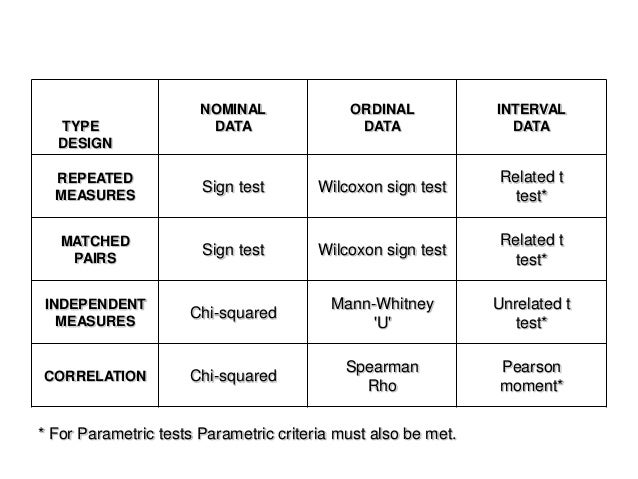
What are the four levels of measurement?
- Nominal. The nominal level of measurement in psychology consists essentially of measurements of ‘ named ’ or ‘ labelled data ’.
- Ordinal data. The ordinal level of measurement in psychology is categorical data, and the values have a fixed set or order.
- Ratio data. The ratio level of measurement in psychology is classified and ranked data. ...
- Interval data. ...
What is the difference between nominal and ordinal data?
- Ordinal data is placed into some kind of order.
- Ordinal numbers only show sequence.
- We can assign numbers to ordinal data.
- We cannot do arithmetic with ordinal numbers.
- We don’t know whether the differences between the values are equal.
What is the difference between ordinal and categorical data?
what type of data is temperature
- Various Types of Thermometers, Measuring Temperature, How They Are Used, Learning For Children
- Types of Data: Nominal, Ordinal, Interval/Ratio – Statistics Help
- Scales of Measurement – Nominal, Ordinal, Interval, & Ratio Scale Data
Can you take the mean of ordinal data?
Can you take the mean of ordinal data? You'll often reach similar conclusions whether you use mode, median, or mean. Using the mean of ordinal data is fine; just be careful not to make interval or ratio statements about your data — even researchers who take a more relaxed view of averaging ordinal data would disagree with that practice.
What does ordinal data mean?
What is Ordinal Data? In statistics, ordinal data are the type of data in which the values follow a natural order. One of the most notable features of ordinal data is that the differences between the data values cannot be determined or are meaningless. Generally, the data categories lack the width representing the equal increments of the underlying attribute.

What is the difference between ordinal and interval data psychology?
Ordinal data are most concerned about the order and ranking while interval data are concerned about the differences of value within two consecutive values.
What are ordinal data examples?
Examples of ordinal variables include: socio economic status (“low income”,”middle income”,”high income”), education level (“high school”,”BS”,”MS”,”PhD”), income level (“less than 50K”, “50K-100K”, “over 100K”), satisfaction rating (“extremely dislike”, “dislike”, “neutral”, “like”, “extremely like”).
What does ordinal data mean?
In statistics, ordinal data are the type of data in which the values follow a natural order. One of the most notable features of ordinal data is that the differences between the data values cannot be determined or are meaningless.
What is nominal and ordinal data psychology?
Nominal data is a group of non-parametric variables, while Ordinal data is a group of non-parametric ordered variables. Although, they are both non-parametric variables, what differentiates them is the fact that ordinal data is placed into some kind of order by their position.
What is nominal data in psychology?
Nominal level data is frequency or count data that consists of the number of participants falling into categories. ( e.g. 7 people passed their driving test the first time and 6 people didn't.
Is gender nominal or ordinal?
nominal variableGender is an example of a nominal variable because the categories (woman, man, transgender, non-binary, etc.) cannot be ordered from high to low. Olympic medals are an example of an ordinal variable because the categories (gold, silver, bronze) can be ordered from high to low.
