
What does oxidation do to your body?
We could go on and on…So, let’s discuss oxidation. Oxidation in the body creates a byproduct called reactive oxygen species (ROS) that could function as free radicals or eventually produce free radicals. This is actually a very natural process. ROS in immune cells can help combat invading pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, and fungi.
What does oxidation have the ability to do?
Oxidation occurs when an atom, molecule, or ion loses one or more electrons in a chemical reaction. When oxidation occurs, the oxidation state of the chemical species increases. Oxidation doesn't necessarily involve oxygen! Originally, the term was used when oxygen caused electron loss in a reaction. The modern definition is more general.
Why is oxidation harmful?
Oxidation happens through chemical reactions in our bodies all the time. The process creates "free radicals," which can cause damage that raises our risk for heart attack, stroke, cancer and other ...
How to reduce oxidative damage?
- Almonds
- Sunflower Seeds
- Strawberries
- Broccoli
- Bell Peppers
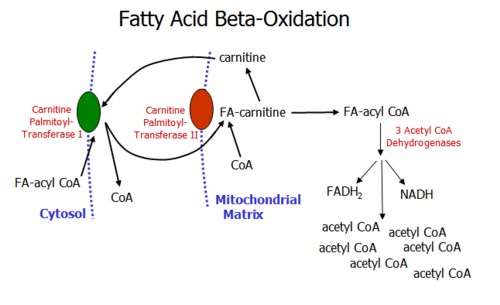
What happens to the body during oxidation?
Oxidation can damage vital molecules in our cells, including DNA and proteins, which are responsible for many body processes. Molecules such as DNA are needed for cells to function properly, so if too many are damaged, the cell can malfunction or die.
What causes oxidation in the human body?
Lifestyle: smoking, alcohol consumption, adequate or inappropriate diet, exercise, training or untrained condition, contribute to oxidative stress. Some research has shown the presence of reactive oxygen species and muscle level and their role in regulating muscle activity.
How does oxidation reaction process occur in human body?
Oxidative metabolism (also called cellular respiration) is a cellular process through which organisms use oxygen to break down food molecules, which are organic compounds such as glucose, in order to extract chemical energy for cell processes.
How do I reduce the oxidation in my body?
Making the following lifestyle changes may help prevent oxidative stress:Quit smoking, if you smoke. ... Include more antioxidant-rich foods in your diet. ... Limit alcohol use. ... Lower your stress levels. ... Protect your skin. ... Get physical. ... Get enough sleep. ... Try antioxidant supplements.
What diseases are caused by oxidation?
Oxidative stress has been linked to several neurological diseases (i.e., Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease (AD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), multiple sclerosis, depression, and memory loss) [32–35].
What foods oxidize in your body?
Highly processed foods, dairy, eggs, butter, meat, fish, and baked goods tend to cause a buildup of oxidized cholesterol. What is the difference between LDL and oxidized LDL? LDL is a type of cholesterol that is considered bad. LDL that has gone through a chemical reaction is called oxidized LDL.
Do humans experience oxidation?
Oftentimes when we think of oxidizing cells, we think of our upper bodies or the vital organs like the heart and lungs there. However, the most important oxidation processes occur in the gut.
What does oxidation mean in metabolism?
Listen to pronunciation. (OK-sih-DAY-tiv meh-TA-buh-lih-zum) A chemical process in which oxygen is used to make energy from carbohydrates (sugars). Also called aerobic metabolism, aerobic respiration, and cell respiration.
What vitamin helps prevent oxidation?
Vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta-carotene, often referred to as "antioxidant vitamins," have been suggested to limit oxidative damage in humans, thereby lowering the risk of certain chronic diseases.
What vitamin helps with oxidation?
Vitamin E (i.e., α-tocopherol) and Vitamin C (i.e., ascorbic acid) are antioxidants that are thought to have a protective effect by either reducing or preventing oxidative damage.
Does oxidation mean removal?
Oxidation means the addition of oxygen to a molecule or the removal of hydrogen from a molecule. Reduction means the addition of hydrogen to a molecule or the removal of oxygen from a molecule.
How do you reduce oxidation and inflammation?
