
What does Asa stand for in medical terms?
ASA Physical Status Classification System | American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) ASA Physical Status Classification System The ASA Physical Status Classification System has been in use for over 60 years. The purpose of the system is to assess and communicate a patient’s pre-anesthesia medical co-morbidities.
What is the difference between Asa 2 and 3?
ASA II: A patient with mild systemic disease: Mild diseases only without substantive functional limitations. Examples include: current smoker, social alcohol drinker, pregnancy, obesity (30 < BMI < 40), well-controlled DM/HTN, mild lung diseaseASA III: A patient with severe systemic disease
What percentage of surgical patients are ASA I and Asa II?
Patients with age group 18 to 60 years planned for surgical procedure under general anaesthesia with ASA I and ASA II were included in study. Assessment of the ASA physical status showed that 78% of the TAP and 76% of the II-IH groups were ASA I and 21.56% of the TAP and 23.5% of the II-IH groups were ASA II (Table 1).
Is general anesthesia safe for Asasa II patients?
ASA II patients with mild systemic disease who have no functional limitations and have a well-controlled one body system disease (e.g., diabetes, hypertension, smoking without chronic obstructive pulmonary disease [COPD]) can tolerate general anesthesia as well as regional anesthesia or nerve blocks.
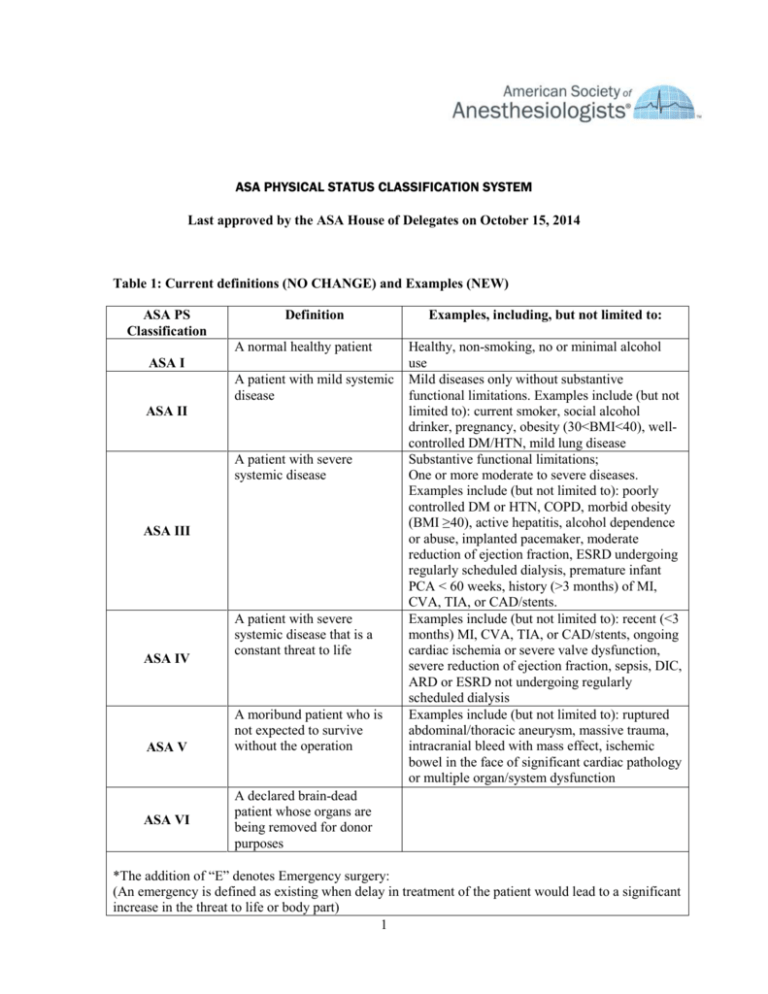
What does ASA 2 mean in medical terms?
ASA 2: A patient with mild systemic disease. Example: Patient with no functional limitations and a well-controlled disease (e.g., treated hypertension, obesity with BMI under 35, frequent social drinker, or cigarette smoker). ASA 3: A patient with a severe systemic disease that is not life-threatening.
What does ASA status mean in medical terms?
