What does the placenta do for the reproductive?
The functions of the placenta include:
- Allows gas exchange so the fetus gets enough oxygen
- Helps the fetus get sufficient nutrition
- Helps regulate the fetus’ body temperature
- Removes waste from the fetus for processing by the mother’s body
- Filters out some microbes that could cause infection
- Transfers antibodies from the mother to the fetus, conferring some immune protection
What does the placenta provide with the embryo with?
The placenta is a complex organ consisting of a thick membrane and blood vessels that connect mother to baby via the umbilical cord. For the fetus, the placenta acts as a filter, delivering oxygen, glucose and other nutrients. It blocks out potentially harmful substances and removes carbon dioxide and waste from the baby’s blood.
How does placenta previa affect the body?
- Preterm birth: Severe bleeding may prompt an emergency C-section before the baby reaches full-term. ...
- Maternal and fetal bleeding/hemorrhage: Severe, life-threatening vaginal bleeding can occur during labor, delivery, or after delivery in cases of placenta previa (2). ...
- Placenta accreta: In cases of placenta previa, placenta accreta is more likely (4). ...
What are the symptoms of retained placenta?
This can cause symptoms that take a while to show up such as:
- Delayed and heavy bleeding
- Blood clots
- Fever
- Chills
- Feeling sick or flu-like
- Foul-smelling vaginal discharge

What are 4 functions of the placenta?
Functions of the placenta include:Provides your baby with oxygen and nutrients.Removes harmful waste and carbon dioxide from your baby.Produces hormones that help your baby grow.Passes immunity from you to your baby.Helps protect your baby.
What are the 3 purposes of the placenta?
gas exchange and the transfer of nutrients and waste products between maternal and fetal plasma; transfer of immunity by transfer of immunoglobulins from the mother to the fetus; secretion of hormones which are important for fetal growth and development.
What is placenta and its function Class 10?
Placenta refers to the temporary vascular organ found in mammals, which attaches the fetus to the uterus of the mother during pregnancy. The placenta is the passage that unites the fetus to the mother. The placenta facilitates the exchange of nutrients and oxygen to the fetus.
What is the weight of placenta?
Placenta: 1 1/2 pounds (about 0.7 kilogram) Amniotic fluid: 2 pounds (about 0.9 kilogram) Increased blood volume: 3 to 4 pounds (about 1.4 to 1.8 kilograms) Increased fluid volume: 2 to 3 pounds (about 0.9 to 1.4 kilograms)
How big is a placenta?
By halfway through a healthy pregnancy, it's about 15 centimetres in diameter (the size of a side plate), and by the end it doubles to become about the size of a Frisbee and the weight of a block and a half of butter.
What are two major functions of placenta?
Functions of Placenta : i Provides large surface area for glucose and oxygen to pass from mother to the embryo. ii Removal of waste generated in the developing embryo into the mothers blood. Related Answer. Placenta acts as an endocrine gland.
What is the function of placenta Class 12?
Placenta's Function: - Provides a large surface area to pass from mother to embryo for glucose and oxygen. - Removal of waste produced in the growing fetus into the mother's blood. The placenta attaches to the uterus wall, and the umbilical cord of the baby arises from it.
What is placenta What is its function Class 12?
Placenta is a circular organ in the uterus of a pregnant mammal. It nourishes the foetus through the umbilical cord throughout the pregnancy. It is a temporary organ. The placenta starts to develop when the fertilized egg called blastocyst implants in the maternal endometrium.
What is the main purpose of the placenta quizlet?
What is the function of the placenta? It allows oxygen and nutrients to pass from the mother to the fetus, and bodily wastes to pass from the fetus to the mother.
What is placenta describe its two major function?
Two function of placenta are: 1 It allows gas exchange so that the fetus gets enough of oxygen and also helps it to get sufficient nuterition. 2 Placenta removes the waste from the fetus for processing by the mother's body, also helps in filteration of microbes that cold was infection.
What are some functions of the placenta quizlet?
Permits the exchange of oxygen, waste products, and nutrients between maternal and fetal blood.
What are the 3 stages of birth?
Labour has three stages: The first stage is when the neck of the womb (cervix) opens to 10cm dilated. The second stage is when the baby moves down through the vagina and is born. The third stage is when the placenta (afterbirth) is delivered.
What Is a Placenta and What Does It Do?
The placenta is a temporary organ which develops in the uterus and helps the baby receiving all the necessary nutrients to develop during the 40 weeks of pregnancy. At 12 weeks of pregnancy, the placenta is completely formed. The placenta has the shape of a disc at delivery, measures around 18 to 20 cm in diameter and only a little over 5 cm in thickness. Its upper part is completely smooth and the hip which adheres to the wall of the uterus is rough. The placenta is richly vascularized. The umbilical cord is the one connecting the placenta to the baby.
Why Is It Good to Keep the Placenta?
The placenta represents an organ created by your body to offer your future baby nutrients and oxygen while he`s still in the uterus. However, once the placenta has finished its duty tour, it`s that all? For some of the mothers out there, there answer is obviously no. Some of them will want to keep it, cook it and eat it later to potentially avoid some of the side effects that come after birth. Other ones will probably want to plant it next to a tree to commemorate the entire event.
How much progesterone is produced during pregnancy?
Progesterone is synthesized from the maternal cholesterol. During the last phase of the pregnancy, the placenta produces 250 – 600mg of progesterone on a daily basis. The production of this hormone depends firstly by the LDL associated cholesterol and an adequate blood flow.