“Specifically, a diet high in minimally processed, high-fiber, plant-based foods such as vegetables and fruits, whole grains, legumes, and nuts,”—antioxidant, anti-inflammatory whole plant foods—“will markedly blunt the post-meal increase” in sugar, fat, and inflammation.
What are the 2 ways to prevent oxidation?
To prevent oxidation at high temperature one must use either a noble metal or something already oxidized so that the process can go no further. The material must be either a stable oxide or one which is covered with an oxide (a nitride) or some sort of impervious cover itself stable against oxidation (and nitridation).
How does oxidative stress affect the body?
Oxidative stress can cause damage to many of your tissues, which can lead to a number of diseases over time. While you can’t completely avoid exposure to free radicals, you can make lifestyle choices regarding diet, exercise, and environment to help keep your body in balance, and prevent damage and disease.
What is oxidative stress?
Overview. Oxidative stress is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in your body. Free radicals are oxygen-containing molecules with an uneven number of electrons. The uneven number allows them to easily react with other molecules. Free radicals can cause large chain chemical reactions in your body because they react so easily ...
How to prevent oxidative stress?
One method of preventing oxidative stress is to ensure that you’re obtaining enough antioxidants in your diet. Eating five servings per day of a variety of fruits and vegetables is the best way to provide your body what it needs to produce antioxidants. Examples of fruits and vegetables include: berries. cherries.
What are the causes of aging?
inflammatory conditions. high blood pressure, which is also known as hypertension. heart disease. neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. cancer. Oxidative stress also contributes to aging.
How can we reduce free radicals?
Be environmentally conscious. Environmentally friendly initiatives like carpooling help reduce free radical production for you and your community.
What is the best way to reduce oxidative stress?
A regular, moderate exercise routine. This has been associated with higher natural antioxidant levels and decreased damage caused by oxidative stress. Regular exercise has been linked with a longer lifespan, fewer effects of aging, and decreased risk of cancer and disease.
What happens when free radicals are present?
When there are more free radicals present than can be kept in balance by antioxidants, the free radicals can start doing damage to fatty tissue, DNA, and proteins in your body. Proteins, lipids, and DNA make up a large part of your body, so that damage can lead to a vast number of diseases over time.
What are the effects of oxidative stress on the body?
When the concentration of free radicals in the body is higher than what the antioxidants can balance, it results in oxidative stress. The free radicals damage the body by damaging the cell membrane and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
How does oxidative stress affect the body?
Oxidative stress can have negative effects on the body. This means the oxidative ions attack our healthy cells instead of germs. Antioxidants are molecules that can donate an electron to a free radical, which makes the free radical stabilize and become less reactive.
What happens to free radicals in oxidation?
What Happens in Oxidation? Center. Free radicals are oxygen-containing molecules with an uneven number of negative charged subatomic particles (electrons). Free radicals are oxygen-containing molecules with an uneven number of negative charged subatomic particles (electrons). The uneven number of electrons makes these highly reactive.
Why are free radicals so reactive?
The uneven number of electrons makes these highly reactive. These free radicals react with oxygen in the body. This process is called oxidation. Oxidation is a normal process that happens in the body. It can help fight pathogens, hence reduces the risk of infections. Oxidative stress happens when there is an imbalance between free radicals ...
How to prevent free radicals?
It is not possible to completely avoid exposure to free radicals and oxidative stress. However, there are ways to minimize the effects of oxidative stress on the body. The main thing you can do is to increase the levels of antioxidants inside the body, which would combat the formation of free radicals as much as possible. Ways to reduce or prevent oxidative stress include: 1 Consuming foods that are rich in antioxidants. This includes fruits, vegetables, and spices (berries, cherries, citrus fruits, dark leafy vegetables, broccoli, carrots, tomatoes, olives, nuts, fish, turmeric, green tea, onion, garlic, cinnamon). 2 Taking supplements that contain vitamin C, B, and E can help reduce oxidative stress. 3 Decreasing the amount of bad fat in the diet. Good fat is present in walnuts, almonds, fatty fish, avocadoes, etc. 4 Reducing alcohol consumption. 5 Regular and moderate exercise routine. At least 30 minutes of exercise daily. 6 Avoiding smoking or exposure to cigarette smoke and other fumes. 7 Using chemicals with caution. These include cleaning chemicals, pesticides, etc. You may switch to environmentally friendly cleaning products, pesticides, and fertilizers. Bio enzymes made from orange peels and lemon peels are excellent surface cleaners. 8 Using sunscreen prevents damage caused by ultraviolet light to the skin. Sunscreen should be used all year round, even in winters or if it is cloudy. 9 Adequate sleep and hydration are a must. 10 Avoiding overeating or binging can reduce oxidative stress. It is best to eat at appropriately spaced intervals and in small or moderate portions.
