
Ordinal Variables
- Ordinal Variables Definition. The variables that classify the data in a specific order are known as ordinal variables. ...
- Overview of Ordinal Variables. ...
- Important terms. ...
- Use of ordinal variables in research and analysis. ...
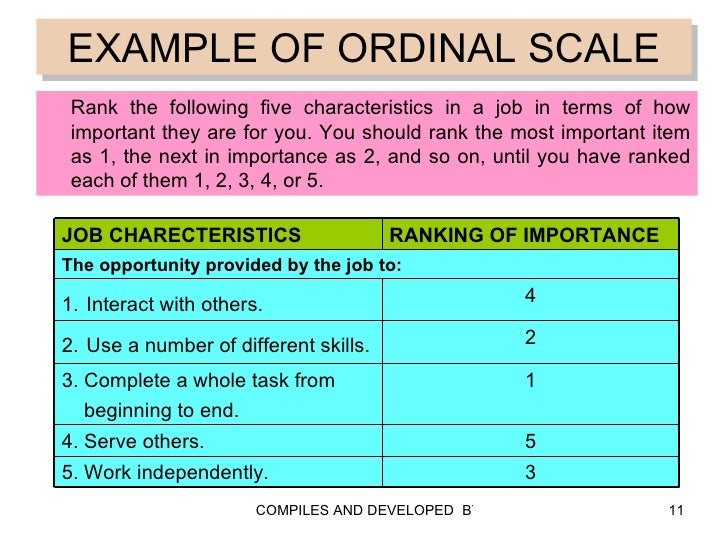
- An example of using ordinal variables method. ...
Is an ordinal variable quantitative or qualitative?
So, ordinal variables sit somewhere between quantitative and qualitative measures. They are numericalised and hence appear quantitative but they represent categories which essentially are qualitative. So which one are they? Strictly, they are qualitative. But have quantitative attributes that lend them to a limited set of quantitative manipulation.
What are the diffrent types of variables?
Variables are broadly categorized into:
- Independent variables
- Dependent variable
- Control variable
What is the difference between ordinal and categorical?
Ordinal.An ordinal variable is similar to a categorical variable. The difference between the two is that there is a clear ordering of the variables. Even though we can order these from lowest to highest, the spacing between the values may not be the same across the levels of the variables.
What are some examples of ordinal data?
What are some examples of ordinal data?
- 70 and above.
- 60-69.
- 50-59.
- 40-49.
- 35-40.
- 34 and below.
What are examples of ordinal variables?
Examples of ordinal variables include: socio economic status (“low income”,”middle income”,”high income”), education level (“high school”,”BS”,”MS”,”PhD”), income level (“less than 50K”, “50K-100K”, “over 100K”), satisfaction rating (“extremely dislike”, “dislike”, “neutral”, “like”, “extremely like”).
What is the example of ordinal in research?
Examples of ordinal data includes likert scale; used by researchers to scale responses in surveys and interval scale;where each response is from an interval of it's own.
How do you know if a variable is ordinal?
A purely nominal variable is one that simply allows you to assign categories but you cannot clearly order the categories. If the variable has a clear ordering, then that variable would be an ordinal variable, as described below.
What are nominal and ordinal variables?
There are two types of categorical variable, nominal and ordinal. A nominal variable has no intrinsic ordering to its categories. For example, gender is a categorical variable having two categories (male and female) with no intrinsic ordering to the categories. An ordinal variable has a clear ordering.
Is age an ordinal variable?
Age can be both nominal and ordinal data depending on the question types. I.e “How old are you” is used to collect nominal data while “Are you the firstborn or What position are you in your family” is used to collect ordinal data. Age becomes ordinal data when there's some sort of order to it.
What is the difference between nominal and ordinal?
Nominal: the data can only be categorized. Ordinal: the data can be categorized and ranked. Interval: the data can be categorized and ranked, and evenly spaced. Ratio: the data can be categorized, ranked, evenly spaced and has a natural zero.
Is education an ordinal variable?
Ordinal Data Levels of Measurement Values of ordinal variables have a meaningful order to them. For example, education level (with possible values of high school, undergraduate degree, and graduate degree) would be an ordinal variable.
Is age an ordinal or interval?
Generally speaking, age is an ordinal variable since the number assigned to a person's age is meaningful and not simple an arbitrarily chosen number/marker.
