What are the disadvantages of spectroscopy?
Disadvantages of Raman spectroscopy
- Raman spectroscopy is very sensitive
- Quite costly equipment.
- Metal or alloy can not be used.
- Difficult to measure low concentrate on samples
- Sample heating through the laser radiation can destroy sample.
What is the importance of spectroscopy?
Why is Spectroscopy Important?
- Astronomers determine the temperature, density, mass, and motion of an object in the space or coming towards Earth through spectroscopy.
- Doppler Effect in a spectral line tells us the speed of the object coming towards Earth.
- It transforms light into a spectrum using a prism that can be observed through a telescope.
What is ultravoilet spectroscopy?
Ultraviolet spectroscopy is performed with a special device known as an ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometer. Ultraviolet spectroscopy, often combined with visible spectroscopy, is a technique that is used in scientific and industrial laboratories to determine which wavelengths of light a chemical solution absorbs.
What is the plural of spectroscopy?
The noun spectroscopy can be countable or uncountable. In more general, commonly used, contexts, the plural form will also be spectroscopy . However, in more specific contexts, the plural form can also be spectroscopies e.g. in reference to various types of spectroscopies or a collection of spectroscopies. Find more words!

What are the main applications of XPS?
XPS is routinely used to analyze inorganic compounds, metal alloys, semiconductors, polymers, elements, catalysts, glasses, ceramics, paints, papers, inks, woods, plant parts, make-up, teeth, bones, medical implants, bio-materials, coatings, viscous oils, glues, ion-modified materials and many others.
What information can be extracted from XPS?
Thus the XPS spectra give the information about elemental composition, empirical formula, chemical state and electronic state of the constituting elements of the material. This technique can be a qualitative, quantitative or semi-quantitative method (Zhang et al., 2016).
How does a photoelectron spectrum work?
1:128:24Introduction to photoelectron spectroscopy | AP ChemistryYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThey move away. And they enter into a magnetic field that will deflect those electrons. And thenMoreThey move away. And they enter into a magnetic field that will deflect those electrons. And then make them hit a detector. And so you can imagine the electrons that are closer to the nucleus. Those
What is the main principle of XPS?
the photoelectric effectThe basic principle of XPS is the photoelectric effect discovered by Hertz in 1887 [7, 8] and extended to surface analysis by K. Siegbahn and his research group at Uppsala University, Sweden, during the mid-1960s. Siegbahn won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1981 for his work in XPS and coined the acronym ESCA [9].
What data does XPS give?
XPS can measure elemental composition as well as the chemical and electronic state of the atoms within a material. XPS spectra are obtained by irradiating a solid surface with a beam of X-rays and measuring the kinetic energy of electrons that are emitted from the top 1-10 nm of the material.
How many types of Photoelectron spectroscopy are there?
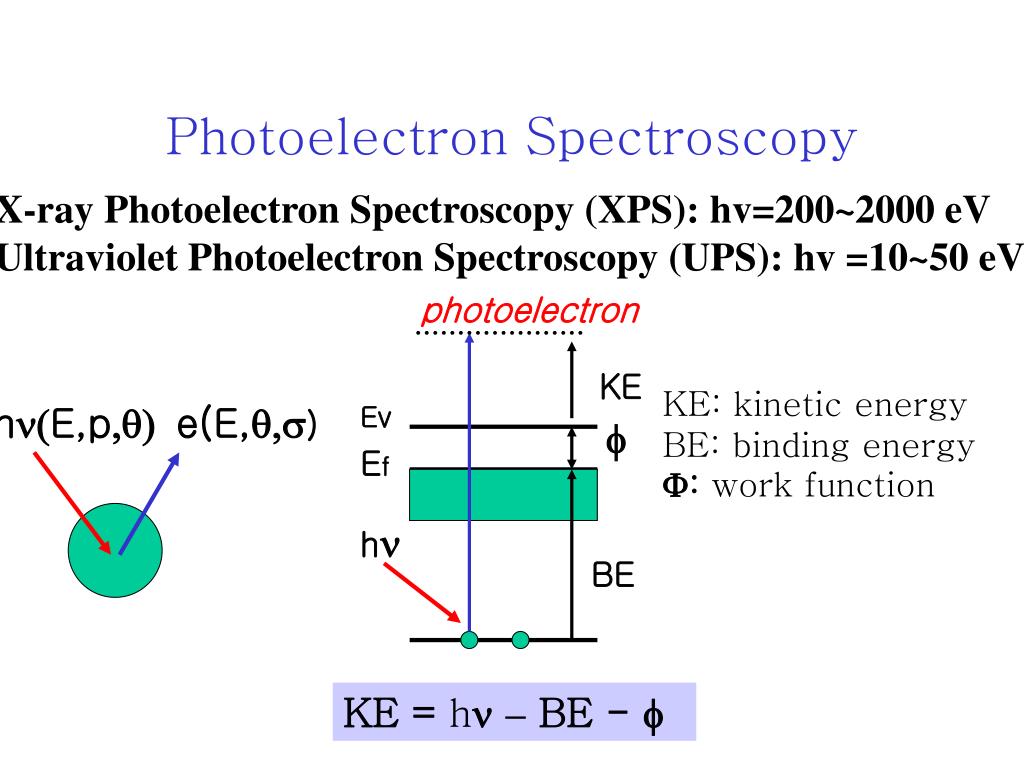