How do you know if you have acid in your stomach?
You would know if you were suffering from stomach acidity if you feel a burning sensation just above the stomach, or right below (the hollow part) your breastbone. This is the most classic sign of acidity.
How long does it take for a body to decompose?
It really depends on the cause of the death. Typically placed 6ft down, without a coffin, in ordinary soil, eight to twelve years to completely decompose into a skeleton. Now if placed in a coffin, it may take many more years, depending on the type of wood used for the coffin. For example, solid Oak will slow down the process. It is believe that one man's process of decomposing took 50 years in an Oak coffin. What also you have to consider is decomposition in the air is twice as fast as when the body is underwater and four times as fast as underground. A corpse left above ground is rapidly bro
What does the stomach do when we eat?
Our stomach produces acid to digest the food that we eat. This is a regular and natural process. Whenever we eat, cells within the lining of the stomach pump acid to liquefy your sumptuous dinner, from mash potatoes to a slab of steak.
Why do ulcers occur in the stomach?
Lack of adequate blood flow to the stomach may contribute to ulcers.
What is the boiling point of ammonia?
Compare ammonia, with moderate intermolecular forces and a boiling point of -33.3°C.
What is a medical guardian?
Medical Guardian provides an array of mobile medical alert devices for seniors. Medical alert systems are a convenient way for seniors to have access to all the help they need while still maintaining their independence. In addition to the alert devices you can keep in your home, Medical Gua
What is reactive oxygen?
Reactive oxygen species is something different: oxygen in a highly reactive form (peroxides, superoxides, singlet oxygen) that can damage cellular structures. They can be a byproduct of oxidative phosphorylation (H2O2 instead of H2O)
What are Antioxidants?
Molecules that can donate an extra electron to a free radical without becoming unstable themselves are known as antioxidant s. To aptly put, antioxidants help neutralize free radicals by donating an electron to make them stable.
What Does Oxidative Stress Do to The Body?
However, oxidative stress only happens when there is a sizable difference in the ratio of free radicals and antioxidants.
How do free radicals affect the body?
However, when these free radicals outnumber the antioxidants that are supposed to keep them in check, they can wreak havoc in your body, causing damage to your DNA, proteins, fatty tissues and even accelerate the aging process.
What are some examples of antioxidants?
Some common examples of antioxidants are vitamins A, C, and E. Both free radicals and antioxidants can emanate from different sources. For example, glutathione is an antioxidant that can be naturally produced in the body’s cells. Fruits and vegetables contain minerals and vitamins required by the body to form antioxidants.
How to reduce oxidative stress?
Certain changes to your diet and lifestyle can help reduce the likelihood of oxidative stress in the body. Some of these changes include: 1 Limiting the consumption of heavily processed food 2 Avoiding a diet high in added sugar and fat 3 Eating a nutritious and balanced diet, including vegetables and fruits 4 Reducing stress 5 Quitting smoking 6 Reducing stress and exercising regularly 7 Reducing the consumption of alcohol 8 Getting enough sleep 9 Avoiding harsh chemicals and pollution
What happens when a free radical reacts with another molecule?
When a free radical reacts with other molecules, the process is known as oxidation . When oxidation occurs, the unpaired electron combines with another molecule. Free radicals are generally a by-product of energy production in the body. Similarly, certain substances, such as ozone, cigarette and cannabis smoke, can increase free radicals in the body.
Why is it important to maintain a healthy weight?
A study conducted in 2015 revealed that maintaining a healthy weight may also be vital to preventing oxidative stress. Excess fat cells are known to produce inflammatory substances that can prompt the production of free radicals by the immune system.
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions in the Body
Oxidation describes chemical reactions where electrons are lost, whereas reduction refers to reactions where electrons are gained. Electrons are stable atomic particles that are negatively charged, and the transfer of electrons between molecules produces energy. Electrons do not exist by themselves; they are always associated with an atom.
