
How to calculate pKa values?
pKa value can be determined by the titration curve. To calculate the pKa of the solution, firstly, we will determine the equivalence point and then find the pH of the solution. pKa of the solution is equivalent to the pH of the solution at its equivalence point. Hence we can quickly determine the value of pKa by using a titration curve.
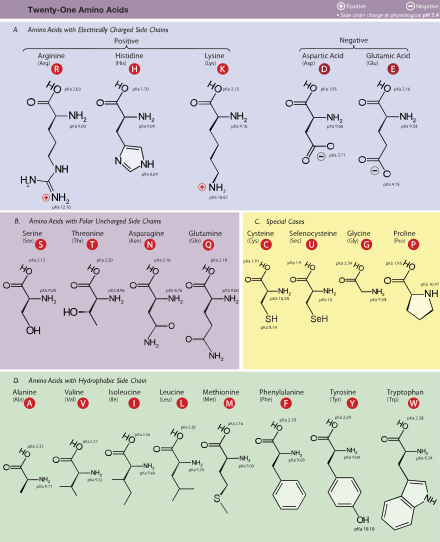
What are the names of 20 amino acids?
Types of Amino Acids
- Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) Branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), which include leucine, isoleucine and valine, are essential amino acids that stimulate protein synthesis in the muscles.
- Acidic and Basic Amino Acids. ...
- Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids. ...
- Glucogenic and Ketogenic Amino Acids. ...
Why does phenol have a low pKa?
Why does phenol have a low pKa? Nitro groups are very powerful electron-withdrawing groups. The phenol derivative picric acid has a pKa of 0.25, lower than that of trifluoroacetic acid. Use a resonance argument to explain why picric acid has such a low pKa. Notice that the methoxy group increases the pKa of the phenol group - it makes it less ...
What are PKA and PKB in acids and bases?
pKa and pKb Table. pKa and pKb are common terms in chemistry that are known as dissociation constants. pKa is acid dissociation constant, and pKb is base dissociation constant. These terms are used to make it easy to work with very large or very small values. The “p” in these terms stands for “negative logarithm”.
What is pKa in amino acids mean?
The proteinogenic amino acids are amphoteric and have two or three pK values, depending on their side chains. pKa1 is the α-carboxyl group, pKa2 is the α-ammonium ion, pKa3 is the side chain group if applicable and pI is the isoelectric point at which the amino acid has no net charge.
Why is pKa An important property of an amino acid?
pKa values of amino acid side chains play an important role in defining the pH-dependent characteristics of a protein. The pH-dependence of the activity displayed by enzymes and the pH-dependence of protein stability, for example, are properties that are determined by the pKa values of amino acid side chains.
How do you determine the pKa of an amino acid?
The pKa-values of the amino acid are determined from the full titration graph. To determine pKa1 and pKa2, locate the volume on the graphs half way between the two equivalence point volumes determined from the expanded derivative curves. The pH at this point is in the titration is equal to pKa2.
What is a pKa value?
The pKa measures how tightly a proton is held by a Bronsted acid. A pKa may be a small, negative number, such as -3 or -5. It may be a larger, positive number, such as 30 or 50. The lower the pKa of a Bronsted acid, the more easily it gives up its proton.
Why pKa value is important?
Acid dissociation constants, or pKa values, are essential for understanding many fundamental reactions in chemistry. These values reveal the deprotonation state of a molecule in a particular solvent. There is great interest in using theoretical methods to calculate the pKa values for many different types of molecules.
What affects pKa of amino acids?
pKa is related to the side chain of the amino acid. This side chain can interact with other residues of the enzyme (hydrogen bonding and others) and this greatly affects the pKa value. pKa is a measure of what proportion of the time an atom is protonated.
How do you find the pKa?
The pKa is defined as the negative log of the Ka. If we wanted to find the pKa for methanol, all we have to do is take the Ka and take the negative log of it. So the pKa is equal to the negative log of 2.9 times 10 to the negative 16.
