
What is primary engineering control (PEC)?
Feb 03, 2020 · What is pec in compounding? The primary engineering control or PEC (hood) is to be cleaned daily. The most common PECs used are laminar airflow workbenches (LAFWs), compounding aseptic isolators (CAIs), biological safety cabinets (BSCs), and compounding aseptic containment isolators (CACIs).
What is the compounding environment of a primary engineering control?
Compounding PEC abbreviation meaning defined here. What does PEC stand for in Compounding? Get the top PEC abbreviation related to Compounding.
What is an ISO Class 5 PEC?
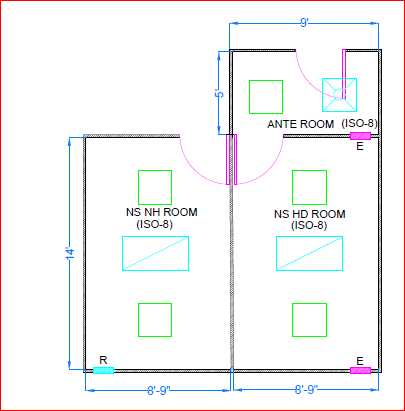
Primary engineering control (PEC): A system that provides an ISO 5 environment for the exposure of critical sites when com- pounding sterile preparations. Primary engineering control work surfaces, counters, floors and work surfaces in the buffer zone area, ante room and segregated compounding areas daily.
How often do you have to clean a PEC?
A-Z. Short first. Long first. PEC Pharmacy Abbreviation. 2. PEC. Primary Engineering Control. Compounding, Sterile, Medical. Compounding, Sterile, Medical.
What does PEC stand for compounding?
What is PEC primary engineering control?
What PECs may HDs be compounded in?
What is a compounding aseptic containment isolator?
What is ISO Class 5 Pec?
What ISO Class is the PEC room?
Why is USP 800 necessary?
What is the USP 797?
What is the difference between USP 797 and USP 800?
What is the difference between CAI and CACI?
What is isolator in pharmaceutical industry?
What are the USP 800 standards in place for hazardous drugs?
Examples of Primary engineering control in a sentence
Primary engineering control (PEC): A system that provides an ISO 5 environment for the exposure of critical sites when com- pounding sterile preparations.
More Definitions of Primary engineering control
Primary engineering control. ( PEC) means a device or room that provides an ISO Class 5 environment for the exposure of Critical Sites when compounding sterile products.
What is total particle count?
Total particle count testing must occur in the BSC during dynamic compounding conditions or with simulated compounding activities that are representative of the actual compounding activities. By requiring dynamic conditions, the testing ensures that the BSC is maintaining the desired classification and state of control during operations. As such, the dynamic conditions must be conducted by pharmacy personnel, not the certification technician.
What is a BSC in pharmacy?
Biological Safety Cabinets. The purpose of a biological safety cabinet (BSC) is to provide product, personnel, and environmental protection. In the pharmacy, BSCs are typically used for sterile compounding of hazardous drugs.
What is smoke pattern test?
An airflow smoke patterns test is required and must be performed at each certification. Do not mistake this test for a dynamic airflow smoke pattern test, as this test is not meant to demonstrate that first air is supplied to the DCA. Rather, the airflow smoke patterns test consists of four separate tests wherein smoke is utilized to visualize the airflow to ensure proper performance: 1 The Downflow Test determines whether airflow within the work area is downward with no dead spots or refluxing. 2 The View Screen Retention Test determines if there is any escape of air to the outside of the cabinet at the work opening. 3 The Work Opening Edge Retention Test determines if there is any ambient air that enters the cabinet and passes along the work surface. 4 The Sash Seal Test determines if there is any escape of air to the outside of the cabinet through the sides and top of the sash.
What is a laminar airflow workstation?
A laminar airflow workstation (LAFW) is used to provide product protection through unidirectional HEPA filtered air in the work zone. The following tests are required for certification, and the associated data must be documented:
Do you need calibration certificates for equipment?
Nonetheless, it is critical that calibration certificates be included with the final report for each piece of certification equipment that requires calibration. This ensures that the equipment used to perform testing is operating within its tolerated calibration interval. Ultimately, calibration documentation provides the evidence needed to establish the credibility of the report’s findings.
What is site assessment test?
Site installation assessment tests are performed during each BSC certification to ensure that the cabinet is integrated properly into the facility and that the alarm functions are operating as intended. The specific tests will depend upon the type of cabinet and whether the cabinet is ducted. Note that for HD applications, USP <800> requires that the cabinets be externally vented; however, if the cabinet is used for non-HD applications and is not externally vented, then not all tests apply. The sash alarm test does apply to all cabinets: When the sash is raised 1” above the manufacturer’s recommended height, an audible and visual alarm must sound. If the cabinet is newer than 2014 and NSF listed, there will also be a requirement to test the sash at 1” below the manufacturer’s recommended height. The sash alarm test and statement of pass or fail must be reported.
Proposed standards for allergen extract compounding under USP Chapter 797
Under the proposed standards, to continue in-office compounding of individual treatment sets for allergen immunotherapy, allergy practices will need to comply with the following:
2. Facilities
Compounding must occur in an ISO Class 5 PEC or in a dedicated Allergenic Extracts Compounding Area (AECA), either of which must not be within one meter from a sink and can’t be near unsealed windows, doors to the outside, or high traffic or other areas that present environmental control challenges such as bathrooms or kitchens.
3. Documentation
All facilities where allergen extracts are prepared must have and maintain written or electronic documentation to demonstrate compliance with the requirements USP Chapter 797. This documentation must include, but is not limited to, the following:
What is the purpose of personal protective equipment?
Use of personal protective equipment (PPE) Purpose: To provide employees protection from hazardous aerosols and drug residue during preparation of products. Sites must have a policy identifying appropriate PPE to be worn . Includes gloves and gowns.
What is PPE gown?
Use of personal protective equipment (PPE) Gowns. Gowns must be worn when handling HDs . Gowns must be able to protect worker from spills/splashes of HD and waste materials. These gowns must have been tested to resist permeability by HDs .
Where should antineoplastics be stored?
Antineoplastics requiring manipulation and HD APIs must be stored separately from non-hazardous drugs and should be stored in an externally ventilated, negative pressure room with at least 12 air pressure changes per hour (ACPH). Ordering, Receiving, and Stocking Hazardous Drugs.
What should I wear to unpack HDs?
Personnel who unpack HDs that are not contained in plastic should wear an elastomeric half-mask with a multi-gas cartridge and P100 filter. PAPR should be worn when there is a risk of respiratory exposure to HDs, including: An HD spill that cannot be contained to a spill kit.
What is HD in medical terms?
Containment, clean up, and disposal procedures . Treatment of personal contact and any unintended exposure to a HD. Overview. Hazardous drugs (HD) are drugs that can cause adverse health effects if health care workers that handle (including distribution, preparation, or administration) these products are exposed to them.
