
What is Piaget's moral development theory?
Piaget conceptualizes moral development as a constructivist process, whereby the interplay of action and thought builds moral concepts. Piaget (1932) was principally interested not in what children do (i.e., in whether they break rules or not) but in what they think.
How many stages are there in Piaget's theory of moral development?
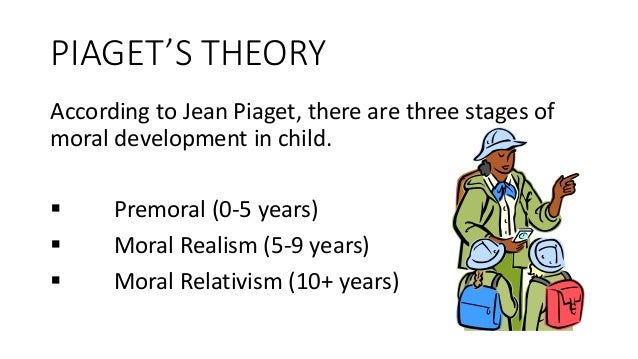
three stagesThere are three stages in Piaget's Theory of Moral Development. In stage one, children are not concerned with moral reasoning as they prioritize other skills such as social development and dexterity.
What two methods did Piaget use for moral development?
Piaget was also one of the first psychologists to specifically outline a theory of moral development. He began by studying the way children interact and play with one another, identifying the different rules they applied and their beliefs about what was right and wrong.
What is moral development theory about?
Kohlberg's theory of moral development is a theory that focuses on how children develop morality and moral reasoning. Kohlberg's theory suggests that moral development occurs in a series of six stages. The theory also suggests that moral logic is primarily focused on seeking and maintaining justice.
Why is moral development important?
Moral development helps you with improving your beliefs because it is possible to believe wrong things while growing up considering many times people don't bother telling you what is wrong or right. Many children don't get proper education about morality and ethics which leads them in the wrong direction.
What did Piaget called the first stage of moral development?
After the age of two, up to the age of seven, children are in the first stage of Piaget's moral development, where they are very rigid in their beliefs of moral concepts. Piaget termed this first stage the "Morality of Constraint" .
What is an example of moral development?
During this stage, moral development is influenced by social expectations or norms. A person makes moral decisions based on how it will affect their interpersonal relationships. For example, a child who acts nice or behaves properly to win the approval of others.
What is the difference between Piaget and Kohlberg's moral development?
Piaget understands moral development as a construction process, i.e. the interplay of action and thought builds moral concepts. Kohlberg on the other hand, describes development as a process of discovering universal moral principles.
What did Piaget believe about the moral development of children quizlet?
Piaget believed that age-related cognitive development is important for the development of moral reasoning, whereas Kohlberg de-emphasized this factor. Piaget believed that the development of moral reasoning is continuous, whereas Kohlberg believed it is discontinuous.
What is moral development in your own words?
Moral development refers to the process whereby people form a progressive sense of what is right and wrong, proper and improper.
Why is moral development important in early childhood?
Knowing good moral values such as kindness, humility, courage, and compassion at an early age builds a child's character. It forms the very core of their being and becomes a foundation of their moral beliefs. This is why it's essential to start teaching them moral values while they're still children.
What are the three theories of moral development?
Based on people's answers, Kohlberg identified three levels of morality: pre-conventional morality, conventional morality and post-conventional morality.
What are the 4 stages of Piaget's theory?
Sensorimotor stage (0–2 years old) Preoperational stage (2–7 years old) Concrete operational stage (7–11 years old) Formal operational stage (11 years old through adulthood)
What are Piaget's 4 stages of development in order?
Piaget's four stages of intellectual (or cognitive) development are:Sensorimotor. Birth through ages 18-24 months.Preoperational. Toddlerhood (18-24 months) through early childhood (age 7)Concrete operational. Ages 7 to 11.Formal operational. Adolescence through adulthood.
What are the 5 stages of moral development?
