They are:
- Inter-Rater or Inter-Observer Reliability: Used to assess the degree to which different raters/observers give consistent estimates of the same phenomenon.
- Test-Retest Reliability: Used to assess the consistency of a measure from one time to another.
- Parallel-Forms Reliability: Used to assess the consistency of the results of two tests constructed in the same way from the same content domain.
What is an example of parallel forms reliability?
Parallel forms reliability example Both groups take both tests: group A takes test A first, and group B takes test B first. The results of the two tests are compared, and the results are almost identical, indicating high parallel forms reliability.
What does parallel forms mean?
Parallel Forms are differing versions of tests or assessments that contain the same information, only in different order. These are used to check test reliability and as a means of curtailing possible cheating through a potential test takers attempts to study, practice or memorize the answers.
Why parallel form reliability is important?
Parallel forms reliability can help you test constructs. Parallel forms reliability (also called equivalent forms reliability) uses one set of questions divided into two equivalent sets (“forms”), where both sets contain questions that measure the same construct, knowledge or skill.
What is the difference between test retest reliability and parallel form reliability?
Test-Retest Reliability: Used to assess the consistency of a measure from one time to another. Parallel-Forms Reliability: Used to assess the consistency of the results of two tests constructed in the same way from the same content domain.
How do you calculate parallel reliability?
R(t) = 1 –F(t) , orR(t) = 1 –Π[1 −Rj(t)] . For example, if two components are arranged in parallel, each with reliability R 1 = R 2 = 0.9, that is, F 1 = F 2 = 0.1, the resultant probability of failure is F = 0.1 × 0.1 = 0.01. The resultant reliability is R = 1 – 0.01 = 0.99.
What are the 4 types of reliability?
4 ways to assess reliability in researchTest-retest reliability. The test-retest reliability method in research involves giving a group of people the same test more than once. ... Parallel forms reliability. ... Inter-rater reliability. ... Internal consistency reliability.
What are the 3 types of reliability?
Reliability refers to the consistency of a measure. Psychologists consider three types of consistency: over time (test-retest reliability), across items (internal consistency), and across different researchers (inter-rater reliability).
What is the difference between alternate forms and parallel forms of a test quizlet?
What is the difference between alternate forms and parallel forms of a test? - Alternate forms do not necessarily yield test scores with equal means and variances. - Alternate forms are different only with respect to how they are administered.
What are the 5 types of reliability?
Types of reliabilityInter-rater: Different people, same test.Test-retest: Same people, different times.Parallel-forms: Different people, same time, different test.Internal consistency: Different questions, same construct.
What are two types of reliability?
There are two types of reliability – internal and external reliability. Internal reliability assesses the consistency of results across items within a test. External reliability refers to the extent to which a measure varies from one use to another.
What is test-retest reliability example?
For example, a group of respondents is tested for IQ scores: each respondent is tested twice - the two tests are, say, a month apart. Then, the correlation coefficient between two sets of IQ-scores is a reasonable measure of the test-retest reliability of this test.
What is test-retest reliability?
Test-Retest Reliability (sometimes called retest reliability) measures test consistency — the reliability of a test measured over time. In other words, give the same test twice to the same people at different times to see if the scores are the same.
What is the meaning of parallel arcs?
A parallel arc occurs when electricity intermittently jumps a gap between wires of different voltages, such as line to line (2 hot conductors of different phases), line to neutral, or line to ground.
What is parallel English?
Parallel structure (also called parallelism) is the repetition of a chosen grammatical form within a sentence. By making each compared item or idea in your sentence follow the same grammatical pattern, you create a parallel construction. Example Not Parallel: Ellen likes hiking, the rodeo, and to take afternoon naps.
What is parallel form reliability?
Parallel forms reliability (also called equivalent forms reliability) uses one set of questions divided into two equivalent sets (“forms”), where both sets contain questions that measure the same construct, knowledge or skill.
How are parallel forms and split half reliability similar?
Parallel forms and split-half reliability are similar, but with parallel forms, the same students take test A and then take test B. With split-half reliability, one group of students is split into two and both groups sit the test at the same time. The two tests in parallel forms reliability are equivalent and can be used independently of each other.
