Common Causes
Other distinct symptoms of dyspnea include: 1 Developing the awarness that shows the increased muscular effort needed to either expand the chest when breathing in or to deflate it when breathing out 2 Being aware of the urgent need to inhale air befoe exhaling is completed and 3 A number of other sensations that signify thightness in the chest
Related Conditions
Valid for Submission. ICD-10 R06.09 is a billable code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other forms of dyspnea. The code is valid for the year 2019 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What are the signs and symptoms of dyspnea?
Chronic dyspnea could be due to: 1 asthma 2 COPD 3 heart problems 4 obesity 5 interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, a disease that causes scarring of the lung tissue
What is the ICD 10 code for dyspnea?
What are the causes of chronic dyspnea?
What does other forms of dyspnea mean?
Shortness of breath — known medically as dyspnea — is often described as an intense tightening in the chest, air hunger, difficulty breathing, breathlessness or a feeling of suffocation. Very strenuous exercise, extreme temperatures, obesity and higher altitude all can cause shortness of breath in a healthy person.
What are the different types of dyspnea?
Types. Orthopnea - it is the sensation of dyspnoea in the recumbent position, relieved by sitting or standing. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea (PND) - it is a sensation of dyspnoea that awakens the patient, often after 1 or 2 hours of sleep, and is usually relieved in the upright position.
What are 3 causes of dyspnea?
The most common causes of short-term dyspnea are:Anxiety disorders.Asthma.A blood clot in your lungs, known as pulmonary embolism.Broken ribs.Excess fluid around your heart.Choking.A collapsed lung.Heart attacks.More items...•
What is the difference between dyspnea and Orthopnea?
Dyspnea is when a person experiences shortness of breath regardless of what position they are in. Orthopnea is when a person experiences shortness of breath when lying down.
What are the three types of shortness of breath?
They include:Orthopnea, when you feel short of breath when you lie down. ... A similar condition called paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea can make you feel so short of breath that you wake up in the middle of the night. ... Trepopnea is a kind of dyspnea that happens when you lie on a certain side.More items...•
What are the 4 types of breathing?
Types of breathing in humans include eupnea, hyperpnea, diaphragmatic, and costal breathing; each requires slightly different processes.
How do you test for dyspnea?
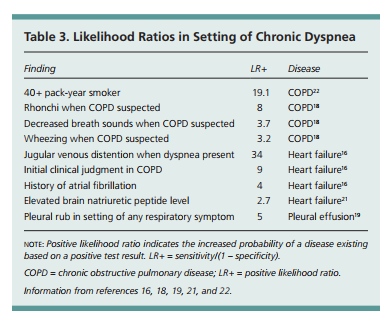
The most useful methods of evaluating dyspnea are the electrocardiogram and chest radiographs. These initial modalities are inexpensive, safe and easily accomplished. They can help confirm or exclude many common diagnoses.
What is the most common cause of dyspnea?
But dyspnea can be a sign of a serious health issue. According to Dr. Steven Wahls, the most common causes of dyspnea are asthma, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), interstitial lung disease, pneumonia, and psychogenic problems that are usually linked to anxiety.
Does anxiety cause dyspnea?
Experiencing shortness of breath (dyspnea) or other breathing difficulties can feel scary. But it's a common symptom of anxiety. Many people worry that a symptom affecting their breathing must come from a physical issue. In fact, your mental health affects your physical health in a number of ways.
What is Hyperpnea?
Definition of hyperpnea : abnormally rapid or deep breathing.
What is dyspnea vs tachypnea?
Dyspnea is the subjective feeling of rapid or difficult breathing. The patient will often say, “I can't get my breath!” Tachypnea is the objective finding of a rapid respiratory rate, and may or may not be associated with the feeling of not being able to breathe properly.
Is tachypnea and dyspnea the same?
Tachypnea describes abnormally rapid breathing. It is not the same as dyspnea, where you feel as if you're not getting enough air. You may experience tachypnea because your body is trying to correct something abnormal that is happening in your body.
What is the most common cause of dyspnea?
