What are the effects of phosphates in a pond?
When there’s an excess amount of phosphates, your pond water loses clarity and becomes polluted by a murky green overcast. The effects of this buildup can become unhealthy to the water, fish, and aquatic organisms. If your pond has nutrient buildup, we recommend reducing phosphorus levels early on to improve the health of the water.
What are phosphates and why are they important?
Phosphates are a form of phosphorus that naturally occur in ponds and water features. Depending on the surrounding environmental factors, like rainfall, fertilizer runoff, and more, the levels of this nutrient can vary.
What are phosphates po4-3 in a pond?
High Phosphates in your Pond/Lake=Toxic. Phosphorus occurs naturally in rocks and other mineral deposits. During the natural process of weathering, the rocks gradually release the phosphorus as phosphate ions which are soluble in water and the mineralize phosphate compounds breakdown. Phosphates PO4-3 are formed from this element.
Will too much phosphate Kill my Fish?
I also read that as long as ammonia Nitrites & PH Are normal a 2.0 ppm reading for phosphate will not kill your fish. Also add plenty of plant life to your pond they need phosphate and will help in balancing the ecosystem in your pond.

What causes high phosphate in a pond?
Erosion. Erosion happens to be a primary cause of phosphate production. Over time, rainfall erodes rocks and similar compositions found in soul. As rain continues to fall and release sediments from erosion, it also causes phosphate runoff into adjacent waters.
How do I lower phosphates in my pond?
Remove old and damaged leaves as the season continues. If you have a filter system, clean out the captured debris regularly. Maintaining a filter in this way can remove those phosphates that are bound to fine particles in the water. This can almost halve the phosphate levels in the pond.
Is phosphate good for ponds?
While using phosphorous to grow beautiful flowers and bountiful crops in agriculture is all fine and good, when excess phosphorous gets into your pond, it accelerates aquatic plant growth and the occurence of algae blooms.
What is a high phosphate level for a pond?
Phosphate – Around 0.05 ppm.
Are phosphates harmful to fish?
If you allow phosphates to build up in your tank, they can contribute to algae blooms, which can starve the water of oxygen, resulting in a poor environment for your fish.
What happens if phosphate levels are too high in water?
Too much phosphorus can cause increased growth of algae and large aquatic plants, which can result in decreased levels of dissolved oxygen– a process called eutrophication. High levels of phosphorus can also lead to algae blooms that produce algal toxins which can be harmful to human and animal health.
What happens if phosphate levels are too low in water?
This rapid growth of aquatic vegetation eventually dies and, as it decays in the water, it uses up dissolved oxygen. This process, in turn, causes the death of aquatic life because of the lowering of dissolved oxygen levels.
What is a healthy level of phosphate in water?
To control eutrophication, the USEPA has established a recommended limit of 0.05 mg/L for total phosphates in streams that enter lakes and 0.1 mg/L for total phosphorus in flowing waters (U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, 1986).
What's the difference between phosphate and phosphorus?
Phosphorus is a multi-valent nonmetal chemical element of the VA group. Phosphate is a chemical derivative of the phosphoric acid, containing the phosphate ion (PO3−4). Formally, any salt of a phosphorus oxoacid is a phosphate. The molar mass of the phosphorus is 30.97 g/mol.
How do I know if my pond water is healthy?
The signs of a well-balanced pond include healthy fish, clear water, thriving plants, and minimal pests such as algae.
What should my pond water readings be?
In an established pond, the ideal alkalinity measurement should be around 100 ppm, but readings from 50 to 200 ppm are acceptable. If the alkalinity is low, even a small amount of acid can cause a large change in pH.
How do you reduce phosphorus in water?
ALUM (aluminum sulfate) is a nontoxic material commonly used in water treatment plants to clarify drinking water. In lakes alum is used to reduce the amount of the nutrient phosphorus in the water.
How do you reduce phosphorus in water?
