What is phonetic vowel reduction?
Phonetic vowel reduction refers to phonetic effects on vowels of reductions in other phonetic dimensions -- that is, to the changes in phonetic vowel quality associated with decreased stress, sonority, duration, loudness, or articulatory effort.
What is phonetic and phonological vowel reduction in Central Catalan?
> Phonetic and phonological vowel reduction in Central... In Central Catalan, phonological vowel reduction causes the stressed seven-vowel system to reduce in number in unstressed position, where only the three reduced vowels [ i ə u] can occur.
What are the effects of reduction in phonetics?
Another, possible effect of reduction is phonetic shift along the path of ongoing sound change. For example, Labov, Yeager & Steiner (1972) found that upward-shifting /æ/ in polysyllabic words (i.e., in relatively short, unstressed syllables), was raised even higher than the most advanced fully-stressed /æ/ realizations.
What is reduction in linguistics?
A well-researched type of reduction is that of the neutralization of acoustic distinctions in unstressed vowels, which occurs in many languages. The most common reduced vowel is schwa .

What is reduction in linguistics?
Linguistic reductions are lost sounds in words, which happens in spoken English. For instance, "going to" changes to "gonna". The most common reductions are contractions. Most contractions are reductions of 'not'. For instance, "cannot" becomes "can't".
What is vowel reduction examples?
The schwa is the most commonly encountered example of a reduced vowel. This vowel occurs in an unstressed word or syllable; examples are the words the, a, the first syllable of about, and the last syllable of sofa. In all such cases, the quality of the vowel is much more central than when the phoneme is stressed.
What is a phonetic sound?
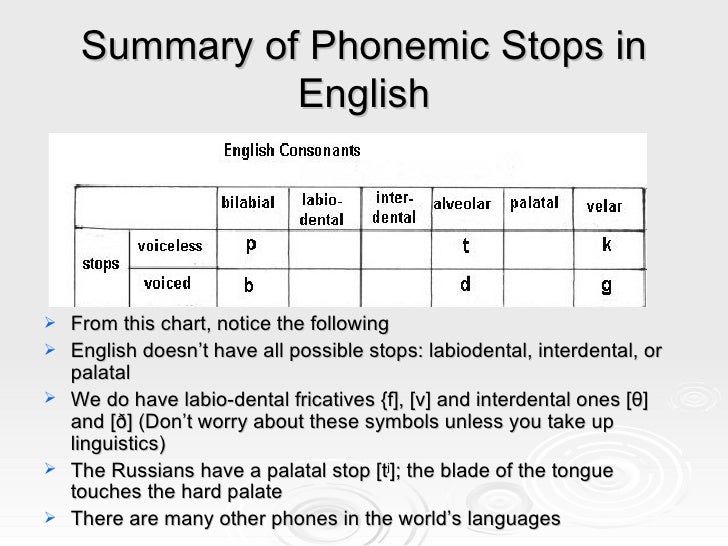
Phonetics is the study of human sounds and phonology is the classification of the sounds within the system of a particular language or languages. • Phonetics is divided into three types according to the production (articulatory), transmission (acoustic) and perception (auditive) of sounds. •
What are reduced sounds?
Reduced Vowel Sounds That means that some syllables are louder, longer, and clearer than others. Syllables that are unstressed are shorter, softer, and less clear. In fact, there are o nly TWO reduced vowel sounds in English. These are the "Schwa" sound and the "barred i" sound.
What is the concept of vowel reduction and how is it measured?
Vowel reduction is when vowels move away from their null context (pure form) toward the schwa context. Vowels experience greater reduction as vowel duration decreases, regardless of the condition, resulting in shorter vowel duration. Shorter vowel duration, greater undershoot.
What are reductions in English?
Reductions or reduced speech is when an English speaker shortens or eliminates particular sounds. This can occur in the form of connected speech, reduced sounds, or contractions. Better understand fast English speakers more easily — in conversations, in podcasts, on TV, etc.
What is phonetic example?
An example of phonetics is how the letter "b" in the word "bed" is spoken - you start out with your lips together. Then, air from your lungs is forced over your vocal chords, which begin to vibrate and make noise. The air then escapes through your lips as they part suddenly, which results in a "b" sound.
What is basic phonetics?
Phonetics is the study of the range of sounds which occur in speech, including the way they are produced by the speech organs and their acoustic properties. Phonology is the study of the distribution of and the relationships between speech sounds, i.e, the system of sounds of a language.
What are phonics examples?
Teaching children to blend the sounds of letters together helps them decode unfamiliar or unknown words by sounding them out. For example, when a child is taught the sounds for the letters t, p, a and s, they can start to build up the words: “tap”, “taps”, “pat”, “pats” and “sat”.
Why are we using reductions in English?
What are reductions? Reductions are reduced forms of English words. Reductions, such as gonna, are not real words in English. You need to use reductions in order to sound more natural.
What can you explain about linking and reduction?
Linking and reduction allow us to connect sounds of words for smooth transitioning and to avoid awkward pauses. In spoken English, we have 3 basic ways of how to link words in a sentence and a unique way of how to reduce words.
