What is the origin and insertion of the gluteus maximus?
Origin: Originates from the posterior surface of the ilium, sacrum, and coccyx. It slopes across the buttock at a 45-degree angle. Insertion: It inserts into the iliotibial tract and the gluteal tuberosity of the femur. Function: The gluteus maximus is the main extensor of the thigh and assists with lateral rotation.
What is the origin and insertion of hyoid bone?
Origin: Along temporal lines of skull Insertion: Coronoid process of mandible and the anterior border of the mandibular ramus Temporalis Origin: Inferior surface of mandible at chin and mastoid region Insertion: Hyoid bone
Which muscles insert on the femur?
- Origin: femur shaft
- Insertion: patella via quadriceps tendon
- Action: extension of the knee
- Innervation: femoral nerve
What is the origin of the rectus femoris?
[1][2] The rectus femoris has two heads of origin: the direct (straight) head and the indirect (reflected) head. The direct head arises from the anterior aspect of the inferior iliac spine (AIIS; a common site of avulsion), while the indirect head originates from the acetabular ridge.
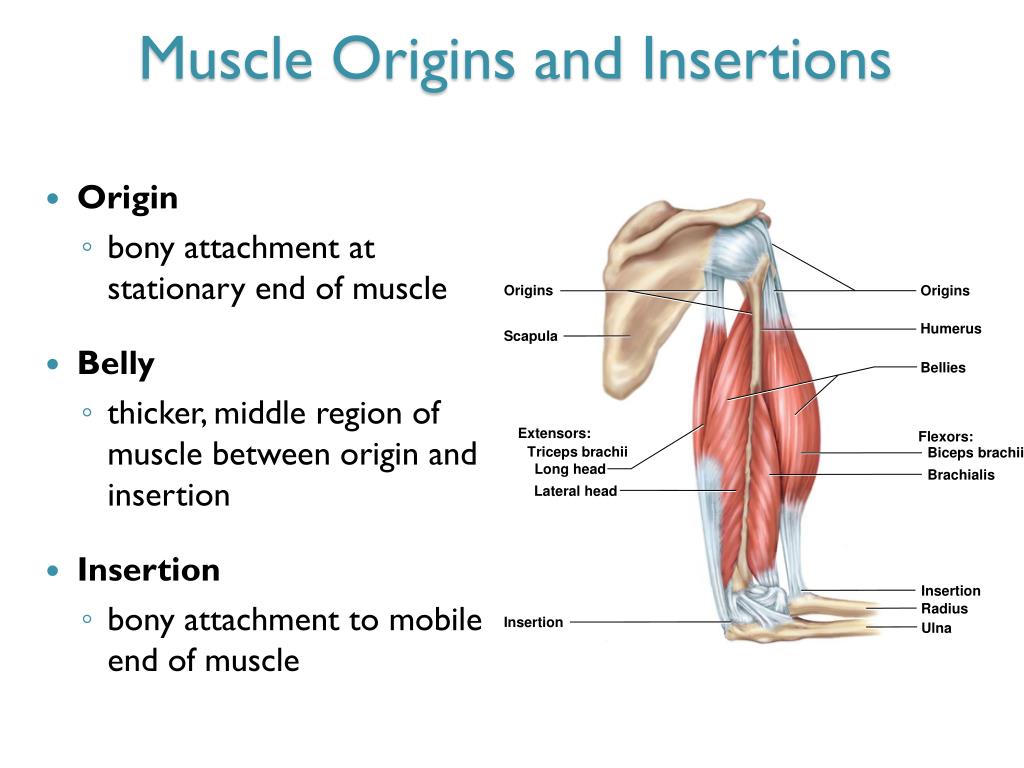
What is origin in muscle?
Muscle Origin Definition Muscle origin refers to a muscle's proximal attachment—the end of the muscle closest to the torso. For example, the bicep muscle's origin is located at the shoulder.
What are the origin and insertion?
Origin is relatively the less movable end of the muscle/tendon that is attached to a bone. Insertion is the more flexible end of the muscle that is usually attached to a bone via tendons. It is the proximal end that is attached to the less movable bone.
What is the insertion of the muscle?
A muscle has two ends that each attach to bone: the muscle's origin and the muscle's insertion. At both of these points, tendons attach the muscle to bone. Muscle insertion refers to a muscle's distal attachment—the end of the muscle furthest away from the torso. For example, the bicep insertion occurs at the elbow.
Why is muscle origin important?
They can help us communicate with one another about body movement. Muscle origin and insertion are useful landmarks to help us understand where one thing is in relationship to something else, but they're not necessarily fixed. A more open-minded way to think about this is that muscles have at least two attachments.
Do all muscles have origin and insertion?
Every time the muscle contracts (concentrically, that is, but that's another post for another day), the origin says 'come to me', and so the insertion does. This is true for all the muscles in the body.
How do you remember the difference between origin and insertion?
1:5514:49What is the Difference between origins and Insertions? [HOJI] - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFrom your heart now origin is a close bit to the heart insertion is the furthest part from the heartMoreFrom your heart now origin is a close bit to the heart insertion is the furthest part from the heart they're the really important key bits to remember in terms the differences.
What is the origin of skeletal muscle?
Skeletal muscle in the limb is formed by cells derived from somites present at the level of the limb buds. The somite can be divided into epaxial and hypaxial parts according to an anatomical division of the body and its musculature, clearly perceptible in fish for example.