The field is usually arbitrarily divided into two classes: ultraviolet photoelectron spectroscopy (UPS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The names derive from the energies of the photons used in the particular spectroscopy.
Does photoelectron depend on frequency?
The number of photoelectrons that are emitted from the metal depends on the intensity of the incident light but is independent of its frequency.
What does a photoelectron spectrum tell us about the structure of an atom?
Photoelectron spectroscopy (PES) allows scientists to determine the ionization energy of not only valence electrons, but all electrons in an atom. In PES, a gaseous sample of atoms is bombarded by X-rays or ultra- violet light (photons) of known energy.
How do you analyze an XPS file?
How to Analyze XPS Spectra DataThe X-Axis: Peak Position.The Y-Axis: Peak Intensity.Overlapping Peaks.More than One Elemental Peak.Analysis of Haze on a Polyimide Substrate.Passivation Integrity of Stainless Steel.
Can XPS detect functional groups?
XPS is one of the most widely used surface analytical techniques. It allows a quantitative elemental analysis of surfaces, however its ability to detect and quantify a number of functional groups is limited [21].
How do I read XPS files?
How to interpret the data it generatesPeaks from the XPS spectra give relative number of electrons with a specific binding energy. The shorter the peak, the less electrons represented. ... The greater the binding energy, the greater the attraction of that electron to the nucleus.
What is survey scan in XPS?
High resolution C1s spectrum showing Carbon-Oxygen and Fluorocarbon bonding states. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) is a highly surface-specific chemical analytical technique used to probe the elemental composition and bonding states in the outermost 2-10 nm of a solid surface.
How does photoelectron spectroscopy work?
Photoelectron spectroscopy simply applies the photoelectric effect to free atoms or molecules instead of metals . In PES, a sample is bombarded with high-energy radiation, usually UV or X-ray, which causes electrons to be ejected from the sample. The ejected electrons travel from the sample to an energy analyzer, where their kinetic energies are recorded, and then to a detector, which counts the number of photoelectrons at various kinetic energies. A simplified diagram of this process is shown below.
What is the basic idea of photoelectron spectroscopy?
The photoelectric effect is as follows: when electrons in a metal are exposed to light of sufficient radiation, the electrons are ejected from the metal surface.
What does the PES spectrum show?
The PES spectrum shows two peaks, which represent electrons in the different subshells of lithium ( and ). The peak that is closer to the origin is twice as intense as the farther peak. The subshell of lithium contains twice as many electrons as the subshell ( vs. ), so the peak closer to the origin must correspond to lithium's subshell.
What is the energy required to eject an electron from a sample?
The energy required to eject an electron from the sample is known as the electron’s ionization energy or binding energy . We know the energy of the radiation () used to eject the electron. So, by measuring the kinetic energy of the photoelectron ( ), we can calculate the binding energy () of the electron in the sample:
What does the peak of a PES spectrum mean?
