
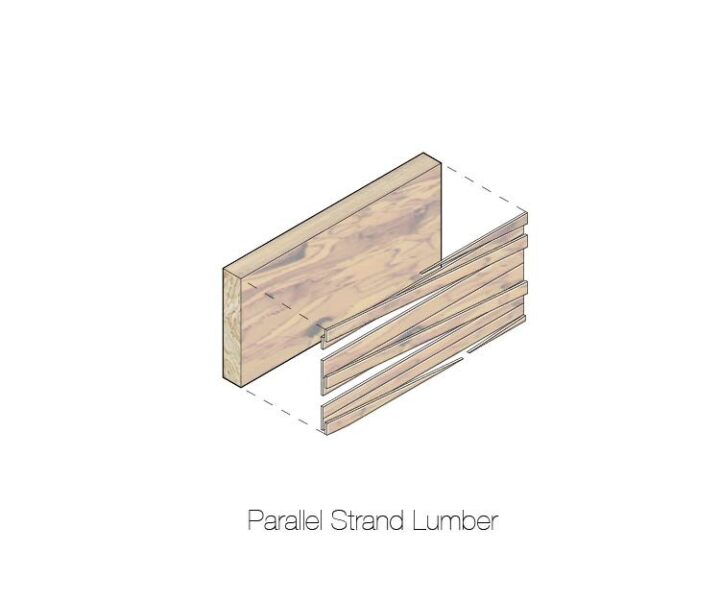
Parallel-strand lumber (PSL) is a form of engineered wood made from parallel wood strands bonded together with adhesive. It is used for beams, headers, columns, and posts, among other uses.
What is Parallam PSL (Parallel strand lumber)?
Parallam ® PSL (Parallel Strand Lumber) is the strongest of Weyerhaeuser’s engineered wood products and a great choice for applications that demand high load capacity. Parallam ® PSL is made by laminating strands of veneer together to form large billets.
What is PSL lumber used for?
Parallel-Strand Lumber (PSL) is one of the types of engineered or manufactured wood that was developed in the late 20th century. PSLs are usually used in wood-framed construction for girders to support smaller beams of laminated veneer lumber (LVL), wood trusses, or wood I-beams. PSL columns are also available.
Can you use parallel strand lumber for floor joists?
If boards or beams can be found that are longer than 16 feet, they are often not straight enough or strong enough to use for floor joists, rafters, or load-bearing studs. Parallel-Strand Lumber (PSL) is one of the types of engineered or manufactured wood that was developed in the late 20th century.
What is PSL beam made of?
Parallel strand lumber (PSL) is made from parallel wood strands joined together using structural adhesives. It is a solid, highly predictable, uniform engineered wood product. PSL is high in strength and stiffness, and is a dimensionally stable product. PSL beam. (Credit: FII Image Library)
What is laminated strand lumber used for?
LSL lumber is most commonly shaped into framing boards for floor joists and support beams. It can also be used for door cores, sill plates, and other applications.
What is parallel strand lumber made from?
Parallel strand lumber (PSL) is made from parallel wood strands joined together using structural adhesives. It is a solid, highly predictable, uniform engineered wood product. PSL is high in strength and stiffness, and is a dimensionally stable product.
What is LSL used for?
What is LSL used for? LSL is used primarily as structural framing for residential, commercial and industrial construction. It is suitable for headers and beams, tall wall studs, rim board, sill plates, millwork and window framing. LSL also offers good fastener-holding strength.
What is TimberStrand LSL used for?
TimberStrand LSL studs and columns provide excellent value when used selectively in the framing zones of a house, where straight studs translate into flush walls. These zones include kitchen cabinet walls, tiled bath walls, tall walls, and other prominent areas, such as staircases and hallways.
Is LSL stronger than wood?
LSL is typically less expensive than other engineered wood beams. Due to its high allowable shear strength, LSL beams have the capacity for larger penetrations than other engineered wood beam options. While not as strong as LVL or PSL beams, LSL is generally cheaper and is ideal for short spans.
Are LSL as strong as LVL?
Laminated Veneer Lumber (LVL) Its shear strength is superior to LSL but doesn't quite match PSL's ability to withstand bending stress. LVL is more expensive than LSL but is affordable compared to PSL and glulam.
Can PSL be used outdoors?
Given its bending strength, PSL is used as long-span beams, heavily loaded columns and large headers and is well-suited to applications where high bending or compression stress is required. It can be used in both interior and exterior applications.
