What does PCA stand for IV?
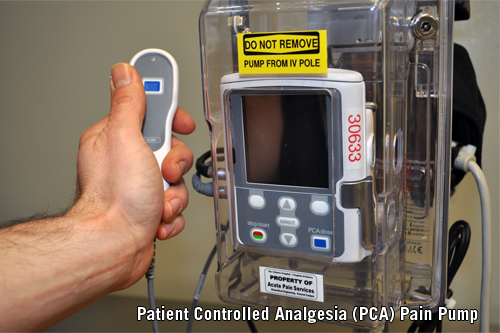
Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) is a method of pain control that gives patients the power to control their pain. In PCA, a computerized pump called the patient-controlled analgesia pump, which contains a syringe of pain medication as prescribed by a doctor, is connected directly to a patient's intravenous (IV) line.
What drugs are used in PCA?
Despite a variety of medication options, morphine remains the gold standard medication for intravenous PCA. Local anesthetics are primarily used for epidural catheter and indwelling nerve catheter PCA. They include the sodium channel blockers (bupivacaine, levobupivacaine, and ropivacaine).
Is PCA an opioid?
PCA involves opioid administration via an infusion pump that delivers a preprogrammed dose of opioid when the patient pushes a demand button with or without a constant-rate background infusion.
How does PCA dosing work?
Your doctor or nurse sets the pump to release the right dose of medicine. The pain medicine flows from the pump into the tubing that goes into your vein. When you feel your pain starting, you press a button that you can hold in your hand. After you press the button, pain medicine is released from the pump.
Why would a patient need a PCA?
The PCA is ordered by the treating anaesthetist, who will assess your need for pain relief and prescribe a PCA as part of a treatment plan. PCAs are used for moderate to severe pain.
What are the side effects of PCA?
A patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pump is a device that releases medicine for pain that you control with a button....Some common side effects of opioid drugs for pain include:Upset stomach.Vomiting.Nausea.Drowsiness.Itching.Dry mouth.Being unable to make a bowel movement (constipation).Slowed breathing.
Is PCA a high risk procedure?
Risks of PCA. PCA is safe and effective. The main risk is having a reaction to the opioid medicine.
What are 5 benefits of PCA?
The Benefits of PCA (Principal Component Analysis)Example 1: Improve Algorithm Runtime.Example 2: Improve Classification Accuracy.Example 3: Visualization.Example 4: Reduce Noise in Data.Example 5: Feature Selection.
What exactly does PCA do?
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a technique for reducing the dimensionality of such datasets, increasing interpretability but at the same time minimizing information loss. It does so by creating new uncorrelated variables that successively maximize variance.
When should PCA be used?
PCA should be used mainly for variables which are strongly correlated. If the relationship is weak between variables, PCA does not work well to reduce data. Refer to the correlation matrix to determine. In general, if most of the correlation coefficients are smaller than 0.3, PCA will not help.
How long can PCA be used?
You will find their contact details on your appointment letter. How long can the PCA be used for? The PCA can be used for between 2 to 5 days, but sometimes for longer. When the time is right, usually when your child's pain has reduced and they don't need to press the PCA button very often, the PCA will be stopped.
Who is a good candidate for PCA?
Simply put, any patient who requires opioid analgesia and who has difficulty taking medications by mouth or who is considered inappropriate for frequent injections may be a good candidate for PCA.
What opioids are used in PCA?
Morphine is the preferred opioid in most circumstances. Fentanyl or hydromorphone are alternative choices. The PCA infusion is prescribed according to the PCA prescription guidelines .
What are the most common medications used with a PCA NCA?
Morphine is the most commonly used opioid for intravenous PCA.
What is PCA medicine?
A method of pain relief in which the patient controls the amount of pain medicine that is used. When pain relief is needed, the person can receive a preset dose of pain medicine by pressing a button on a computerized pump that is connected to a small tube in the body. Also called patient-controlled analgesia.
Can a PCA give medication?
F The PCA may administer medication directly to the individual. T A PCA never gives the individual injections. T The PCA may assist the individual with opening the pill bottle and remind the individual to take the medication as prescribed.