Oxidative Metabolism: Cellular Respiration
Food is converted to usable energy through metabolic processes in the cells of the body. Metabolism is defined as the sum of chemical reactions that occur within each cell to supply energy for important reactions and processes.
Cellular Oxidation in the Body
During oxidative metabolism, or cellular respiration, food molecules are oxidized to produce energy in the form of ATP.
What is slow oxidizer?
A slow oxidizer releases energy too slowly to maintain adequate health. This is analogous to a wood stove whose fire is too small to heat the room. To improve his health status and energy level, his metabolic furnace, i.e., oxidation rate, must be increased. The slow oxidizer has exhausted thyroid and adrenal glands. These major energy producing glands must be stimulated through proper diet and supplements to restore them to normal function.
Is a mixed oxidizer fast or slow?
A mixed oxidizer has an erratic metabolism. Sometimes it is too fast, other times it is too slow. The mixed oxidizer, to achieve a higher energy level, must stabilize his oxidation rate. The mixed oxidizer's adrenal and thyroid gland are out of synchronization, that is, the thyroid gland may be overactive and the adrenal glands underactive, or vice versa. The dietary and supplemental requirements are balanced between the fast and slow oxidizer.
What is rust from?
Rust is from oxidation of the iron. But oxidation doesn’t mean aging for people
Why is my hair gray?
A white cell uses oxidation to kill harmful bacteria. The gray hair so many color– it is gray because of the “bleaching” effect of anti-oxidants.
Why do we oxidize hair?
You want your body to oxidize some things (my hair, now the true platinum color) – you want to kill invading bacteria, cells that go wild (unlike the teenage daughter who wants to go to Mexico for spring break – although oxidizing the boys in Mexico might be a good thing).
Do you need oxidants to wash clothes?
Ok – yes, you need the oxidants to wash your clothes. Nothing like some oxy-clean to whiten the stains. But, the body uses oxidation in a variety of ways that are useful.
Where did Terry Simpson get his medical degree?
Dr. Terry Simpson received his undergraduate, graduate, and medical degrees from the University of Chicago where he spent several years in the Kovler Viral Oncology laboratories doing genetic engineering. Until he found he liked people more than petri dishes.
Does oxidation cause heart disease?
There is a theory that the stress of oxidation leads to many diseases including heart disease, cancer, and even aging. As a result, there has been a rush of studies examining the role of anti-oxidants and to see if diets rich in anti-oxidants will show a decrease in those disease.
Can oxidation harm us?
We have a balance in our bodies– those things that can help us- oxidation against bacteria and cancer – -can harm us if it runs wild. Just like our immune system can turn against us.
Which compounds can acquire a prooxidant behavior?
6.2. Polyphenols. Under conditions like high concentrations, high pH, and the presence of redox-active metals, phenolic compounds can acquire a prooxidant behavior [157, 158], mainly based on the generation of an aroxyl radical or a labile complex with a metal cation exerting redox activity.
What are the causes of free radicals?
Free radicals are generated from both endogenous and exogenous sources. Immune cell activation, inflammation, ischemia, infection, cancer, excessive exercise, mental stress, and aging are all responsible for endogenous free radical production. Exogenous free radical production can occur as a result from exposure to environmental pollutants, heavy metals (Cd, Hg, Pb, Fe, and As), certain drugs (cyclosporine, tacrolimus, gentamycin, and bleomycin), chemical solvents, cooking (smoked meat, used oil, and fat), cigarette smoke, alcohol, and radiations [15–25]. When these exogenous compounds penetrate the body, they are degraded or metabolized, and free radicals are generated as by-products.
What is H2O2(a nonradical)?
H2O2(a nonradical) is produced by multiple oxidase enzymes, that is, amino acid oxidase and xanthine oxidase.
What are the two types of reactions that produce ROS?