Introduction.Theoretical framework. Level 1: Preconventional level. Stage 1: Punishment/obedience orientation. Stage 2: Instrumental purpose orientation. Level 2: Conventional level. Stage 3: Good Boy/Nice Girl orientation. Stage 4: Law and order orientation. ... Basic tenets of Kohlberg's theory.Measurement of moral development.
Who developed the 12 stages of moral development?
Lawrence Kohlberg was, for many years, a professor at Harvard University. He became famous for his work there beginning in the early 1970s. He started as a developmental psychologist and then moved to the field of moral education.
What Is Piaget's Theory of Moral Development?
His theory of children’s moral development is an application of his ideas on cognitive development. Within this theory are two types of moral thinking: heteronomous morality and autonomous morality.
What did Piaget want to know about morals?
Piaget was mainly interested in three aspects of children’s understanding of moral issues: rules, moral responsibility, and justice.
How is moral development related to cognitive development?
In other words, children are only capable of making advanced moral judgments once they become cognitively mature and see things from more than one perspective.
Why did Piaget do experiments?
Piaget devised experiments to study children’s perceptions of right and wrong. He would tell a story about something another child did, like break a jar of cookies, and then asked children whether they thought that action was right or wrong. He wanted to know the logic behind their moral reasoning.
How do children overcome egocentrism?
Children are now beginning to overcome the egocentrism of middle childhood. Their appreciation of morality changes as a result of their newly acquired ability to view situations from other people's perspectives. They are, therefore, also capable of considering rules from someone else’s point of view. Moral rules are not perceived as being absolute anymore. Instead, older children realize that rules are socially agreed-upon guidelines. They are designed to benefit all the group members and are adjustable.
What age is heteronomous morality?
The stage of heteronomous morality, also known as moral realism or other-directed morality, is typical of children between the ages of 5 and 10.
What is the basis of children's reasoning and judgment about rules and punishment?
According to Piaget, the basis of children’s reasoning and judgment about rules and punishment changes as they get older. Just as there are universal stages in children’s cognitive development, there are stages in their moral development.
What factors must be taken into account in Piaget's theory?
Motivation, intent, personal abilities, and situational context are all factors that must be taken into account. Piaget determined that youth had adequately reached this stage when they rejected the absolute reasoning of authorities and the idea that rules should never be questioned.
What was Piaget's first stage?
Piaget’s first stage included children between the ages of five and ten, whose moral reasoning had a “heteronomous” lens, or external to the self. This meant that laws were created and enforced by authority and were not to be broken at any cost. According to their understanding, the power of authorities was absolute and the regulations were imposed indefinitely. Their reasoning for this acceptance is directly linked to the punishment for not following the rules. At this age, children worked hard to avoid consequences, and their moral reasoning for behaviors was simply to escape punishment.
What are the stages of moral development?
There are three stages in Piaget’s Theory of Moral Development. In stage one, children are not concerned with moral reasoning as they prioritize other skills such as social development and dexterity. In stage two, children submit to authority and show absolute respect for regulations. In stage three, children acknowledge the flexibility ...
Which philosopher outlined the morality of cooperation as the stage reached after the age of ten?
See also: Andragogy Theory – Malcolm Knowles. Piaget outlined the morality of cooperation as the stage reached after the age of ten.
Who was Jean Piaget?
Jean Piaget (1896-1980) was a Swiss psychologist known for his work on child development.
Is Piaget's timing incompatible with the development of children?
Piaget’s work is sometimes vague and many sections have been difficult to prove in studies. His timing is also incompatible with the development of children, with some sections starting too early and others too late.
Do teenagers refine their moral reasoning?
Continued studies on this theory have shown that teenagers continue to refine their moral reasoning with the accumulation of life experiences even into adulthood. Each dilemma presented throughout early adulthood sharpens decision-making skills, even with the same presented criteria.
Morality During Childhood
The understanding of morals begins to develop in a child around age 5. Before age 5, a child’s concept of moral thinking is based on actions and consequences. During this time, a child makes their decisions based on what they expect will cause negative consequences.