What is parallel form reliability?from statology.org
In statistics, parallel forms reliability measures the correlation between two equivalent forms of a test.
Why is the correlation between the halves of a test high?from statology.org
Ideally we would like the correlation between the halves to be high because this indicates that all parts of the test are contributing equally to what is being measured.
Is there a guarantee that the two halves are parallel?from statology.org
2. There is no guarantee that the two halves are actually parallel.
When to Use Parallel Forms Reliability
Parallel forms reliability is often used in academic settings when a professor doesn’t want students to be able to have access to test questions in advance.
Parallel Forms Reliability vs. Split-Half Reliability
Parallel forms reliability is similar to split-half reliability, but there’s a slight difference:
How to measure parallel forms reliability?
The most common way to measure parallel forms reliability is to produce a large set of questions to evaluate the same thing, then divide these randomly into two question sets.
When to consider reliability?
It’s important to consider reliability when planning your research design, collecting and analyzing your data, and writing up your research. The type of reliability you should calculate depends on the type of research and your methodology.
What is interrater reliability?
Interrater reliability (also called interobserver reliability) measures the degree of agreement between different people observing or assessing the same thing. You use it when data is collected by researchers assigning ratings, scores or categories to one or more variables.
Why is interrater reliability important?
In an observational study where a team of researchers collect data on classroom behavior, interrater reliability is important: all the researchers should agree on how to categorize or rate different types of behavior.
What is the importance of reliability in quantitative research?
When you do quantitative research, you have to consider the reliability and validity of your research methods and instruments of measurement. Reliability tells you how consistently a method measures something. When you apply the same method to the same sample under the same conditions, you should get the same results.
Why is reliability important in testing?
Test-retest reliability can be used to assess how well a method resists these factors over time.
How to measure test-retest reliability?
To measure test-retest reliability, you conduct the same test on the same group of people at two different points in time. Then you calculate the correlation between the two sets of results.
Why is internal consistency technique called internal consistency technique?
These techniques are referred to as internal consistency technique because what is being assessed in this case is the consistency that occurs within the test rather than between two administrations of the same test or separate administration of the alternate forms.
Why are two test forms parallel?
The two test-forms of the same test are said to be parallel or equivalent because they are made up of the same types of items covering the same materials or the same types of information. These forms are so made that if one form correlates to a certain extent with some other measures, then the other form also correlates to the same degree.
What is the sound recognition test?
The Sound Recognition Test is a test for a condition known as auditory agnosia, or a person’s ability to recognize familiar environmental sounds, such as a bell, a whistle, or crowd’s sounds.
What is the parallel form method?
In the parallel-forms method, two tests that are equivalent in the sense that they contain the same kinds of items of equal difficulty but not the same items are administered to the same individuals. This technique is also referred to as the method of equivalent forms.
How many minutes were given to write a letter in the form A?
In form “A,” the persons were given five minutes to write as many words as they could that began with a given letter, say, ‘s’.
What is parallel form reliability?
Parallel-Forms Reliability: Used to assess the consistency of the results of two tests constructed in the same way from the same content domain.
Why are reliability estimates lower than parallel forms?
In general, the test-retest and inter-rater reliability estimates will be lower in value than the parallel forms and internal consistency ones because they involve measuring at different times or with different raters. Since reliability estimates are often used in statistical analyses of quasi-experimental designs (e.g. the analysis of the nonequivalent group design ), the fact that different estimates can differ considerably makes the analysis even more complex.
How to find inter-rater reliability?
If your measurement consists of categories – the raters are checking off which category each observation falls in – you can calculate the percent of agreement between the raters. For instance, let’s say you had 100 observations that were being rated by two raters. For each observation, the rater could check one of three categories. Imagine that on 86 of the 100 observations the raters checked the same category. In this case, the percent of agreement would be 86%. OK, it’s a crude measure, but it does give an idea of how much agreement exists, and it works no matter how many categories are used for each observation.
Why are inter-rater reliability estimates lower than test-retest?
In general, the test-retest and inter-rater reliability estimates will be lower in value than the parallel forms and internal consistency ones because they involve measuring at different times or with different raters.
