What does peptide mapping mean?
Peptide mapping is a component of the analytical toolbox used within the biopharmaceutical industry to aid in the identity confirmation of a protein therapeutic and to monitor degradative events such as oxidation or deamidation. These methods offer the advantage of providing site-specific information regarding post-translational and chemical ...
Which peptides to use?
The three most important groups of peptides used in bodybuilding are listed below:
- Growth Hormone Releasing Peptides (GHRP)
- Growth Hormone Releasing Hormones (GHRH)
- Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1)
What is vital peptide?
What Is Vital Proteins Collagen Peptides? To start, Vital Proteins Collagen Peptides is a revitalizing protein that comes in multiple flavors, including dark chocolate blackberry, vanilla, mixed berry, and unflavored. The product comes in powder, drink, and shot form.
What is polypeptide and peptide?
Peptides and polypeptides are amino acid chains of various lengths. A peptide contains two or more amino acids, and a polypeptide, on the other hand, contains ten or more amino acids. Peptide bonds hold together both peptides and polypeptides. The T cells in your body recognize peptides and polypeptides as very small proteins.

How is peptide mapping done?
The basic workflow of peptide mapping involves enzymatic digestion of the protein followed by separation of the resulting peptides via liquid chromatography prior to mass spectrometry assessment. The procedure generates a 'fingerprint' or set of unique peptides of the interrogated protein.
What do you need for peptide mass mapping?
PMF can be measured by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization ion source (MALDI) and time-of-flight (TOF) mass analyzer. It is the most commonly used method in proteomics research. MALDI uses a laser to irradiate a co-crystal thin film formed by a sample and a substrate.
What is the basic principle of identifying proteins by peptide mass mapping?
Peptide mass mapping is a technique that uses powerful search engines (e.g. Mascot) to identify a protein from mass spectrometry data and primary sequence databases. The general approach is to take a small sample of the protein and digest it with a proteolytic enzyme, such as trypsin.
What are peptides used for?
Peptides are sold in dietary supplements including pills or protein shakes. They claim to help you build muscle, boost weight and fat loss, and help with muscle recovery. But there's little direct evidence to back up most of these statements. And it's not clear how well your body can absorb peptides from supplements.
What does a peptide mass fingerprint do?
Peptide Mass Fingerprinting (PMF), also known as mass fingerprinting, was developed in 1993. It is a high throughput protein identification technique in which the mass of an unknown protein can be determined.
How do you identify a peptide sequence?
Mass Spectrometry-based Protein Sequencing Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) is a common method used to determine peptide sequences due to its ease of use and high-throughput workflows.
How do you analyze protein structure?
To determine the three-dimensional structure of a protein at atomic resolution, large proteins have to be crystallized and studied by x-ray diffraction. The structure of small proteins in solution can be determined by nuclear magnetic resonance analysis.
How can peptide mass fingerprinting be used to identify proteins?
Conclusion: Peptide-mass fingerprints can prove as discriminating as linear peptide sequences, but can be obtained in a fraction of the time using less protein. In many cases, this allows for a rapid identification of a sample protein before committing it to protein sequence analysis.
How do you identify proteins?
3. PROTEIN IDENTIFICATION. There are two methods that are commonly used to identify proteins: Edman Degradation and Mass Spectrometry. Developed by Pehr Edman, Edman Degradation is a method of sequencing amino acids in a peptide.
What are examples of peptides?
Examples of peptides include the hormone oxytocin, glutathione (stimulates tissue growth), melittin (honey bee venom), the pancreatic hormone insulin, and glucagon (a hyperglycemic factor).
Does peptides have side effects?
Reported side effects of peptides and hormones include: Water retention. Numbness of the hands and feet. Increased tiredness.
What is a peptide simple definition?
Traditionally, peptides are defined as molecules that consist of between 2 and 50 amino acids, whereas proteins are made up of 50 or more amino acids.
How do you determine the primary structure of peptides by Edman degradation?
The sequence of amino acids in a protein or peptide can be identified by Edman degradation, which was developed by Pehr Edman. This method can label and cleave the peptide from N-terminal without disrupting the peptide bonds between other amino acid residues.
What is a tryptic peptide?
A trypsin digest is used to cleave the proteins in a sample downstream to every K (lysine) or R (arginine), except when followed by P (proline). The individual components that result after the cleavage step are called tryptic peptides.
How do you identify an epitope antibody?