How do you get pKa from pH?
Each dissociation has a unique Ka and pKa value. When the moles of base added equals half the total moles of acid, the weak acid and its conjugate base are in equal amounts. The ratio of CB / WA = 1 and according to the HH equation, pH = pKa + log(1) or pH = pKa.
What is the pKa of histidine?
By following the chemical shifts of the hydrogens attached to C2 and C4 of the imidazole ring [36] of the tripeptide, the pKa of histidine in HVD was found to be 6.87 (Figure 6), which is within 0.05 pH units of and statistically identical (p = 0.95 assuming Gaussian error) to the pKa determined by Raman spectroscopy.
What is difference between pH and pKa?
Difference Between pKa and pH pKa is the negative value of the logarithm of Ka. pH is the logarithmic value of the inverse of H+ concentration. pKa indicates whether an acid is a strong acid or a weak acid. pH indicates whether a system is acidic or alkaline.
Is a higher pKa more acidic?
In addition, the smaller the pKa value, the stronger the acid. For example, the pKa value of lactic acid is about 3.8, so that means lactic acid is a stronger acid than acetic acid.
Does a high pKa mean a strong base?
The greater is the value of pKa, the weaker will be the acid and the stronger will be the base. The greater is the value of pH, the weaker will be the acid and the stronger will be the base. For acids, pH<7 and for bases, pH>7.
What is the relationship between the pH and pKa of each amino acids?
At a pH below the pKa for each functional group on the amino acid, the functional group is protonated. At a pH above the pKa for the functional group it is deprotonated. If the pH equals the pKa, the functional group is 50% protonated and 50% deprotonated.
What is the relationship between pKa and pH?
How are pKA and pH related? pH is equal to the sum of the pKa value and the log of the conjugate base concentration divided by the weak acid concentration.
What happens at pKa?
pH, pKa, and Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation The pKa is the pH value at which a chemical species will accept or donate a proton. The lower the pKa, the stronger the acid and the greater the ability to donate a proton in aqueous solution.
What does not affect the pKa value of an amino acid?
The factor which does not affect the PKA value of an amino acid is its molecular weight. All the other environmental factors can effect the PKA value of amino acids. The loss of charge in the α-carboxyl and α-amino groups affects the PKA value directly as loss of charge directly affects it.
How many pKas are in an amino acid?
An amino acid has at least two pKa’s, one for the amino group and one for the carboxyl group. The pKa for each group is the negative logarithm (base 10) of the equilibrium constant for its deprotonation. Put more simply, this works out to the pH at which the group is protonated (e.g. - N H 3 +, − C O O H) on half the molecules and deprotonated ( − N H 2, C O O −) on half. If the amino acid has an ionizable group in its side chain, it has a third pKa.
What does pka mean in math?
pKa, or simply pK, represents the tendency towards ionization for a given acidic/basic substance or group. However attention must be paid here, as we’re dealing with -log (Ka), have in mind that lower pK values indicate acidic species that easily ionize, while higher pK values indicate basic species, that do the exact opposite, to remain protonated. Making it simple, the lower the pK, the stronger the acid.
What is the net charge of aspartic acid at pH 3?
The pI is ~3. So at a pH of ~3 the net charge of aspartic acid is 0 . To understand why, one needs to think about what is happening to the alpha-amino and carboxylic groups and carboxyl side chain group. At pH 3, the alpha-amino group will be fully protonated given that the pKa is 9.9. So that contributes a charge of +1. So that means that at pH 3, the sum of the net charge on the alpha carboxylic group and carboxyl R group must add up to -1.
What is the total amount of the alpha carboxyl group at pH 3?
At pH 3, the fraction of the alpha carboxyl group existing as A- is 0.91 and the fraction of the R carboxyl group existing as A- is 0.09. The total amount of A- is 1.0 and contributes a total charge of -1. Adding in the +1 charge of the alpha amino group gives a net charge of 0.