What is the strongest engineered wood beam?
Power Beam® - 3000Fb - 2.1E - 300F Power Beam® is the strongest engineered wood product (EWP) on the market with design values of 3000Fb - 2.1E - 300Fv.
What is the difference between OSB and LSL?
LSL resembles oriented strand board (OSB) in appearance as they are both fabricated from the similar wood species and contain flaked wood strands, however, unlike OSB, the strands in LSL are arranged parallel to the longitudinal axis of the member.
Is LVL stronger than CLT?
If CLT is known as plywood on steroids, LVL is like plywood on a diet. It is used like Glulam, for columns and beams, but compared to lumber it is stronger, straighter and more uniform, and takes greater stresses than Glulam.
Which is stronger glulam or LVL?
The laminated beam is stronger but more expensive and used when bigger cross-sections are required. Generally made from hardwood, rather than the lvl softwood.
Can you drill through LSL?
Laminated Strand Lumber (LSL) 1.55E TimberStrand® LSL, larger holes can be drilled through the beam. TimberStrand® LSL Headers are designed for short span applications. Instead of wasting time cobbling together headers, crew can quickly install this affordable engineered lumber option.
Can LSL be used for rafters?
Since it is manufactured straight and in very long lengths, it is ideal to use as roof rafters in steep slope cathedral ceilings as well as conventional roof framing. 1-1/4” 1.3E TimberStrand® LSL which is typically used as rim board is also an ideal product for your stair stringer material.
What are Microlam beams?
Microllam is the brand name for a type of engineered lumber made by Weyerhauser and used for heavy structural support. Each piece of this lumber is actually composed of smaller, micro-thin layers of wood that are glued together—or laminated.
What size LVL beam do I need to span 14 feet?
What size lvl beam for a 14 foot span:- as per general thumb rule, for a 14 foot span, size of LVL beam or GLULAM should be 7 to 8 inches deep and 3 inches wide, thus you need something like a 7-8″ GLULAM or LVL to span upto 14 feet and can use simple 2×10 dimensional lumber at 16″ apart from centre as floor joists ...
What are the disadvantages of LVL?
Disadvantage of LVL Due to its production from many layers of the veneer, the LVL can have some defects such as warping, delamination, so it requires high production technology and good workmanship to have a stable quality LVL.
Are I-joists cheaper than lumber?
Engineered floor joists are more expensive than 2×10 lumber, but are much lighter and easier to handle. One of the reasons engineered floor joists, particularly I-beams, are so common is that they can come in lengths of up to 60 feet and can be cut to length on the job site just like regular lumber.
What is the strongest wood beam material?
Douglas firPerhaps the strongest wood beams made this way are Douglas fir. There may be a stronger wood, but I'm not aware of it. Today, lumber mills make beams like they make plywood. They use layers of solid wood that are glued together to make incredibly strong structural engineered timbers.
What is stronger LVL or I joist?
LVL may be stronger, but inch-for-inch it is more expensive. The balance of cost vs performance is leaning in favor of sawn flanges for residential applications. Many builders prefer sawn flanges. Once builders use I-joists they are usually converted for life.
What can you use instead of LVL beams?
Long, straight, stable and cost efficient – the GLT alternative to LVL. With excellent nail holding capability, LGL is a breeze to work with. H3 treated as standard for protection outdoors, it can be used in conjunction with other termite and fungal resistant materials to provide total peace of mind.
What is CLT made of?
A CLT panel consists of several layers of kiln-dried lumber boards stacked in alternating directions, bonded with structural adhesives, and pressed to form a solid, straight, rectangular panel.
What type of wood is PSL?
Parallel-strand lumber (PSL) is a form of engineered wood made from parallel wood strands bonded together with adhesive. It is used for beams, headers, columns, and posts, among other uses.
What is structural composite lumber?
Structural composite lumber (SCL) is a family of engineered wood products created by layering dried and graded wood veneers, strands or flakes with moisture-resistant adhesive into blocks of material known as billets, which are subsequently resawn into specified sizes.
What is oriented strand lumber?
Oriented Strand Board is a widely used, versatile structural wood panel. Manufactured from waterproof heat-cured adhesives and rectangularly shaped wood strands that are arranged in cross-oriented layers, OSB is an engineered wood panel that shares many of the strength and performance characteristics of plywood.
