What is Periductal mastitis and what causes it?
Periductal mastitis occurs when the ducts (tubes) under the nipple become inflamed and infected. Periductal mastitis is a benign (not cancer) breast condition and does not increase your risk of developing breast cancer. 2. What are the symptoms of periductal mastitis? Symptoms of periductal mastitis may include:
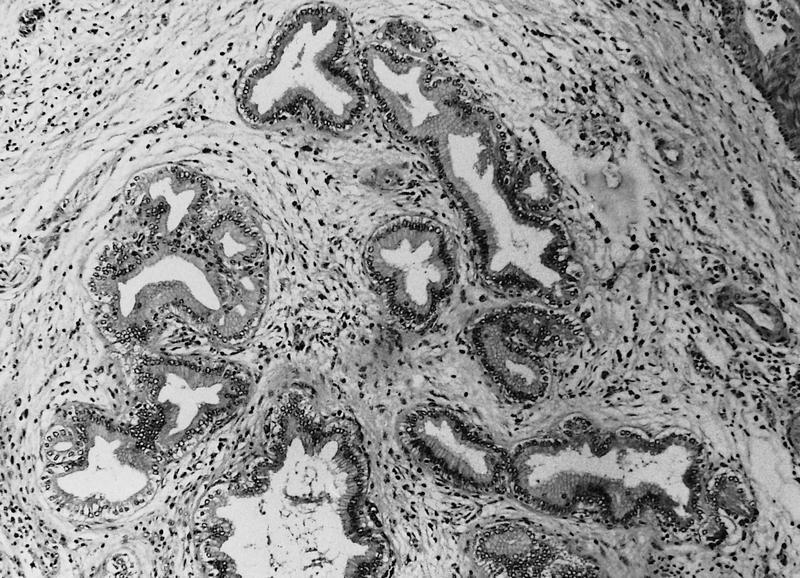
Is periductal fibrosis a normal ageing process?
Periductal fibrosis can occur in the absence of duct ectasia or of inflammation 20 and probably represents part of the normal involutional process. Duct ectasia is so common in the postmenopausal breast that it must be regarded as part of the normal ageing process.
What's the difference between acute and chronic inflammation?
That's acute inflammation: it has an obvious cause, and it elicits a temporary and well-orchestrated response. Your rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes, however, involve chronic inflammation.
How long does chronic inflammation last?
These symptoms can range from mild to severe and last for several months or years. What causes chronic inflammation? Several things can cause chronic inflammation, including: untreated causes of acute inflammation, like an infection or injury an autoimmune disorder, which involves your immune system mistakenly attacking healthy tissue

What is chronic inflammation of the breast?
Mastitis describes inflammation of the breast tissue, both acute or chronic. By far the most common cause is from infection, typically through S. Aureus, but can occasionally be granulomatous.
What causes inflammation in breast tissue?
Mastitis, which mainly affects breast-feeding women, causes redness, swelling and pain in one or both breasts. Mastitis is an inflammation of breast tissue that sometimes involves an infection. The inflammation results in breast pain, swelling, warmth and redness. You might also have fever and chills.
What is Periductal inflammation?
What is periductal mastitis? Periductal mastitis occurs when the ducts (tubes) under the nipple become inflamed and infected. Periductal mastitis is a benign (not cancer) breast condition and does not increase your risk of developing breast cancer.
What causes periductal mastitis?
Periductal: Menopausal and postmenopausal women and smokers are more prone to periductal mastitis. Also called mammary duct ectasia, this condition occurs when milk ducts thicken. The nipple on the affected breast may turn inward (inverted nipple) and produce a milky discharge.
How do you reduce inflammation in the breast?
What you can doTake an OTC pain reliever. ... Apply ice or heat. ... Avoid caffeine. ... Wear a “period bra.” You probably have period underwear, so complete the set with a larger bra that won't squish your swollen breasts.Reduce your salt intake. ... Practice mindfulness.
