What is oxaloacetate (OAA) and what does it do?
When oxaloacetate (OAA) is reduced to malate, it generates NAD+, which plays a role in many cellular processes. It plays a role in gluconeogenesis, amino acid and fatty acid synthesis, and the Krebs/citric acid cycle that produces most of our energy. It’s reportedly able to cross the blood-brain barrier and is sometimes used as a nootropic.
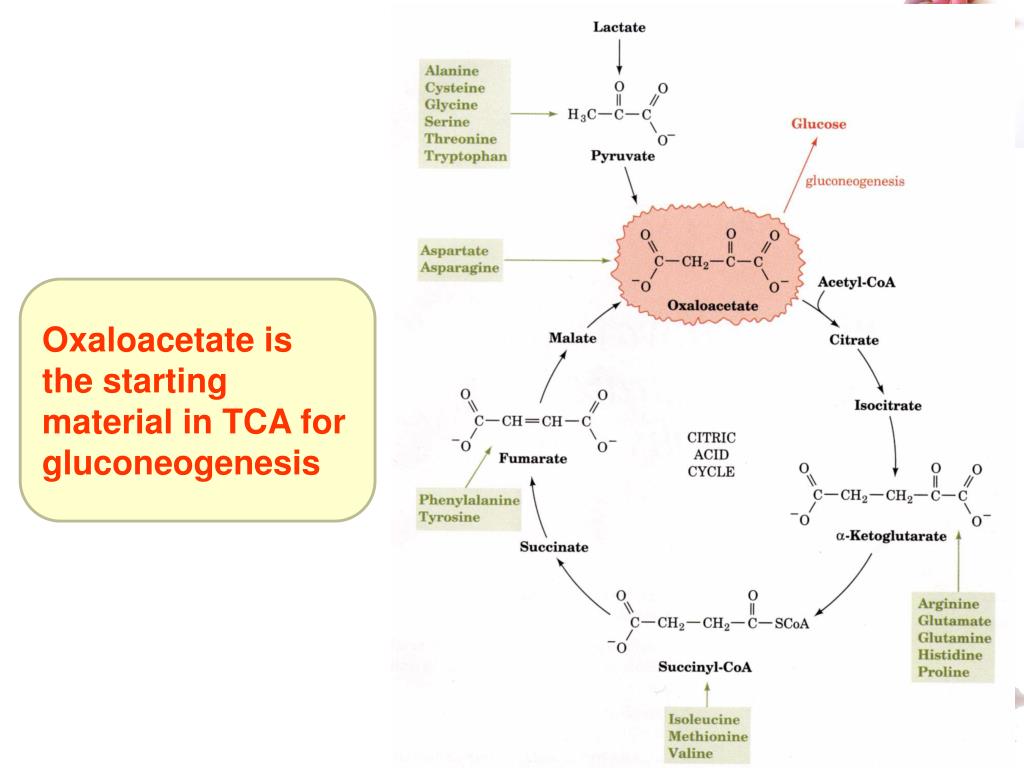
Why is oxaloacetate used in gluconeogenesis?
Certain tissues such as the heart and brain rely on the glucose produced by gluconeogenesis and without that glucose they are severely affected. One of the breakdown products of oxaloacetate is aspartic acid, which is required for the urea cycle.
What is an example of an oxaloacetate reaction?
In nature, there are many biochemical reactions that involve oxaloacetate, which include gluconeogenesis, the glyoxylate cycle, glyoxylate degradation, mixed acid fermentation, anaerobic respiration, aerobic respiration (Krebs cycle), aspartate biosynthesis and degradation and glutamate degradation.
What is the oxaloacetate Kaufman used for?
The oxaloacetate Kaufman (Jubilance) used can be found here. (It’s advertised as a PMS/mood supplement.) Kaufman, who seems to attend every conference possible, and appears determined to unearth every treatment option possible, also reported on New Frontiers for ME/CFS at the IACFS/ME conference.

What are sources of oxaloacetate?
Oxaloacetate food sources Oxalacetic acid can be found in a number of food items such as daikon radish, sacred lotus, cucurbita (gourd) and tarragon, which makes oxalacetic acid a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products.
What is oxaloacetate converted to?
Under gluconeogenic conditions, the TCA cycle intermediates oxaloacetate or malate are converted to pyruvate and PEP by decarboxylation (C4-decarboxylation) [1, 4] and thus, the PEP–pyruvate–oxaloacetate node provides the direct precursors for gluconeogenesis.
What would be the effect of an oxaloacetate deficiency?
The lack of oxaloacetate prevents gluconeogenesis and urea cycle function. Metabolic acidosis caused by an abnormal lactate production is associated with nonspecific symptoms such as severe lethargy, poor feeding, vomiting, and seizures, especially during periods of illness and metabolic stress.
What are the importance of oxaloacetate in the metabolic process?
Oxaloacetate, an intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid cycle, plays important roles in regulating mitochondrial function, gluconeogenesis, the urea cycle, and amino acid syntheses.
Is oxaloacetate an enzyme?
This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme oxaloacetate tautomerase.