What is the pKa of glycine?
The pKa of glycine (H2N-CH2-COOH) is 2.34. So, if we add two F we can estimate the pKa of difluoroglycine to be
What is the pKa of trichloroacetic acid?
You can get below one with acids like trichloroacetic acid (Cl3COOH) and trifluoroacetic acid (F3COOH) with pKas of 0.7 and 0.23, respectively.
How to separate pKa?
One classic method is to do 2-D separation: chromatography in one dimension, electrophoresis or another chromatography in the other. Knowing the pKa in advance isn’t particularly a help, unless you think electrophoresing near its isoionic point will help separate it from other candidates.
Why are amino acids called amino acids?
Amino acids are so called because they all contain two common components. One is an amine, or a tetrahedral nitrogen attached to a carbon. The other is a carboxylic acid, which is a carbon that is double bonded to an oxygen and also attached to an OH or hydroxyl group. We have seen that carboxylic acids are moderately acidic.
Where are the acidic and basic sites found in amino acids?
However, peptides and proteins do have basic and acidic sites. These sites are found on the side chains of the amino acids, the part that varies from one amino acid to another.
How are amino acids joined together?
Amino acids are joined together via "amide linkages" to form peptides and proteins. In these structures, the individual amino acids no longer have the same acidic carboxylic acid group; the carbonyl (or C=O) no longer has a hydroxyl group attached.
Which amino acid has the least basic group?
There is a big difference in basicity between these three compounds. The difference can be seen by looking at the pKa's of the conjugate acids in each case. The higher the pKa of the conjugate acid, the more tightly the proton is held, and so the more basic the nitrogen atom. Arginine is by far the most basic and histidine is the least basic.
What are proteins used for?
Proteins, which are very large peptides, have a variety of uses. They form the key components of muscles, for instance, and they also form enzymes that carry out a multitude of chemical reactions necessary for life. Amino acids are so called because they all contain two common components.
Which compound holds the proton more tightly than the acid?
The ammonium holds the proton more tightly than does the acid. The proton stays on the nitrogen. Amino acids are zwitterionic. A zwitterion is a compound that has no overall charge but that has charge separation within it. The zwitterionic nature of amino acids has an effect on their properties.
Which side chain is weakly acidic?
There are other side chains that are weakly acidic. For example, tyrosine is sometimes able to supply protons, and so is cysteine. The proton comes from the OH and SH groups, respectively, on these two compounds. However, neither of these compounds can supply protons as easily as aspartic acid or glutamic acid.
What is the pKa of an acid?
pKa is defined as the negative log 10 of the dissociation constant of an acid, its K a. Therefore, the pK a is a quantitative measure of how easily or how readily the acid gives up its proton [H +] in solution and thus a measure of the "strength" of the acid. Strong acids have a small pKa, weak acids have a larger pKa.
What happens when pH is equal to pKa?
This means that when the pH is equal to the pKa there are equal amounts of protonated and deprotonated forms of the acid. For example, if the pKa of the acid is 4.75, at a pH of 4.75 that acid will exist as 50% protonated and 50% deprotonated.
How to determine the strength of an acid?
The strength of the acid can be determined by the electronegativity of the atom the oxygen is bound to. For example, the weak acid Acetic Acid, the oxygen is bound to carbon, an atom with low electronegativity. In the strong acid, Hypochlorous acid, the oxygen atom is bound to an even more electronegative Chloride atom.
What is the most common acid in BIS2A?
Strong acids have a small pKa, weak acids have a larger pKa. The most common acid we will talk about in BIS2A is the carboxylic acid functional group. These acids are typically weak acids, meaning that they only partially dissociate (into H + cations and RCOO - anions) in neutral solution.
Is HCL a strong acid?
HCL (hydrogen chloride) is a common strong acid, meaning that it will fully dissociate into H + and Cl -. Note that the key difference in the figure below between a strong acid or base and a weak acid or base is the single arrow (strong) versus a double arrow (weak).
