
What is a dorsiflexing 1st metatarsal osteotomy?
A Dorsiflexing 1st Metatarsal Osteotomy procedure is indicated for patients with a high-arched foot, which can lead to a variety of critical problems, including recurring ankle sprains, ankle instability, peroneal tendonitis, 5th metatarsal stress fractures, and sesamoiditis.
What are the different types of osteotomies?
Three types of osteotomies can be performed: Lateral Closing Wedge Osteotomy: In this osteotomy, a lateral wedge of bone is resected from the tibia. This is the most stable form of osteotomy and has the highest union rate.
Is dorsiflexed osteotomy a good option for Charcot-Marie Tooth disease?
However, surgical reconstruction, which may include a dorsiflexed osteotomy, may be beneficial for some patients where non-operative management has failed. A common condition that leads to this type of surgery is Charcot-Marie Tooth disease, a condition where patients develop high-arched feet that can lead to significant symptoms.
What grade of osteotomy is appropriate for the treatment of hallux valgus?
With the Level III and IV evidence, a grade B recommendation can be made for the closing wedge proximal first metatarsal osteotomy in the correction of hallux valgus, with the observation that dorsiflexion malunion and considerable shortening of the first metatarsal are frequent.
What is the condition where the big toe is angled down more than the other toes?
How is a metatarsal incision made?
What happens if your foot ends up in a less than ideal position?
Can you remove hardware after dorsiflexing?
Can you have a dorsiflexed osteotomy without surgery?
Making Things Easier: A Simple Novel Method to Fix a Dorsiflexion ...
A first ray dorsiflexion osteotomy is commonly performed for cavovarus foot correction. There are multiple techniques to fix this osteotomy, ranging from wires, screws, and plates or a combination of these. We present our results using a varisation staple (Biomet©) as an alternative fixation device. …
1st Metatarsal Dorsiflexion Osteotomy 28306 | eORIF
synonyms:1st Dorsiflexion osteotomy. 1st MT Dorsiflexion Osteotomy CPT-10. 28306 1st MT Dorsiflexion Osteotomy Indications Flexible cavovarus foot with lateral foot pain which fails to improve with conservative management
First Metatarsal Osteotomy Nonunion and Malunion
Request PDF | First Metatarsal Osteotomy Nonunion and Malunion | Although nonunion and malunion may occur after distal or proximal metatarsal corrective osteotomies, proper surgical technique and ...
Dorsiflexion metatarsal osteotomy for treatment of recalcitrant ...
Twenty diabetic patients underwent 22 dorsiflexion metatarsal osteotomies for treatment of chronic persistent or recurrent neuropathic forefoot ulcers. Mean duration of nonoperative treatment was 13 months. The procedure consisted of irrigation and debridement of the ulcer followed by basilar closin …
Podiatry Management Online
Podiatry Management •1062 E. Lancaster Ave, Rosemont Plaza Ste 15 F, Bryn Mawr, PA 19010
What is the condition where the big toe is angled down more than the other toes?
A common condition that leads to this type of surgery is Charcot-Marie Tooth disease, a condition where patients develop high-arched feet that can lead to significant symptoms. One of the main features of a high-arched foot is a plantarflexed first metatarsal, where the big toe is angled down more than the other toes.
How is a metatarsal incision made?