What is oxaloacetate in biology?
Oxaloacetic acid (also known as oxalacetic acid or OAA) is a crystalline organic compound with the chemical formula HO2CC(O)CH2CO2H. Oxaloacetic acid, in the form of its conjugate base oxaloacetate, is a metabolic intermediate in many processes that occur in animals.
Is oxaloacetate natural?
Oxaloacetate, sometimes called oxaloacetate acid, is a naturally occurring compound in the body. While it is not considered a vitamin or a nutrient, it does contribute to many key functions in the human body.
How is oxaloacetate regenerated?
In the last step of the citric acid cycle, oxaloacetate—the starting four-carbon compound—is regenerated by oxidation of malate.
Which of the following will occurs if a cell is lacking oxaloacetate?
If a cell is lacking in oxaloacetate, which of the following will occur? Explanation: If a cell is lacking in oxaloacetate, the Krebs cycle will be unable to continue. Therefore, there will be no way for the electron transport chain to receive the high energy electrons it requires to create ATP.
Is oxalic acid the same as oxaloacetate?
While oxaloacetate in the English language sounds very similar to “oxalate,” the two compounds are chemically quite different.
Can oxaloacetate be converted to glucose?
Oxaloacetate (an intermediate in the citric acid cycle) can also be used for gluconeogenesis. The gluconeogenic pathway can also generate glucose from amino acids, with the exception of lysine and leucine.
How does oxaloacetate regulate the citric acid cycle?
The citric acid cycle begins with the reaction that combines the two-carbon acetyl CoA with a four-carbon oxaloacetic acid to produce the six-carbon molecule citrate. Acetyl-CoA is regulated by the controlled amounts of pyruvate that is converted into acetyl-CoA in the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex reaction.
How is OAA converted to malate?
In the cytosol, oxaloacetate is reduced to malate by electrons from NADH. Malate is then transported into the mitochondrial matrix via an oxaloacetate/malate antiporter. Inside the mitochondrion, malate is oxidized by NAD+ back to oxaloacetate forming NADH.
What enzyme converts oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate?
PEPCKPEPCK is another key rate-limiting gluconeogenic enzyme, catalyzing the conversion of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate and water.
What amino acids are derived from oxaloacetate?
The oxaloacetate/aspartate family of amino acids is composed of lysine, asparagine, methionine, threonine, and isoleucine. Aspartate can be converted into lysine, asparagine, methionine and threonine. Threonine also gives rise to isoleucine.
How is oxaloacetate used in gluconeogenesis?
Oxaloacetate is reduced to malate using NADH, a step required for its transportation out of the mitochondria. Malate is oxidized to oxaloacetate using NAD+ in the cytosol, where the remaining steps of gluconeogenesis take place.
What is Oxaloacetate?
Oxaloacetate is an organic compound that has been getting a lot of press over the last few years. Also known as Oxaloacetic acid, this compound which plays a number of key roles in the body has been the subject of an increasing body of research.
When oxaloacetate was used in conjunction with Temozolomide – an antitum?
When oxaloacetate was used in conjunction with Temozolomide – an antitumor medication, excellent synergistic results occurred and survival rates of the animals increased above 200%. (3)
Is oxaloacetate low in food?
The levels of oxaloacetate found in food is way too low to make much of a difference to your health. For this reason, a supplement may be the best option for you.
Does oxaloacetate help the brain?
Clinical research has demonstrated that the use of oxaloacetate is linked to a number of benefits while animal studies have also proved encouraging. At the top of that list is the ability of oxaloacetate to preserve brain health and protect against neurotoxicity. Studies also indicate that it can help the brain recover from injury because it stimulated the production of new mitochondria.
Is oxaloacetate a good anticancer?
Although we are still scratching the surface with regard to the potential of oxaloacetate, the studies done to date have been extremely positive. This is certainly the case when it comes to its potential as an anticancer or antitumor agent.
Does oxaloacetate offset biomarkers?
Studies appear to suggest that oxaloacetate offsets various biomarkers that are associated with the aging process.
Does glutamate prevent neurotoxicity?
It prevents neurotoxicity also known as glutamatergic excitotoxicity.
What is the carbon of oxaloacetate?
Oxaloacetate produced from labeled pyruvate via the anaplerotic reaction will be labeled at carbon 3, if the bicarbonate is unlabeled, or at carbons 3 and 4, if the bicarbonate is labeled.
How to determine the product of 2-oxo acid?
A second method is to incubate the amino acid with a very small amount of 2-oxo acid and determine the product 2-oxo acid by formation of a dinitrophenylhydrazone. Alanine aminotransferase may be assayed by incubating the enzyme with 100 mM alanine and 2 mM 2-oxoglutarate in 0.1 M Tris-HCl buffer pH 7.4. The pyruvate formed may be determined by reaction with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine and measuring the colour at 546 nm. A standard curve of varying pyruvate concentrations must, of course, be constructed.
Is oxaloacetate bypassed in Fig. 7.6b?