What is reduction in connected speech?
Elision. Elision is the process of reduction in connected speech that results in the loss of segments. So a phoneme which would be pronounced in its citation form may be elided in connected speech. As Rogerson-Revell points out, phonemes are most likely to be lost in unstressed syllables (2011: 166).
What is vowel deletion?
Vowel deletion is a phonological process in which an unstressed /inverted e/ (schwa) vowel is deleted during pronunciation.
Which of the following is an example of metathesis?
METATHESISDefinition:The rearrangement of two consonants in a syllable.Examples:ask /ɑsk/ → /ɑks/ (switching) star /stɑ/ → /sɑt/ (transposition)1 more row•Jul 31, 2016
What is elision and examples?
Elision is the omission of sounds, syllables or words in speech. This is done to make the language easier to say, and faster. 'I don't know' /I duno/ , /kamra/ for camera, and 'fish 'n' chips' are all examples of elision.
What is stress dependent vowel reduction?
It is a feature of English that reduced vowels frequently alternate with full vowels: a given word or morpheme may be pronounced with a reduced vowel in some instances and a full vowel in other instances, usually depending on the degree of stress (lexical or prosodic) given to it.
Abstract
In this paper, we describe the second stage of the study aimed at describing the factors that influence the phonetic reduction of words in Russian speech using machine learning algorithms.
1 Introduction
Over the past 20 years, many studies have shown that we need to study natural speech both for understanding speech production and spoken word recognition, and for solving practical issues associated with automatic speech recognition and synthesis [ 1, 2, 3 ].
2 The Previous Study: What Went Wrong?
In our previous study [ 4 ], we used such machine learning algorithms as a random forest [ 14 ], an extremely randomized tree [ 15 ], and logistic regression [ 16] for predicting phonetic reduction and identifying the factors that determine its occurrence.
3 Random Forest, Gradient Boosting, Perceptron and Feature Selection
As we stated above, in the previous study, we used a random forest and an extremely randomized tree to select the most important features for the occurrence of phonetic reduction.
4 Discussion and Conclusion
In this study, six different sets of features were obtained using three different algorithms on two different datasets, i.e., single words and multiword units. When working with single words at the stage of feature selection, the gradient boosting algorithm showed the best result: the balanced accuracy for it was 76.20%.
Acknowledgments
The research is supported by the grant #19-012-00629 from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research. We are very grateful to the anonymous peer-reviewers for constructive comments on an earlier version of the article.
Why are phonetic spelling guides location specific?from study.com
Because there are many accents and dialects used by speakers of English, phonetic spelling guides are location-specific out of necessity. An American dictionary and a British dictionary will give different pronunciation guides for many words.
Why do dictionaries use phonetic spelling?from study.com
Because English is not an entirely phonetic language, the majority of dictionaries employ a phonetic spelling guide. This is a way to help readers learn the correct pronunciation of a word, which may not be evident from the word's spelling. There are certain conventions that one can learn to make reading these guides easier, as dictionaries are fairly standard when it comes to how to do phonetic spelling. A phonetic spelling guide entry might look like this:
Who uses phonetic spelling?from dictionary.com
A system of true phonetic spelling would make things easier for all us. (Especially those of us reading names at commencement!)
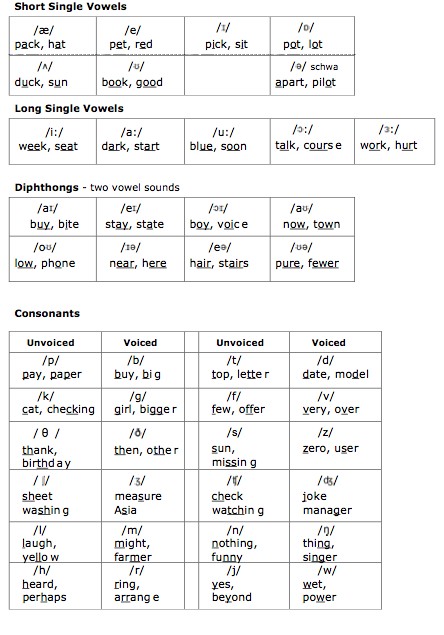
What is the difference between unvoiced and voiced sounds?from wikihow.com
The only difference between the 2 is that voiced sounds, like [b], cause the throat to vibrate, whereas unvoiced sounds, like [p], do not.
What are the two common sounds that are approximants?from wikihow.com
This creates air turbulence when making the sound. 2 common sound classes, retroflex [r] and lateral [l], only exist in English as approximants.
