What is peristalsis, and why should I Care?
Peristalsis is a fancy word for the process that moves the food we eat, starting (naturally) at the mouth mouths, traveling through our digestive system, and exiting our bodies as waste. When something like a disease or illness interrupts this process, it can cause serious complications. So if you’re wondering what peristalsis is, check out ...
What happens when there is no peristalsis?
What happens if there is no peristalsis? Answer: if there is no peristaltic movement in oesophagus , then there will be difficulty is transportation and digestion of food. Explanation: contraction and relaxation of oesophageal muscles bring in a wave like motion that propels the food into the stomach which is peristalsis .
What is the function of the peristaltic?
Functions of Peristalsis. Some of the functions of Peristalsis are as follows: i. The peristaltic movement pushes the food down the oesophagus and into the stomach. ii. In the stomach, the peristaltic movement helps in storing food and breaking down the food particles and mixing them with gastric juices that are secreted from the stomach lining.
What are the symptoms of peristalsis?
Symptoms of peristalsis dysfunction such as dysphagia, chest pain, heartburn, vomiting, constipation, and diarrhea can mimic severe, life-threatening disorders. It is essential to understand the physiology and pathophysiology of peristalsis to distinguish between emergent and non-emergent ailments.

WHat are the two main functions of peristalsis?
Peristalsis is an automatic and important process. It moves: Food through the digestive system. Urine from the kidneys into the bladder.
What is the function of peristalsis Class 10?
Peristalsis created by the muscle contraction facilitates food movement downwards via the esophagus to the stomach. Peristalsis propels the food downwards in the bolus form. The stomach converts the food into chyme form.
What does peristalsis mean in simple words?
(payr-ih-STAL-sis) The rippling motion of muscles in the intestine or other tubular organs characterized by the alternate contraction and relaxation of the muscles that propel the contents onward.
What is peristalsis and where does it occur?
Peristalsis is a series of muscle contractions. These contractions occur in your digestive tract. Peristalsis is also seen in the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. Peristalsis is an automatic and important process.
What is the benefit of peristalsis?
Peristalsis is a particular, wave-like kind of muscle contraction because its purpose is to move solids or liquids along within the tube-like structures of the digestive and urinary tracts.
Which foods increase peristalsis?
Fiber-rich foods such as whole grains, leafy vegetables and fresh fruits will add bulk to your feces and help stimulate the bowel to push food along.
What nerve controls peristalsis?
the vagus nerveThe parasympathetics control peristalsis via the vagus nerve. The medullary vagal postganglionic efferents arise from the lower motor neurons in the nucleus retrofacialis and the compact formation of the nucleus ambiguus.
What is another word for peristalsis?
In this page you can discover 9 synonyms, antonyms, idiomatic expressions, and related words for peristalsis, like: contractility, motility, anastalsis, lipolysis, vasodilation, respiration, vermiculation, distension and vasoconstriction.
What are the types of peristalsis?
There are three types of esophageal contractions: primary, secondary, and tertiary. Primary peristaltic contractions are progressive and move down the esophagus at a rate of 2 to 4 cm/sec and reach the LES about 9 seconds after the initiation of swallowing (Fig. 42.14).
What happens if peristalsis is too slow?
Slow transit constipation is characterised by the reduced motility of the large intestine, caused by abnormalities of the enteric nerves. The unusually slow passage of waste through the large intestine leads to chronic problems, such as constipation and uncontrollable soiling.
What causes peristalsis to stop?
Typically, muscles in the intestines contract and relax to cause a wave-like motion called peristalsis. This movement helps food travel through the intestines. When an ileus occurs, it stops peristalsis and prevents food particles, gas, and liquids from passing through the digestive tract.
What causes slow peristalsis?
Infection, usually from a virus. Certain medications that slow the rate of stomach emptying, such as narcotic pain medications. Scleroderma — a connective tissue disease. Nervous system diseases, such as Parkinson's disease or multiple sclerosis.
What is peristalsis Class 10 Brainly?
Peristalsis is responsible for pushing food through the digestive tract. Peristalsis or peristaltic movement are contraction and expansion movements of food pipe walls to push partially digested food to stomach. This movement is helpful in moving food forward for digestion.
