
Classical conditioning involves associating an involuntary response and a stimulus, while operant conditioning is about associating a voluntary behavior and a consequence. In operant conditioning, the learner is also rewarded with incentives, while classical conditioning involves no such enticements.
What are the basic principles of classical conditioning?
Key Principles
- Acquisition. Acquisition is the initial stage of learning when a response is first established and gradually strengthened. ...
- Extinction. Extinction is when the occurrences of a conditioned response decrease or disappear. ...
- Spontaneous Recovery. ...
- Generalization. ...
- Discrimination. ...
What is the difference between operational and classical conditioning?
• Theory:
- Association between behavior and results:
- In classical conditioning, the association cannot be controlled.
- In operant conditioning, the association between behavior and results is learned.
What therapy is based on classical conditioning?
With repeated presentations, the two stimuli become associated and the person develops an aversion towards the stimuli which initially caused the deviant behavior. Aversion therapy is based on classical conditioning. According to learning theory, two stimuli become associated when they occur frequently together (pairing).
What are the key elements in operant conditioning?
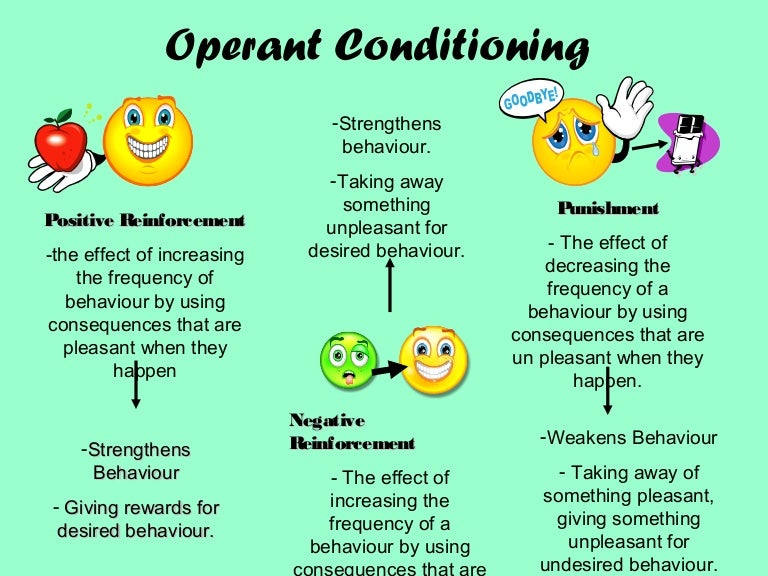
Elements of Operant Conditioning. There are 4 elements that describe operant conditioning: positive reinforcement; negative reinforcment; punishment; extinction . Reference
What are examples of classical and operant conditioning?
While classical conditioning is training dogs to salivate to the sound of a metronome, operant conditioning is training them to sit by giving them a treat when they do.
What is the difference between classical & operant conditioning?
The main difference between classical and operant conditioning is that classical conditioning associates involuntary behavior with a stimulus while operant conditioning associates voluntary action with a consequence. Classical and operant conditioning are two central concepts in behavioral psychology.
What is operant conditioning with examples?
In operant conditioning, behavior is controlled by external stimuli. For example, a child may learn to open a box to get the sweets inside, or learn to avoid touching a hot stove; in operant terms, the box and the stove are "discriminative stimuli". Operant behavior is said to be "voluntary".
What is an example of a classical conditioning?
For example, whenever you come home wearing a baseball cap, you take your child to the park to play. So, whenever your child sees you come home with a baseball cap, he is excited because he has associated your baseball cap with a trip to the park. This learning by association is classical conditioning.
What is classical conditioning theory?
Discovered by Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov, classical conditioning is a type of unconscious or automatic learning. This learning process creates a conditioned response through associations between an unconditioned stimulus and a neutral stimulus.
What are the 4 types of operant conditioning?