The ASA (American Society of Anesthesiology) score is a metric to determine if someone is healthy enough to tolerate surgery and anesthesia. The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) Physical Status Classification System is a tool used in preparation for surgery to help predict risks in a given patient.
What is an ASA score of 2?
ASA Physical Status Classification SystemASA PS ClassificationDefinitionASA IA normal healthy patientASA IIA patient with mild systemic diseaseASA IIIA patient with severe systemic diseaseASA IVA patient with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life2 more rows•Dec 13, 2020
What does physical status mean?
A classifying of physical condition by the Am Soc of Anesthesiologists that stratifies Pts undergoing surgery into categories of relative risk of suffering complications during surgery or in the immediate post-operative period.
What is an ASA level?
The ASA score is a subjective assessment of a patient's overall health that is based on five classes (I to V). Patient is a completely healthy fit patient. Patient has mild systemic disease. Patient has severe systemic disease that is not incapacitating.
What is class 2 mild systemic disease?
Class 2. Mild-to-moderate systemic disturbance caused either by the condition to be treated surgically or by other pathophysiologic processes (mild-to-moderate condition, well controlled with medical management; examples include diabetes, stable coronary artery disease, stable chronic pulmonary disease).
What is considered a mild systemic disease?
A patient with mild systemic disease. Mild diseases only without substantive functional limitations. Examples include (but not limited to): current smoker, social alcohol drinker, pregnancy, obesity (30 < BMI < 40), well-controlled DM/HTN, mild lung disease.
What are ASA codes?
Procedures and services are reported with codes and modifiers from the CPT® code set. CPT stands for Common Procedural Terminology and this code set is owned and maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA). Anesthesia codes – sometimes referred to as “ASA codes” are part of the CPT code set.
Is ASA 3 morbidly obese?
15 Consistent with the widespread belief that obesity is a systemic disease, one that is strongly associated with increased morbidity and mortality, the panel expressly included elevated body mass index (BMI) ranges as criteria for higher ASA-PS classification—i.e., ASA-II for “obese” patients with BMI of 30-40 kg·m−2 ...
Does age affect ASA classification?
Technically the ASA status, an assessment of the severity of preoperative co- morbid illnesses, does not include age as a criterion.
Which ASA physical status represents a patient who presents with severe systemic disease of at least one organ system that does cause functional limitation?
26.2. 1 Preoperative ConsiderationsASA PS ClassificationDefinitionASA IA normal healthy patientASA IIA patient with mild systemic diseaseASA IIIA patient with severe systemic diseaseASA IVA patient with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life3 more rows
What are ASA codes?
Procedures and services are reported with codes and modifiers from the CPT® code set. CPT stands for Common Procedural Terminology and this code set is owned and maintained by the American Medical Association (AMA). Anesthesia codes – sometimes referred to as “ASA codes” are part of the CPT code set.
What does ASA 3 mean in medical terms?
ASA 3: A patient with severe systemic disease with significant functional limitation, as follows: Alcohol dependence or abuse. Morbid obesity - BMI of more than 40. Poorly controlled DM and hypertension.
What does a patient with mild systemic disease mean?
Patients with mild systemic disease. No functional limitations; has a well-controlled disease of one body system; controlled hypertension or diabetes without systemic effects, cigarette smoking without chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD); mild obesity, pregnancy.
What does ASA mean in pharmacy?
Reviewed on 6/3/2021. ASA (drug caution code): Abbreviation on a medication that indicates it contains acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). This special caution code is intended to be a warning for patients with specific medical conditions.
What is the ASA Classification?
The American Society of Anesthesiologists Classification, or ASA Classification, is a physical status classification that is used to assess and communicate a patient’s pre-anaesthetic co-morbidities. By assessing this, we can then gauge potential complications we may encounter peri-operatively and try to mitigate/minimise these.
Is ASA I or II safe?
Generally, ASA I and II patients are safe to treat in general practice with none or minor modifications.
What is the ASA classification system?
The ASA physical status classification system is a system for assessing the fitness of patients before surgery. In 1963 the American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) adopted the five-category physical status classification system; a sixth category was later added. These are:
What is ASA 1?
Thus, in such hospitals, ASA 1 may still refer to a severe medical emergency, such as for example a moribund person due to a traumatic aortic rupture (which indicates the surgery) but otherwise being healthy.
Why do anesthesia providers use a preoperative scale?
