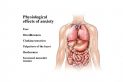
What happens physiologically during anxiety?
The release of adrenaline triggered by the Sympathetic Nervous System is what creates the symptoms of anxiety. For any known or unknown reason, the body senses a danger and needs to prepare to fight or flee. It automatically puts the body into a state of anxiety as a survival mechanism.
What is the physiology of anxiety?
The physiology of anxiety is the reason for worrying to understand what is wrong. To understand event, there must be a stimuli for what is that.
How to reduce the physical symptoms of anxiety?
Take Care of Yourself Physically
- Avoid certain foods or drinks that may trigger or worsen anxiety. ...
- Physical exercise can help relieve stress and tension felt throughout the body, increase energy levels, and improve mood.
- Stress-reducing relaxation exercises, such as yoga and meditation can help you learn how to control your body sensations and remain calm in the face of anxiety.
What are the signs of anxiety?
What are the major signs of anxiety?
- Restlessness, or feeling on edge
- Being easily fatigued
- Difficulty concentrating
- Irritability
- Muscle tension
- Sleep disturbance
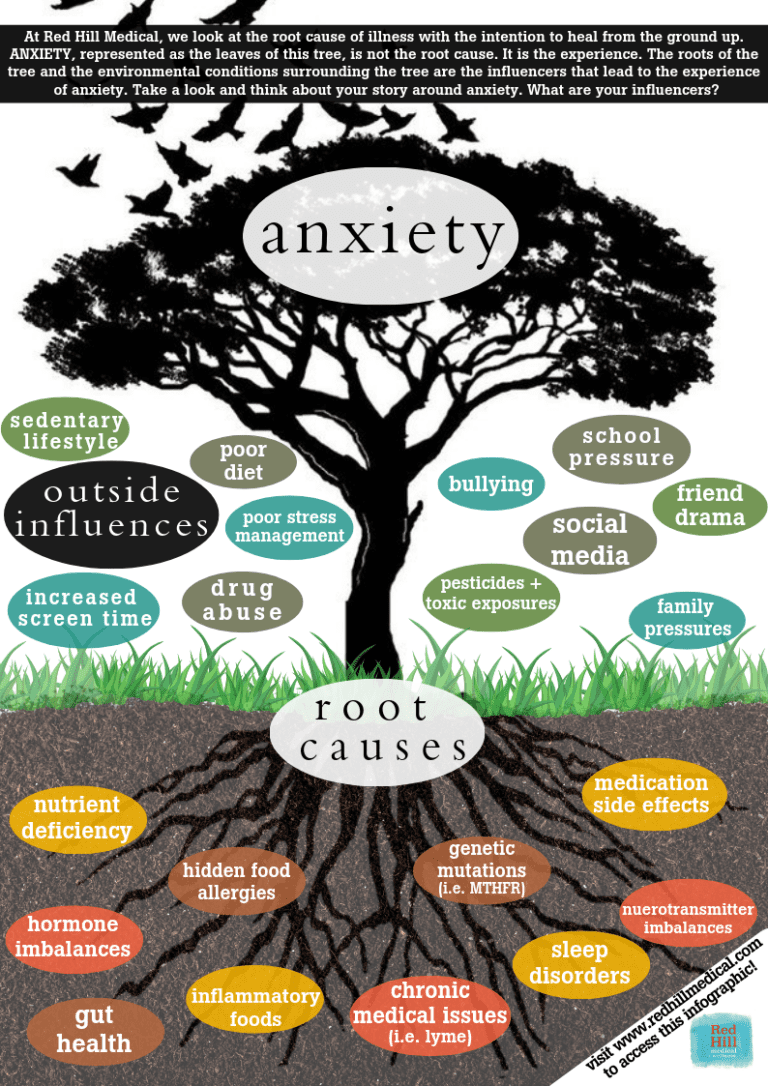
What are the physiological symptoms of anxiety?
Common anxiety signs and symptoms include:Feeling nervous, restless or tense.Having a sense of impending danger, panic or doom.Having an increased heart rate.Breathing rapidly (hyperventilation)Sweating.Trembling.Feeling weak or tired.Trouble concentrating or thinking about anything other than the present worry.More items...
What is psychology anxiety?