But dyspnea can be a sign of a serious health issue. According to Dr. Steven Wahls, the most common causes of dyspnea are asthma, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), interstitial lung disease, pneumonia, and psychogenic problems that are usually linked to anxiety.
What is acute dyspnea?
Dyspnea is a subjective experience of breathing discomfort; patients experience qualitatively distinct sensations that vary in intensity. Acute dyspnea might be secondary to an acute problem, or it might be an exacerbation of an existing disease (eg, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, heart failure).
What are the signs of dyspnea?
What are the symptoms of dyspnea?heart palpitations.weight loss.crackling in the lungs.wheezing.night sweats.swollen feet and ankles.labored breathing when lying flat.high fever.More items...
What is external dyspnea?
Dyspnoea can also be quantified (“intensity”). Exertional dyspnoea can be easily defined as “the perception of respiratory discomfort that occurs for an activity level that does not normally lead to breathing discomfort”.
What causes dyspnea?
Steven Wahls, the most common causes of dyspnea are asthma, heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), interstitial lung disease, pneumonia, and psychogenic problems that are usually linked to anxiety.
What are the symptoms of dyspnea?
Emergency medical treatment is needed if an individual has any of these symptoms: sudden onset of severe dys pnea. loss of ability to function due to shortness of breath. chest pain. nausea. Not all cases of dyspnea call for immediate medical treatment, but shortness of breath can indicate serious medical problems.
How do you know if you have dyspnea?
Signs that a person is experiencing dyspnea include: shortness of breath after exertion or due to a medical condition. feeling smothered. Trusted Source. or suffocated as a result of breathing difficulties. labored breathing. tightness in the chest. rapid, shallow breathing.
What is the medical term for shortness of breath?
Dyspnea is the medical term for shortness of breath, sometimes described as “air hunger.”. It is an uncomfortable feeling. Shortness of breath can range from mild and temporary to serious and long-lasting. It is sometimes difficult to diagnose and treat dyspnea because there can be many different causes.
What is the Dyspnea Lab?
The Dyspnea Lab, a research center specializing in shortness of breath, report that people find these programs helpful, even if the root causes of the problem remains. If tests indicate low levels of oxygen in the blood, supplemental oxygen may be supplied.
What causes shortness of breath in infants?
Diseases of the upper respiratory system that cause acute dysnpea are a relatively common pediatric emergency. They are one of the most common causes of shortness of breath in infants. Croup, inhaling a foreign object, and inflammation of the epiglottis are all common causes of dyspnea in infants.
Why is it so hard to breathe with dyspnea?
Environmental pollutants such as chemicals, fumes, dust, and smoke can make it more difficult for people with dyspnea to breathe. People with asthma may find that exposure to allergens such as pollen or mold may trigger episodes of dyspnea.
How to treat dyspnea?
To treat asthma, different inhalers can be prescribed and used, which help ease the dyspnea. Other treatments focus more on the disease than the lack of breath. One such disease would be pulmonary embolism, and treating it requires blood thinners and potentially surgery.
What causes dyspnea in the chest?
Medical diseases, like myocardial infarction, cause dyspnea thru sudden chest pain, decreasing the ability to breath. Allergic reactions can cause dyspnea thru inflaming the airways, decreasing the ability for air to come in or out of the body. Fortunately there are treatments to combat these medical conditions.
What is the medical term for shortness of breath caused by strenuous physical activity, an allergic reaction, asthma,?
Dyspnea is the medical term for shortness of breath caused by strenuous physical activity, an allergic reaction, asthma, and other severe conditions. Learn how to define dyspnea, then explore its causes and treatments. Updated: 10/11/2021
What is pulmonary embolism?
A pulmonary embolism is a sudden blockage of an artery in the lung from a clot. Typically the clots come from other areas of the body but lodge in the lung. One of the signs that there is a problem is dyspnea or shortness of breath. At this point it is critical to get medical attention.
What is the lesson about labored breathing called?
Lesson Summary. In this lesson, we learned about difficult or labored breathing, which is called dyspnea. While dyspnea can be only shortness of breath from strenuous exercise or poor physical conditioning, it is often of a more serious condition.
What are some examples of medical treatment for asthma?