What cancers are associated with chronic inflammation?
The inflammatory diseases colitis, pancreatitis and hepatitis, for example, are linked to a greater risk of colon, pancreatic and liver cancers, respectively. In these diseases, immune cells create highly reactive molecules containing oxygen and nitrogen that can damage DNA. Inflammation also may cause cells to divide.
What antibiotics treat periductal mastitis?
Antibiotics considered appropriate are flucloxacillin or erythromycin (if penicillin sensitive) for lactational and skin‐associated infection, and coamoxiclav, or flucloxacillin or cephalexin or erythromycin with metronidazole for non‐lactational infection.
Does duct ectasia show on mammogram?
Bilateral symmetric subareolar ductal ectasia is a common finding on mammography that is typically benign. It is often seen in “mammary duct ectasia,” a benign entity described by Haagensen [1] that is characterized by the histologic triad of ductal dilatation, periductal inflammation, and fibrosis.
Is periductal mastitis painful?
Initial presentation of periductal mastitis is often with periareolar inflammation (either with or without an associated mass), but abscess can also be already established. Associated symptoms include central noncyclical breast pain and purulent nipple discharge.
What happens if you leave mastitis untreated?
A breast abscess can be a complication of mastitis, and if left untreated, can lead to gangrene and permanent damage. If the infection spreads into the bloodstream, it can lead to sepsis (life-threatening bacterial blood infection) and organ failure.
Does menopause cause mastitis?
Breast infections (mastitis) or abscesses can happen at any age, but it's more common before menopause. The pain is only in the infected breast.
Can you get a breast infection after menopause?
In postmenopausal women, breast infections may be associated with chronic inflammation of the ducts below the nipple. Hormonal changes in the body can cause the milk ducts to become clogged with dead skin cells and debris. These clogged ducts make the breast more open to bacterial infection.
What does inflammatory breast disease look like?
Symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer include swelling (edema) and redness (erythema) that affect a third or more of the breast. The skin of the breast may also appear pink, reddish purple, or bruised. In addition, the skin may have ridges or appear pitted, like the skin of an orange (called peau d'orange).
Why Does My breast hurt when I press it?
This sensitivity is known as cyclic mastalgia or fibrocystic changes. Around 50 percent of all women over the age of 30 experience this. Right before your period starts, your breasts may feel especially tender if you press on them, or they may ache.
What does IBC pain feel like?
tenderness, heaviness, or dull pain in both breasts. dense, coarse, or lumpy feeling breast tissue. growth and enlargement of breasts. aching in the breasts and surrounding area.
Do breast cysts cause inflammation?
This condition causes redness, heat, lumpiness and pain in the affected breast tissue. Most commonly, this is caused by an infection during breastfeeding, but it can occur at other times due to blockage and inflammation of the breast duct with an infection.
What is the difference between periductal mastitis and duct ectasia?
It typically occurs with a younger age group than mammary duct ectasia, but the main difference between periductal mastitis and duct ectasia is that the mass develops ‘ around ‘ the nipple, rather than ‘ behind ‘.
What does periductal mastitis look like?
(NOT helpful, not funny, grow up Doc…) It looks like an inflamed skin red area extending outward from the edge of the areola.
Can smoking cause periductal mastitis?
If there is a residual mass, surgery may be required, both to confirm that it is not breast cancer, and to help prevent recurrence and infection. There is some suggestion that smoking might be a factor in developing periductal mastitis, or at least in slowing down the healing process.
Why does chronic inflammation develop and persist?
Perhaps there was a germ or a toxin that got into the joint, leading to inflammation — but the inflammation lost the ability to turn itself off.
What is the word for a wound that is red, warm, swollen, and painful?
Roman physicians 2,000 years ago noted that wounds that were healing and joints that suffered from arthritis (like yours) became red, warm, swollen, and painful. It was like they were on fire: inflammare was the verb for setting on fire. But why did a wound become red, warm, swollen, and painful? They had no idea.