What is peristaltic movement class 10 Mcq?
Peristalsis is a wave-like movement of the muscles to push down food to different processing stations for the food to be disintegrated further. This process commences in the oesophagus and is an involuntary progressive movement.
What is peristalsis Ncert?
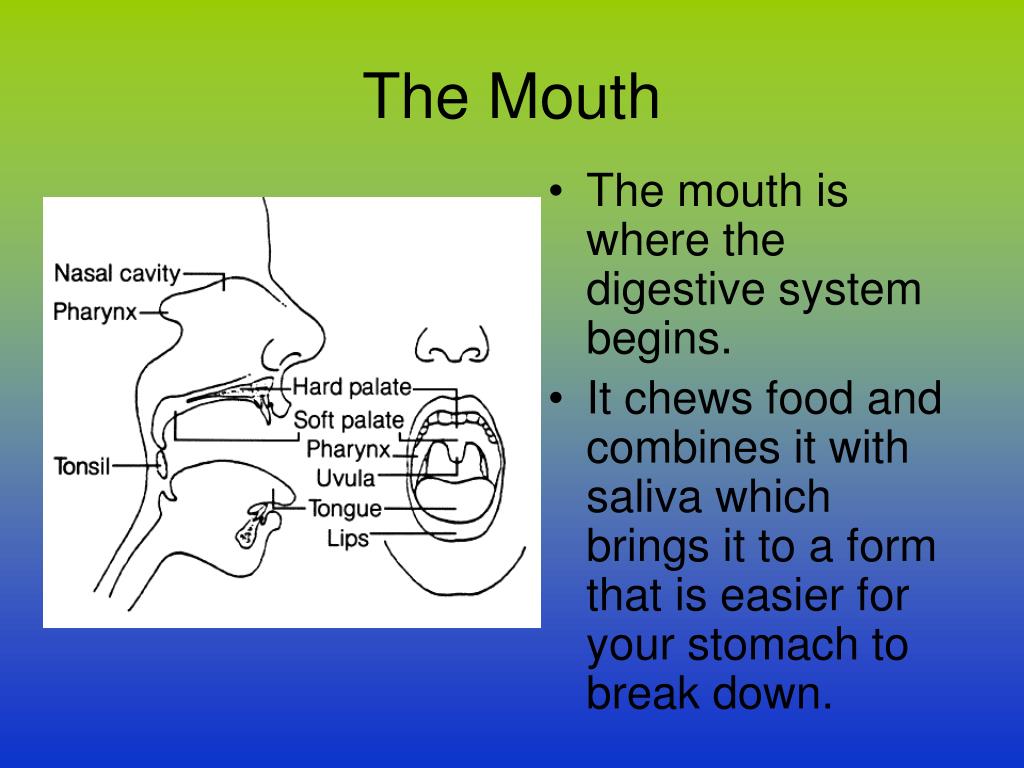
Mucus in saliva helps in lubricating and adhering the masticated food particles into a bolus. The bolus is then conveyed into the pharynx and then into the oesophagus by swallowing or deglutition. The bolus further passes down through the oesophagus by successive waves of muscular contractions called peristalsis.
What is peristalsis 9th class?
Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that help in moving food to different processing areas in the digestive tract. The process of peristalsis begins in the oesophagus when a bolus of food is swallowed and moves till the anus.
Q.1. What is peristalsis, and what is its function?
Ans: Peristalsis is a series of wave-like muscle contractions that move food through the digestive tract. It is important because it helps for the...
Q.2. What are the 2 functions of peristalsis?
Ans: The two functions of peristalsis are as follows: i. The peristaltic waves push the swallowed bolus down the oesophagus. ii. In the stomach, pe...
Q.3. How does peristalsis protect against intestinal infection?
Ans: Peristaltic waves are important in removing the gas from the large intestine, and it helps in controlling bacterial growth and their infections.
Q.4. What organ does peristalsis occur in?
Ans: The organs where peristalsis occurs are the oesophagus, stomach, small and large intestines.
Q.5. What happens to food during reverse peristalsis?
Ans: It usually occurs as a precursor to vomiting. In this reverse peristalsis, the food moves in the opposite direction, often from the duodenum i...
Q.6. What is dysphagia?