What is split half reliability?
the split-half reliability estimate, as shown in the figure, is simply the correlation between these two total scores. In the example it is .87.
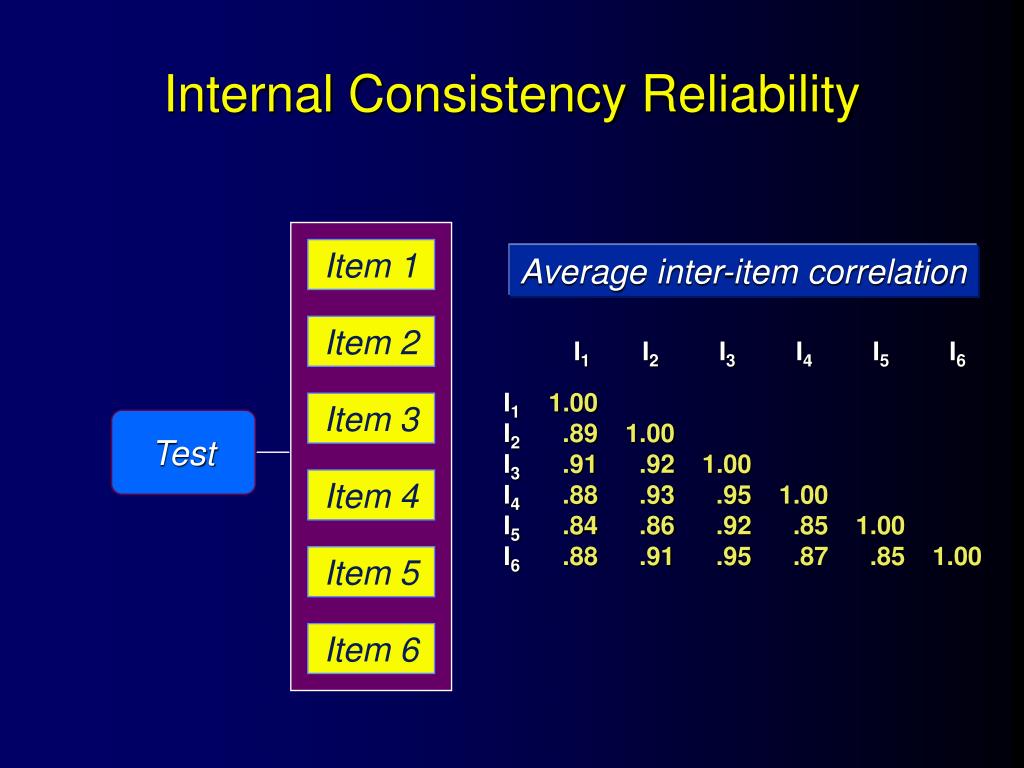
What is the average inter-item correlation?
For example, if we have six items we will have 15 different item pairings (i.e., 15 correlations). The average interitem correlation is simply the average or mean of all these correlations. In the example, we find an average inter-item correlation of .90 with the individual correlations ranging from .84 to .95.
How to estimate test-retest reliability?
This approach assumes that there is no substantial change in the construct being measured between the two occasions. The amount of time allowed between measures is critical. We know that if we measure the same thing twice that the correlation between the two observations will depend in part by how much time elapses between the two measurement occasions. The shorter the time gap, the higher the correlation; the longer the time gap, the lower the correlation. This is because the two observations are related over time – the closer in time we get the more similar the factors that contribute to error. Since this correlation is the test-retest estimate of reliability, you can obtain considerably different estimates depending on the interval.

What Is Parallel Forms Reliability?
Similarity to Split-Half Reliability
- Parallel forms and split-half reliability are similar, but with parallel forms, the same students take test A and then take test B. With split-half reliability, one group of students is split into two and both groups sit the test at the same time. The two tests in parallel forms reliability are equivalent and can be used independently of each other.
Advantages and Disadvantages
- Advantages: 1. Parallel forms reliability can avoid some problems inherent with test-resting. Disadvantages: 1. You have to create a large number of questions that measure the same construct. 2. Proving that the two test versions are equivalent (parallel) can be a challenge. Reference: Henchy, Alexandra Marie, “REVIEW AND EVALUATION OF RELIABILITY GENERALIZA…