Some examples of treatments include asthma inhalers, blood thinners, surgery, and oxygen. If the cause is foreign body aspiration, the Heimlich maneuver, or a specific type of abdominal thrust that can be used to remove foreign bodies from an airway.
What is the focus of obstructive lung disease?
For example, in obstructive lung disease, lungs may have difficulty moving air in or out, so the focus of the treatment would be to improve lung functioning with medication or add oxygen to improve the availability of oxygen to the lungs. Lesson Summary.
What is dyspnea on exertion?
Dyspnea, Orthopnea, and Paroxysmal Nocturnal Dyspnea - Clinical Methods - NCBI Bookshelf. Dyspnea refers to the sensation of difficult or uncomfortable breath ing. It is a subjective experience perceived and reported by an affected patient. Dyspnea on exertion (DOE) may occur normally, but is considered indicative of disease when it occurs ...
How to know if you have dyspnea?
The conditions in which dyspnea occurs should be ascertained. Response to activity, emotional state, and change of body position should be noted. Ask about associated symptoms: chest pain, palpitations, wheezing, or coughing.
What are the two types of breathlessness?
Two uncommon types of breathlessness are trepopnea and platypnea. Trepopneais dyspnea that occurs in one lateral decubitus position as opposed to the other. Platypnearefers to breathlessness that occurs in the upright position and is relieved with recumbency. Technique.
What is the sensation of shortness of breath in the recumbent position?
Orthopneais the sensation of breathlessness in the recumbent position, relieved by sitting or standing. Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea( PND) is a sensation of shortness of breath that awakens the patient, often after 1 or 2 hours of sleep, and is usually relieved in the upright position.
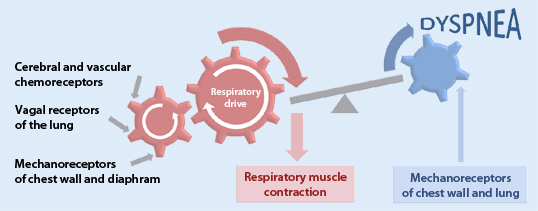
How does dyspnea affect ventilatory capacity?
Dyspnea may be induced in four distinct settings: (1) increased ventilatory demand such as with exertion, febrile illness, hypoxic state, severe anemia, or metabolic acidosis; (2) decreased ventilatory capacity such as with pleural effusion, pneumothorax, intrathoracic mass, rib injury, or muscle weakness; (3) increased airway resistance such as with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; and (4) decreased pulmonary compliance such as with interstitial fibrosis or pulmonary edema.
What is the term for the sensation of difficult or uncomfortable breathing?
Dyspnea refers to the sensation of difficult or uncomfortable breathing. It is a subjective experience perceived and reported by an affected patient. Dyspnea on exertion (DOE) may occur normally, but is considered indicative of disease when it occurs at a level of activity that is usually well tolerated.
What causes orthopnea in the lungs?
Orthopnea is caused by pulmonary congestion during recumbency. In the horizontal position there is redistribution of blood volume from the lower extremities and splanchnic beds to the lungs. In normal individuals this has little effect, but in patients in whom the additional volume cannot be pumped out by the left ventricle because of disease, there is a significant reduction in vital capacity and pulmonary compliance with resultant shortness of breath. Additionally, in patients with congestive heart failure the pulmonary circulation may already be overloaded, and there may be reabsorption of edema fluid from previously dependent parts of the body. Pulmonary congestion decreases when the patient assumes a more erect position, and this is accompanied by an improvement in symptoms.
What is the synonym for dyspnea?
Synonym (s): dyspnoea. [G. dyspnoia, fr. dys-, bad, + pnoē, breathing]
What does dyspnea mean?
dyspnea. [ disp-ne´ah] breathlessness or shorthess of breath; labored or difficult breathing. It is a sign of a variety of disorders and is primarily an indication of inadequate ventilation or of insufficient amounts of oxygen in the circulating blood. adj., adj dyspne´ic. Dyspnea can be symptomatic of a variety of disorders, both acute and chronic.
How to help dyspnea patients?