Ans: Dysphagia occurs when the peristalsis in the oesophagus is affected. People having dysphagia have difficulty in swallowing food and it takes m...
What is peristalsis and its function?
Peristalsis is a sequence of muscular contractions that sends a wave along a tube in the alimentary canal, allowing food to flow. The smooth muscle...
What is meant by peristaltic movement?
Peristalsis is a succession of wave-like muscular contractions that helps food pass through the digestive tract. Peristalsis in the large intestine...
What is meant by the term "peristaltic action"?
Peristalsis. 1. Rhythmic contractions of tubular organ walls that drive contents forward, such as food in the gut. 2. Muscle contraction waves that...
What is Peristalsis?
Peristalsis is a contraction and relaxation of food in the oesophagus where the food is forced to move down to the stomach. It can be referred to as successive wave-like contractions of the muscles that are involved in the food movement and in the movement of other particles in the digestive tract to other various processing organs that are located in the digestive system.
How long does a peristaltic movement last?
i. When this chyme reaches the small intestine from the stomach, one peristaltic movement lasts only a couple of seconds and travels a few centimetres per second.
What is the process of breaking down food molecules into smaller components that can be absorbed or assimilated?
Peristalsis: Digestion is the complex process that pertains to the mechanical and chemical processes of breaking down food molecules into smaller components that can be absorbed or assimilated. How does food move through the oesophagus to the stomach? In human beings, the food moves through the oesophagus to the stomach by a special wave-like contraction and relaxation known as Peristalsis. This article covers the definition, the different organs where Peristalsis occurs, and much more. To know more interesting facts about Peristalsis, scroll down the article.
What is the name of the ball-like particles that the stomach receives after oesophageal per?
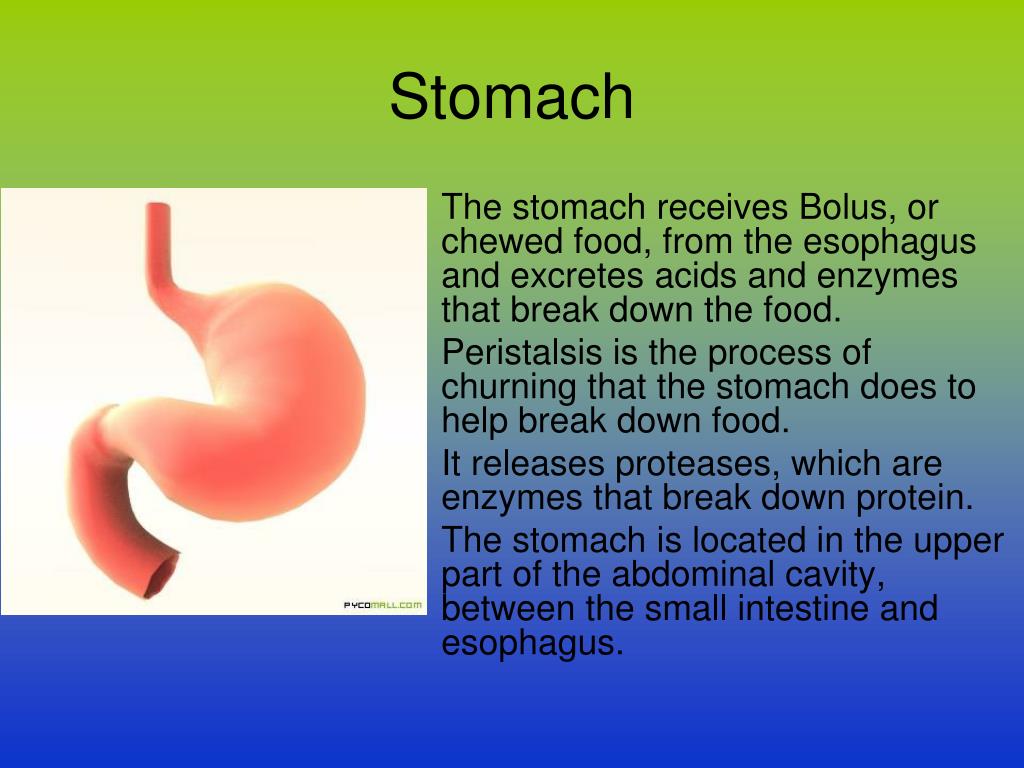
i. After oesophageal peristalsis, the stomach receives ball-like food particles which are also known as bolus.