What is ordinal qualitative data?
A definition. Ordinal data is a type of qualitative (non-numeric) data that groups variables into descriptive categories. A distinguishing feature of ordinal data is that the categories it uses are ordered on some kind of hierarchical scale, e.g. high to low.
What is ordinal variable in research?
An ordinal variable is a categorical variable for which the possible values are ordered. Ordinal variables can be considered “in between” categorical and quantitative variables.
What is nominal and ordinal?
Nominal: the data can only be categorized. Ordinal: the data can be categorized and ranked. Interval: the data can be categorized and ranked, and evenly spaced. Ratio: the data can be categorized, ranked, evenly spaced and has a natural zero.
What is nominal data?
Nominal data is data that can be labelled or classified into mutually exclusive categories within a variable. These categories cannot be ordered in a meaningful way. For example, for the nominal variable of preferred mode of transportation, you may have the categories of car, bus, train, tram or bicycle.
What is categorical data in psychology?
a variable that is defined by a set of two or more categories. Examples include a person's sex, marital status, or rankings of particular stimuli (such as the relative loudness of different sounds).
What is the difference between nominal and ordinal variables?
Nominal: the data can only be categorized. Ordinal: the data can be categorized and ranked. Interval: the data can be categorized and ranked, and evenly spaced. Ratio: the data can be categorized, ranked, evenly spaced and has a natural zero.
What is ordinal data?
Ordinal data is classified into categories within a variable that have a natural rank order. However, the distances between the categories are uneven or unknown. For example, the variable “frequency of physical exercise” can be categorized into the following: 1. Never.
What are the characteristics of ordinal data?
Ordinal data has two characteristics: The data can be classified into different categories within a variable. The categories have a natural ranked order. However, unlike with interval data, the distances between the categories are uneven or unknown.
How does interval data differ from ordinal data?
Interval data differs from ordinal data because the differences between adjacent scores are equal.
How to visualize data?
To visualize your data, you can present it on a bar graph. Plot your categories on the x-axis and the frequencies on the y-axis. Unlike with nominal data, the order of categories matters when displaying ordinal data. Example: Bar graph.
Can the median be found with ordinal data?
While the mode can almost always be found for ordinal data, the median can only be found in some cases. The mean cannot be computed with ordinal data. Finding the mean requires you to perform arithmetic operations like addition and division on the values in the data set.
What is ordinal data?
In statistics, ordinal data are the type of data in which the values follow a natural order. One of the most notable features of ordinal data is that the differences between the data values cannot be determined or are meaningless.
How to analyze ordinal data?
How to Analyze the Data? The simplest way to analyze ordinal data is to use visualization tools. For instance, the data may be presented in a table in which each row indicates a distinct category. In addition, they can also be visualized using various charts.
Is income ordinal or ratio?
For example, the ranges of income are considered ordinal data while the income itself is the ratio data. Unlike interval or ratio data, ordinal data cannot be manipulated using mathematical operators. Due to this reason, the only available measure of central tendency.
What is ordinal data?
Ordinal Data Definition: Ordinal data is a statistical type of quantitative datain which variables exist in naturally occurring ordered categories. The distance between two categories is not established using ordinal data. In statistics, a group of ordinal numbers indicates ordinal data and a group of ordinal data are represented using an ordinal ...
Is ordinal data neutral or unimportant?
Neutral. Unimportant . Very Unimportant. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ordinal data is thus a collection of ordinal variables, i.e., if you have variables in a particular order – “low, medium, high”, they can be represented as ordinal data.
Why is it important to know the difference between nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio?
Knowing the difference between nominal, ordinal, interval and ratio data is important because these influence the way in which you can analyse data from experiments. For example, when data is collected from an experiment, the experimenter will run a statistical test on the data to see whether the results are significant.
What is nominal data?