Uses. While anesthesia providers use this scale to indicate a person's overall preoperative health, it may be misinterpreted by hospitals, law firms, accrediting boards and other healthcare organizations as a scale to predict risk, and thus decide if a patient should have – or should have had – an operation.
What is a moderate but definite systemic disturbance?
A moderate but definite systemic disturbance, caused either by the condition that is to be treated or surgical intervention or which is caused by other existing pathological processes, forms this group.
What is a Class 5 emergency?
A moribund person who is not expected to survive without the operation. A declared brain-dead person whose organs are being removed for donor purposes. If the surgery is an emergency, the physical status classification is followed by “E” (for emergency) for example “3E”. Class 5 is usually an emergency and is therefore usually "5E".
When was ASA class 1-4 first published?
The first four points of their scale roughly correspond to today's ASA classes 1-4, which were first published in 1963. The original authors included two classes that encompassed emergencies which otherwise would have been coded in either the first two classes (class 5) or the second two (class 6).
Can local diseases change physical status?
Local diseases can also change physical status but has not been mentioned in ASA classification. This classification system assumes that age has no relation to physical fitness, which is not true. Neonates and the elderly, even in the absence of any systemic disease, tolerate otherwise similar anesthetics poorly in comparison to young adults.
What does ASA mean in medical terms?
Definition. ASA 1: No organic pathology or patients in whom the pathological process is localized and does not cause any systemic disturbance or abnormality. ASA 2: A moderate but definite systemic disturbance. Examples: Mild diabetes.
What is ASA 3?
ASA 3: Severe systemic disturbance from any cause or causes. It is not possible to state an absolute measure of severity, as this is a matter of clinical judgment. Examples: Complicated or severe diabetes. Functional capacity IIb. Combinations of heart disease and respiratory disease or others that impair normal functions severely. Complete intestinal obstruction that has existed long enough to cause serious physiological disturbance. Pulmonary tuberculosis that, because of the extent of the lesion or treatment, has induced vital capacity sufficiently to cause tachycardia or dyspnea. Patients debilitated by prolonged illness with weakness of all or several systems. Severe trauma from accident resulting in shock, which may be improved by treatment. Pulmonary abscess.
What is the ASA classification system?
The American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status Classification System (ASA PS Classification System) was originally introduced in 1941. The “six degrees of Physical State” have undergone modification over the years ( Table 26.1 ), but remain meagerly changed ( Saklad, 1941 ). It remains relevant today having strong associations between 2- through 30-day mortality. While ASA Class communicates the risk of undergoing any procedure that requires anesthesia relative to the patient's underlying systemic illness, it has limitations in terms of interobserver reliability, type of surgery, and patient age ( Peersman, Laskin, Davis, Peterson, & Richart, 2008; Wolters, Wolf, Stützer, Schröder, & Pichlmaier, 1997 ). Recently, others have attempted to address some of the shortcomings of the ASA PS classification system. The Preoperative Score to Predict Postoperative Mortality (POSPOM) was validated against all surgical cases in France during the calendar year 2010. Over 5 million index surgical cases were performed. Interventional Neuroradiology had the fourth highest odds ratio of mortality at 1.19 with an observed mortality rate of 2.53% (out of 25 surgical cohorts) as defined by death after surgery and before discharge. Sixteen preoperative factors plus the type of surgery were shown to be predictive of mortality ( Le Manach et al., 2016) ( Table 26.2 ). In reality, chronic diseases such as those listed are effectively nonmodifiable risk factors for the interventionalist. In addition, recent data from the ACS-NSQIP program clearly shows that emergency procedures have patterns of statistically different risk estimates than elective procedures ( Hyder et al., 2016 ).
What is the ASA score?