There are several methods available for mapping antibody epitopes on target antigens:X-ray co-crystallography and cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM). ... Array-based oligo-peptide scanning. ... Site-directed mutagenesis mapping. ... High-throughput shotgun mutagenesis epitope mapping. ... Hydrogen–deuterium exchange (HDX).More items...
What is intact mass analysis?
Intact mass analysis is the assessment of a protein's total molecular weight by mass spectrometry (MS) without prior digestion or fragmentation of the molecule of interest.
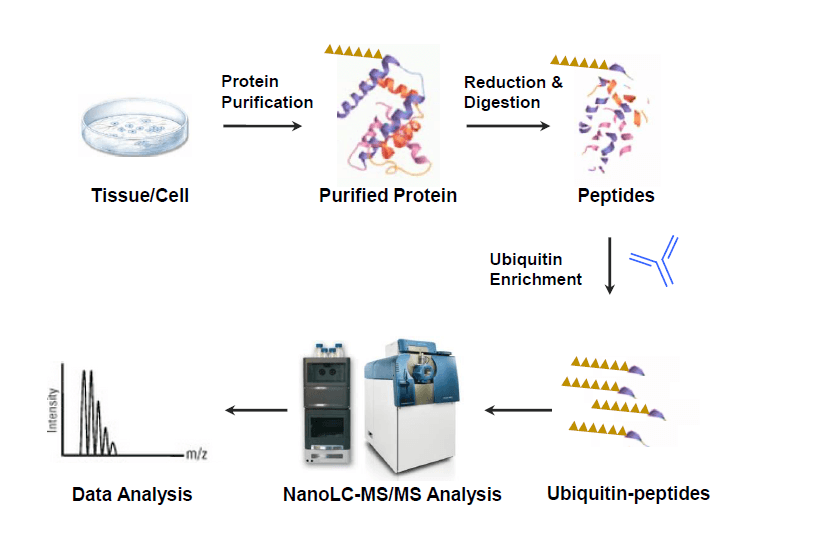
What is peptide mapping?
Peptide mapping is a widely used analytical technique to identify or verify a protein’s primary structure (amino acid sequence and chemical modifications). Briefly, peptide mapping identifies a protein by first determining peptides’ molecular weights and then matching these peptide masses to a protein’s calculated theoretical mass.
Why is peptide mapping needed?
As monoclonal antibody and recombinant protein drugs are becoming the fastest growing sectors of the pharmaceutical industry, careful inspection of the complete product properties ( e.g. , purity, biochemical properties, and stability) is critical throughout the development and manufacturing processes. Of particular importance is the heterogeneity of antibodies. The latter’s various post-translational modifications often occur over the molecule’s lifecycle. These modifications ( Figure 1) play significant contributions on antigen-binding, folding, and biological function of antibodies, consequently and directly impacting drug efficacy, stability, and safety.
What is peptide mapping?
Peptide mapping is a critical workflow in biotherapeutic protein characterization and is essential for elucidating the primary amino acid structure of proteins. For recombinant protein pharmaceuticals, such as monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), peptide mapping is used for proof of identity, primary structural characterization and quality assurance/quality control (QA/QC). Global regulatory agencies, including US Food and Drug Administration (US FDA) and European Medicines Agency (EMA), look to harmonized guidelines from the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH). ICH Q6B covers the test procedures and acceptance criteria for biologic drug products, and specifies the use of peptide mapping as a critical quality test procedure for drug characterization used to confirm desired product structure for lot release purposes.
Why is peptide mapping performed?
Due to its complexity and inherent variability, peptide mapping is generally performed in a comparative manner; for example, biosimilars would be compared to a reference or control substance, such as the innovator biologic, in a side-by-side experiment. An in-depth analysis is then required to identify minor and even isobaric differences in protein ...
How to generate a peptide map?
In order to generate a peptide map, the therapeutic protein must first be digested into its constituent peptides via a chemical or enzymatic reaction. Robust separation and identification of the resultant peptides then provides insight into a protein’s full sequence information; displaying each amino acid component and the surrounding amino acid microenvironment, including disulfide linkage information. Structural characterization at this level highlights post translational modifications (PTMs) such as site-specific glycosylation, amino acid substitutions (sequence variants) and/or truncations which may result from erroneous transcription of complementary DNA. Within a bioproduction environment, peptide mapping is necessary for manufacturing process monitoring and QC. It facilitates product comparability testing, which is necessary to identify any product-related impurities, such as deamidation and/or oxidation following any formulation, manufacturing process or storage change.