What Is The Patient-Controlled Analgesia Pump?
The patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pump is a computerized machine that gives you a drug for pain when you press a button. In most cases, PCA pu...
What Should I Know About The Patient-Controlled Analgesia Pump?
Your health care provider will set controls on the pump, which will be programmed for the pain-relieving drug that the doctor orders. The PCA pump...
Who Might Use A Patient-Controlled Analgesia Pump?
Your doctor might give you a PCA pump to use in the hospital after surgery. Pumps also can be used by people who are dealing with other kinds of pa...
How Often Should The Patient-Controlled Analgesia Pump Be used?
You can use the pump whenever you feel pain. If you are feeling sleepy, you should not push the button. The goal of the pump is to keep your pain a...
What Are The Benefits of A Patient-Controlled Analgesia Pump?
People who use the pumps often use less of a pain drug and are less tired as a result. People who are less tired move around more, cutting down on...
What Are The Side Effects of Opioid Drugs?
Some common side effects of opioid drugs for pain include: 1. Upset stomach 2. Vomiting 3. Nausea 4. Drowsiness 5. Itching 6. Dry mouth 7. Being un...
How Else Can I Get Relief from Pain?
Cleveland Clinic offers a variety of complementary services to help improve your well-being and improve your pain management and healing. The Heali...
How Often Should the PCA Pump Be Used?
The pump can be used whenever the patient is feeling pain. However, patients should not press the button on the machine if they are feeling too sleepy. The more alert the patient is, the more likely they are to participate in a therapy program to aid and possibly shorten recovery. Once the acute pain from surgery is controlled, the patient will be switched to pills for pain relief.
What is PCA in medical terms?
Patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) is a method of pain control that gives patients the power to control their pain. In PCA, a computerized pump called the patient-controlled analgesia pump, which contains a syringe of pain medication as prescribed by a doctor, is connected directly to a patient's intravenous (IV) line.
How old do you have to be to use a PCA pump?
The machines also can be used by people coping with other kinds of pain. Children who are 4 to 6 years old may be able to use PCA with the help of a parent or nurse. Many children who are as young as 6 can independently use the PCA pump.
Is a PCA pump safe?
PCA pumps have built-in safety features. The total amount of analgesic (pain reliever) that the patient can self administer is within a safe limit.
What is the patient-controlled analgesia pump?
The patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) pump is a computerized machine that gives you medicine for pain when you press a button. In most cases, PCA pumps supply opioid pain-controlling medicines such as morphine, fentanyl and hydromorphone. The pump is attached to a thin, flexible tube (intravenous or IV line) that is placed in your vein. This medicine is usually delivered only when you press the button (bolus), but a continuous rate may be added by your doctor if needed (basal rate).
What are the side effects of a syringe?
Vomiting. Nausea. Drowsiness. Itching. Dry mouth. Being unable to make a bowel movement (constipation). Slowed breathing. Less common side effects may include having stiff muscles and being more sensitive to pain. Ask your providers about any side effects that you’re worried about.
Can you use a PCA pump after surgery?
Your doctor might give you a PCA pump to use in the hospital after surgery. Pumps also can be used by people who are dealing with other kinds of pain, including cancer pain and chronic pain problems. If your pain is severe even though you are using the pump, tell a member of your healthcare team.
Is it safe to use a PCA pump?
Remember, no one should press the button on the PCA pump except you. When the pump is empty, an alarm lets the nursing staff know.
When to use a pain pump?
You can use the pump whenever you feel pain. If you’re feeling sleepy, you shouldn’t push the button. The goal of the pump is to keep your pain at a level you can tolerate.
Is Cleveland Clinic a non profit?
Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not endorse non-Cle veland Clinic products or services. Policy
What Is a PCA Pump?
PCA is a method of pain management that lets the patient decide when they need a dose of pain medicine. The pump is accessible 24/7 and the patient simply presses a button to administer a pre-set dosage of medication to alleviate pain. This system allows the patient to receive smaller doses of medication, more often (compared to traditional pain medication administration). 1 There is a max dose programmed on the PCA pump as well to ensure there's no risk of overdose or toxicity.
