Why tibial plateau fractures are overlooked?
Why Tibial Plateau Fractures Are Overlooked - PubMed The major reasons for overlooking TPFs were 1) difficulty in recognizing the fractures on X-rays and 2) that X-ray decision rules were not employed. Two thirds of the patients, for whom a radiograph had not been prescribed, would have had an X-ray, if the PKRs had been used.
What are the long term prognosis of tibial plateau fractures?
The length of time it takes to recover from a tibial plateau fracture depends on the severity of the fracture and your overall health. Most fractures take 4 months to completely heal. In more severe cases, it can take up to 6 months. It’s important to strictly follow your doctor’s instructions to ensure that the bone heals properly.
When to begin weight-bearing after tibial plateau fracture?
Patients with tibial plateau fractures will be instructed to touch down (toe touch or foot flat) weight bear (approximately 10% of body weight) for at least 6 weeks. After the 6 week post op visit, patients may begin weight bearing as tolerated until full weight bearing is achieved.
When is surgery indicated for tibial plateau fractures?
Tibial Plateau Fracture Surgery is required when the bone breaks into two or more fragments and surgery is normally needed. This fracture involves the proximal (upper) portion of the tibia which extends through the articular surface (into the knee joint). It is a serious type of knee injury that can affect all types of men and women athletes.
What does tibial plateau mean?
The tibial plateau is the flat top portion of your tibia bone, which runs from your knee to your ankle. The bottom end of your thigh bone (femur) and the top end of your tibia form your knee joint. The tibial plateau is a relatively flat surface of bone covered in cartilage.
How serious is a tibial plateau fracture?
Tibial plateau fractures affect the knee alignment, joint, stability and movement. Thus, fractures of the tibial plateau are considered quite serious as this upper surface of the bone contains structures which are critical to the knee functioning.
What happens after tibial plateau surgery?
After tibial plateau fracture surgery you will experience pain, swelling, stiffness and decreased range of movement in your knee. You will also experience a reduction in muscle strength and control in the post operative period.
How long does it take to fully recover from a tibial plateau fracture?
Non-displaced tibial plateau fractures take up to 3-4 months without surgery to heal. When surgery is required these cases take around 4 months to heal.
Can you make a full recover from tibial plateau fracture?
We conclude that there is significant impairment of movement and muscle function after fracture of the tibial plateau and that the majority of patients have not fully recovered one year after injury. Loss of movement and reduced muscle function affects recovery after intra-articular fractures.
Can you bend your knee with a tibial plateau fracture?
You can walk and bend your knee as much as tolerated. Use your crutches as needed for the first week.
How long will I be on crutches after tibia surgery?
Use crutches non-weight bearing for 6 weeks. Brace for 6 weeks in full extension.
How do you sleep after tibial plateau surgery?
Sleep on your back with a pillow between your knees. Avoid crossing your surgical leg across the middle of your body. Sleep on your non-operative side with pillows between your legs. Avoid bending your knees.
Can I get disability for tibial plateau fracture?
If you have suffered a fracture of your femur, tibia, or pelvis and it has resulted in ongoing problems, you may be eligible for Social Security Disability benefits. If you have been in a serious accident, you may have suffered multiple broken bones.
When can I return to work after ORIF surgery?
You will probably need to take 1 to 2 weeks off from work. It depends on the type of work you do and how you feel. Do not shower for 1 or 2 days after surgery.
Do you need a cast for a tibial plateau fracture?
Tibial Plateau Fracture Care For fractures that have not shifted, surgery may not be needed. The most common non-surgical treatment is a short leg, non-weightbearing cast or a hinged knee brace, combined with physical therapy and rest. Fractures that have shifted require surgery.
How long are you in the hospital after tibia surgery?
You will have to use crutches, and you probably will not be able to bear weight on your leg for as long as six weeks. After surgery to repair a fractured shinbone (tibial plateau), some patients remain in the hospital for at least overnight.
When does a tibial plateau fracture require surgery?