Is gender nominal or ordinal?
nominal variableGender is an example of a nominal variable because the categories (woman, man, transgender, non-binary, etc.) cannot be ordered from high to low. Olympic medals are an example of an ordinal variable because the categories (gold, silver, bronze) can be ordered from high to low.
What is a nominal variable example?
A nominal variable is qualitative, which means numbers are used here only to categorize or identify objects. For example, the number at the back of a player's jersey is used to identify the position he/she is playing. They can also take quantitative values.
What is nominal variable in research?
A nominal variable is a type of categorical variable that can have two or more categories. However, there is no ordering within these categories. A nominal variable does not have any numerical characteristics and is qualitative in nature.
Which of the following is an example of an ordinal scale?
Some examples of variables that use ordinal scales would be movie ratings, political affiliation, military rank, etc. One example of an ordinal scale could be "movie ratings".
What is the example of nominal?
Nominal data are used to label variables without any quantitative value. Common examples include male/female (albeit somewhat outdated), hair color, nationalities, names of people, and so on. In plain English: basically, they're labels (and nominal comes from "name" to help you remember).
What is nominal scale with example?
A nominal scale is a scale (of measurement) that uses labels to classify cases (measurements) into classes. Some examples of variables that use nominal scales would be religious affiliation, sex, the city where you live, etc. Example. One example of a nominal scale could be "sex".
What is interval example?
To identify whether a scale is interval or ordinal, consider whether it uses values with fixed measurement units, where the distances between any two points are of known size. For example: A pain rating scale from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain) is interval.
What is ordinal variable?
Ordinal variables are those variables which have discrete values but has some order involved. The variables do not have to necessarily directly correlate to a specific value, but is often used as a qualitative way of understanding data.
How does an Ordinal Variable work?
Imagine, for example, a patient is at the doctor because they have a sprained ankle. The doctor may come in an ask "On a scale from 1 to 10, how would you rate your pain?" This is an example of an ordinal variable. Naturally, pain is not usually measured internally on a discrete basis, however the answer to the question is informative nonetheless. If the patient indicates a 7, the doctor would be able to infer that they are in more pain than if they reported a 4 out of 10. Ordinal variables, while not necessarily directly correlated to the associated data they represent, are nevertheless informative due to the order of the values.
What is ordinal data?
Ordinal Data Definition: Ordinal data is a statistical type of quantitative datain which variables exist in naturally occurring ordered categories. The distance between two categories is not established using ordinal data. In statistics, a group of ordinal numbers indicates ordinal data and a group of ordinal data are represented using an ordinal ...
How to compare more than two ordinal groups?
To compare more than two ordinal groups, Kruskal–Wallis H test should be used – In this test, there is no assumption that the data is coming from a particular source. This test concludes whether the median of two or more groups is varied. It will show the difference between more than two ordinal data groups.
Which test is used to compare two ordinal data groups?
To compare two ordinal data groups, the Mann-Whitney U test should be used. – This test allows a researcher to conclude that a variable from one sample is greater or lesser than another variable randomly selected from another sample.
Is the difference between variables uniform?
The difference between variables is not uniform.
Is ordinal data neutral or unimportant?
Neutral. Unimportant . Very Unimportant. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ordinal data is thus a collection of ordinal variables, i.e., if you have variables in a particular order – “low, medium, high”, they can be represented as ordinal data.
What are ordinal variables?
Ordinal variables can be classified into 2 main categories, namely; the matched and unmatched category. This ordinal variable classification is based on the concept of matching - pairing up data variables with similar characteristics.
Why is ordinal variable different from other qualitative variables?
Ordinal variables differs from other qualitative variables because parametric analysis median and mode is used for analysis. This is due to the assumption that equal distance between categories does not hold for ordinal data.
How is ordinal data analysis different from nominal data analysis?
Ordinal data analysis is quite different from nominal data analysis, even though they are both qualitative variables. It incorporates the natural ordering of the variables in order to avoid loss of power. Ordinal variables differs from other qualitative variables because parametric analysis median and mode is used for analysis
What are univariate statistics?
Univariate statistics: Used in place of mean and standard deviation, the appropriate univariate statistics for ordinal data include the median, quartiles, percentiles and quartile deviation.
What is the difference between median and ordinal?