Morality of Constraint
The term ‘Morality of Constraint’ is used in Piaget’s theory. It refers to a child’s rigid beliefs of morals in terms of action and consequence. Morality of Constraint refers to a child’s inability to see rules as negotiable or flexible. In this stage, rules are very black and white. They are fixed and unwavering.
Relative Morality
As a child grows and develops, they begin to understand the perspective of different people. Through developing this understanding, children begin to challenge the rules. This marks the beginning of relative morality. This relative morality continues to mature during adolescence.
Morality of Cooperation
A child’s perspective of morality begins to change around age 9. Instead of seeing Morality of Constraint, they begin to see ‘Morality of Cooperation’. Morality of Cooperation develops around the same time as the child develops autonomy from their parents. The child begins to learn how to relate to others.
Morality During Adolescence
During adolescence, a child begins to realize that different people have different standards of moral behavior. They understand that different people have different perspectives on morality. These different perspectives are based on each individual’s own experiences.
Reciprocity of Moral Decisions
A major lesson learned in adolescence is that there is something to gain from being moral. Moral decisions can be beneficial to everyone, including oneself. With this discovery, the appreciation of morality strengthens.
Simple Reciprocity vs. Ideal Reciprocity
The concept of making moral decisions for one’s own personal interest develops in stages. To begin, the adolescent understands morality in a simple fashion. They view it as an even exchange of manners and politeness. The adolescent understands moral reciprocity in the concept of ‘if you wash my back I will wash yours’.
What did Piaget believe about the development of cognitive skills?
Piaget believed that cognitive development did not progress at a steady rate, but rather in leaps and bounds. Equilibration is the force which drives the learning process as we do not like to be frustrated and will seek to restore balance by mastering the new challenge (accommodation).
What did Piaget believe?
Piaget believed that all human thought seeks order and is uncomfortable with contradictions and inconsistencies in knowledge structures. In other words, we seek 'equilibrium' in our cognitive structures.
What is the effect of Piaget's work on children's cognitive abilities?
When tasks were altered, performance (and therefore competence) was affected. Therefore, Piaget might have underestimated children’s cognitive abilities. For example, a child might have object permanence (competence) but still not be able to search for objects (performance).
What is the basic building block of cognitive models?
According to Piaget, children are born with a very basic mental structure (genetically inherited and evolved) on which all subsequent learning and knowledge are based. Schemas are the basic building blocks of such cognitive models, and enable us to form a mental representation of the world. Piaget (1952, p.
How did Piaget change the world?
He was an inspiration to many who came after and took up his ideas. Piaget's ideas have generated a huge amount of research which has increased our understanding of cognitive development.
What are the cognitive abilities of the sensorimotor stage?
These include: object permanence; self-recognition; deferred imitation; and representational play. They relate to the emergence of the general symbolic function, which is the capacity to represent the world mentally.
How does cognitive development occur?
Cognitive development occurs through the interaction of innate capacities and environmental events, and children pass through a series of stages. Piaget's stages are:
What did Jean Piaget call the morality of constraint?
He called this the morality of constraint or heteronomy.
What is moral development?
Moral development is the development of an understanding of right and wrong in children in order to later apply this knowledge in situations with moral choices. It also covers the development of a strong and independent character, which, when faced with such a situation, will make the right moral choices, even in the face of the discomfort of opposition. Moral development has always played an essential role in the society, and has been a studied topic throughout human history, first by pedagogues and philosophers, and nowadays by sociologists and psychologists. However, it did not become the focus of scientific study until the late 1950s.
How long does it take for Piaget to develop distributive justice?
The first one is until 7-8 years when children defer to adult authority on the issue; the second is from 8 to 11 years, While Piaget is widely known for the idea of stages in development that he introduced, he did not, in actuality, ...
Which is more applicable, Kohlberg's or Piaget's theories?