Tibial Plateau Fracture Surgery is required when the bone breaks into two or more fragments and surgery is normally needed. This fracture involves the proximal (upper) portion of the tibia which extends through the articular surface (into the knee joint).
How do you fix a tibial plateau fracture?
The injury is usually fixed with metal plates and screws placed through a large incision. The type of fracture usually dictates what types of incisions and how many plates and screws are needed. Sometimes bone graft or types of bone cement are needed to support the joint surface.
How common is a tibial plateau fracture?
Tibial plateau fractures comprise 1% of all fractures. The incidence of tibial plateau fractures is 10.3 per 100,000 people annually[2].
How long is non weight bearing after tibial plateau fracture?
The standard aftercare treatment (according to the AO guideline) for surgically treated trauma patients with fractures of the tibial plateau is non-weight bearing or partial weight bearing for 10–12 weeks.
What is an ORIF fracture?
If you fracture your tibia or fibula, you might need ORIF to bring your bones back into place and help them heal. During an “open reduction,” orthopedic surgeons reposition your bone pieces during surgery to put them back into their proper alignment. In a “closed reduction,” a healthcare provider physically moves the bones back into place without surgically exposing the bone.
What is tibia/fibula fracture open reduction and internal fixation?
Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is a type of surgery used to stabilize and heal a broken bone. You might need this procedure to treat your broken shin bone (tibia) or your fibula.
What is the bone in the lower leg called?
The tibia , or shin bone, is the larger bone in your lower leg. Beside it, more toward the outside of the leg, is the fibula. The tibia forms part of the knee joint. The ends of the tibia and the fibula both form part of the ankle joint. Different kinds of injury can damage the tibia or the fibula, causing them to break into one or more pieces.
Do you need ORIF for a fibula fracture?
You might not need ORIF if you fracture your tibia or your fibula. Many people don’t. If possible, your healthcare provider will treat your fracture with more conservative treatments, like pain medicines, casts, or braces.
Can you have your leg held while waiting for ORIF?
In some cases, your healthcare providers might perform your ORIF a little later. You might have your leg held immobile while you wait for your surgery. Talk to your healthcare provider about how to prepare for the surgery. Ask whether you should stop taking any medicines ahead of time, like blood thinners.
Do you need ORIF for a broken tibia?
You probably won’t need ORIF unless there is some reason your fracture might not heal normally with these conservative treatments. You are more likely to need ORIF if: The pieces of your leg are significantly out of alignment. Your broken tibia or fibula pierced through the skin.
What causes a fracture of the tibial plateau?
Fractures of the tibial plateau result from axial loads applied to the lower limb with varying degrees of varus or, more commonly, valgus moment.9 Mechanisms of injury include both high-energy trauma, such as motor vehicle and motorcycle accidents, and athletic injuries. Patients frequently present with a tense effusion and are unable to ambulate ( Table 74-4 ). Arthrocentesis reveals a hemarthrosis with fat globules. The lower limb may appear to be in valgus malalignment. Often bony tenderness localizes to the lateral aspect of the proximal tibia, with varying degrees of medial tenderness along the medial collateral ligament. Signs and symptoms of compartment syndrome or neurovascular compromise must be elicited. Assessment of ligamentous stability is critical to the evaluation of tibial plateau fractures. However, this is often better accomplished under general anesthesia in the operating room.
Which part of the tibial plateau is the lateral condyle?
The lateral condyle is the lateral part of the tibial plateau. Its femoral articulation is smaller and rounder than the medial articulation.
What bone is affected by a proximal tibial fracture?
These fractures invariably involve the articular surface, which is usually displaced and impacted down into the softer cancellous bone of the proximal tibia. Restoration of an adequate joint surface is an important treatment consideration, as is preservation of the complex ligamentous stabilizing structures of the knee.
How much margin of tibial condyle should be perpendicular?
On the AP view a perpendicular line drawn at the most lateral margin of the femoral condyle should not have more than 5 mm of the lateral margin of the tibial condyle outside of it ( Fig. 12.2)
Where is the superior fibular articular facet located?