The ASA physical status classification system is the most commonly used risk scoring system for surgical patients. Though the original scoring did not include obesity as a risk factor, BMI ≥ 40 kg/m 2 is considered as ASA Status III in the recent update. 54 The Obesity Surgery Mortality Risk Score is mainly used for patients undergoing gastric bypass, but it can be used for non-bariatric surgeries. This includes 5 risk factors: hypertension, BMI ≥ 50 kg/m 2, male sex, ≥ 45 years, and known risk factors for pulmonary embolism (OHS, previous thromboembolism, preoperative vena cava filter, pulmonary hypertension). 55 This risk score stratifies mortality risk into low (0 or 1 comorbidity), intermediate (2 to 3 comorbidities) and high (4 to 5 comorbidities) with mortality of 0.2%, 1.2%, and 2.4% respectively. 55 However, obesity is not included in other commonly used surgical risk scoring systems like POSSUM (Physiological and Operative Severity Score for the enumeration of Mortality and Morbidity), SORT (Surgical Outcome Risk Tool) and NSQIP (National Surgical Quality Improvement Program) surgical risk calculator. 56–58
What is the greatest predictor of sedation-related airway complications?
ASA class III or greater is the greatest predictor of sedation-related airway complications ( Wani et al., 2011 ). Cardiopulmonary risk increases in ASA III and doubles for every level increase in ASA class. Age and BMI > or = to 30 are independent risk factors for sedation-related complications as well. The age-adjusted rate of obesity in America is 33.8%. Thus, the obese patient is a common participant in the endovascular suite. The most common sedation-related event is hypoxemia and the need for airway maneuvers. However, despite this, the overall rate of procedure termination and the need for intubation should remain low, at less than 1% ( Wani et al., 2011 ). Patients with a history of congestive heart failure are of significant concern relative to the constant flushing of catheters at the access site and for each point in the vascular access construct. The surgeon should assess the patient airway and acquire a history relative to any anesthesia-related complications in the past.
What is the USC physical evaluation system?
The University of Southern California (USC) physical evaluation system is based on the ASA's physical status classification system. 32 It details four risk categories based on a patient's medical history and physical evaluation. The ASA categories for BP recordings in adults are presented in Table 4-5. 33,34
What is inadequate preoxygenation?
Inadequate preoxygenation, defined as a FEO 2 <90% after 3 min of tidal volume breathing , is seen frequently in practice (56% in a sample of 1050 patients) [54]. The effective FiO 2 delivered was observed to be lower in patients with a FEO 2<90%. Risk factors for inadequate preoxygenation were determined to be bearded male, beardless male, ASA physical status classification system >1, lack of teeth, and age >55 years. These predictive factors overlap with those previously associated with difficult mask ventilation [56].
What is the ASA classification?
American Society of Anesthesiologists physical status classification system ASA physical status classification Definition ASA I A normal healthy patient ASA II A patient with mild systemic disease ASA III A patient with severe systemic disease ASA IV A patient with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life ASA V A moribund patient who is not expected to survive without the operation ASA VI A declared brain-dead patient whose organs are being removed for donor purposes ASA = American Society of Anesthesiologists.
What is the American Society of Anesthesiology classification?
American Society of Anesthesiology Classification. A system used by anesthesiologists to stratify severity of patients' underlying disease and potential for suffering complications from general anesthesia. American Society of Anesthesiology patient classification status. ASA I.

What Is The Asa Classification?
- The American Society of Anesthesiologists Classification, or ASA Classification, is a physical status classification that is used to assess and communicate a patient’s pre-anaesthetic co-morbidities. By assessing this, we can then gauge potential complications we may encounter peri-operatively and try to mitigate/minimise these. It has been used fo...
The Asa Classes
- Below is a table that describes the classes with their definitions and examples as provided by the American Society of Anesthesiologists. A patient just needs one of the conditions listed to put them in to that category and we take the highest class for that patient. If we consider the dental implications of these classes: 1. Generally, ASA I and II patients are safe to treat in general pract…
Examples of The Asa Classification
- Example 1
In this example, we are told the patient is a type 2 diabetic. The reading we are provided is a HbA1c of 5%. Ideally, for well-controlled diabetes, the HbA1c should be below 7% – therefore this patient is well-controlled. Additionally, the patient is an asthmatic but they rarely use their inhale… - Example 2
As discussed above, this patient’s diabetes would be classed as well-controlled given the HbA1c reading. Her BMI is 33, which would also put her in an ASA 2 group like the diabetes. However, the patient has had an MI in the last 3 months and therefore, they would fall in to an ASA IVgroup. El…
Asa Classification Summary
- The ASA Classification is a physical status classification used to determine a patient’s risk with anaesthesia.
- The classification runs from ASA I to ASA VI. The higher the number, the greater the risk.
Useful Links & Recommended Reading