Does diabetes cause inflammation?
And how is chronic inflammation connected to your diabetes? That, too, is largely a mystery. Most people with type 2 diabetes also suffer from obesity, and the abundant fat cells in obese people can make many of the chemicals that cause inflammation.
What causes chronic inflammation?
In addition to contributing to the development of illness, chronic inflammation can also be a symptom — in autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, for example.
Why is chronic inflammation dangerous?
Because the signs are difficult to spot, many people don’t find out chronic inflammation is a problem for them until they are diagnosed with a serious illness.
What is inflammation?
Inflammation is part of our natural healing process. When our bodies are faced with injury, illness or harmful toxins, our immune systems send inflammatory cells and substances to defend themselves and jump-start the healing process.
What is the number to call for periductal mastitis?
If you have any questions about periductal mastitis or just want to talk things through, you can call Breast Cancer Care’s Helpline free on 0808 800 6000 and speak with one of our team.
How to treat a fistula?
This may involve using a fine needle and a syringe to draw off (aspirate) the pus using an ultrasound scan for guidance. This may need to be repeated over a period of time until all the pus has been removed. Sometimes an opening is made in the skin to allow the pus to be drained. This can be done under local or general anaesthetic.
Can men get periductal mastitis?
Men can also get periductal mastitis, but this is very rare. People who smoke have an increased risk of periductal mastitis because substances in cigarette smoke can damage the ducts behind the nipple. Smoking can also slow down the healing process after treatment. Nipple piercings can increase the chances of infection and may make periductal ...
Does periductal mastitis increase the risk of breast cancer?
Having periductal mastitis does not increase your risk of breast cancer. However, it’s still important to be breast aware and go back to your GP if you notice any further changes in your breasts regardless of how soon these occur after having periductal mastitis. 7.
Can periductal mastitis be treated?
Most cases of periductal mastitis will be treated with antibiotics. However, some people may not need any treatment and it will clear up by itself. Go back to your GP if your symptoms return or if you have any new symptoms, as it can come back. If your breast is painful, you may want to take pain relief such as paracetamol.
Can periductal mastitis be removed with antibiotics?
This can be done under local or general anaesthetic. If periductal mastitis doesn’t get better after taking antibiotics, or if it comes back, you may need to have an operation to remove the affected area. This operation is usually done under a general anaesthetic, and you’ll be in hospital for the day or overnight.
What are the features of a florid periductal mastitis?
Microscopic sections of lesions demonstrate a florid periductal mastitis characterized by an impressive plasma cell reaction to retained ductal secretions. Key features for diagnosis include ductal epithelial hyperplasia accompanied by an associated intense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate. Xanthomatous features can often be observed as lymphocytes and plasma cells surround zones of histiocytes engulfing disrupted ductal material. Neutrophils and periductal fibrosis are uncommonly observed.91
Is mastitis a benign disease?
This form of mastitis represents a notable mimic of benign or malignant neoplasia in breast lesions, typically in women of young to middle age. A significant number of cases are associated with parity or oral contraceptive pills; however, many cases have no well-defined causes and are designated as idiopathic. It is characterized histologically by multiple necrotizing granulomata and/or abscesses located in association with or in approximation to segmental and subsegmental lactiferous ducts in a lobulocentric pattern. 93–96 Acid fast and/or Gomori methenamine silver stains may be needed to exclude mycobacterial and fungal infections.
Is periductal mastitis an involutional process?
An alternative theory se es the primary process as periductal mastitis, perhaps on an autoimmune basis, leading to weakening of the muscle layer of the ducts and secondary dilatation. It is likely that both processes may occur separately or in conjunction, thus explaining the wide spectrum of clinical behaviour in this condition. Both duct dilatation and duct sclerosis may represent an aberration of involution. Periductal fibrosis can occur in the absence of duct ectasia or of inflammation 20 and probably represents part of the normal involutional process. Duct ectasia is so common in the postmenopausal breast that it must be regarded as part of the normal ageing process.