What is parallel strand lumber?
Parallel-strand lumber. Parallel-strand lumber (PSL) is a form of engineered wood made from parallel wood strands bonded together with adhesive.
What is PSL used for?
It is used for beams, headers, columns, and posts, among others uses. The strands in PSL are clipped veneer elements having a least dimension of not more than 0.25 inches (6.4 mm) and an average length of at least 300 times this least dimension (around 6 ft or 1.8 m).
How wide is a beam?
Typical widths are 3. 7⁄8 , 14, 16 and 18 inches (240, 300, 360, 410 and 460 mm). Typically the beams are made to a maximum length of 60 feet (18 m).
Who invented the Parallam?
Parallam is the brand name for the product invented, developed, commercialized and patented by MacMillan Bloedel (now Weyerhaeuser ). It is the world's only commercially manufactured and marketed parallel-strand lumber product.
Is PSL wood stronger than sawn wood?
It is a member of the structural composite lumber (SCL) family of engineered wood products. The design strength of PSL is greater than that of sawn lumber as the strands are glued together in a directional manner and under high pressure. This results in a much denser and stronger material. Because knots and other imperfections are randomly ...
What is a parallam?
Parallam PSL (Parallel Strand Lumber) uses a process patented by MacMillan Bloedel to bond together thin strands of wood typically 4-8 feet long. PSL manufacturing involves little waste, as almost all parts of a log are used in the product.
Is PSL a good material?
Due to its uniformity, PSL offers good connection strength and ductility - it is not prone to splitting failures at connections like sawn timber or Glulam. It also has strong insect resistance. Materials. Southern Pine, Yellow Poplar, Douglas Fir, Western Hemlock. Carbon.
Is PSL more uniform than sawn timber?
PSL is much more uniform than sawn timber or Glulam, as all defects such as knots are distributed uniformly in the glue matrix; this gives PSL one of the highest strengths of any engineered wood product.
Why use parallel strand lumber?
They allow longer clear spans than other types of wood beams and girders, and are used to support lightweight components like wood trusses and wood I-beams. Like any wood product, they can be weakened and rot from constant or repeated exposure to moisture. Like any manufactured wood product, they can be weakened and burn in a fire, especially if the wood strands on the surface are loosened by the heat.
What is PSL wood?
PSLs are made of long, thin strips of wood (usually Douglas fir or hemlock) that are coated with high-strength waterproof resin glue; aligned so that the strips are parallel; formed into large billets that are pressed to their proper thickness; and heated to cure the glue. One manufacturer uses microwaves to cure the PSL instead of heat from conventional fuel. The billets of PSL are then sawn to form beams in the same dimensions as those sawn from logs. The result is straight, stable beams that can be purchased in lengths as long as 44 feet. These are of uniform strength and density throughout. The manufacturing process reduces the waste from each log to less than 1/3 of its volume.
Where does lumber come from?
Most ordinary sawn lumber today comes from tree farms or second-growth timber. If boards or beams can be found that are longer than 16 feet, they are often not straight enough or strong enough to use for floor joists, rafters, or load-bearing studs. Parallel-Strand Lumber (PSL) is one of the types of engineered or manufactured wood that was developed in the late 20th century. PSLs are usually used in wood-framed construction for girders to support smaller beams of laminated veneer lumber (LVL), wood trusses, or wood I-beams. PSL columns are also available.
Can you cut holes in PSL?
One manufacturer will allow holes to be cut horizontally through PSL girders and beams only if they are in the center 1/3 of the vertical dimension and only in the center 1/3 of the span. Only round holes are allowed. If there are multiple holes, they must be spaced so that there is at least twice the diameter of the largest hole between them. Square or rectangular holes or edge notches are not allowed.
What is parallel strand lumber?from en.wikipedia.org
Parallel-strand lumber. Parallel-strand lumber (PSL) is a form of engineered wood made from parallel wood strands bonded together with adhesive.
How does PSL compare to other building materials?from naturallywood.com
PSL is a solid, highly predictable, uniform lumber product. Its efficient use of wood fibre adds to its ecofriendly benefits and makes it an attractive alternative to more carbon intensive materials. Like most wood products, it is well-suited to prefabrication. As an attractive structural material, PSL is a good choice when finished appearance is important. As an engineered product PSL offers high bending strength and is well suited to long-span designs.