ALUM (aluminum sulfate) is a nontoxic material commonly used in water treatment plants to clarify drinking water. In lakes alum is used to reduce the amount of the nutrient phosphorus in the water.
What is phosphate remover?
Phosphate reducers are specialty chemicals used to remove phosphates from pool water. They are typically salts of aluminum or lanthanum which, when added to water, produce insoluble phosphate compounds which are removed through filtration, vacuuming or both.
How do I lower the nutrients in my pond?
Dredging. Dredging can be a quick and effective way of removing nutrients. It will remove a vast amount of the organic “muck” on the bottom of the pond. Additionally, it will leave you with a deeper pond with less overall nutrients.
What causes phosphorus in lakes?
Under normal water flows, roughly two- thirds of the total phosphorus load to lakes and rivers comes from nonpoint sources such as runoff from pasture and croplands, atmospheric deposition and stream bank erosion.
Why are phosphates added to tap water?
Not only can phosphates be found in the rivers used for water supplies, but phosphates are added to tap water to reduce pipe corrosion and prevent lead from entering our drinking supply.
What is the source of phosphorus in fish?
Another source is fish food , which contains some phosphorus as it’s an essential part of their diet. A large proportion will pass through the koi, which is released into the fish waste. This waste releases phosphates into the water.
How high should a pond be above ground?
For example, ensure the edge of your pond is at least six inches above ground level. Regularly maintain your filtration system. By keeping up on the backwashing of your system, you’ll remove phosphates that are bound to fine particulates in the water.
What is the most important element in a pond?
Phosphorus is an essential element of life. Usually, it is bound with oxygen and other minerals to form phosphates. However, when high levels of phosphates are found in your pond, the chances of your pond having issues with algae blooms increase.
How much phosphorus should I put in my koi?
Also, take a look at the labels on your koi food, as some will list the phosphorus levels. Your food should have 1% or less. If it has more, you may want to look into switching foods.
Can a pond wash phosphates?
In addition, run-off from lawns, borders, and surrounding paving can wash phosphates into the pond, especially if the garden has had fertilizers applied .
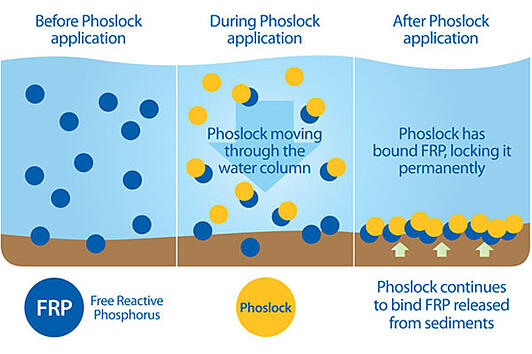
Can you use Orenda PR-10,000 to remove phosphates from a pond?
This can prove to be very useful in eliminating the phosphates in your pond. Last but not least, you can use a chemical to remove the phosphates from your pond. We suggest using Orenda PR-10,000 Phosphate Remover. While designed for pools in mind, we’ve found it safe and successful for use in koi ponds. Aeration.
What is phosphate in ponds?
Phosphates are a form of phosphorus that naturally occur in ponds and water features. Depending on the surrounding environmental factors, like rainfall, fertilizer runoff, and more, the levels of this nutrient can vary. When there’s an excess amount of phosphates, your pond water loses clarity and becomes polluted by a murky green overcast.
What happens if you add too much phosphate to your pond?
When there’s an excess amount of phosphates, your pond water loses clarity and becomes polluted by a murky green overcast. The effects of this buildup can become unhealthy to the water, fish, and aquatic organisms.
How does excess nutrients affect ponds?
Excess nutrients will stimulate the growth of aquatic weeds in the pond. Meaning, ponds weeds grow rapidly with high phosphate levels. The result of too many weeds affects the pond ecosystem in a negative way. Plus, the appearance of the pond overall isn’t pleasant. 2.
Why do we clean our water with phosphate negator?