Anxiety is an emotion characterized by feelings of tension, worried thoughts, and physical changes like increased blood pressure. People with anxiety disorders usually have recurring intrusive thoughts or concerns. They may avoid certain situations out of worry.
What causes anxiety physiologically?
Anxiety may be caused by a mental condition, a physical condition, the effects of drugs, stressful life events, or a combination of these. The doctor's initial task is to see if your anxiety is a symptom of another medical condition. Anxiety disorders are different from normal anxiety.
How do I stop physiological anxiety?
Physical exercise can help relieve stress and tension felt throughout the body, increase energy levels, and improve mood. Stress-reducing relaxation exercises, such as yoga and meditation can help you learn how to control your body sensations and remain calm in the face of anxiety.
Is anxiety a mental or psychological?
An anxiety disorder is a type of mental health condition. If you have an anxiety disorder, you may respond to certain things and situations with fear and dread. You may also experience physical signs of anxiety, such as a pounding heart and sweating. It's normal to have some anxiety.
What is a physiological problem?
A physiological disorder is a condition in which the organs in the body malfunction causes illness. Examples are Asthma, Glaucoma, Diabetes.
What is the chemical imbalance that causes anxiety?
The “Chemical Imbalance” Theory The neurotransmitters serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) are specifically believed to be linked to mood and anxiety disorders.
Can anxiety damage the brain?
Summary: Pathological anxiety and chronic stress lead to structural degeneration and impaired functioning of the hippocampus and the PFC, which may account for the increased risk of developing neuropsychiatric disorders, including depression and dementia.
Can a brain scan show anxiety?
Brain imaging can reveal unsuspected causes of your anxiety. Anxiety can be caused by many things, such as neurohormonal imbalances, post-traumatic stress syndrome, or head injuries. Brain scans can offer clues to potential root causes of your anxiety, which can help find the most effective treatment plan.
How do you calm down psychologically?
Here's Why, and How...9 answers for how to calm down—straight from psychologists.Get yourself out of the situation (if you can) ... Picture your emotions visually to understand them better. ... Crack open a journal and let the words flow out of you. ... Meditate or practice all the yoga. ... Carve out time to exercise.More items...•
The Amygdala: Where It All Starts
The amygdala, a pair of small, almond-shaped clusters of neurons near the base of the brain, is thought to be the starting point of anxiety reactio...
The Medulla Oblongata: Where's My Air?
The amygdala starts by communicating with the parabrachial nucleus, a structure looking something like a small gray horseshoe, which, in turn, trig...
The Nucleus ambiguus and Hypothalamus: Getting on Your Nerves
The nucleus ambiguus, located just below the medulla oblongata, is the part that receives its urgent call for more blood to transport extra oxygen....
Adrenal Medulla: Energy Plus Crash
Your sympathetic nerves alert the adrenal medulla to release that famous hormone that goes by the name of adrenaline into the body, along with a sm...
Medial Prefrontal Cortex: What Do You think?
The amygdala is connected to the prefrontal cortex of the brain by way of neuronal pathways, which is the part of your brain that thinks about your...
What Causes Anxiety Physiological?
Maladaptive Beliefs are the main cause of anxiety. For some people it is some event that happened in their childhood. For others, it is the person’s lifestyle. Once you discover what is causing your anxiety, you can work on it. But first, you have to figure out what is causing your anxiety. This means you have to do some research on your mind.
Is anxiety a physiological problem?
Anxiety is a state of mind characterized by feelings of tension, worries, fears, apprehensions, and/or ruminations. It may also include physical sensation of shortness of breath, increased heart rate, muscle tension, restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, etc.
What does physiological anxiety mean?
Physiological anxiety can be both a medical and a psychological problem. In case of a medical problem, the best thing to do is to see your doctor. In case of a psychological problem, you can go to a psychiatrist or speak to a close friend or a family member about it. The best cure for this is to go out and do something you like doing.
What is the 3 3 3 rule for anxiety?
The 3-3-3 Rule is an exercise that supposedly helps you deal with anxiety. When you feel anxious, stop what you’re doing and focus on your breathing. After three deep breaths, look around for 3 things that are different. Spend 3 minutes on each of your three observations..
Why does one person cause me anxiety?