Both theories have had a significant impact on the development of child psychology, but Kohlberg’s is more refined and developed and is more applicable in education. His stages explain the tools a pedagogue or a psychologist has at their disposal for directing the moral development of a child in kindergarten, school, and later in life. While Kohlberg’s stages mirror the Piaget’s two morality types, Kohlberg extrapolates upon the changes in the child’s perceptions of right and wrong, and what is influencing them.
Who developed the concept of stages of moral development?
While Piaget is widely known for the idea of stages in development that he introduced, he did not, in actuality, elaborate on them very much, and his insight is somewhat limited, as he conceded, and instead focused on the transition from one type of morality to the second one. However, these ideas were developed and expanded further by Kohlberg, creating his landmark theory of stages of children’s moral development.
Did Kohlberg base his theories on Piaget?
While Kohlberg based his theories on those of Piaget, by expanding and modifying them to fit his perspectives, both of their views have enough differences between them and applicability to be still relevant in psychology and highly regarded by modern researchers. It is important to understand them both on their own, ...
What is Kohlberg's theory of moral development?
This study is anchored on Kohlberg’s Moral Development Theory. This theory proposed that moral reasoning of human beings is associated with the stages of development in solving moral issues that an individual encounters (Bjorklund & Blasi, 2010). Kohlberg’s moral development sees moral reasoning as progressing through three levels to support his claims. First, pre-conventional moral reasoning, it is characterized by apparent and physical events. The presentation of moral issues at this stage is concentrated with the rewards and punishments after the occurrence of their action.
What is the moral development model of Kohlberg?
In Kohlberg's model of cognitive moral development, he explored “how people determined what was right or wrong in a particular situation ” (Trevino 604). This model focuses on the “reasons an individual uses to justify a moral choice, rather than the decision itself” (Trevino 604). It is also concluded that “ [o]ur biology does not prescribe the specific forms our morality takes” (Singer 337). An experiment in which situational ethics are present would be the Trolley Problem. This experiment provides participants with two options, “turn the train down the side track, killing one person, or continue straight ahead and kill the five workers” (Thomson 1).
How many stages of moral development did Kohlberg propose?
Kohlberg proposed that moral reasoning advanced through six stages of moral development, stages 1 to 4 occurred through a “natural evolution of cognitive skills,” while stages 5 and 6 require a teacher (Williams & Arrigo, [2012], p. 123). Moreover, Kohlberg proposed that there were three levels of moral development, each categorized by two stages. Preconventional Morality (Lv. I) is categorized by self-interest, first existent ages 1 through 10. Kohlberg’s stage 1: punishment obedience orientation, is categorized by a perception influenced by punishment and reward.
What is the moral foundation theory?
Haidt’s (2001) moral foundation theory came around with the notion that the human brain have been prewired to learn values about the social world (Graham et al., 2012). The main idea behind this theory is that, we are born with a universal system of values; called foundations. Throughout our lives, we add or build on these universal foundations a number of cultural virtues and values. This concept explains why there are a number of similar moralities across the world yet different and unique ones at the same time. The five foundations identified by Haidt and Joseph (2007) are the following: Care/Harm, Fairness/Cheating, Loyalty/betrayal, authority/subversion, Sanctity/degradation and in 2012, Haidt added a sixth one Liberty/oppression. This theory support the idea that our moral reasoning is somewhat intuitive. It is important to note, however, that even though all five or six foundations are universal, some cultures build on one foundation more than other which will eventually cause a difference about the idea of what virtue a culture values
What is Kohlberg's theory?
• Kohlberg’s theory is really one of cognitive development as applied to moral understanding because he believed that children developed their moral principles primarily though thinking about them. • Both these theories are stage theories • Both theories says social interaction helps children to develop their ability of understanding and identifying others feeling • • Piaget proposed a stage theory of cognitive development. Kohlberg posited a model of moral development or moral reasoning based on many of Piaget's
What is the most compelling and broadly investigated hypothesis of moral reasoning and moral development?