We recommend cleaning with our Phos Negator product to maintain healthy phosphate levels.
How does phosphorus affect fish?
Too much of it can be deadly for aquatic life. According to the Water Research Center, the increase of nutrients reduces the amount of dissolved oxygen, endangering the lives of fish.
What to do if pond has nutrient buildup?
If your pond has nutrient buildup, we recommend reducing phosphorus levels early on to improve the health of the water.
What happens when phosphorus is added to water?
So, when phosphorus is added to water, algae and plants are able to grow and the water becomes “Eutrophic”. “Eutrophic is the term used to describe the condition of nutrient enrichment when aquatic plant growth becomes excessive. One of the key concerns of eutrophication is the impact of oxygen levels.” (Bruulsema, et al., 2011).
What is Nature's Pond?
Nature’s Pond three-step program is designed to fight phosphorus and nutrient pollution in ponds. With three simple steps you can Renew, Revive, and Remove to:
Why is phosphorus so difficult to manage?
The majority of phosphorus pollution in rural areas come from non-point sources such as cropland erosion and runoff, which is why nutrient pollution can be so difficult to manage. In freshwater untouched by nutrient pollution, plant and algae growth is slow and limited due to the low levels of phosphorus that occur naturally.
How to clean a pond?
Nature’s Pond three-step program is designed to fight phosphorus and nutrient pollution in ponds. With three simple steps you can Renew, Revive, and Remove to: 1 Create clean, clear water 2 Remove algae and weeds 3 Reduce pond sludge and odors 4 Be safe for people, pets, plants, fish, birds, livestock and wildlife
How can management help reduce phosphorus pollution?
Management practices can help reduce phosphorus pollution. Each case of nutrient pollution is unique , as different point or non-point sources can be at fault. Therefore, practices are usually specific to the sources, and what works for one case may not be suitable for every farm operation. However, there are some guiding principles that can apply to many agricultural operations.
What happens when a pond is bottom up aerated?
Once the phosphorus and other polluting nutrients have been broken down, bottom up aeration infuses the water with oxygen, allowing the digested nutrients to make its way out of the pond and into the air.
What happens when phosphorus is released into the environment?
When excessive amounts of phosphorus are released into the natural environment it causes environmental issues such as reduced levels of oxygen, accelerated plant and weed growth, and algae blooms of blue and green algae. The poor quality of water will cause a number of problems whether the water is used for irrigation, livestock, or drinking, contaminated water can be costly and difficult to treat.
How to know if a pond has phosphate?
Most of the time, the presence of phosphate in ponds and aquariums is not noticed until nuisance plant-like creatures start to grow. In outdoor ponds specifically, you will know if phosphate compounds are present if the color of the water starts to become pea green. Since phosphate is used as a fertilizer for plants to grow fast, expect to see algae to develop in your phosphate-infested pond water. Cyanobacteria or most commonly known as blue - green algae have bigger chance of residing in your pond if the phosphate contamination is not controlled.
Why should we check phosphate levels in the water?
Phosphates trigger the growth of unwanted living creatures in the pond like algae and blanket weed. If the origin is dealt with first, it is much easier to deal with the by-products. The less phosphate compounds present in your pond, the easier the maintenance will be . The use of algaecides and other pond necessities will surely be lessened once the phosphate levels in the pond are controlled.
Can a water pond test help with headaches?
Most of the problems in a water pond or an aquarium leave their owners confused since they are do not appear right away unless a water test is done. What is often disregarded can actually help lessen the headache that water parasites give the owners. This is the phosphate test.
Can salt water be used in ponds?
2. For those who use saltwater in ponds, try to test a sample before and after mixing the salt into the water. There is a high possibility that the phosphate will come from the salt.
Is phosphate in tap water dangerous?
The phosphate in tap waters usually comes from soil or run-off which normally contains fertilizers. This is most likely to occur in agricultural areas. Although the levels of phosphate are not dangerous to humans, there is a high chance for them to accrue in ponds and aquariums. Aside from tap water, phosphate can also instigate from saltwater used in aquariums and even from the decorations used in the either the pond or aquarium.