In Operant Conditioning Theory, there are essentially four quadrants: Positive Reinforcement, Positive Punishment, Negative Reinforcement, and Negative Punishment.
What theory is operant conditioning?
Operant conditioning is a theory of learning in behavioral psychology which emphasises the role of reinforcement in conditioning. It emphasises the effect that rewards and punishments for specific behaviors can have on a person's future actions.
Which of the following is the best example of classical conditioning?
Have you heard of Pavlov's dogs? That's the experiment conducted by Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov wherein his dogs started to salivate when he rang a bell. This is the best-known example of classical conditioning, when a neutral stimulus is paired with a conditioned response.
What is an example of operant behavior?
Operant responses can include everything from a rat's lever press maintained by food, an infant's crying maintained by maternal attention, and small talk maintained by social companionship.
What is an example of operant conditioning in everyday life?
A child is scolded (unpleasant event) for ignoring homework (undesirable behavior.) A parent gives a child a time-out (unpleasant consequence) for throwing tantrums (unwanted behavior.) The police gives a driver a ticket (unpleasant stimulus) for speeding (unwanted behavior.)
What are the 5 principles of classical conditioning?
Let's take a closer look at five key principles of classical conditioning:Acquisition. Acquisition is the initial stage of learning when a response is first established and gradually strengthened. ... Extinction. ... Spontaneous Recovery. ... Stimulus Generalization. ... Stimulus Discrimination.
Why is classical conditioning important?
Most psychologists now agree that classical conditioning is a basic form of learning. Furthermore, it is well-known that Pavlovian principles can influence human health, emotion, motivation, and therapy of psychological disorders. There are many clinically related uses of classical conditioning.
What is the difference between Pavlov and Skinner?
Pavlov's theory focused more on how behavior can be affected by specific stimuli while Skinner focused more on what occurs after a behavior. Skinner's research and study was centered on what happens after a behavior and the consequences from such an action.
What is operant conditioning in psychology?
Operant conditioning (also known as instrumental conditioning) is a process by which humans and animals learn to behave in such a way as to obtain rewards and avoid punishments. It is also the name for the paradigm in experimental psychology by which such learning and action selection processes are studied.
Why is classical and operant conditioning important?
Understanding classical and operant conditioning provides psychologists with many tools for understanding learning and behavior in the world outside the lab. This is in part because the two types of learning occur continuously throughout our lives.
When you compare classical conditioning to operant conditioning the main distinction between them would be that quizlet?
What is the main difference between classical conditioning and operant conditioning? Classical conditioning requires learning that two events are related, whereas operant conditioning demonstrates that behavior leads to a consequence.
What is an example of operant conditioning in psychology?
An example of operant conditioning would be a child who is trained to do a chore at home by being given a reward for completing it, such as sticker...
How can classical conditioning be used?
Classical conditioning can be used in therapeutic treatment for people who have phobias to help them learn new associations. Since fear responses a...
What are the 4 types of operant conditioning?
Positive reinforcement strengthens a particular behavior by adding something pleasant as a consequence. Negative reinforcement strengthens a parti...
What is an example of classical conditioning in psychology?
An example of classical conditioning would be if you visit your grandmother (unconditioned stimulus) and it makes you feel happy (unconditioned res...
How do you explain operant conditioning?
Operant conditioning is the shaping or modifying of behaviors through the use of consequences. These consequences can either be rewards used to str...
What is operant conditioning?
Also known as instrumental conditioning, operant conditioning uses reinforcement or punishment to increase wanted behaviors and decrease unwanted behaviors. Depending on the amount, frequency and type of reinforcements or punishments, humans develop, modify and abandon behaviors at different rates, known as schedules of reinforcement. Here are the five types of reinforcement schedules that impact the behavior change rate differently:
How does operant conditioning help students?