Literature Review 2.1 Inrtoduction Individuals fluctuate impressively in moral thinking. Kohlberg’s theory of moral development is the most compelling and broadly investigated hypothesis of moral reasoning and moral development. Indeed, even today more than a quarter century after Kohlberg’s demise, there is significant research directed using his theory. A lot of this impact can be ascribed to this current hypothesis’s focal and much tried supposition that a person’s ethical thinking will foresee moral conduct. To catch such individual contrasts in moral improvement, Kohlberg’s hypothesis characterized moral development into three levels: pre-conventional level (persuaded without anyone else’s input intrigue); Conventional
Is religion a guide to morality?
Some might argue that morality is inessential for the growth of an individual's morality, but when one considers religion as a guide to morality, the argument for the importance of religion in morality becomes more clear. To represent this statement, Broom argued, “religions are essentially structures underpinning morality” (Broom “The Evolution”). Along those same lines Reagan provides that “And as morality's foundation is religion ...We need religion as a guide; we need it because we are imperfect” (Reagan 10). Both of these arguments provide that religion is the foundation of morality. Religion is a
What Is Moral Development?
How do people develop morality? This question has fascinated parents, religious leaders, and philosophers for ages, but moral development has also become a hot-button issue in psychology and education. 1 Do parental or societal influences play a greater role in moral development? Do all kids develop morality in similar ways?
What is Kohlberg's theory of moral development?
Kohlberg's theory suggests that moral development occurs in a series of six stages. The theory also suggests that moral logic is primarily focused on seeking and maintaining justice.
How many levels of moral development did Kohlberg have?
Kohlberg's theory is broken down into three primary levels. At each level of moral development, there are two stages. Similar to how Piaget believed that not all people reach the highest levels of cognitive development, Kohlberg believed not everyone progresses to the highest stages of moral development.
How did Piaget and Kohlberg differ?
3 Kohlberg extended Piaget's theory, proposing that moral development is a continual process that occurs throughout the lifespan. His theory outlines six stages of moral development within three different levels.
Which level of moral development did Kohlberg believe everyone progressed to?
Level 1. Preconventional Morality. Preconventional morality is the earliest period of moral development.
What is the final stage of Kohlberg's moral reasoning?
Stage 6 (Universal Principles): Kohlberg’s final level of moral reasoning is based on universal ethical principles and abstract reasoning. At this stage, people follow these internalized principles of justice, even if they conflict with laws and rules.
What is Kohlberg's theory?
Kohlberg's theory played an important role in the development of moral psychology. While the theory has been highly influential, aspects of the theory have been critiqued for a number of reasons:
Morality During Childhood
Morality of Constraint
Relative Morality
- Piaget’s theory of children’s moral development can be seen as an application of his ideas on cognitive developmentgenerally. As such his theory here has both the strengths and weaknesses of his overall theory. Piaget uses qualitative methods (observation and clinical interviews). His research is based on very small samples. His methods are not sta...
Morality of Cooperation
Morality During Adolescence
- The term ‘Morality of Constraint’ is used in Piaget’s theory. It refers to a child’s rigid beliefs of morals in terms of action and consequence. Morality of Constraint refers to a child’s inability to see rules as negotiable or flexible. In this stage, rules are very black and white. They are fixed and unwavering.
Reciprocity of Moral Decisions
- As a child grows and develops, they begin to understand the perspective of different people. Through developing this understanding, children begin to challenge the rules. This marks the beginning of relative morality. This relative morality continues to mature during adolescence. As a child approaches adolescence, their understanding of morality becomes less about right and wr…
Simple Reciprocity vs. Ideal Reciprocity
- A child’s perspective of morality begins to change around age 9. Instead of seeing Morality of Constraint, they begin to see ‘Morality of Cooperation’. Morality of Cooperation develops around the same time as the child develops autonomy from their parents. The child begins to learn how to relate to others. In learning how to relate to others, they also learn how to cooperate with othe…