What is the phosphate system in a lake?
Phosphorus is one of the key elements necessary for growth of plants and animals and in lake ecosystems it tends to be the growth limiting nutrient and is a backbone of the Kreb’s Cycle and DNA. The presence of phosphorus is often scarce in the well-oxygenated lake waters and importantly, the low levels of phosphorus limit the production of freshwater systems (Ricklefs, 1993).Unlike nitrogen, phosphate is retained in the soil by a complex system of biological uptake, absorption, and minerialization. Phosphates are not toxic to people or animals unless they are present in very high levels. Digestive problems could occur from extremely high levels of phosphate. The soluble or bio-available phosphate is then used by plants and animals. The phosphate becomes incorporated into the biological system but the key areas include: ATP, DNA, and RNA. ATP, adenosine triphosphate, which is important in the storage and use of energy and a key stage in the Kreb’s Cycle. RNA and DNA are the backbones of life on this planet, via genetics. Therefore the availability of phosphorous is a key factor controlling photosynthesis.
Why are phosphates harmful to aquatic plants?
These phosphates become detrimental when they over fertilize aquatic plants and cause stepped up eutrophication. Eutrophication is the natural aging process of a body of water such as a bay or lake. This process results from the increase of nutrients within the body of water which, in turn, create plant growth.
What is the phosphate that is bound or tied up in plant tissue?
In water, they are transform into orthophosphate and available for plant uptake. Organic phosphates is typically estimated by testing for total phosphate. The organic phosphate is the phosphate that is bound or tied up in plant tissue, waste solids, or other organic material.
How does phosphate affect the ecosystem?
Phosphate will stimulate the growth of plankton and aquatic plants which provide food for larger organisms, including: zoo plankton, fish, humans, and other mammals. Plankton represent the base of the food chain. Initially, this increased productivity will cause an increase in the fish population and overall biological diversity of the system. But as the phosphate loading continues and there is a build-up of phosphate in the lake or surface water ecosystem, the aging process of lake or surface water ecosystem will be accelerated. The over production of lake or water body can lead to an imbalance in the nutrient and material cycling process (Ricklefs, 1993). Eutrophication (from the Greek – meaning “well nourished”) is enhanced production of primary producers resulting in reduced stability of the ecosystem. Excessive nutrient inputs, usually nitrogen and phosphate, have been shown to be the main cause of eutrophication over the past 30 years. This aging process can result in large fluctuations in the lake water quality and trophic status and in some cases periodic blooms of cyanobacteria.
How does phosphorus affect aquatic life?
How phosphorous affects aquatic life. If too much phosphate is present in the water the algae and weeds will grow rapidly, may choke the waterway, and use up large amounts of precious oxygen (in the absence of photosynthesis and as the algae and plants die and are consumed by aerobic bacteria.)
How does rain affect phosphates?
Environmental Impact: Rainfall can cause varying amounts of phosphates to wash from farm soils into nearby waterways. Phosphate will stimulate the growth of plankton and aquatic plants which provide food for fish.
What happens to the water in anaerobic conditions?
In anaerobic conditions (absence of oxygen), as conditions worsen as more phosphates and nitrates may be added to the water, all of the oxygen may be used up by bacteria in trying to decompose all of the waste. Different bacteria continue to carry on decomposition reactions, however the products are drastically different. The carbon is converted to methane gas instead of carbon dioxide, sulfur is converted to hydrogen sulfide gas. Some of the sulfide may be precipitated as iron sulfide. Under anaerobic conditions the iron phosphate precipitates in the sediments may be released from the sediments making the phosphate bioavailable. This is a key component of the growth and decay cycle. The pond, stream, or lake may gradually fill with decaying and partially decomposed plant materials to make a swamp, which is the natural aging process. The problem is that this process has been significantly accelerated.