Unlike in nominal data where only the mode can be calculated, ordinal data has a median. Median is the value in the middle but not the middle value of a scale and can be calculated with data which has an innate order. Consider the ordinal variable example below. .
Why is ordinal data used?
Ordinal data is used to carry out surveys or questionnaires due to its “ordered” nature. Statistical analysis is applied to collected responses in order to place respondents into different categories, according to their responses. The result of this analysis is used to draw inferences and conclusions about the respondents with regard to specific variables. Ordinal data is mostly used for this because of its easy categorization and collation process.
Why should positional measures be used instead of descriptive statistics?
This is due to the assumption that equal distance between categories does not hold for ordinal data. Therefore, positional measures like the median and percentiles, in addition to descriptive statistics appropriate for nominal data should be used instead.
What are nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio variables?
Nominal, Ordinal, Interval & Ratio Variable + [Examples] Measurement variables, or simply variables are commonly used in different physical science fields—including mathematics, computer science, and statistics. It has a different meaning and application in each of these fields. In algebra, which is a common aspect of mathematics, ...
Which variable has an intrinsic order?
The ordinal variable has an intrinsic order while nominal variables do not have an order.
What is a Measurement Variable?
A measurement variable is an unknown attribute that measures a particular entity and can take one or more values. It is commonly used for scientific research purposes. Unlike in mathematics, measurement variables can not only take quantitative values but can also take qualitative values in statistics.
What are nominal variables?
A nominal variable is one of the 2 types of categorical variables and is the simplest among all the measurement variables. Some examples of nominal variables include gender, Name, phone, etc.
What are the variables in personal biodata?
Personal Biodata: The variables included in a personal biodata is a nominal variable. This includes the name, date of birth, gender, etc. E.g
What are some examples of interval variables?
Examples of interval variables include; temperature measured in Celsius or Fahrenheit, time, generation age range, etc.
What is variable in math?
In algebra, which is a common aspect of mathematics, a variable is simply referred to as an unknown value. This meaning is what is adopted in computer science, where it is used to define values when writing in various computer programming languages.
What is a variable in statistics?
First, let’s understand what a variable is. A quantity whose value changes across the population and can be measured is called variable. For instance, consider a sample of employed individuals.
Which scale is the most fundamental in quantitative research?
This is the fundamental of quantitative research, and nominal scale is the most fundamental research scale.
What is nominal scale?
Nominal scale is a naming scale, where variables are simply “named” or labeled, with no specific order. Ordinal scale has all its variables in a specific order, beyond just naming them. Interval scale offers labels, order, as well as, a specific interval between each of its variable options. Ratio scale bears all the characteristics ...
Why is interval scale important?
In statistics, interval scale is frequently used as a numerical value can not only be assigned to variables but calculation on the basis of those values can also be carried out. Even if interval scales are amazing, they do not calculate the “true zero” value which is why the next scale comes into the picture.
Is SPSS a scale variable?
Upon importing the data for any variable into the SPSS input file, it takes it as a scale variable by default since the data essentially contains numeric values. It is important to change it to either nominal or ordinal or keep it as scale depending on the variable the data represents.
Which test can determine if a variable is bigger or smaller than another variable?
In the Mann-Whitney U test, researchers can conclude which variable of one group is bigger or smaller than another variable of a randomly selected group. While in the Kruskal–Wallis H test, researchers can analyze whether two or more ordinal groups have the same median or not.
Is ordinal scale a nominal scale?
This is where ordinal scale is a step above nominal scale – the order is relevant to the results and so is their naming.
What is variable in statistics?
Published on November 21, 2019 by Rebecca Bevans. Revised on March 2, 2021. In statistical research, a variable is defined as an attribute of an object of study. Choosing which variables to measure is central to good experimental design. Example.
What are the two types of quantitative variables?
There are two types of quantitative variables: discrete and continuous.
How to tell if a variable is independent or dependent?
You can think of independent and dependent variables in terms of cause and effect: an independent variable is the variable you think is the cause, while a dependent variable is the effect. In an experiment, you manipulate the independent variable and measure the outcome in the dependent variable.
What are the three types of categorical variables?
There are three types of categorical variables: binary, nominal, and ordinal variables.
Why do you need to know what types of variables you are working with?