A lot of people get anxious when speaking to someone they don’t know. Some people think they will get anxious when speaking to anyone they don’t know. The cause of this anxiety is something called the “Uncertainty Principle”..
How do I stop physiological anxiety?
Physiological anxiety is a nervousness which comes from your brain and nervous system. It is a natural part of our lives, and we learn to cope with it over time. The severity of this issue can be minimised by avoiding the cause of it. The best way to get rid of it is to avoid the triggers.
What is a physiological cause?
A physiological cause is a cause of a physical nature. The physiological causes of disease and disability include both genetic and nongenetic factors. Because a physiological cause is a physical cause, it is a cause that can be detected through a physical examination. The physical examination is a means of finding a physiological cause.
Why does anxiety get worse?
Aside from external factors anxiety can be triggered (and/or worsened) due to physiological reasons within the body. In her book, “The Mood Cure”, Julia Ross explains that, “ much of our increasing emotional distress stems from easily correctable malfunctions in our brain and body chemistry- malfunctions that are primarily the result of critical, unmet nutritional needs ” (2).
What amino acid causes anxiety?
For example deficiencies in, GABA, tryptophan, tyrosine, and glutamine have all been found to be connected to anxiety levels (6)
Is anxiety a physiological or physiological problem?
So, to answer the question of “what causes anxiety? ” – it’s important to understand that yes, there are often external factors that trigger anxiety – however there’s also underlying physiological causes for anxiety and/or physiological reasons that can make it worse.
Can food allergies cause anxiety?
Undiagnosed food sensitivities or allergies can be a very sneaky cause of anxiety that one might not think to look for! In his book, Nutrition and Mental Illness, Dr. Pfeiffer explains, that food sensitivities can create imbalances in key chemicals in the brain (7). These imbalances can go on to cause anxiety, panic attacks, phobias, depression, irritability, and mood swings (8).
Can birth control cause anxiety?
It’s also important to note that anxiety can be a side effect of hormonal birth control . If you’ve struggled with anxiety for a long time and have also been on the pill – it could be a good idea to consider going off of it. Be sure to talk to a holistic health care practitioner to help set your body up for success as you transition off of it (9).
Does anxiety affect the luteal phase?
Most often , females who menstruate experience increased levels of anxiety in the luteal phase (pre-menstrual phase) of their cycle . This can often indicate estrogen dominance and can cause a lot of frustrating conditions within the body – anxiety being one of them!
Does eating whole foods cause anxiety?
A 2010 study done on woman found that those who ate a more “traditional” whole foods & nutrient dense diet of vegetables, fruit, fish, whole grains, and grass fed lean red meat and lamb had lower likelihood of both anxiety and depression (12).
What is the pathophysiology of anxiety?
Written by. Micah Abraham, BSc. Last updated October 10, 2020. The pathophysiology of anxiety is the way that the pathology of anxiety manifests itself in the body. It may be easier to think of it as the path anxiety follows through your body to result in the anxious state. While scientists think they know how anxiety is produced, ...
Where does anxiety start?
The Amygdala : Where It All Starts. The amygdala, a pair of small, almond-shaped clusters of neurons near the base of the brain, is thought to be the starting point of anxiety reactions. While it is not responsible for what you think when you encounter anxiety-producing stimuli, it is responsible for what your body does.
What does it mean when anxiety becomes overwhelming?
When anxiety starts to become overwhelming it may be a sign that you have moderate to severe anxiety. With this free 7 minute anxiety test, you can receive: Take the anxiety test today to gain better insight into your anxiety and its symptoms. Start The Test.
What is the job of the amygdala?
The job of the amygdala is to manage the storage of memories according to the strength of the emotional reaction associated with the memory. The right amygdala, primarily responsible for the action, is generally more active in men than in women. The left amygdala, on the other hand, is primarily responsible for storage of ...
Why do my muscles feel tired?
Your muscles, particularly those in your chest, may also be tired and even sore from the tension that helped to bring them their extra fuel, and from the rapid breathing that the lungs were doing to keep the blood of the heart supplied with oxygen.
Does the amygdala react to anxiety?
This means that although your amygdala reacts just like anyone else's, the thoughts and memories stored by the amygdala in the cortex are your own, and therefore what the amygdala reacts to can vary widely. The hyperactivity of the amygdala can only tell you that you may have an anxiety disorder, but not what specific type of disorder you have. ...