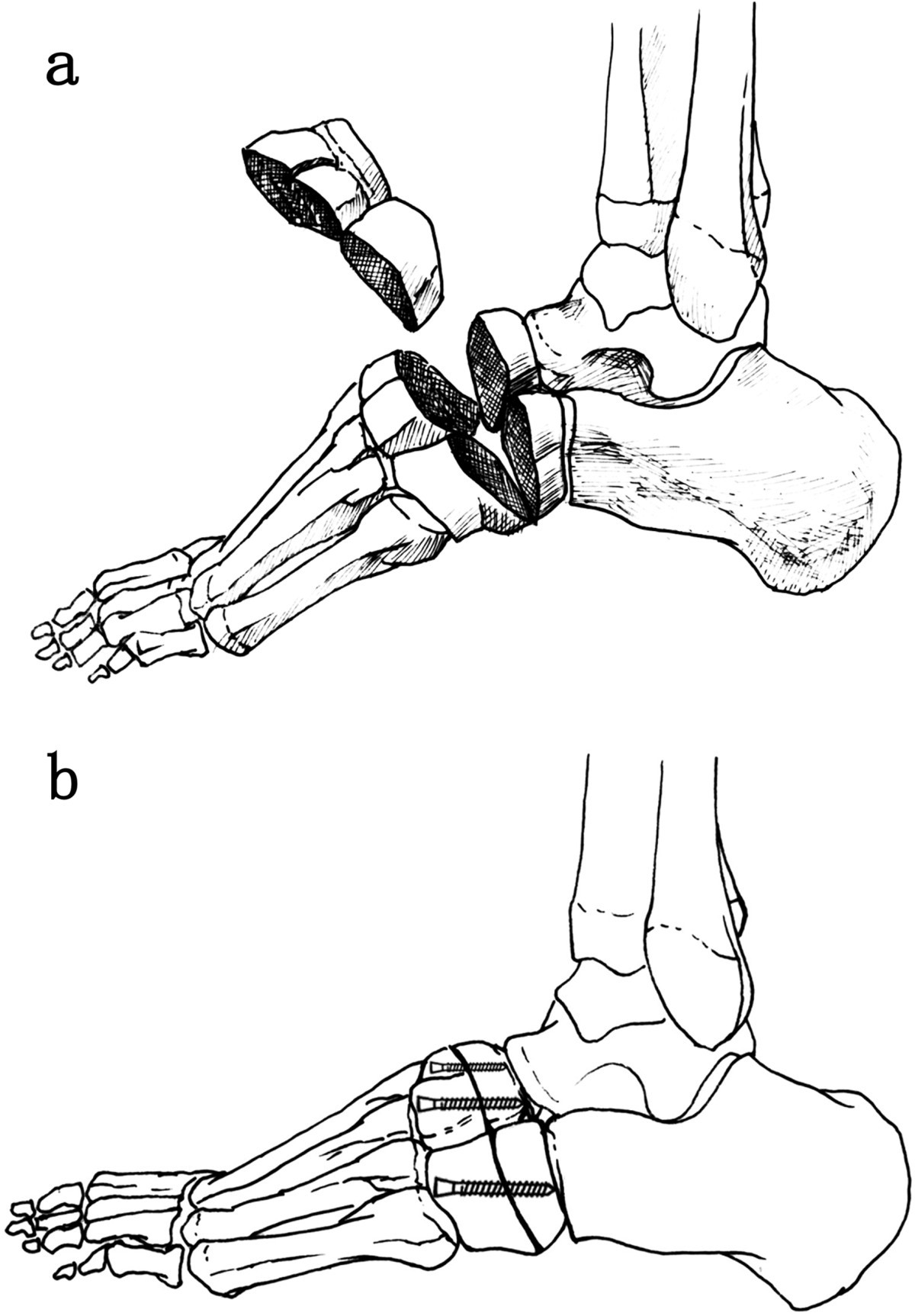
An incision is made over the top of the first metatarsal and dissected down to the bone. Once the top and side regions of the toe are exposed, a wedge of bone is removed. The toe is then repositioned upward to reduce the high-arch, and secured with screws, plates, or staples (Figure 1).
What happens if your foot ends up in a less than ideal position?
If the foot ends up in a less than an ideal position, the patient may end up with more symptoms and other conditions, such as metatarsalgia.
Can you remove hardware after dorsiflexing?
Another potential complication with this procedure is having pain associated with the hardware used to secure the first metatarsal. It is not uncommon for patients to benefit from hardware removal after a dorsiflexing 1st metatarsal osteotomy, once the bone has healed.
Can you have a dorsiflexed osteotomy without surgery?
However, surgical reconstruction, which may include a dorsiflexed osteotomy, may be beneficial for some patients where non-operative management has failed.
What is the condition where the big toe is angled down more than the other toes?
A common condition that leads to this type of surgery is Charcot-Marie Tooth disease, a condition where patients develop high-arched feet that can lead to significant symptoms. One of the main features of a high-arched foot is a plantarflexed first metatarsal, where the big toe is angled down more than the other toes.
How is a metatarsal incision made?
An incision is made over the top of the first metatarsal and dissected down to the bone. Once the top and side regions of the toe are exposed, a wedge of bone is removed. The toe is then repositioned upward to reduce the high-arch, and secured with screws, plates, or staples (Figure 1).
What happens if your foot ends up in a less than ideal position?
If the foot ends up in a less than an ideal position, the patient may end up with more symptoms and other conditions, such as metatarsalgia.
Can you remove hardware after dorsiflexing?
Another potential complication with this procedure is having pain associated with the hardware used to secure the first metatarsal. It is not uncommon for patients to benefit from hardware removal after a dorsiflexing 1st metatarsal osteotomy, once the bone has healed.
Can you have a dorsiflexed osteotomy without surgery?
However, surgical reconstruction, which may include a dorsiflexed osteotomy, may be beneficial for some patients where non-operative management has failed.