ROS production basically relies on enzymatic and nonenzymatic reactions. Enzymatic reactions able to generate ROS are those involved in respiratory chain, prostaglandin synthesis, phagocytosis, and cytochrome P450 system [10–20]. Superoxide radical (O2•−) is generated by NADPH oxidase, xanthine oxidase, and peroxidases. Once formed, it is involved in several reactions that in turn generate hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl radical (OH•), peroxynitrite (ONOO−), hypochlorous acid (HOCl), and so on. H2O2(a nonradical) is produced by multiple oxidase enzymes, that is, amino acid oxidase and xanthine oxidase. Hydroxyl radical (OH•), the most reactive among all the free radical species in vivo, is generated by reaction of O2•−with H2O2, with Fe2+or Cu+as a reaction catalyst (Fenton reaction) [12–19]. Nitric oxide radical (NO•), which plays some important physiological roles, is synthesized from arginine-to-citrulline oxidation by nitric oxide synthase (NOS) [12–19].
How is cancer driven?
Cancer can be driven and/or promoted by chromosomal abnormalities and oncogene activation determined by oxidative stress. Hydrolyzed DNA bases are common by-products of DNA oxidation and are considered one of the most relevant events in chemical carcinogenesis [14, 22].
What are the reactive oxygen species?
Superoxide radicals (O2•−), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), hydroxyl radicals (•OH), and singlet oxygen (1O2) are commonly defined reactive oxygen species (ROS); they are generated as metabolic by-products by biological systems [1, 2]. Processes, like protein phosphorylation, activation of several transcriptional factors, apoptosis, immunity, and differentiation, are all dependent on a proper ROS production and presence inside cells that need to be kept at a low level [3]. When ROS production increases, they start showing harmful effects on important cellular structures like proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids [4]. A large body of evidences shows that oxidative stress can be responsible, with different degrees of importance, in the onset and/or progression of several diseases (i.e., cancer, diabetes, metabolic disorders, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular diseases) [5].
How does oxidative stress affect cancer?
Cancer onset in humans is a complex process, which requires both cellular and molecular alterations mediated by endogenous and/or exogenous triggers. It is already well known that oxidative DNA damage is one of those stimuli responsible for cancer development [14, 15, 22]. Cancer can be driven and/or promoted by chromosomal abnormalities and oncogene activation determined by oxidative stress. Hydrolyzed DNA bases are common by-products of DNA oxidation and are considered one of the most relevant events in chemical carcinogenesis [14, 22]. The formation of such kind of adducts impairs normal cell growth by altering the physiological transcriptomic profile and causing gene mutations. Oxidative stress can also cause a variegated amount of modifications against DNA structure, for example, base and sugar lesions, DNA-protein cross-links, strand breaks, and base-free sites. For instance, tobacco smoking, environmental pollutants, and chronic inflammation are sources of oxidative DNA damage that could contribute to tumor onset [14, 17, 29]. Oxidative stress resulting from lifestyle reasons can also play an important role in cancer development, as suggested by the strong correlation between dietary fat consumption (a factor that exposes the organism at greater risk of lipid peroxidation) and death rates from different types of cancer [16, 21].

Overview
- Oxidative stress is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in your body. Free radic…
Antioxidants are molecules that can donate an electron to a free radical without making themselves unstable. This causes the free radical to stabilize and become less reactive.
Effects of oxidative stress on the body
- Oxidation is a normal and necessary process that takes place in your body. Oxidative stress, on t…
When there are more free radicals present than can be kept in balance by antioxidants, the free radicals can start doing damage to fatty tissue, DNA, and proteins in your body. Proteins, lipids, and DNA make up a large part of your body, so that damage can lead to a vast number of diseas… - •diabetes
•atherosclerosis, or the hardening of the blood vessels
What are the risk factors?
- Everyone produces some free radicals naturally in their body through processes like exercise or i…
You may also be exposed to free radicals in the environment. Some sources include: - •ozone
•certain pesticides and cleaners
Managing and preventing oxidative stress
- It’s impossible to completely avoid free radical exposure and oxidative stress. However, there ar…
One method of preventing oxidative stress is to ensure that you’re obtaining enough antioxidants in your diet. Eating five servings per day of a variety of fruits and vegetables is the best way to provide your body what it needs to produce antioxidants. Examples of fruits and vegetables incl… - •berries
•cherries
The takeaway
- While free radicals and antioxidants are part of your body’s natural and healthy functioning, oxid…
While you can’t completely avoid exposure to free radicals, you can make lifestyle choices regarding diet, exercise, and environment to help keep your body in balance, and prevent damage and disease.