You need to know which types of variables you are working with in order to choose appropriate statistical tests and interpret the results of your study.
What are the variables that determine if a plant is salt tolerant?
If you want to test whether some plant species are more salt-tolerant than others, some key variables you might measure include the amount of salt you add to the water, the species of plants being studied, and variables related to plant health like growth and wilting.
Why do you have variables that you hold constant?
You will probably also have variables that you hold constant ( control variables) in order to focus on your experimental treatment.
What is the ordinal scale?
Ordinal scale is the 2nd level of measurementthat reports the ranking and ordering of the data without actually establishing the degree of variation between them. Ordinal level of measurement is the second of the four measurement scales. “Ordinal” indicates “order”.
What is the central tendency of the ordinal scale?
The central tendency of the ordinal scale is Median.
Which level of measurement reports the ranking and ordering of the data without establishing the degree of variation?
Ordinal scale is the 2nd level of measurement that reports the ranking and ordering of the data without establishing the degree of variation.
Is the property of the interval known?
The properties of the interval are not known.
Is linear rating scale more informative than nominal scale?
As the values are indicated in a relative manner using a linear rating scale, the results are more informative than the nominal scale.
Levels of Measurement
Examples of Ordinal Scales
- In social scientific research, ordinal variables often include ratings about opinions or perceptions, or demographic factors that are categorized into levels or brackets (such as social status or income).
How to Collect Ordinal Data
- Ordinal variables are usually assessed using closed-ended surveyquestions that give participants several possible answers to choose from. These are user-friendly and let you easily compare data between participants.
Definition of Ordinal Data
Ordinal Data Examples
- Examples of ordinal data includes likert scale; used by researchers to scale responses in surveys and interval scale;where each response is from an interval of it's own. Unlike nominal data, ordinal data examples are useful in giving order to numerical data. 1. Likert Scale: ALikert scaleis a point scale used by researchers to take surveys and get people's opinion on a subject matter. It is usu…
Categories of Ordinal Variables
- Ordinal variables can be classified into 2 main categories, namely; the matched and unmatched category. This ordinal variable classification is based on the concept of matching - pairing up data variables with similar characteristics. According to Wikipedia, matching is a statistical techniquewhich is used to evaluate the effect of a treatment by c...
Ordinal Data Analysis and Interpretation
- Ordinal data analysis is quite different from nominal data analysis, even though they are both qualitative variables. It incorporates the natural ordering of the variables in order to avoid loss of power. Ordinal variables differs from other qualitative variables because parametric analysis median and mode is used for analysis This is due to the assumption that equal distance betwee…
Graphical Techniques to Analyse Ordinal Variables
- Ordinal data can also be analysed graphically with the following techniques. 1. Bar chart 2. Pie chart 3. Tables 4. Mosaic plots 5. Bump chart 6. Colour or grayscale gradation.
Disadvantages of Ordinal Data
- The options do not have a standardised interval scale. Therefore, respondents are not able to effectively gauge their options before responding.
- The responses are often so narrow in relation to the question that they create or magnify bias that is not factored into the survey. For example, in the customer service example cited above, a cust...
- The options do not have a standardised interval scale. Therefore, respondents are not able to effectively gauge their options before responding.
- The responses are often so narrow in relation to the question that they create or magnify bias that is not factored into the survey. For example, in the customer service example cited above, a cust...
- It does not allow respondents the opportunity to fully express themselves. They are usually restricted to some predefined options.
Why Formplus Is The Best Tool For Collecting Ordinal Data
- 30+ Field Types
- With a wide range of field types, you can easily collect ordinal data.
- Fields like matrix and scales make it easy to collect any set of ordinal data you need from your respondents.
- Do you need your respondents to give you repeatable data where they specify how many tim…
- 30+ Field Types
- With a wide range of field types, you can easily collect ordinal data.
- Fields like matrix and scales make it easy to collect any set of ordinal data you need from your respondents.
- Do you need your respondents to give you repeatable data where they specify how many times they want to fill a field?
Conclusion
- Ordinal data is designed to infer conclusions, while nominal data is used to describe conclusions. Descriptive conclusions organise measurable facts in a way that they can be summarised. If a restaurant carries out a customer satisfaction survey by measuring some variables over a scale of 1-5, then satisfaction level can be stated quantitatively. However, no inference can be drawn abo…