Which part of the body receives its urgent call for more blood to transport extra oxygen?
The nucleus ambiguus, located just below the medulla oblongata, is the part that receives its urgent call for more blood to transport extra oxygen. In response, the nucleus ambiguus causes the body's arterioles to constrict by way of its interaction with the parasympathetic nervous system, which makes the heart pump harder and faster.
What is anxiety disorder?
According to cognitive behavioural theories, anxiety disorders result from inappropriate thought processes and belief systems. According to psychoanalytic theory, anxiety disorders have their origins in childhood events such as separation or loss, and in unresolved childhood conflicts of psychosexual development.
What is anxiety in therapy?
Anxiety can be defined as ‘a state consisting of psychological and physical symptoms brought about by a sense of apprehension at a perceived threat’. Fear is similar to anxiety, except that with fear the threat is, or is perceived to be, more concrete, present, or imminent.
What are the mental disorders associated with anxiety?
Mental disorders associated with anxiety include mood disorders such as depression, psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia, and eating disorders such as anorexia or bulimia. Physical disorders associated with anxiety include endocrine disorders such as hyperthyroidism, Cushing’s disease, phaeochromocytoma, and hypoglycaemia, and drug and alcohol intoxication or withdrawal.
Why is anxiety considered a medical problem?
From a medical standpoint, anxiety becomes problematic when it becomes so severe, frequent, or longstanding as to prevent us from fulfilling our occupational or social obligations. This often owes to a primary anxiety disorder, although in some instances the anxiety is secondary to another mental disorder such as depression or schizophrenia, or to a medical disorder such as hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid gland) or alcohol withdrawal.
How common is anxiety disorder?
Primary anxiety disorders are very common, affecting almost one in every five people in the US in any given year. As broadly conceived, they present in a great variety of forms, including phobic anxiety disorders, panic disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, and post- traumatic stress disorder.
What hormones cause tremors?
In mild to moderate anxiety, a surge in the hormone adrenaline (epinephrine) gives rise to physical symptoms such as tremor, perspiration, and muscle tension. In severe anxiety, hyperventilation (over-breathing) can lead to a fall in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood.
What is the purpose of fear and anxiety?
In short, the purpose of fear and anxiety is to preserve us from harm, and, above all, from death —whether it be literal or metaphorical, biological or psychosocial. Problem.
What are the symptoms of social anxiety?
Physiological symptoms are the physical symptoms that occur when you feel anxious or under display. These are bodily reactions, and may be apparent to other people. Note that they are always stronger and more apparent to the person exhibiting them than to the person displaying them.
Can social anxiety be overcome?
Social anxiety can be overcome if it is done in the appropriate manner, and these symptoms dissipate along with it. Overcoming social anxiety isn't possible unless all the symptoms are alleviated as well. Thousands of people have overcome social anxiety based on our online therapy series. The good news is that all these conditions go away.
How does anxiety affect your body?
Specific types of anxiety might have additional physical symptoms. If you’re having a panic attack, you might: fear that you’re going to die. have trouble breathing or feel as if you’re choking. have numb or tingling sensations in parts of your body.
What does it feel like to have anxiety?
If you have anxiety, you might frequently feel worried, nervous, or afraid about ordinary events. These feelings can be upsetting and difficult to manage. They can also make daily life a challenge.
What is OCD in phobias?
phobias. obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) Some types of anxiety have unique symptoms specific to the fears linked to the anxiety. In general, though, anxiety disorders share many physical symptoms. Read on to learn more about anxiety’s physical symptoms and how they can affect you.
What is the best test for anxiety?
While there’s no medical test for anxiety, there are screening tools a psychiatrist, psychologist, therapist, or counselor may use to help determine if you have anxiety.
Why do we breathe when we are stressed?
When your body responds to danger, you breathe rapidly because your lungs are trying to move more oxygen through your body in case you need to escape.
Can anxiety cause asthma?
Research has further linked asthma and anxiety. A 2016 study suggested that either asthma or anxiety can cause or result from the other.
Can anxiety go away on its own?