Although oxaloacetate was partly bypassed in the pathway of Fig. 7.6b, a key question is whether this metabol ite can be bypassed altogether and whether pathways can be constructed for the production of lysine from pyruvate or glucose without the involvement of oxaloacetate at any point.
What Does Oxaloacetate Do In Your Body?
Oxaloacetate plays a role in the Kreb’s cycle and the stage that goes immediately before the formation of pyruvate ( via pyruvate carboxylase) and immediately after the NAD+-consuming conversion from L- malate (via malate dehydrogenase).
What is glutamate oxaloacetate?
Glutamate is considered a very important neurotransmitter but large quantities of glutamate can lead to serious brain damage. Oxaloacetate, when combined with an enzyme called glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase or GOT, breaks down glutamate (into 2-ketoglutarate and aspartate). However, it is still unclear how applicable this can be when oxaloacetate is used as a supplement.
What is the role of oxaloacetate in the Kreb cycle?
Oxaloacetate plays a role in the Kreb’s cycle and the stage that goes immediately before the formation of pyruvate (via pyruvate carboxylase) and immediately after the NAD+-consuming conversion from L-malate (via mala te dehydrogenase).
How is oxaloacetate formed?
Oxaloacetate is essentially formed by the carboxylation of pyruvate when it reacts with the catalyzed biotin-dependent enzyme pyruvate carboxylase.
What is the name of the molecule that is similar to oxaloacetic acid?
Oxaloacetate is the name for the molecule 3-carboxy-3-oxopropanoic acid and it is very similar to oxaloacetic acid (Although, this depends on the acidity of oxaloacetate). It is also a metabolic intermediate in a big number of processes that occur in animals. It has a role in gluconeogenesis, the urea cycle, amino acid synthesis, fatty acid synthesis, and the citric acid cycle.
Does oxaloacetate help with Alzheimer's?
For example, in a study with rats with Alzheimer’s disease oxaloacetate has shown promise in encouraging the formation of new mitochondria, activating insulin signaling, and reducing brain inflammation (Which are all common symptoms of Alzheimer’s). It has been shown that it can even promote the birth of new neurons.
Is oxaloacetate controversial?
Also, all the research regarding oxaloacetate has been very controversial because the company that produces most of the oxaloacetate supplements has a history of violating FDA regulations regarding the marketing and sale of “new drugs” and medical foods.
Why is oxaloacetate important?
Proper levels of oxaloacetate are crucial for healthy metabolism, glucose system support and overall cellular function. The body already has oxaloacetate inside its cells. In fact, you need a certain amount of it just to stay ...
What is Oxaloacetate?
Oxaloacetate is a naturally-occurring compound needed by every human cell to produce energy in the Krebs Cycle.
Does oxaloacetate reduce inflammation?
In human cell tests and laboratory animal tests, oxaloacetate also reduces inflammation and promotes neurogenesis to support both physiological and neurological wellbeing. Because oxaloacetate works by imitating calorie restriction, benaGene triggers many of the same anti-aging pathways that calorie restriction is known for.
Does oxyaloacetate help the Krebs cycle?
Oxa loacetate not only provides the building blocks needed for the Krebs cycle to produce ATP energy, but in fact promotes mitochondrial biogenesis—helping new mitochondria form within cells and boosting the body’s energy production. This dual action of promoting mitochondrial density, and providing the basic building blocks, is what makes benaGene a unique dietary supplement.
Does the body have oxaloacetate?
The body already has oxaloacetate inside its cells. In fact, you need a certain amount of it just to stay alive—children born with an inability to produce oxaloacetate die early in childhood. Your oxaloacetate is normally replenished from natural processes in your cells.
Does oxaloacetate help the mitochondria?
As a result, our bodies sometimes need a little extra help. Supplementing with oxaloacetate not only provides the metabolites necessary for the mitochondria to do their job, but also helps form fresh new mitochondria for increased energy production.
What is the role of oxaloacetate in cellular processes?
When oxaloacetate (OAA) is reduced to malate, it generates NAD+, which plays a role in many cellular processes. It plays a role in gluconeogenesis, amino acid and fatty acid synthesis, and the Krebs/citric acid cycle that produces most of our energy. It’s reportedly able to cross the blood-brain barrier and is sometimes used as a nootropic. Animal trials suggest it may be activating mitochondrial biogenesis pathways and enhancing antioxidant and brain insulin signaling pathways in the brain.
How much does oxaloacetate cost?
The worm in the ointment is the cost. You can purchase oxaloacetate online, but it’s very expensive – probably around $5-600 a month at the higher, more effective doses. The oxaloacetate Kaufman (Jubilance) used can be found here. (It’s advertised as a PMS/mood supplement.)
Is oxaloacetate in Lee Know's book?
Like the last overview on n-acetyl-cysteine (NAC), this supplement – called oxaloacetate (OAA) – does not appear in Lee Know’s book “ Mitochondria and the Future of Medicine ” . The supplement is unusual in other ways: for one, it’s rare that for an “omics” study to spark an interest in a new treatment or that an experienced ME/CFS doctor has gotten excited about a supplement.