Nominal data is named data which can be separated into discrete categories which do not overlap. A common example of nominal data is gender; male and female. Other examples include eye colour and hair colour. An easy way to remember this type of data is that nominal sounds like named, nominal = named. Ordinal Data.
How to collect ordinal data?
Collecting Ordinal Data. If the exam question stipulates that you should collect ordinal data, then the easiest way of doing that is to use a self-report questionnaire with rating scales. Remember that you can use questionnaires within experiments, if the question also stipulates that you have to use an experiment.
What is the most important part of collecting ordinal data from structured observations?
When you complete the observation you give each behaviour a rating. Giving the behaviours a rating is the most important part of collecting ordinal data from structured observations.
What is nominal data?
Quite simply, Nominal Data is data which cannot be assigned a numerical value of any true mathematical significance. Let’s look at an example. Suppose we have four participants in an exam: This is nominal data because the name assigned to each participant, while numerical, does not have any mathematical significance.
Why is ratio data more precise than interval data?
Ratio data is more precise than interval data because it has an absolute zero. One of the most common examples of ratio data is time, because 0 seconds really is the lowest amount of time, unlike temperature, which does go into negative numbers.
Why is participant 4 nominal data?
Participant 4. This is nominal data because the name assigned to each participant, while numerical, does not have any mathematical significance. From these names alone we cannot rank the participants because they simply have been assigned a random number.
Can nominal data be used to measure central tendency?
Firstly, as nominal data is simply a name we cannot use any measures of central tendency, such as the mean, mode and median with this type of data. We cannot work out what the mean name of exam participants is, nor would there be any use in doing so.

An Introduction to The Four Different Types of Data
What Is Ordinal Data? A Definition
- Ordinal data is a type of qualitative (non-numeric) datathat groups variables into descriptive categories. A distinguishing feature of ordinal data is that the categories it uses are ordered on some kind of hierarchical scale, e.g. high to low. On the levels of measurement, ordinal data comes second in complexity, directly after nominal data. While...
What Are Some Examples of Ordinal Data?
- What are some examples of ordinal data? 1. Economic status (poor, middle income, wealthy) 2. Income level in non-equally distributed ranges ($10K-$20K, $20K-$35K, $35K-$100K) 3. Course grades (A+, A-, B+, B-, C) 4. Education level (Elementary, High School, College, Graduate, Post-graduate) 5. Likert scales (Very satisfied, satisfied, neutral, dissatisfied, very dissatisfied) 6. Milit…
How Is Ordinal Data Collected and What Is It Used for?
- Ordinal data are usually collected via surveys or questionnaires. Any type of question that ranks answers using an explicit or implicit scale can be used to collect ordinal data. An example might be: 1. Question: Which best describes your knowledge of the Python programming language? Possible answers:Beginner, Basic, Intermediate, Advanced, Expert. This commonly recognized ty…
How to Analyze Ordinal Data
- As discussed, the level of measurement you use determines the kinds of analysisyou can carry out on your data. In general, these fall into two broad categories: descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. We use descriptive statistics to summarize the characteristics of a dataset. This helps us spot patterns. Meanwhile, inferential statistics allow us to make predictions (or inf…
Summary and Further Reading
- In this guide, we: 1. Introduced the four levels of data measurement: Nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio. 2. Defined ordinal data as a qualitative (non-numeric) data type that groups variables into ranked descriptive categories. 3. Explained the difference between ordinal and nominal data: Both are types of categorical data. However, nominal data lacks hierarchy, whereas ordinal data rank…
Levels of Measurement
Examples of Ordinal Scales
- In social scientific research, ordinal variables often include ratings about opinions or perceptions, or demographic factors that are categorized into levels or brackets (such as social status or income).
How to Collect Ordinal Data
- Ordinal variables are usually assessed using closed-ended surveyquestions that give participants several possible answers to choose from. These are user-friendly and let you easily compare data between participants.