How to use PCA pump?
When pain is first detectable, you press a handheld button, and pain medication is released from the system, through your IV, and into your vein. The medication travels from the pump into the tubing that goes into the needle and then to your vein.
How effective is pain control?
More effective pain control: From not having to wait until the pain is severe to get medication from the nurse. Less anxiety and depression: Many people feel a sense of comfort that they are able to manage their own pain management. Less medication: This can lower side effects such as drowsiness.
What is a contraindication for a PCA pump?
A contraindication is a specific situation in which a drug or procedure should not be used because it could cause harm. There are some scenarios in which a PCA pump is contraindicated, these include: Elderly people who are confused. Very young children who cannot follow the instructions for proper use of the pump.
What is a PCA patient?
A person with allergies to the selected medication. A person who has had burns or trauma in the area of the PCA placement.
How is pain medication delivered?
The pain medication, that is controlled by the pump, can be delivered via several modes of administration, including: Intravenously: Through a needle placed in a vein, usually in the arm, but also in the epidural space. Via an epidural: A type of anesthetic used for pain control.
What is hospice pain control?
A method of pain control for hospice patients with moderate to severe pain—such as pain caused by cancer—to be utilized in a home care environment. Children—as young as 7 years of age—provided they can follow the instructions. A method of pain control for women during labor.
What is PCA in nursing?
PCA can be used to reduce the stress on the nursing staff and the patient of having to adhere to a predetermined dosing schedule of as-needed analgesics that may not adequately align with the patient’s fluctuation of pain. PCA can be useful in the acute pain setting where there is inadequate pain control from the initial opioid administration in the emergency department, and continued opioid dosing has been proven to improve patient outcomes. Common examples are vaso-occlusive pain crisis, trauma, pancreatitis, or burns. PCA would be used as an adjunct therapy to treat the pain while the underlying cause gets diagnosed and treated. Patients with chronic illnesses who are suffering from lower levels of constant chronic pain would also be candidates for PCA. The most common examples are metastatic cancer, phantom limb syndrome, and complex regional pain syndrome.[7] Post-surgical patients, especially those with indwelling nerve or epidural catheters, are also ideal candidates for PCA. The ability of a post-surgical patient to titrate and administer their own pain medication allows for superior pain control to scheduled nursing dosing. It also increases patient satisfaction and will result in less intervention by PACU and acute pain service staff. Patients in labor pain are also well-established candidates for epidural PCA. The pain associated with contractions, especially when exacerbated by induction agents such as oxytocin, can be adequately reduced and controlled by the patient. [8]
What are the different types of PCA administration?
Modalities for PCA administration include intravenous lines, central lines, epidural catheters, peripheral nerve catheters, or transdermal delivery systems . Any peripheral vein can be used to insert a catheter and begin the administration of PCA. Central lines placed in the internal jugular, subclavian, or femoral veins.[5] Epidural catheters placement is in the epidural space between the dura and the ligamentum flavum, which lines the anterior portions of the vertebral lamina. Within the epidural space sits spinal nerves, blood vessels, and fat.[6] Indwelling epidural catheter placement is at thoracic and lumbar spinal levels. Peripheral nerve catheters are placed adjacently to the nerve or plexus; they are intended to block continuously. These will run through the skin and potentially muscle depending on the desired target location.[2] Transdermal PCA delivery is through a fentanyl iontophoretic transdermal system, which is placed on the epidermis and will provide a dose of fentanyl when the patient pushes a button on the patch. [3]
What is PCA pump?
Patient-Controlled Analgesia (PCA) has been utilized to optimize pain relief since 1971, with the first commercially available PCA pump appearing in 1976. The goal of PCA is to efficiently deliver pain relief at a patient's preferred dose and schedule by allowing them to administer a predetermined bolus dose of medication on-demand at the press of a button. Each bolus can be administered alone or coupled with a background infusion of medication. PCA is used to treat acute, chronic, postoperative, and labor pain.[1] These medications can be administered intravenously, epidurally, through a peripheral nerve catheter, or transdermally.[2][3] Drugs commonly administered are opioids and local anesthetics, but dissociatives or other analgesics are also options. PCA has proven to be more effective at pain control than non-patient opioid injections and results in higher patient satisfaction.[4]
What is local anesthetic used for?