Which movement pushes partially digested food from the stomach to the small intestine?
iii. In the small intestine, the peristaltic movement pushes the partially digested food from the stomach to the small intestine and helps in the digestion process. It also helps in absorbing nutrients from the digested food into the bloodstream.
Where do peristaltic waves start?
iii. It is usually observed that peristaltic waves start as weak contractions at the starting of the stomach and then become stronger at the distal regions or parts of the digestive system.
What are the four organs of the digestive system?
These Four organs are the oesophagus, the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine.
What is the function of peristalsis?
Peristalsis Function. Peristalsis is a wave-like motion which brings about the movement of food and liquid through muscle contractions. It is an involuntary action of the muscles and hence cannot be under one’s will. But, the muscles that are involved in peristalsis, the smooth muscles, function when they are triggered to do so.
What is Peristalsis?
The peristaltic movement also called as the Peristalsis refers to the contraction and relaxation of the food in the oesophagus and the food pipe and the food is forced down the track to the stomach. This movement is involuntary and is necessary for the movement of food down the stomach and bowels down the anus.
What is the term for a series of wave-like contractions of the muscles that are involved in the food movement?
Peristalsis Definition. “Peristalsis is a series of wave-like contractions of the muscles that are involved in the food movement and in the movement of other liquid particles in the digestive tract to various processing organs that are located in the digestive system.”.
What is the purpose of peristaltic movement?
The liquid, due to the peristaltic movement, eliminates from the body through structures called the urethra in the form of urine.
How many peristaltic waves are there in the stomach?
These waves help in mixing the stomach content and drive the food into the small intestine. Normally, two to three waves exist at once in separate areas of the stomach.
What is the term for the process of eliminating food particles from the oesophagus?
This could be termed as Esophageal Peristalsis. The food particles left behind the oesophagus begins with the secondary peristaltic waves that eliminate leftover particles. A single wave moves along the complete length of the tube. In cud-chewing animals like cattle, sheep, giraffes, and camels the reverse peristalsis happens such ...
Why is peristalsis important?
The process of peristalsis is important in digestion and in some conditions, it does not function properly. In such cases, when there is no peristalsis, a person faces diarrhoea or constipation. These are usually subtle signs indicating dysfunctioning of the peristalsis motion. It can emerge as a result of a medication or due to a condition known as motility disorder. The condition of motility disorders can be difficult to treat, hence needs to be taken care of.
What is the purpose of the small intestinal peristaltic movement?
The primary purpose of the small intestinal peristaltic movement is to continue the digestion of food and absorb nutrients.
Which organs are affected by peristalsis?
These organs are the esophagus, stomach and the large and small intestines. Oesophagus: Peristalsis pushes the food down the esophagus and into the stomach.
What is the name of the part of the stomach that is partially digested after hydrolysis?
After hydrolysis, all food particles are partially digested and it is known as chyme . The chyme or partially digested food will stay in the stomach for a while until further peristaltic movement propels it into the duodenum, the first part of the small intestine for further processing.
What is the term for the process of food moving from the stomach to the duodenum?
It generally occurs as a precursor to vomiting. Food poisoning or stomach irritation activates the emetic centre of the brain which signals for this type of intestinal contractions and food moves from the duodenum to the stomach. Reverse peristalsis is also known as retro peristalsis.
What is the term for the process of breaking down food particles in the stomach?
Peristalsis in Stomach. After esophageal peristalsis , the stomach receives a ball of food which is also called a bolus. Through stomach peristalsis, stomach muscles compress and break down the bolus even more which is followed by a certain degree of hydrolysis of the food particles. It is observed that peristaltic waves start as weak contractions ...
What is the peristaltic movement of the large intestine?
Large Intestine: The peristaltic movement in the large intestine is the same as the small intestine. General contractions called mass movements to take place one to three times a day to propel the chyme which is now faeces or bodily waste towards the rectum so it could be expelled from the body.
What is the term for the movement of food particles in the digestive system?