Why is peptide mapping important?
Peptide mapping is a widely used technique to examine the primary structure of biopharmaceuticals. 1 It is used to help confirm the identity of a protein therapeutic and to monitor degradations such as oxidation or deamidation. Unlike intact protein analysis, peptide mapping has the advantage of being able to provide side-specific information on ...
What is the first step in peptide mapping?
Protein digestion. To first stage in peptide mapping is to break the protein down into peptide fragments by proteolytic enzymes. A good understanding of this process will help to ensure the maximum sequence coverage and sensitivity are achieved.
What is the most common agent used for peptide mapping?
2 This is due to their site-specific cleavage locations, which produce very predictable peptide fragments. Trypsin is the most common agent used for peptide mapping due to its well-defined specificity. Trypsin hydrolyses only peptide bonds in which a carbonyl group is followed either by an arginine (Arg) or a lysine (Lys). 2 This cleavage pattern can be observed in Figure 1. Depending on the protein amino acid sequence, other enzymes may also need to be used to improve sequence coverage of the resulting peptide mapping. Some of the most frequently used enzymes are summarised in Table 2 along with their cleavage site.
Why are enzymatic approaches used for peptide mapping?
2 This is due to their site-specific cleavage locations, which produce very predictable peptide fragments.
What wavelength is UV peptide detection?
UV detection for peptides is usually carried out at 210-220 nm and or/ 280 nm (Figure 5). Tryptophan, tyrosine and phenylalanine amino acids are sensitive at 280 nm whereas detection at 210 nm is relatively unselective. Although detection at 210 nm will also detect other biological molecules in the sample matrix, it is 2-4 fold more sensitive than 280 nm – so detection at 210 and 280 nm is often done in parallel. Figure 5 shows a peptide mapping separation comparison between detection at 220 and 280 nm, demonstrating the differences in absorbance sensitivity and UV peak profiles.
How to determine peptide identity?
Mass spectrometry has become an important method of detection for characterizing peptides and peptide maps, making it possible to quickly determine the identity of peptide fragments. This is particularly important in the biopharmaceutical industry where establishing and monitoring the sequence identity of a therapeutic target is critical. 3 Peptides can be analysed through direct infusion of the isolated peptides, or by the use of online LC/MS. The results can be correlated to the protein, to confirm the specific amino acid sequences covered by the peptide map and the protein identity. By comparing the measured masses from the MS information to the predicted values from the intact protein or protein database, the mass and sequence coverage information can be used to identify the protein. 3 The goal of characterization through peptide mapping is to achieve at least 95 % sequence coverage of the theoretical composition of the protein structure.
How to reduce disulphide bonds?
2 Once the disulphide bonds are exposed they can be reduced using a reagent such as 1,4-dithiothreitol (DTT), mercaptoethanol, or tris (2-carboxethyl)phosphine (TCEP). 3 Once the disulphide bonds are exposed they can be reduced using a reagent such as 1,4-dithiothreitol (DTT), mercaptoethanol, or tris (2-carboxethyl)phosphine (TCEP). 3 Most commonly denaturation and reduction are combined (i.e. heating the sample in the presence of DTT) which avoids the problem of renaturation during the process. Following this step, alkylation of the cysteine is needed to avoid reformation of the disulphide bonds in the protein (renaturation). To this effect, the protein is incubated with an alkylating agent such as 2-iodoacetamide (IAA). 3
Why is peptide mapping important?
Peptide mapping is a critical step during biotherapeutic characterization. The so-called “bottom up” characterization of biologic drugs by protein digestion to their constituent peptides is necessary to ensure a full sequence coverage of the biopharmaceutical molecule.
What is the orbitrap Exploris 480?
Read the latest application note which demonstrates the capability of the Orbitrap Exploris 480 mass spectrometer to confidently identify and characterize monoclonal antibody post-translational modifications (PTMs) in a high-throughput peptide mapping analysis using shortened chromatographic separations while maintaining full sequence coverage.
What is the purpose of the Orbitrap Exploris 240 mass spectrometer?
Thermo Scientific Orbitrap Exploris 240 mass spectrometers add superior denatured and native MS intact analysis and subunit top/middle-down analysis capabilities to one of the most powerful benchtop peptide mapping instruments available. When combined with Thermo Scientific BioPharma Finder software it provides a complete integrated hardware and software solution for biotherapeutic characterization.
What is the peptide map?