Local anesthetics are primarily used for epidural catheter and indwelling nerve catheter PCA. They include the sodium channel blockers (bupivacaine, levobupivacaine, and ropivacaine).
What is the route of PCA?
The route for PCA administration can be through an intravenous catheter, epidural catheter, indwelling nerve catheter, or an iontophoretic transdermal system. The equipment and procedure for the placement of these devices appear in the articles for those specific modalities.
Why is PCA used in nursing?
PCA has also been found to be preferred by nurses because it allows for a reduction in their workload. PCA will enable patients to be in more control over their pain and helps them shift toward a more internal locus of control over their care.
What is patient controlled analgesia?
Patient-controlled analgesia is used to treat acute, chronic, postoperative, and labor pain. A variety of medications can be used for patient-controlled analgesia and are administered intravenously (IV), through an epidural or peripheral nerve catheter, and transdermally. This activity outlines and reviews the role of the interprofessional team in managing patients who undergo patient-controlled analgesia.
Why is it important to not use continuous opioid infusions?
1-4 The American Pain Society cautions against using continuous basal infusions because studies have failed to demonstrate significant differences in the quality of analgesia with or without basal infusions. 4 There may also be an increased risk of programming errors when basal infusions are prescribed. 5
What is the range of a HYDRO morphone?
For example, the range for a HYDRO morphone basal infusion dose was 0.1 to 0.5 mg/hour, and there was no guidance for selecting appropriate candidates for basal infusions.
When is continuous pulse oximetry required for PCA?
Continuous pulse oximetry (or capnography if appropriate) is required while on PCA if the patient has a continuous opioid infusion or sleep apnea, or if the patient is morbidly obese or older than 64 years.
Why were opioid orders rearranged?
Opioid orders were rearranged to match the sequence in which the medications appear on the facility’s smart IV pumps.
How often should you evaluate a patient for respiratory failure?
Evaluate the patient’s level of pain, alertness, and vital signs, including rate and quality of respirations, every 2-4 hours.
Can you give basal infusions if you are opioid tolerant?
In our February 22, 2007 newsletter, we recommended avoiding basal infusions unless the patient is opioid-tolerant. Unfortunately, the term “opioid-tolerant” is not well understood. It is defined as “those patients who have received opioids regularly for approximately 7 days or more.” Opioid-naïve patients who present with high opioid requirements may be an exception and require a basal infusion, but additional safety steps should be instituted under these conditions. Our July 24, 2003, newsletter includes many recommendations to improve PCA safety, including the following.
When should you monitor patients for hypoventilation?
Monitor patients more frequently during the first 24 hours and at night, when hypoventilation and nocturnal hypoxia may occur.
What is insulin pump?
Insulin pump - A pump typically used to deliver insulin to patients with diabetes. Insulin pumps are frequently used in the home. Infusion pumps may be powered electrically or mechanically. Different pumps operate in different ways. For example:
What is an external infusion pump?
An external infusion pump is a medical device used to deliver fluids into a patient’s body in a controlled manner. There are many different types of infusion pumps, which are used for a variety of purposes and in a variety of environments. Infusion pumps may be capable of delivering fluids in large or small amounts, ...
What is an ambulatory infusion pump?
Others, called ambulatory infusion pumps, are designed to be portable or wearable. A number of commonly used infusion pumps are designed for specialized purposes. These include: Enteral pump - A pump used to deliver liquid nutrients and medications to a patient’s digestive tract.
What is a multi channel pump?
In a multi-channel pump, fluids can be delivered from multiple reservoirs at multiple rates.
Where is fluid held in a syringe pump?
In a syringe pump, fluid is held in the reservoir of a syringe, and a moveable piston controls fluid delivery.