The patient should respond favorably to a calm, reassuring manner and an explanation of what is being done to relieve the shortness of breath. High Fowler's position or orthopneic position with the arms resting on pillows on an overbed table will help improve chest expansion. Helping the patient relax muscles not needed for breathing conserves oxygen and promotes rest. If abdominal distention, ascites, or a massive tumor interferes with chest expansion and produces dyspnea, having the patient lie on one side and supporting the abdomen with pillows may provide some relief.
What is the meaning of "sob" in medical terms?
Breathlessness, shortness of breath, SOB Pulmonary medicine Difficult painful breathing, SOB or respiratory distress; dyspnea is subjective, difficult to quantify, and may indicate serious disease of the heart, lungs, or airways. See Nocturnal dyspnea, Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea.
What is the term for a person who has difficulty breathing?
Dyspnea. A difficulty in breathing or shortness of breath, typically associated with some form of heart or lung disease. Also known as air hunger. Mentioned in: Coarctation of the Aorta, Mesothelioma, Shortness of Breath. Gale Encyclopedia of Medicine.
What are the special observations and methods of assessment of a patient who has dyspnea?
Special observations and methods of assessment of a patient who has dyspnea include: auscultation of the chest for abnormal breath and voice sounds, lung aeration, rales, and rhonchi; inspection of the chest for respiratory rate and rhythm and for symmetrical expansion; inspection of the skin, lips, and nail beds for cyanosis; and percussion of the chest for abnormal resonance. Results of arterial blood gas analyses should be monitored and the patient observed for fatigability when engaged in various levels of activity.
What is the procedure to intubate a patient with acute respiratory distress?
In cases of acute respiratory distress, it may be necessary to intubate the patient, begin oxygen therapy, and obtain laboratory arterial blood gas data. If there is airway obstruction, clearing the airway is necessary, or a tracheotomy may be performed.
What is the code for dyspnea?
R06.09 is a billable diagnosis code used to specify a medical diagnosis of other forms of dyspnea. The code R06.09 is valid during the fiscal year 2021 from October 01, 2020 through September 30, 2021 for the submission of HIPAA-covered transactions.
What causes shortness of breath?
Many conditions can make you feel short of breath: 1 Lung conditions such as asthma, emphysema, or pneumonia 2 Problems with your trachea or bronchi, which are part of your airway system 3 Heart disease can make you feel breathless if your heart cannot pump enough blood to supply oxygen to your body 4 Anxiety and panic attacks 5 Allergies
Why do I feel breathless?
Heart disease can make you feel breathless if your heart cannot pump enough blood to supply oxygen to your body. Anxiety and panic attacks .
What does it mean when you have dyspnea?
Kathrin Ziegler/Getty Images. Dyspnea on exertion means that a person feels short of breath during exercise. It can cause someone to feel as though they are running out of air and cannot breathe fast or deep enough while exercising or exerting physical effort. Dyspnea on exertion can also cause:
What is the best treatment for dyspnea?
Common treatment options for respiratory causes include: inhalers, such as antimuscarinics, corticosteroids, and short- or long-acting bronchodilator inhalers. supplemental oxygen therapy.
How to treat dyspnea from smoking?
The treatment for dyspnea on exertion that occurs due to chemical or environmental irritants depends on the specific cause, but common options include: stopping smoking or avoiding exposure to tobacco smoke. wearing protective covering and breathing devices when exposed to chemical fumes.
What causes dyspnea when exerting?
Respiratory conditions are a common cause of dyspnea on exertion. Common respiratory causes include:
When to consult a doctor for dyspnea?
It is important to consult a doctor when dyspnea during exertion is unexplained, sudden, severe, or disabling, or if one of the more serious symptoms listed above accompanies it. Last medically reviewed on February 26, 2021. Asthma. Lung Cancer.
Can dyspnea cause tight chest?
Depending on the cause, dyspnea can occur alongside other symptoms, such as a tight chest and anxiety. Read on to learn more about dyspnea on exertion, including the possible causes and when to see a doctor.
Is dyspnea a condition that usually gets better when you rest?
Dyspnea on exertion is a common. Trusted Source. , often harmless condition that usually gets better when a person rests. However, if a person experiences dyspnea that comes on suddenly for no apparent reason or is very intense, they may require medical care. Dyspnea can also.