Denatured proteins are digested to completion using a proteolytic enzyme and the peptides are resolved. The resulting patterns of bands, spots or peaks are referred to as peptide map.
What is the principle behind peptide mapping?
The principle behind peptide mapping is straightforward . If two proteins have the same primary structures, then cleavage of each protein with a specific protease or chemical cleavage reagent will yield identical peptide fragments.
How is autohydrolysis of trypsin monitored?
The possibility of auto-hydrolysis of trypsin is monitored by producing a blank peptide map, that is, the peptide map obtained when a blank solution is treated with trypsin.
What is the selection of the approach used for the cleavage of peptide bonds?
The selection of the approach used for the cleavage of peptide bonds will depend on the protein under test. This selection process involves determination of the type of cleavage to be employed either enzymatic or chemical, and the type of cleavage agent within the chosen category.
Which enzymes are used to complete cleavage of peptide bonds?
Complete cleavage of peptide bonds is more likely to occur when enzymes such as endoproteases (e.g., trypsin) are used, instead of chemical cleavage reagents. A map should contain enough peptides to be meaningful.
Why is peptide mapping considered a comparative procedure?
Peptide mapping is a comparative procedure because the information obtained, compared to a Reference Standard or Reference Material similarly treated, confirms the primary structure of the protein, is capable of detecting whether alterations in structure have occurred, and demonstrates process consistency and genetic stability.
What is the purpose of peptide preparation?
To prepare individual peptides to determine amino acid composition and sequence.
Thermo Scientific SMART Digest Kit
Obtain high quality analytical results from protein digests by using Thermo Scientific™ SMART Digest™ Kits.
Take the SMART Route to Protein Digestion
In part 1 of this peptide mapping webinar series join Merck and to learn how to digest biotherapeutic proteins more efficiently & reproducibly. Peptide mapping is an essential step in biotherapeutic drug characterization. In this series 4 new technologies will be demonstrated that dramatically improve upon established mapping workflows.
Peptide Separations with Pinpoint Precision
In part 2 of this webinar series join NIBRT and learn how cutting edge UHPLC provides the ultimate retention time reproducibility and high resolution separation of peptides. Peptide mapping is an essential step in biotherapeutic drug characterization.
High-precision, Automated Peptide Mapping of Proteins
Hear Dr. Amy Farrell of the National Institute of Bioprocessing Research and Training (NIBRT) discuss the development of a robust and reproducible, high-precision, automated, protein digestion workflow that is appropriate as an easy-to-use, general approach to peptide mapping characterization with both LC-only and LC-MS processes.
What is peptide mapping?
2. Peptide mapping is a key part of the ICH Q6B guidelines for characterization and confirmation of biopharmaceuticals in support of new marketing applications. Note: PEPTIDE MAPPING Peptide mapping is an identity test for proteins, especially those obtained by r-DNA technology. Peptide mapping is a comparative procedure because the information obtained, compared to a Reference Standard or Reference Material similarly treated, confirms the primary structure of the protein, is capable of detecting whether alterations in structure have occurred, and demonstrates process consistency and genetic stability. Peptide mapping or PMF refers to the identification of proteins using data from intact peptide masses. It is a powerful test that is capable of identifying single amino acid changes resulting from events such as errors in the reading of complementary DNA (cDNA) sequences or point mutations.
What is the principle of peptide mapping?
Principle It involves the thermal chemical or enzymatic treatment of a protein resulting in the formation of peptide fragments followed by separation and identification of the fragments by mass spectroscopy Peptide mapping is a comparative procedure because the information obtained , compared to a Reference Standard or Reference Material similarly treated Digested peptide are analysed by MALDI-TOF MS in order to determine the masses of intact peptide. These masses can be used in correlative database searches to identified exact matches.
Why do we use reference material in parallel with protein?
The use of a Reference Standard or Reference Material in parallel with the protein under test is critical in the development and establishment of system suitability limits. In addition a specimen chromatogram should be included with the Reference Standard or Reference Material for additional comparison purposes.
What is peptide mapping?