The superior fibular articular facet is located on the posteroinferior edge of the lateral condyle.
Which bone is the weight bearing bone of the lower leg?
The tibia is the major weight-bearing bone of the lower leg. It articulates proximally with the distal femur, twice laterally with the fibula (once proximally and once distally), and distally with the talus.
Where is the fabella bone?
The fabella is a common sesamoid bone in the tendon of the lateral head of the gastrocnemius muscle. Its posterior position is characteristic ( Fig. 12.5 ). It should not be confused with a fracture fragment or a loose body.
What are the risks?
Generally, this is a safe procedure. However, problems may occur, including:
What happens before the procedure?
Follow instructions from your health care provider about hydration, which may include:
What happens during the procedure?
To lower your risk of infection: Your health care team will wash or sanitize their hands. Hair may be removed from the surgical area. Your skin will be washed with soap.
What happens after the procedure?
Your blood pressure, heart rate, breathing rate, and blood oxygen level will be monitored until the medicines you were given have worn off.
Summary
A tibial plateau fracture is a break in the bone that forms the bottom of the knee joint.
Follow these instructions at home
Wear the brace as told by your health care provider. Remove it only as told by your health care provider.
Get help right away if you
Notice that the edges of your incision have come apart after the sutures or staples have been removed.
What is the plateau of the tibia?
The tibial plateau is the flat top portion of your tibia bone, which runs from your knee to your ankle. The bottom end of your thigh bone (femur) and the top end of your tibia form your knee joint. The tibial plateau is a relatively flat surface of bone covered in cartilage. This is a very smooth, low-friction surface, designed to allow your knee joint to bend and straighten. There are two menisci, or shock absorbers made of cartilage, that sit between your tibia and the femur. These are commonly injured in sports activities.
What are the red arrows on a tibial plateau?
Figure 3: An example of a patient with a tibial plateau fracture. The red arrows point to the broken areas of the bone.
What is plateau fracture?
A tibial plateau fracture is an injury in which you break your bone and injure the cartilage that covers the top end of your tibia (bottom part of your knee). The break can range from a single crack in your bone to shattering into many pieces. This fracture typically happens after a fall or a motor vehicle accident.
What is an external fixator?
An external fixator is a device made up of pins that are put in your femur (thigh bone) and tibia (leg bone) and bars that connect the pins together.
What is the knee shock absorber?
This is a very smooth, low-friction surface, designed to allow your knee joint to bend and straighten. There are two menisci, or shock absorbers made of cartilage, that sit between your tibia and the femur. These are commonly injured in sports activities. There is a large blood vessel that runs behind your knee.
How to know if you broke your tibial plateau?
After you break your tibial plateau it will be very painful, and you will most likely not be able to walk on it. You will likely need to go to an emergency room because of the pain. In the emergency room you will get x-rays as well as a CT scan. Depending on how bad the break is, you may be able to go home or you may be admitted to the hospital. Often, you will be put into a brace or a splint. Either way you will not be able to walk or put weight on the leg.
Where is the blood vessel in the knee?
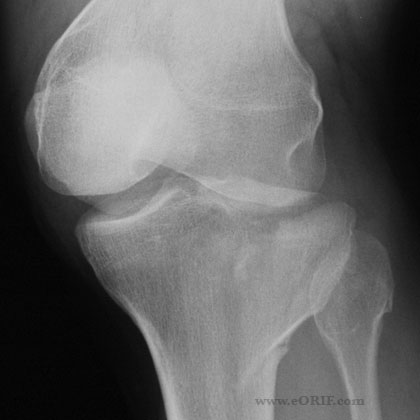
There is a large blood vessel that runs behind your knee. The main nerves that supply your leg and foot are also found in the back of your knee, and two of them wrap around the outside of your knee. Figure 1: Skeleton model showing the knee joint. Figure 2: X-rays of the knee.