Mild anxiety may go away on its own or after the event causing the anxiety is over, but chronic anxiety often persists and may get worse. If you aren’t sure how to find a therapist, you can ask your primary care provider for a referral. Therapist directories can also help you locate a therapist in your area.
What is anxiety disorder?
Anxiety disorder due to a medical condition includes symptoms of intense anxiety or panic that are directly caused by a physical health problem.
Why do people have anxiety disorders?
The causes of anxiety disorders aren't fully understood. Life experiences such as traumatic events appear to trigger anxiety disorders in people who are already prone to anxiety. Inherited traits also can be a factor.
What is separation anxiety disorder?
Separation anxiety disorder is a childhood disorder characterized by anxiety that's excessive for the child's developmental level and related to separation from parents or others who have parental roles.
What is the term for a sudden feeling of fear and anxiety?
Often, anxiety disorders involve repeated episodes of sudden feelings of intense anxiety and fear or terror that reach a peak within minutes (panic attacks). These feelings of anxiety and panic interfere with daily activities, are difficult to control, are out of proportion to the actual danger and can last a long time.
What is a specific phobia?
Specific phobias are characterized by major anxiety when you're exposed to a specific object or situation and a desire to avoid it. Phobias provoke panic attacks in some people.
What is the urge to avoid things that trigger anxiety?
Having the urge to avoid things that trigger anxiety. Several types of anxiety disorders exist: Agoraphobia (ag-uh-ruh-FOE-be- uh) is a type of anxiety disorder in which you fear and often avoid places or situations that might cause you to panic and make you feel trapped, helpless or embarrassed.
What is it called when you feel a sudden sensation of fear and anxiety?
Panic disorder involves repeated episodes of sudden feelings of intense anxiety and fear or terror that reach a peak within minutes (panic attacks). You may have feelings of impending doom, shortness of breath, chest pain, or a rapid, fluttering or pounding heart (heart palpitations).
How do fear and anxiety differ?
How Anxiety and Fear Differ in the Brain. Anxiety and fear have quite a bit of overlap in terms of brain structures and chemical signaling in the brain. Remember, however, that fear is a response to immediate, present danger; anxiety is a response to unclear or imagined potentialities. Some researchers feel that anxiety is a more "elaborate" form ...
What are the two pathways of fear?
Any fear-eliciting situation always takes two simultaneous "paths" in the brain. The "low road" (thalamus, amygdala, hypothalamus) sends an immediate uncontexutalized call to act on the stimulus. The "high road" (thalamus, sensory cortex, hippocampus, amygdala, hypothalamus) takes into account conscious interpretation—"Is this really something I need to be scared of?" The trick is, your "low road" response always happens first—the body protects itself full-stop and only later asks questions. Knowing this two-tiered system exists is itself a great confidence booster--you are neither "weak" nor "childish" for reacting in accordancd with fear's "low road" response.
What is the function of the autonomic nervous system?
These brain structures work in concert to interpret, contextualize, and store your sensory reactions and emotional experiences, fear and anxiety included. They themselves are part of a larger system called the autonomic nervous system, itself divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems. ...
What is the product of unconscious stimuli/thought connections which themselves have origins in initial sensory perception and interpretation?
Consistent fear and anxiety are the product of unconscious stimuli/thought connections which themselves have origins in initial sensory perception and interpretation. Much of the work of coping with or "unlearning" your fears and anxieties involves making new associations between sensation, perception, and cognition in a conscious way.
What is the junction box for sensory information?
Thalamus – A junction box for sensory information. The thalamus reroutes specific sensory information to other parts of the brain. ACTH, Cortisol, Oxytocin, Epinephrine (Adrenaline), and Norepinephrine – A sampling of the over 30 hormones and chemicals released during "flight, fight, or freeze" responses.
Which structure of the brain is responsible for storing fearful memories?
Amygdala – The brain's emotional organizational center. The amygdala separates your emotional responses into threatening or non-threatening camps and is the storehouse of fearful memories and associations. Hippocampus – A primary brain structure for memory.
Which brain structure is responsible for making sense of fear?
Here is a brief overview of the major brain structures responsible for creating and making sense of anxiety and fear: Adrenal Gland – Part of you endocrine system. It produces many kinds of hormones that activate and regulate anxious, fearful, and stress responses. As the name suggests, it is the brain's adrenaline factory.