What is short-term phonological memory?
Short-term phonological memory is the ability to temporarily maintain speech-related information through a combination of passive and active mechanisms.
What is short term memory in psychology?
Short Term Memory. Short-term memory (STM) is the second stage of the multi-store memory model proposed by the Atkinson-Shiffrin. The duration of STM seems to be between 15 and 30 seconds, and the capacity about 7 items.
Why is phonological memory important for students?
Students must be able to hold information long enough to process it, use it, and then transfer it to long-term memory. Poor phonological memory can hinder a student’s ability to accomplish most tasks including: For example, when decoding an unfamiliar but lengthy word, a student must figure out each sound and then each syllable.
What is short term memory (STM)?
Short-term memory (STM) is the second stage of the multi-store memory model proposed by the Atkinson-Shiffrin. The duration of STM seems to be between 15 and 30 seconds, and the capacity about 7 items. Short term memory has three key aspects: 1. limited capacity (only about 7 items can be stored at a time) 2.
What is phonological memory?
The ability to hold on to speech-based information in short-term memory is called phonological memory. We rely heavily on our phonological memory when reading and spelling. This skill is assessed by asking students to remember strings of numbers or to repeat nonsense words of increasing length and complexity.
Is phonological memory the same as working memory?
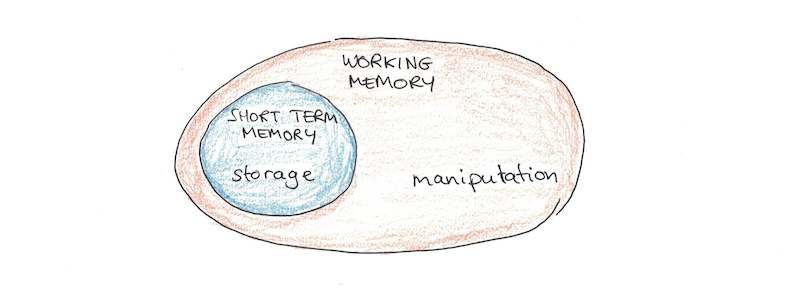
The phonological loop component of working memory is commonly referred to as phonological working memory; working memory that allows for processing sounds and then doing something with those sounds such as successfully blending them together to form a word.
What is phonological memory used for?
Phonological memory is the ability to hold information (numbers, sounds, words) in working or short-term memory for temporary storage. Students must be able to hold information long enough to process it, use it, and then transfer it to long-term memory.
What are the three types of short-term memory?
Short term memory has three key aspects:limited capacity (only about 7 items can be stored at a time)limited duration (storage is very fragile and information can be lost with distraction or passage of time)encoding (primarily acoustic, even translating visual information into sounds).
What is a symptom of a problem with phonological working memory?
Difficulty following multi-step directions. Difficulty staying engaged in class. Test anxiety, especially on multiple choice tests. A need for more time and repetition.
Why is phonological memory important for reading?
Phonological memory predicted word identification and decoding. In addition, phonological awareness and rapid automatized naming predicted every aspect of reading assessed, supporting the notion that phonological processing is a core contributor to reading ability.
How can I help my phonological working memory?
Phonological memory can be supported by developing strategies to compensate for the underlying phonological weakness.Break words into bigger units, using chunking. ... Teach learners how to use rehearsal e.g. saying words or sounds over and over again while they are working out the sounds that they need to manipulate.
How do you assess phonological working memory?
Phonological working memory is assessed using 'digit span', 'digit span-running', and 'nonword repetition' tasks. The 'digit span' task requires children to repeat lists that vary in length from 2-8 digits. This task is presented to children in the context of playing a copycat game with a robot.
Is phonological processing dyslexia?
Phonological dyslexia is extreme difficulty reading that is a result of phonological impairment, meaning the ability to manipulate the basic sounds of language. The individual sounds of language become 'sticky', unable to be broken apart and manipulated easily. This type of dyslexia is synonymous with dyslexia itself.
What are the two types of short-term memory?
Within Baddeley's influential 1986 model of working memory two short-term storage mechanisms appear: the phonological loop and the visuospatial sketchpad.
Which type of memory is first affected by dementia?
Loss of memory is among the first symptoms reported by patients suffering from Alzheimer's disease (AD) and by their caretakers. Working memory and long-term declarative memory are affected early during the course of the disease.