What is the definition of insertion in anatomy?
The insertion of a muscle is defined as the place where one end of a muscle is attached to the freely moving bone of its joint.
What are the 4 functional groups of muscle action?
To describe how muscles work together, we can use the following four functional types: agonist, antagonist, synergist, and fixator.
How do you remember the difference between origin and insertion?
1:5514:49What is the Difference between origins and Insertions? [HOJI] - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFrom your heart now origin is a close bit to the heart insertion is the furthest part from the heartMoreFrom your heart now origin is a close bit to the heart insertion is the furthest part from the heart they're the really important key bits to remember in terms the differences.
What are the 7 most common diseases of the muscular system?
Primary muscular system diseases include:Polymyositis.Dermatomyositis.Muscular dystrophy.Myasthenia gravis.Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)Rhabdomyolysis.Cardiomyopathy.Sarcopenia.
What is the difference between an organ and an insertion?
Origin and insertion are two attachment points. Origin is the attachment to an immovable bone while insertion is the attachment to a movable bone. Therefore, the origin is the end that doesn't move during the contraction of the muscle while the insertion is the opposite end of the muscle that moves.
What is the origin and insertion of muscles?
The Origin and Insertion of Muscles. When reading anatomy books you will see reference to the origin and insertion of muscle as they are connected to bones. These terms reflect the types of movement available in our muscles and joints. In an endless attempt to simplify the workings of the body I often describe the process as: The bones hold you up, ...
What is the difference between the origin and insertion of a muscle?
Usually, the origin is the end that doesn’t move when the contraction occurs, and the insertion is the opposite end of the muscle that moves.
Which muscle is home to a great many muscle insertions?
Here is a little test. The greater trochanter of the femur is the home to a great many muscle insertions.
How are the bones connected to each other?
The bones are connected to each other with ligaments and the muscles are connected to the bones with tendons. Our bodies move when muscles contract and exert force on the bones to initiate an action. Even though, as a yoga teacher, I am often imploring students to engage a particular muscle when performing an action, ...
How to hide origin and insert points?
Origin and Insertion points are available as a layer of the Skeletal System, which show a map of all attachment points across the full skeleton. Tap the Skeletal System Icon, and press the Plus button until you come to the Origin and Insertion layer (the fourth layers of the system). To hide the points, tap the Skeletal System icon and press the Minus button.
How to see attachment points in a muscle?
To see a muscle’s attachment points, select the muscle from the model. The Infobox for that structure will appear on the left of the screen. Under the title of the structure you will see the option to view the attachment points for that muscle.
How to learn orgins and insertions?
Learning all of the muscles can feel overwhelming and frustrating. Staring at a manual and learning from the smallest of images.
What is muscle contraction?
Muscular contraction produces an action, or a movement of the appendage. We will use examples to describe how the origin and insertion affect the action of a skeletal muscle. Muscle contraction results in different types of movement. There are several different types of movements, including flexion, extension, hyperextension, abduction, adduction, ...
What is the difference between a distal and a proximal insertion?
The insertion is usually distal, while the origin is proximal, relative to the insertion.
What is the name of the muscle that crosses the shoulder?
Knowing the muscle name and its location in the body. for example, the biceps are the upper arm and anterior of the body. Knowing the joint (s) the muscle crosses. for example, the biceps cross the Shoulder and elbow. Understanding that origins are above the joint or proximal end of the bone intended to move.
How many muscles are there in anatomy?
As part of your Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology Exam, there are 50 muscles, each with an origin, insertion, name, location, and muscle action to learn and remember.
What is the term for the muscle that is attached to the bone on its ends?
Skeletal muscle is attached to the bone on its ends by way of what we call tendons.
How to describe a muscle's action?
The second way to describe a muscle’s action is based on the joint or the articulation. For example, that same muscle, the biceps brachii, performs flexion at the elbow, in which the elbow is the joint. Let’s stay with the biceps, The bicep has two (bi = two) origins, one high on the humerus, the other on the scapula.
The Role of a Muscle Origin And Insertion
Origins and Insertions are both names given to the attachment point whereby the tendon connects the bone.
Movement based on Muscle Origins And Insertions
Whereby you have one team at the origin and one team at the insertion.
Take the example of the Pectoralis Major
The muscle fibres are organised in lines running from the origin to the insertion.
Test your knowledge with 3 Mock Questions
Look at the Muscle Anatomy and Physiology Mock questions below and jot down your answer on scrap paper or as a note on your phone.
Answers
If you want more mock questions like this, then you can download more Free Mock Questions: DOWNLOAD NOW
How to learn orgins and insertions?
Learning all of the muscles can feel overwhelming and frustrating. Staring at a manual and learning from the smallest of images.
Which ligaments are pulled away from the midline and forward?
abducts and laterally rotates the cartilage, pulling the vocal ligaments away from the midline and forward and so opening the rima glottidis
How many muscles are there in the human body?
List of Body muscles are nearly 600 muscles. The three main types of muscles – skeletal, smooth and cardiac. Here we Update List of Skeletal Body Muscles.
When the neck is fixed, what is the first rib?
When the neck is fixed, elevates the first rib to aid in breathing or when the rib is fixed, bends the neck forward and sideways and rotates it to the opposite side