Peptide mapping is a component of the analytical toolbox used within the biopharmaceutical industry to aid in the identity confirmation of a protein therapeutic and to monitor degradative events such as oxidation or deamidation. These methods offer the advantage of providing site-specific information regarding post-translational and chemical modifications that may arise during production, processing or storage. A number of such variations may also be induced by the sample preparation methods themselves which may confound the ability to accurately evaluate the true modification levels. One important focus when developing a peptide mapping method should therefore be the use of sample preparation conditions that will minimize the degree of artificial modifications induced. Unfortunately, the conditions that are amenable to effective reduction, alkylation and digestion are often the same conditions that promote unwanted modifications. Here we describe the optimization of a tryptic digestion protocol used for peptide mapping of the NISTmAb IgG1κ which addresses the challenge of balancing maximum digestion efficiency with minimum artificial modifications. The parameters on which we focused include buffer concentration, digestion time and temperature, as well as the source and type of trypsin (recombinant vs. pancreatic; bovine vs porcine) used. Using the optimized protocol we generated a peptide map of the NISTmAb which allowed us to confirm its identity at the level of primary structure.
Why is peptide mapping important?
Peptide mapping can be used as an orthogonal tool to support primary structure analyses performed at the intact or protein subunit level and to provide additional site-specific information. For example, charge-based separations of intact proteins provide a birds-eye view of molecular status (i.e. global levels of deamidation), while peptide mapping techniques provide the ability to assign a specific location to the attribute. Because peptide mapping can provide a rather comprehensive and specific profile of a biological substance/product in one analytical package, efforts are being made to promote the development of qualified LC-MS peptide mapping assays for extended use in process monitoring and quality control [20]. Specificity is a key component of any analytical method used to evaluate the identity of a drug substance/product [21]. The peptide mapping method must therefore provide a high level of sequence coverage including the product-specific complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) to give the user confidence that no critical regions of the molecule go undetected. Optimization of a peptide map to minimize artificially induced variations that occur due to sample handling or processing provides confidence that changes in peak profiles are due to sample differences and are not artificially induced variations.
How are peptides mapped?
Peptide identifications were mapped to chromatographic peaks using ByoMap v 2.3 (Protein Metrics Inc., San Carlos, CA). The Xcalibur RAW file generated from the MS1 only analysis of the PS 8670 tryptic digest was used as the reference total ion chromatogram, while peptide identifications were imported from the Byonic search of MS/MS data using the following filters: 1) Byonic search score > 20; 2) a precursor m/zerror < ± 10 ppm; and 3) minimum alternate rank score/primary rank score > 0.95. TIC peaks were picked as those having a minimum peak area of > 0.5 % of the area of the sum of all peaks in the chromatogram. Peak boundaries and mapped peptide identifications were manually reviewed. Peptides identified from additional searches (e.g. targeted glycopeptide search) were manually incorporated into the peptide map.
What wavelength detector is used to measure UV absorption?
Heavy and light chain species eluting from the chromatography column first passed through a variable wavelength detector (Dionex UltiMate™ 3000 Variable Wavelength Detector) (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA; P/N VWD-3400RS) set to measure UV absorption at 280 nm. Ions were then introduced into an LTQ Orbitrap Discovery mass spectrometer fitted with a heated electrospray ionization source probe (HESI-II). MS data were collected in the 300 m/zto 2000 m/zrange with a resolving power of 30,000.
How does peptide mapping help in QC?
In the quality control (QC) environment, identity is confirmed when the chromatographic profile of a peptide map conforms to expectation in comparison to a reference map (e.g. peak retention time, peak height, no new or missing peaks). Likewise, differences in the comparator peptide map are indicative of a change in, or degradation of, the drug substance/product. Thus, peptide mapping is also a valuable tool for evaluating the stability of reference standards. When coupled with mass spectrometry, changes in the landscape of the map can be pinpointed to a particular attribute, such as increased oxidation of a certain methionine residue [2–5] appearance of a new sequence variant [6–9] or changes in glycan composition [10–12]. These principles also apply to the use of peptide mapping techniques for the purposes of assessing biosimilarity to an originator drug product [13–19].
How much guanidine HCl is in denaturing buffer?
Reducing the concentration of the chaotrope in the denaturing buffer by half, to 3.0 mol/L guanidine HCl, and keeping all other conditions the same resulted in the incomplete reduction of intrachain disulfides within both heavy and light chains (data not shown). Thus, we chose to continue using the denaturing buffer comprising 6 mol/L guanidine HCL (in 0.1 mol/L Tris, 1 mmol/L EDTA) to ensure complete disulfide bond reduction. It should be noted that 6 mol/L refers to the concentration of guanidine HCl in the prepared stock solution. In our protocol, after the addition of the IgG and the DTT solution to the denaturing buffer the actual concentration of guanidine HCl during the reduction step is 5.34 mol/L (see ESM Document S1).