Teachers may also use operant conditioning to promote positive behaviors like excellence in particular subjects, hard work on challenging projects or assignments and engaged learning in the classroom. For example, teachers of young students may use "token economy," which is a system of using secondary reinforcers that take the place of primary reinforces after the fact, and provide a star to each student who turns in their homework on time. This can help reinforce the wanted behavior of meeting deadlines and decreasing the unwanted behaviors of missing deadlines or neglecting to turn in homework.
What is variable interval reinforcement?
Variable-interval reinforcement: After the wanted behavior occurs once, a positive reinforcement is given after a random, unpredictable amount of time. This results in a fast response rate and a slow extinction rate.
What is continuous reinforcement?
Continuous reinforcement: This schedule of reinforcement involves positively reinforcing a wanted behavior each time the behavior occurs. This results in a slow response rate, which is the frequency of the behavior occurring, and a fast extinction rate, the rate at which the behavior decreases completely.
What is fixed ratio reinforcement?
Fixed-ratio reinforcement: This schedule involves positively reinforcing a wanted behavior after it has occurred a certain number of times, which results in a fast response rate and a medium-speed extinction rate.
Why is classical conditioning important?
Classical conditioning can help investors better navigate severe shifts in the stock market after instantaneous reactions from weary investors.
Who discovered classical conditioning?
Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov developed and studied classical conditioning in the late 1890s. This scientist discovered this type of conditioning when he rang a bell every time his test subjects—dogs—got food. Every time the dogs were given food, they would begin to salivate, which is a natural reaction. When Pavlov rang the bell before they got fed, the dogs developed a conditioned response, sometimes referred to as a Pavlovian response, to salivate anytime they heard the bell regardless of whether they received food.
What is operant conditioning?
In operant conditioning, learning refers to changes in behavior as a result of experiences that occur after a response. Operant conditioning involves changing voluntary behaviors.
What is classical conditioning?
He studied what is called classical conditioning. You'll sometimes also hear this referred to as respondent conditioning. In classical conditioning, learning refers to involuntary responses that result from experiences that occur before a response.
How Are Behaviors Learned?
Skinner, two behavioral psychologists who pioneered the theories of classical and operant conditioning, respectively. Let's examine how the theories they studied help us understand the way the way we learn.
What is the term for the disappearance of a conditioned response?
Extinction is a term that refers to the disappearance of a conditioned response. The response weakens and eventually disappears due to removal of the reinforcement or punishment in operant conditioning or the removal of the paired stimulus in classical conditioning.
What is an example of a stimulus that evokes an unconditioned response?
For an example of a stimulus that evokes an unconditioned response, let's imagine a kiss. Kissing creates involuntary arousal responses; it causes you to experience an elevated heart rate, for example. This is a natural response, it is not learned, and it happens automatically.
What is conditioning in psychology?
Conditioning is a learning technique that associates a stimulus to a certain behavior or response. Learn about the differences between classical conditioning and operant conditioning, as well as relevant examples, and discover phenomena associated with behavioral conditioning. Updated: 08/28/2021
What is the difference between punishment and negative reinforcement?
The key difference is that negative reinforcement involves the removal of a negative consequence to increase the likelihood of a response. Reinforcement always increases the occurrence of a response, while punishment always decreases the occurrence of a response. Now, let's think of the example of the kiss again.
What is Operant Conditioning?
If we want to get all formal and jargony about it, we could say it is "conditioning in which an operant response is brought under stimulus control by the presentation of a consequence contingent upon the occurrence of the operant response."
What is getting linked in classical conditioning?
In classical conditioning, what is getting linked is just two events, as they happen, regardless of what the learner is doing in that scenario.
What is classical conditioning for dogs?
For dog training purposes, you can think of Classical Conditioning as governing associations, reflexes, and by extension, emotional responses.
How many kinds of consequences are there in operation conditioning?
In Operant Conditioning there are 4 kinds of consequences you can apply, helpfully arranged into quadrants for us for the sake of organization.
What happens when a dog performs a behavior?