How is PSL made?from naturallywood.com
PSL is made from strands bonding together in a continuous press using waterproof adhesives with a phenol-formaldehyde base. It can made using waste materials from plywood and LVL production, with species commonly including Douglas-fir, pine and western hemlock, among others. PSL exhibits a rich texture and retains numerous dark glue lines. PSL can be stained to enhance the warmth and texture of the wood. It is sanded at the end of the production process to ensure precise dimensions and to provide a high-quality surface for appearance.
Will PSL rot or mold?from naturallywood.com
Manufactured at a moisture content of 11 percent, PSL will resist shrinking, warping, cupping, bowing and splitting. Similar to other wood products, PSL will not rot or acquire mold when designed and installed correctly. In fact, the relatively large porous voids in PSL means preservatives are able to better saturate and penetrate into the product. This makes it a good choice for use in exterior conditions as well as interior applications. Treated PSL can be specified in high humidity exposures. Wrapping of the product for shipment to the job site is important in providing moisture protection. End and edge sealing of the product will enhance its resistance to moisture penetration. Following best practices for managing moisture in wood construction will safeguard the product from damage or decay.
How long is PSL?from en.wikipedia.org
The strands in PSL are clipped veneer elements having a least dimension of not more than 0.25 inches (6.4 mm) and an average length of at least 300 times this least dimension (around 6 ft or 1.8 m). It is a member of the structural composite lumber (SCL) family of engineered wood products.
Why is PSL sanded?from naturallywood.com
It is sanded at the end of the production process to ensure precise dimensions and to provide a high-quality surface for appearance.
Where is Eastern Parallam manufactured?from weyerhaeuser.com
Eastern Parallam PSL is manufactured at the Buckhannon, WV plant and provides enhanced protection from the elements when it matters most - during construction. You’ll see the difference from the start—thanks to our new and innovative proprietary sealant.
How does LSL compare to other building materials?
LSL a solid, highly predictable, uniform wood product made from smaller, fast-growing trees not suitable for conventional solid-sawn lumber. Its consistency in quality streamlines construction and reduces waste on the job site.
What is LSL used for?
LSL is used primarily as structural framing for residential, commercial and industrial construction. It is suitable for headers and beams, tall wall studs, rim board, sill plates, millwork and window framing. LSL also offers good fastener-holding strength. It can also be left exposed as a design feature.
How is LSL similar to LVL?
LSL is similar to LVL in many ways, with the exception that it uses flakes, and not layers of veneers. The flakes are pressed together with heat—using a steam injection press— and bonded by adhesives.
Does LSL have a common standard of production?
LSL does not have a common standard of production and common design values. Design values are derived from test results analysed in accordance with CSA O86 and ASTM D5456 and the design values are reviewed and approved by the Canadian Construction Materials Centre (CCMC). Civic Duty.
Will LSL rot or mold?
Similar to other wood products, LSL will not rot or acquire mold when designed and installed correctly. Exposure to water should be avoided during and after construction. Sealing the ends and edges of LSL will help ensure resistance to moisture penetration. Following best practices for managing moisture in wood construction will safeguard the product from damage or decay.
What is laminated strand lumber?
Similar to PSL, laminated strand lumber is made from flaked wood strands that have a length-to-thickness ratio of approximately 150. Combined with an adhesive, the strands are oriented and formed into a large mat or billet and pressed. LSL is used in a variety of applications from studs to millwork components.
What is SCL lumber?
Structural composite lumber (SCL), which includes laminated veneer lumber (LVL), parallel strand lumber (PSL), laminated strand lumber (LSL) and oriented strand lumber (OSL), is a family of engineered wood products created by layering dried and graded wood veneers, strands or flakes with moisture resistant adhesive into blocks of material known as billets, which are subsequently resawn into specified sizes. In SCL billets, the grain of each layer of veneer or flakes runs primarily in the same direction. The resulting products out-perform conventional lumber when either face- or edge-loaded. SCL is a solid, highly predictable, and uniform engineered wood product that is sawn to consistent sizes and is virtually free from warping and splitting.
What is SCL wood?
SCL is a solid, highly predictable, and uniform engineered wood product that is sawn to consistent sizes and is virtually free from warping and splitting.
What is PSL used for?
The length-to-thickness ratio of the strands in PSL is around 300. Like LVL and glulam, this product is used for beam and header applications where high bending strength is needed. PSL is also frequently used as load-bearing columns .