Peristalsis Definition. Peristalsis could be defined as a series of involuntary movements of the longitudinal and circular muscles that are involved in the movement of food and other liquid particles in the digestive tract to various processing organs that are located in the digestive system. The movements occur in progressive wavelike contractions ...
Where does peristalsis move?
It moves: Food through the digestive system. Urine from the kidneys into the bladder. Bile from the gallbladder into the duodenum. Peristalsis is a normal function of the body. It can sometimes be felt in your belly (abdomen) as gas moves along. Watch this video about: Peristalsis.
What is the term for a series of muscle contractions?
Peristalsis. Peristalsis is a series of muscle contractions. These contractions occur in your digestive tract. Peristalsis is also seen in the tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. Peristalsis is an automatic and important process.
What is the function of peristalsis?
Peristalsis Position and Function. Peristalsis is a radially in proportion contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagates in a wave down a tube, in an anterograde instructions.
What Is the Peristalsis?
Peristalsis is a series of muscle relaxations and contractions that occur in the lining of the intestinal tracts. This procedure makes it possible for waste and food products to be pressed through the intestines. Sometimes, it is in fact possible to feel these muscular contractions as they take place. This is specifically common for the large intestinal tracts. Peristalsis is just possible since the human digestive system is adapted to peristaltic pumps. These are muscular devices that utilize the same strategy as those used by the system to press fluids through the body.
How does the gastro-intestinal tract work?
In this procedure, when water or food enters the gastro-intestinal tract, the muscles in this tract relax and compress in a motion that is wave prefer to allow the material to go through. For instance, when you swallow an apple, smooth muscles in the esophagus relax and contract to allow the apple to pass through. The contracted muscles permit the material to pass to the area with unwinded muscles lower in the esophagus. This continues until the food reaches the stomach. The muscles above stay contracted to avoid the food from flowing back.
What is peristaltic contraction?
Peristalsis can be specified as muscular contractions that happen in the digestive tract. These contractions are also very common in organs that connect the kidney to the bladder. This is an involuntary procedure, and it is essential.
What is the movement of the peristaltic muscle?
Peristaltic movement comprises relaxation of circular smooth muscles, then their contraction behind the chewed product to keep it from moving backwards, then longitudinal contraction to press it forward. Through peristalsis: Food is moved through the digestion system. Urine is passed from the kidney to the bladder.
Where does food go when it moves from the esophagus to the stomach?
First, the food is relocated to the little intestinal tracts for food digestion.
What is the function of peristalsis?
Along with segmentation or mixing of food, peristalsis is an essential part of providing the body with nutrients. The gastrointestinal tract is innervated by the enteric nervous system (ENS), and the parasympathetic nervous system activates peristalsis through the myenteric plexus.
Where is peristalsis found?
Peristalsis is primarily found throughout the gastrointestinal tract and is the involuntary propulsion of food. This movement begins in the pharynx, once a food bolus is formed, and ends in the anus.
Why is there no peristalsis in adults?
A lack of peristalsis is most likely due to the dysfunction of the myenteric plexus in the esophagus.
Which muscles contract and relax in the peristaltic movement?
The circular and longitudinal muscles contract and relax, leading to the peristaltic movement. When there is a bolus of food, circular muscles behind the bolus contract and relax in the front, whereas longitudinal muscles behind the bolus relax and contract in the front. On a chemical level, when the bolus passes through the intestine, ...
What is released when a bolus passes through the intestine?
On a chemical level, when the bolus passes through the intestine, serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) is released by enterochromaffin cells, and sensory neurons are activated. The contraction of circular muscle behind the bolus is due to excitatory transmitters such as acetylcholine, substance P, and neuropeptide Y.
Where is peristaltic movement found?
Peristalsis is mainly found within the smooth muscle, and other areas of this type of movement are found in bile ducts, glandular ducts, and ureters. Function. There are two types of peristaltic contractions: primary and secondary. The primary peristaltic wave helps to move food forward.
Which nucleus triggers peristalsis?
For peristalsis in the skeletal muscle, the vagal nucleus triggers the neurons, and in smooth muscle, it is triggered by the dorsomotor nucleus via the vagus nerve. [5] The muscularis externa is comprised sequentially of the inner circular layer, the myenteric plexus, and the outer longitudinal layer.