Specifically, dogs notice that performing that behavior leads to that consequence, and they make a decision to engage in that behavior again. In classical conditioning, what is getting linked is just two events, as they happen, regardless of what the learner is doing in that scenario.
What is an unconditioned response?
And an "unconditioned response" would be, by extension, a behavior that doesn't have to be learned. Your response to food is innate, and not conditioned.
What is an operating response?
Also in that definition is the term "operant response." For our purposes, we're going to think of that as "a behavior done on purpose." It's a freely-chosen, voluntary, planned action, and it is modifiable rather than rigid.
What is operant conditioning?
dancing with the tiger plate!). In operant conditioning, the consequences which come after a behavior will vary, to alter that behavior. Imagine years down the road you are still enamored of delicious PB&J sandwiches, and now are trying to teach yourself to be a good roommate. The house rule is that whoever leaves their dishes unwashed the longest has to take out the trash. You hate taking out the trash, so you develop a system - whenever you remember to wash your plate, you are allowed to surf the internet, otherwise you’re not allowed. The more dishes you wash, the more you get to procrastinate on your favorite sites. Initially, you leave the plate in the sink a few times, then you begin to remember after a day or so, and finally you start to wash your dishes immediately after using them. This process of shaping involves intermediate behaviors (leaving the plate in the sink and beginning to come back to wash the dishes within hours) that start moving you towards the goal behavior (washing your dishes immediately).
What is classical conditioning?
Imagine your favorite snack is peanut butter and jelly sandwiches. Whenever you get that snack, it makes you happy and you start to jump around, doing your happy PB&J dance. Your sandwich always comes on the same plate – it’s big and orange and has a picture of a tiger on it. Eventually, you might start doing your PB&J dance whenever you see your tiger plate on the table, in anticipation of the sandwich arriving.
What is conditioning?
Conditioning is a type of learning that links some sort of trigger or stimulus to a human behavior or response. When psychology was first starting as a field, scientists felt they couldn’t objectively describe what was going on in people’s heads. However, they could observe behaviors so that’s what they focused on in their experiments. The major theories about learning come from the conclusions drawn from these experiments.
How effective is the conditioning?
Imagine your tiger plate was one of a set of plates – jungle cat plates. There is a lion, a jaguar, and a leopard as well
How many ways can operant conditioning affect behavior?
There end up being 4 different ways we can affect behavior with operant conditioning:
When is reinforcement given?
Reinforcement is given when a desired action occurs. The positive/negative only refers to whether something additional is added (positive) or something is taken away (negative). Comment on Brenden's post “It has to do with what a ...”.
What is the difference between operant and classical conditioning?
The main difference between classical and operant conditioning is the way the behavior is conditioned. In classical conditioning, a neutral stimulus is paired with a conditioned response. In operant conditioning, a desired behavior is paired with a consequence.
What Is Operant Conditioning?
In contrast to classical conditioning, operant conditioning involves encouraging or discouraging a specific behavior using reinforcement. While classical conditioning is training dogs to salivate to the sound of a metronome, operant conditioning is training them to sit by giving them a treat when they do.
What was Pavlov's conditioned response?
Pavlov would use the metronome every time the dogs were fed, and the dogs began to associate the sound with food. Salivating was their conditioned response. You can see real-world examples of classical conditioning in everything from your response to your cell phone to the way you react when you hear holiday music.
What is classical conditioning?
Classical conditioning is when a conditioned response is paired with a neutral stimulus. The most famous example of this is Pavlov’s dogs, where Ivan Pavlov trained dogs to salivate at the sound of a metronome. The metronome was a neutral stimulus, since the dogs previously had no reaction to it. Pavlov would use the metronome every time ...
Who developed operant conditioning?
B.F. Skinner proposed the theory of operant conditioning, and he used a simple experiment with a rat to develop the theory. In the experiment, a hungry rat is placed in a box. As the rat explores, it discovers a lever. When it pushes the lever, it gets food. Over time, the rat learns to push the lever to receive food.