What are examples of short-term memory?
For the purpose of a discussion on memory loss, short term memory is equivalent to very recent memories, usually measured in minutes-to-days. Examples of short term memory include where you parked your car this morning, what you had for lunch yesterday, and remembering details from a book that you read a few days ago.
What are the 3 components of working memory?
The three subcomponents involved are phonological loop (or the verbal working memory), visuospatial sketchpad (the visual-spatial working memory), and the central executive which involves the attentional control system (Baddeley and Hitch, 1974; Baddeley, 2000b).
What is meant by working memory?
Working memory is the small amount of information that can be held in mind and used in the execution of cognitive tasks, in contrast with long-term memory, the vast amount of information saved in one's life. Working memory is one of the most widely-used terms in psychology.
How do you assess phonological working memory?
Phonological working memory is assessed using 'digit span', 'digit span-running', and 'nonword repetition' tasks. The 'digit span' task requires children to repeat lists that vary in length from 2-8 digits. This task is presented to children in the context of playing a copycat game with a robot.
What does phonological processing mean?
Definition. The ability to quickly and correctly hear, store, recall, and make different speech sounds.
Abstract
In our research we addressed the question what the relationship is between phonological short-term and working memory capacity and performance in an end-of-year reading, writing, listening, speaking and use of English test.
Access options
Get access to the full version of this content by using one of the access options below. (Log in options will check for institutional or personal access. Content may require purchase if you do not have access.)
Footnotes
Judit Kormos has been supported in writing this article by the Bolyai Scholarship of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences.
Introduction
The model of phonological short-term memory (pSTM) proposed by Baddeley et al. in 1984 [1] includes two components: a phonological buffer or store that can hold memory traces for a few seconds, and a subvocal rehearsal process used to refresh memory traces ( Figure 1 a ).
How does speech affect pSTM performance?
The phonological buffer is assumed to store verbal information transiently, and verbal information seems to be stored independently of non-verbal information. Recall performance is better with speech sounds than non-speech sounds [7] and recall of speech and non-speech sounds can be selectively damaged in patients [8].
One or two phonological buffers?
Debate continues as to whether there are two separate phonological buffers in perception and in production, or only one perceptual buffer [18].
What is the role of pSTM in speech processing?
Models of speech processing do not emphasize the role of pSTM, although both perception and production systems arguably require some buffer capacities to be operative.
Conclusion
Buffering is essential when interacting processes function on different timescales, and both speech production and perception require that activation be maintained at various points in processing.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by ESRC (C.J.) and the Wellcome Trust (S.K.S.).
What is Phonological Memory?
Phonological memory is the ability to hold information (numbers, sounds, words) in working or short-term memory for temporary storage. Students must be able to hold information long enough to process it, use it, and then transfer it to long-term memory.
Why Poor Phonological Memory is a Problem
Poor phonological memory can hinder a student’s ability to accomplish most tasks including:
How to Help a Child with Poor Phonological Memory
Helping a child with weak phonological memory to be successful in the classroom requires us to be mindful of the following:
C.A.R.S.: Remember this mnemonic and your students will be off and running!
C hunk Information into smaller parts for mental storage. Only introduce one or two concepts at a time and pause strategically when talking.
Why is short term memory 7?
He though that short term memory could hold 7 (plus or minus 2 items) because it only had a certain number of “slots” in which items could be stored. However, Miller didn’t specify the amount of information that can be held in each slot.
What are the three aspects of short term memory?
Short term memory has three key aspects: 2. limited duration (storage is very fragile and information can be lost with distraction or passage of time) 3. encoding (primarily acoustic, even translating visual information into sounds). There are two ways in which capacity is tested, one being span, the other being recency effect. ...
What is the rapid loss of information from memory when rehearsal is prevented?
The rapid loss of information from memory when rehearsal is prevented is taken as an indication of short term memory having a limited duration. Baddeley and Hitch (1974) have developed an alternative model of short-term memory which they call working memory.
Which technique prevents the possibility of retrieval by having participants count backwards in 3s?
Using a technique called the Brown-Peterson technique which prevents the possibility of retrieval by having participants count backwards in 3s. Peterson and Peterson (1959) showed that the longer the delay, the less information is recalled. The rapid loss of information from memory when rehearsal is prevented is taken as an indication ...