A typical PES spectrum features peaks at different binding energies. Because electrons in a particular subshell of an atom have the same binding energy, each of these peaks corresponds to electrons in a different subshell. The binding energy of a peak tells us how much energy is required to remove an electron from the subshell, and the intensity of the peak tells us the relative number of electrons in the subshell.
What is the purpose of photoelectron spectroscopy?
Photoelectron spectroscopy involves the measurement of kinetic energy of photoelectrons to determine the bonding energy,intensity and angular distributions of these electrons and use the information obtained to examine the electronic structure of molecules.
What is XPS in chemistry?
XPS is also known under its former name of electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA). UPS focuses on inoization of valence electrons, while XPS involves ionizing core electrons. Photoelectron Spectroscopy: Theory. Photoelectron spectroscopy involves the measurement of kinetic energy of photoelectrons to determine the binding energy, ...
Hydrogen Chloride
The molecular energy level diagram for HCl is reproduced in Figure 10.4.5
Water
In the simplified valence bond theory perspective of the water molecule, the oxygen atom form four s p 3 hybrid orbitals. Two of these are occupied by the two lone pairs on the oxygen atom, while the other two are used for bonding.
Summary
A photoelecton spectrum can show the relative energies of occupied molecular orbitals by ionization. (i.e. ejection of an electron). A photoelectron spectrum can also be used to determine energy spacing between vibrational levels of a given electronic state.
What is X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy?
Provenance: Imaging and Chemical Analysis Laboratory, Montana State University; used by permission.
How are XPS spectra used?
XPS data are presented as spectra that plot Binding Energy (eV) on the X-axis vs. measured photoelectron counts on the Y-axis. Data are typically collected in a) Survey mode to obtain the complete inventory of elements on a material surface, and b) high resolution scans of peaks of interest to reveal the bound state (chemical bonds) involving elements of interest. The binding energies of the numerous photoelectrons emitted from a surface sample are used as a "fingerprint" to identify elements present. Chemical shifts in XPS spectra are observed when an element enters a different bound state, which results in changes in the binding energy of core electrons. In general, increased oxidation state (removal of valence electrons) increases the Binding Energy and addition of valence electrons decreases the Binding Energy.
What is XPS in physics?
XPS is an application of the photoelectric effect (Acrobat (PDF) 184kB Jul29 21) described by Einstein (19 05, and was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1921), in which electrons are emitted from atoms in response to impinging electromagnetic radiation. Einstein predicted that photoelectrons would be produced from a material when the energy of impinging photons exceed the binding energy of electrons in that material; the energy is proportional to the frequency ( ℎν ) not the intensity or duration of exposure to the incident electromagnetic radiation. The kinetic energy of an emitted electron is related to the binding energy of each electron, and because atoms have multiple orbitals at different energy states, the resulting response will be a range of emitted electrons with different binding energies (and kinetic energies) thus producing an XPS spectrum.
Why are samples used for XPS analysis analyzed as received?
Typically, samples used for XPS analysis are analyzed "as received" because any chemical treatments will leave a contaminating residue. Here are some practical tips:
What is an electron energy analyzer?
An electron energy analyzer is used to discriminate among the energies of the photoelectrons that are produced. This is typically a Concentric Hemispherical Analyzer (CHA).
How to find the intensity of photoelectrons?
The intensity of photoelectrons emitted at the surface (I s) is determined by the Beer-Lambert Law: I s = I o e -d/λ where I o is the intensity of the photoelectrons emitted at depth d below the surface and λ is the inelastic mean free path of the electron in the material. Most λ 's are on the order of 1-3.5 nm for AlK α X-rays, so the sampling depth is typically3-10 nm.
What is the purpose of argon ion gun?
It is common practice to use an argon ion gun to gently "dust off" these surfaces to expose the actual materials of interest.

What Is Photoelectron Spectroscopy ?
Table of Contents
Photoelectron Spectroscopy Principle
Ultraviolet Photoelectron Spectroscopy
Photoelectric Effect
Application of Photoelectron Spectroscopy
- Electronic spectroscopy is used for detecting contaminants, controlling purification, studying the kinetics of chemical reactions, determining molecular weight, and determining unknown concentrations. Because it can probe down to core electrons, XPS has a wider range of possible applications than UPS. XPS is effective in identifying all elements ex...