Is operant conditioning a part of behavioral psychology?
Both Are Part of Behaviorism. Both classical and operant conditioning are important in the field of behavioral psychology. Examples of behaviorism include both kinds of conditioning, and it’s fascinating to learn about the way these concepts are applied.
Why is operant conditioning considered incomplete?
First, operant conditioning is accused of being an incomplete explanation for learning because it neglects the role of biological and cognitive elements.
How is operation conditioning used?
Operant conditioning is also used in behavior modification, an approach to the treatment of numerous issues in adults and children, including phobias, anxiety, bedwetting, and many others. One way behavior modification can be implemented is through a token economy, in which desired behaviors are reinforced by tokens in the form of digital badges, buttons, chips, stickers, or other objects. Eventually these tokens can be exchanged for real rewards.
What is shaping in behavioral science?
Behavior Shaping. Operant conditioning can lead to increasingly complex behaviors through shaping, also referred to as the “method of approximations.”. Shaping happens in a step-by-step fashion as each part of a more intricate behavior is reinforced. Shaping starts by reinforcing the first part of the behavior.
Why is Skinner's observation about operant conditioning flawed?
Finally, because Skinner’s observations about operant conditioning relied on experiments with animals, he is criticized for extrapolating from his animal studies to make predictions about human behavior. Some psychologists believe this kind of generalization is flawed because humans and non-human animals are physically and cognitively different.
What is the process of learning through reinforcement and punishment?
Operant conditioning is the process of learning through reinforcement and punishment.
How did Skinner study operant conditioning?
To study operant conditioning, Skinner conducted experiments using a “Skinner Box,” a small box that had a lever at one end that would provide food or water when pressed. An animal, like a pigeon or rat, was placed in the box where it was free to move around. Eventually the animal would press the lever and be rewarded. Skinner found that this process resulted in the animal pressing the lever more frequently. Skinner would measure learning by tracking the rate of the animal’s responses when those responses were reinforced.
Why are conditional reinforcers not innately desirable?
Conditioned reinforcers reinforce behavior not because they are innately desirable, but because we learn to associate them with primary reinforcers. For example, Paper money is not innately desirable, but it can be used to acquire innately desirable goods, such as food and shelter.
What is operant conditioning?
Operant conditioning, also known as instrumental conditioning, is a method of learning normally attributed to B.F. Skinner, where the consequences of a response determine the probability of it being repeated. Through operant conditioning behavior which is reinforced (rewarded) will likely be repeated, and behavior which is punished will occur less ...
Why did the Skinner study show that rats learned to repeat behavior?
In the Skinner study, because food followed a particular behavior the rats learned to repeat that behavior, e.g., operant conditioning. • There is little difference between the learning that takes place in humans and that in other animals. Therefore research (e.g., operant conditioning) can be carried out on animals (Rats / Pigeons) ...
How did Skinner show positive reinforcement?
Skinner showed how positive reinforcement worked by placing a hungry rat in his Skinner box. The box contained a lever on the side, and as the rat moved about the box, it would accidentally knock the lever. Immediately it did so a food pellet would drop into a container next to the lever.
How does positive reinforcement help rats?
Positive reinforcement strengthens a behavior by providing a consequence an individual finds rewarding.
Why is negative reinforcement important?
This is known as negative reinforcement because it is the removal of an adverse stimulus which is ‘rewarding’ to the animal or person. Negative reinforcement strengthens behavior because it stops or removes an unpleasant experience. For example, if you do not complete your homework, you give your teacher £5.
What is punishment in psychology?
Punishment is defined as the opposite of reinforcement since it is designed to weaken or eliminate a response rather than increase it. It is an aversive event that decreases the behavior that it follows.
When is behavior reinforced?
Behavior is reinforced only after the behavior occurs a specified number of times. e.g., one reinforcement is given after every so many correct responses, e.g., after every 5th response. For example, a child receives a star for every five words spelled correctly.