Why do doctors use the term "comedomastitis"?
This is because plasma cells begin to infiltrate the discharge, but there is nothing wrong with the plasma cells, and they are not the cause of the condition ) Medics use the term ‘comedomastitis’, in general, to indicate the acute presence of the sticky discharge.
What is comedo mastitis?
Duct Ectasia is a chronic inflammatory condition affecting the subareolar periductal (an area beneath the nipple and beside the ducts) region on the breast. If left untreated, it can eventually lead to the obliteration of a breast duct.
Is duct ectasia benign?
Duct Ectasia is Benign ( not breast cancer) Duct ectasia is completely benign and is not breast cancer. It often occurs around the time of menopause and is most common in older women. The development of this condition has also been linked to the use of breast implants. The image above shows a normal breast duct, ...
What is the name of the inflammation of the salivary gland that progresses with increasing fibrosis and par?
Chronic sclerosing sialadenitis is a chronic inflammation of the salivary gland that progresses with increasing fibrosis and parenchymal atrophy. It is also called Küttner's tumor.
What is a sialadenitis?
Chronic obstructive sialadenitis is associated with lymphoplasmacytic inflammation, fibrosis, and acinar atrophy to varying degrees. Mild neutrophilic inflammation may be present. Inflammation tends to aggregate periductally. Lymphoid aggregates with germinal centers are common. Acinar atrophy may be marked so that acini are completely lacking. Ducts and acini often appear ectatic. The ductal epithelium is prone to metaplastic changes, including squamous cell and mucous cell metaplasia. Oncocytic change is common in inflamed minor salivary glands. A granulomatous inflammatory response may be seen, with extravasation of saliva secondary to duct rupture. 97 The Küttner tumor is characterized by periductal lymphoplasmacytic inflammation with incorporation of the interlobular and intralobular ducts in thick fibrous trabeculae. 98
What is sarcoidosis of the salivary gland?
Sarcoidosis of the salivary gland is characterized by several epithelioid granulomas and less fibrosis and ductal ectasia. Lymphoepithelial complexes distinguish LESA. Immunohistochemical staining for markers such as CD10 and Bcl-2 help differentiate follicular lymphoma from chronic sclerosing sialadenitis with numerous lymphoid follicles.
What causes sialadenitis in cats?
Granulomatous sialadenitis can be caused by infection (fungi, mycobacteria, toxoplasmosis, and cat scratch disease), sarcoidosis, cyst rupture, and rarely neoplasia (Hodgkin lymphoma, T-cell lymphoma, or metastatic carcinoma ). 60–62 Aspirates are characterized by a variable background of granular, necrotic cell debris and inflammation, together with aggregates of epithelioid histiocytes, frequently with multinucleated forms. Epithelioid histiocytes have abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and cytologically bland, elongated, folded nuclei with indistinct nucleoli. Asteroid bodies, Schaumann bodies, and calcium oxalate crystals can be present in sarcoidosis, but these findings are not specific, and an infectious etiology must be excluded by special stains or microbiologic cultures. 63
Is sialadenitis a bacterial infection?
Acute sialadenitis is rarely aspirated because it is usually diagnosed clinically as a postoperative complication, viral or fungal infection, or secondary bacterial infection resulting from an obstruction such as sialolithiasis 52–55 ( Fig. 10.3 ). There is usually no discrete mass, and most cases affect the parotid gland.
Is a sclerosing sialadenitis a parotid gland?
The submandibular gland is by far the salivary gland most often involved, but in rare cases Küttner’s tumor involves the parotid gland.
Is sialadenitis a FNA?
As with acute sialadenitis, FNA of chronic sialadenitis can be associated with pain. Chronic sialadenitis is more likely to present as a clinically discrete mass, often in the submandibular gland. Common causes include sialolithiasis and radiation therapy for head and neck cancer (usually squamous cell carcinoma).