Why are front vowels called bright?from wikihow.com
Tackle front vowels. Front vowels are generally described as “bright” because their tone is often brighter than those farther back in the mouth. The IPA lists over 12 potential front and near-front vowels. The four most common American English front vowels follow:
How many different vowels are in a diphthong?from wikihow.com
Commit diphthongs to memory. Diphthongs combine 2 different vowel sounds in the same syllable. Separate vowels frequently get absorbed into a single diphthongized sound when people speak quickly. American English uses the following diphthongs:
What are the phonetic consequences of a reduced vowel?from en.wikipedia.org
Bolinger (1986) observes that a preceding voiceless stop is likely to retain its aspiration before an unstressed full vowel, but not before a reduced vowel; and that flapping of /t/ and /d/ in American English is possible before a reduced vowel but not before a full vowel. Hence the /t/ in manatee would be an aspirated [tʰ], while that in humanity would be unaspirated [t] or a flap [ɾ]. Wells (1990) explains such phenomena by claiming that, in the absence of morpheme boundaries or phonotactical constraints, a consonant between a full and a reduced vowel generally belongs to the syllable with the full vowel, whereas a consonant between two reduced vowels belongs to the preceding syllable. According to this analysis, manatee is /ˈmæn.ə.tiː/ and humanity is /hjʊ.ˈmæn.ᵻt.i/; it is then asserted that voiceless stops are only aspirated at the beginning of syllables, and /t/ can only be flapped at the end of a syllable (as in might I /maɪt.aɪ/ → [mʌɪɾaɪ] versus my tie /maɪ.taɪ/ → [maɪtʰaɪ] ).
What are the sounds of reduced vowels?from en.wikipedia.org
Certain vowel sounds in English are associated strongly with absence of stress: they occur practically exclusively in unstressed syllables; and conversely, most (though not all) unstressed syllables contain one of these sounds. These are known as reduced vowels, and tend to be characterized by such features as shortness, laxness and central position. The exact set of reduced vowels depends on dialect and speaker; the principal ones are described in the sections below.
What happens when the stress pattern of words changes?from en.wikipedia.org
When the stress pattern of words changes, the vowels in certain syllables may switch between full and reduced. For example, in photograph and photographic, where the first syllable has (at least secondary) stress and the second syllable is unstressed, the first o is pronounced with a full vowel (the diphthong of GOAT ), and the second o with a reduced vowel ( schwa ). However, in photography and photographer, where the stress moves to the second syllable, the first syllable now contains schwa while the second syllable contains a full vowel (that of LOT ).
What is the final vowel of coffee?from en.wikipedia.org
The final vowel of words like happy and coffee is an unstressed front close unrounded vowel most commonly represented with [i], although some dialects (including more traditional Received Pronunciation) may have [ɪ]. This [i] used to be identified with the phoneme /iː/, as in FLEECE. See happy tensing. However, some contemporary accounts regard it as a symbol representing a close front vowel that is neither the vowel of KIT nor that of FLEECE; it occurs in contexts where the contrast between these vowels is neutralized; these contexts include unstressed prevocalic position within the word, such as react /riˈækt/. For some speakers, however, there is a contrast between this vowel and /ɪ/ in such pairs as taxis vs. taxes and studied vs. studded. See English phonology: § Unstressed syllables under § Vowels .
What are the peaks of reduced syllables?from en.wikipedia.org
The other sounds that can serve as the peaks of reduced syllables are the syllabic consonants, which can result in syllables with no vowel sound. Alternative pronunciations of syllabic consonants are however also possible. For example, cycle may be pronounced as either /ˈsaɪkl/ with only a dark l sound or as /ˈsaɪkəl/ with a schwa and the dark l sound.
What is a r-colored schwa?from en.wikipedia.org
In many rhotic dialects, an r-colored schwa, [ɚ], occurs in words such as water and standard. Non-rhotic dialects simply have schwa in these positions, except where the dialect has linking R. The r-colored schwa can be analyzed phonemically as /ər/ .
What is rounded vowel?from en.wikipedia.org
Phonologically, this vowel is an archiphoneme representing the neutralization of /uː/ and /ʊ/ .
Why do children use phonological processes?from wpspublish.com
They do this because they lack the ability to appropriately coordinate their lips, tongue, teeth, palate and jaw for clear speech.
When to seek help for a child who omits consonants?from banterspeech.com.au
When to consider seeking help: if your child is regularly omitting final consonants in words at the age of 3 years, 3 months.
What are clusters of consonants?from banterspeech.com.au
Many words in English contain combinations or ‘clusters’ of consonants, e.g. squawk, crab or flower. It’s common for young children to omit one or more of the consonants in a cluster (so called cluster reduction ), and there are some clever rules of thumb speech pathologists use to help us predict which ones.
What is the repetition of a complete or incomplete syllable in substation for a word?from wpspublish.com
2.Reduplication – the repetition of a complete or incomplete syllable in substation for a word
What is the J sound?from banterspeech.com.au
the “j” sound – transcribed as /d ʒ/ in IPA – is a combination of /d/ (as in “dog”) and “zh” (/ ʒ/ in IPA), as in the middle of “vision”.
What is the error of the tongue?from banterspeech.com.au
This type of error is called fronting. It occurs when sounds normally produced with the tongue positioned at the back of the mouth (e.g. k, g and sh) are instead produced with the tongue positioned towards the front of the mouth (e.g. like t, d, and s).
What is the term for the sound that should be made in the back of the mouth?from wpspublish.com
5.Fronting - the term used when sounds that should be made in the back of the mouth (velar) are replaced with a sound made in the front of the mouth (alveolar)