between the legs of the woman in labour to limit discomfort.
How does a midwife perform randomisation?
Randomisation will be performed using randomly permuted blocks of varying size (4, 6 and 8) , stratified by parity (nulliparous/multiparous) and epidural analgesia (yes/no). The ratio for hands and knees versus expectant management is 1:1. After confirming eligibility and consent, the system will return the allocation of the women to the midwife.
How many women are fetal OP?
Approximately 15% of women will present a fetal OP position during the first stage of labour and this will concern 600 women per year at our maternity. By our previous experience, we estimate that around 50% of potentially eligible women will be screened (difficulty of the diagnosis during labour) and/or informed (depending on workload in the delivery rooms, emergencies). Thus, we estimate that study entry will be proposed to around 300 eligible women per year. We plan to enrol 150 women per year (12–13 per month). The required sample size could then be reached in around 35 months.
What position do women stay in after randomisation?
Immediately after randomisation, they will stay in their position, other than the hands and knees’ position. After one hour and following ultrasound verification of the fetal head position, they will be given the option to adopt a hands and knees’ position, if they wish to do so. The position of the woman (standing, sitting, semi-sitting, lying on the back or the side) during this hour will be reported in the data collection form.
How long after randomization is fetal head position recorded?
Fifteen minutes after randomisation, women in both groups will complete a short questionnaire on two aspects previously measured just before randomisation, i.e., the perceived pain measured by the VAS and the comfort of their position evaluated by the Likert scale. One hour after randomisation, verification of the fetal head position will be performed, for assessing the primary outcome. Fetal head position will also be recorded at full dilatation of the cervix (before starting pushing efforts). The head position at delivery will also be reported in the data collection forms. Obstetrical and neonatal data will be collected in the medical record.
Why is it important to evaluate the efficacy of maternal position?
If the technique demonstrates efficacy, it would reduce the physical and psychological consequences of complications at birth related to persistent OP position.
What is the best position for a baby to be in during delivery?
The narrowest part of the head can press on the cervix and help it to open during delivery. Most babies generally settle in the head-down position around the 33- to 36-week range. This is the ideal and safest position for delivery.
Why does my baby stay in a posterior position during labor?
These tips don’t always work. If your baby stays in a posterior position when labor starts, it may be because of the shape of your pelvis rather than your posture. In some cases, a cesarean delivery will be necessary.
Why do babies turn their heads down?
This is because there is a small risk of the umbilical cord prolapsing (coming out of the womb before the baby) when your water breaks.
What is the name of the presentation of a baby with a chin?
The baby is able to flex their head and neck, and tuck their chin into their chest. This is usually referred to as occipito-anterior, or the cephalic presentation.
How many babies rotate in the first stage of labor?
In the first stage of labor, about one-tenth to one-third of babies are in this position. Most of these babies will spontaneously rotate themselves to face in the right direction before birth. But a number of cases, the baby doesn’t rotate.
How to know if baby is facing up or down?
Just follow these easy steps: Lie down on your bed and put slight pressure around your pelvic area to feel around for the baby’s head. It’ll feel like a mini bowling ball.
Where are the buttocks in a breech?
Complete breech. The buttocks are pointing toward the birth canal (downward), with the legs folded at the knees. The feet are near the buttocks. Frank breech. The buttocks are toward the birth canal, but the baby’s legs are straight up in front of their body, and the feet are near the head. Footling breech.
What is the OP position in labor?
The occiput posterior (OP) position is one of the most frequent malposition during labor. During the first stage of labor, the fetal head may stay in the OP position in 30% of the cases, but of these only 5-7% remains as such at time of delivery. The diagnosis of OP position in the second stage of labor is made difficult by the presence of the caput succedaneum or scalp hair, both of which may give some problem in the identification of fetal head sutures and fontanels and their location in relationship to maternal pelvic landmarks. The capability of diagnosing a fetus in OP position by digital examination has been extremely inaccurate, whereas an ultrasound approach, transabdominal, transperineal and transvaginal, has clearly shown its superior diagnostic accuracy. This is true not only for diagnosis of malpositions, detected in both first and second stage of labor, but also in cases of marked asynclitism.
What is the occiput posterior position?
The occiput posterior (OP) position is one of the most frequent malposition during labor. During the first stage of labor, the fetal head may stay in the OP position in 30% of the cases, but of these only 5-7% remains as such at time of delivery. The diagnosis of OP position in the second stage of l …
What is the OP position of a baby?
A knee may slide past under the navel. The OP position (occiput posterior fetal position) is when the back of the baby’s head is against the mother’s back. Here are drawings of an anterior and posterior presentation. Baby Positions.
Which position is direct OP?
Four starting positions often lead to (or remain as) direct OP in active labor. Right Occiput Transverse (ROT), Right Occiput Posterior (ROP), and Left Occiput Posterior (LOP) join direct OP in adding labor time. The LOP baby has less distance to travel to get into an LOT position.
What causes a baby to be posterior?
There is a rising incidence of posterior babies at the time of birth. We know now that epidural anesthesia increases the rate of posterior position at the time of birth from about 4% (for women who don’t choose an epidural in a university birth setting) up to about 13% (Lieberman, 2005). Low thyroid function is associated with fetal malposition such as posterior or breech. (See Research & References .)
How many babies are OP in labor?
Studies estimate 15-30% of babies are OP in labor. Jean Sutton in Optimal Fetal Positioning states that 50% of babies trend toward posterior in early labor upon admission to the hospital. Strong latent labor swings about a third of these to LOT before dilation begins (in “pre-labor” or “false labor”).
How to tell if a baby is OP?
The best way to tell if your baby is OP or not, usually, is if you feel little wiggles in the abdomen right above your pubic bone. These are the fingers. They’d feel like little fingers wiggling, not like a big thunk or grinding from the head, though you might feel that, too.
What does it mean when a baby's back is extended?
The posterior baby’s back is often extended straight or arched along the mother’s spine. Having the baby’s back extended often pushes the baby’s chin up. Attention: Having the chin up is what makes the posterior baby’s head seem larger than the same baby when it’s in the anterior position.
Where does a baby go in labor?
Most babies go on to OA at the pelvic floor or further down on the perineal floor.