Why is iodine important for a fetus?
Anions – Since the thyroid hormones don`t cross the placenta, providing iodine to the fetus is essential. The transportation is made actively and the fetal concentrations are higher than the maternal ones.
What organs produce estrogen, progesterone, and hCG?
Progesterone, estrogen and hCG are produced by the placenta. The placenta is the organ responsible for functioning as a trading post between blood supply of the mother and baby. There are tiny blood vessels that carry fetal blood through this organ, which is already full of maternal blood. Oxygen and nutrients from the blood ...
How long does it take for a placenta to develop?
The placenta is a temporary organ which develops in the uterus and helps the baby receiving all the necessary nutrients to develop during the 40 weeks of pregnancy. At 12 weeks of pregnancy, the placenta is completely formed. The placenta has the shape of a disc at delivery, measures around 18 to 20 cm in diameter and only a little ...
Which organ produces hormones during pregnancy?
It`s known that the human placenta produces over 30 hormones and has receptors for almost all factors of regulation, being the main major endocrine organ during pregnancy. Syncytiotrophoblast and villous cytotrophoblast are the main places of the hormonal production.
What is the function of the placenta?
Tests. The placenta develops within the uterus during pregnancy, playing a key role in nourishing and providing oxygen to the fetus, as well as removing waste material. This organ is attached to the wall of the uterus, with the baby’s umbilical cord arising from it.
Where does the placenta form?
Placenta previa: This condition occurs when the placenta forms partially or totally toward the lower end of the uterus, including the cervix , rather than closer to its upper part. In cases of complete previa, the internal os —that is, the opening from the uterus to the vagina —is completely covered by the placenta.
Why is the placenta insufficient?
Placental insufficiency: Arising for a range of reasons, this is when the placenta is unable to provide enough nourishment for the fetus. This can be due to genetic defects, deficiencies of vitamins C and E, chronic infections (such as malaria), high blood pressure, diabetes, anemia, or heart disease, as well as other health issues. 6 Treatment can range from ensuring better diet to taking medications like low-dose aspirin, heparin, or sildenafil citrate.
How many pregnancies are there with placenta previa?
Occurring in about 1 in 200 to 250 pregnancies, risk factors for placenta previa include a history of smoking, prior cesarean delivery, abortion, other surgery of the uterus, and older maternal age, among others. Depending on the case, cesarean delivery may be required.
What is the placenta ejected from?
At birth, the placenta is also ejected from the body. Crucial to placenta (and, by extension, embryonic) development is the formation of small, finger-like structures called chorionic villi, which are composed of two types of cells—cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts.
What is the largest organ in the fetus?
The largest fetal organ, the placenta undergoes rapid development over the course of pregnancy. By the time the baby is brought to term, it has a flat, round disc-like shape that is about 22 centimeters (cm) in diameter, with walls that are typically between 2 and 2.5 cm. 3
When does the placenta change?
The placenta undergoes consistent change throughout the course of pregnancy; between week 0 and 13 after conception, the fertilized blastocyst (what the embryo becomes once its cells start differentiating at about five days after the egg is fertilized) embeds itself in the mucous membrane (endometrium) of the uterine wall, allowing for the fetus and placenta to start forming. 1 By the fourth or fifth month of pregnancy, the placenta takes up about half of the uterine surface, though this percentage shrinks as the fetus grows. At birth, the placenta is also ejected from the body.
What is the function of the placenta?
Function of Placenta. The placenta acts as a lifeline between the mother and fetus, ensuring that the fetus gets what it needs from the mother’s body to survive. At the same time, it acts as a protective barrier, shielding the fetus from some maternal infections. The functions of the placenta include:
How does the placenta work?
The placenta works mainly by allowing substances to be exchanged between maternal and fetal blood. This allows the fetus to obtain nutrients, oxygen, antibodies, and other vital substances without having to share the mother’s blood supply directly.
Why does the placenta separate the maternal and fetal blood supply?
The placenta separates the maternal and fetal blood supplies, to prevent the mother’s immune system from attacking fetal blood cells. However, it does allow some substances such as nutrients, gases, and antibodies to be exchanged.
Why are mammals such as dogs, cats, and humans called “placental mammals?
1. Why are mammals such as dogs, cats, and humans called “placental mammals?”#N#A. Because the placenta is the evolutionary adaptation we all share , while monotremes, marsupials, and non-mammals do not.#N#B. Because all placental mammals have placentas, while only some non-mammals have placentas.#N#C. Both of the above.
What is the placenta?
The placenta is an organ which is responsible for nourishing and protecting a fetus during pregnancy. It is unique in that it is a temporary organ; it grows alongside the fetus during pregnancy, and then is expelled along with the fetus at birth. The placenta is also sometimes called “afterbirth,” as it is expelled through the vagina after ...
Why does the placenta not develop properly?
This can occur either because of problems with the development of maternal uterine tissue, or because of problems with development of the fetal placental tissue.
What is it called when a mammal gives birth to a fully developed young?
Mammals who give birth to live, fully-developed young, rather than laying eggs or carrying underdeveloped offspring in pouches, are often called “placental mammals .” The evolution of the placenta is one of the primary characteristics shared by all mammals except for marsupials and egg-laying mammals such as the platypus.
What is Placenta?
The placenta is an organ that is in charge of feeding and protecting the fetus throughout pregnancy. It is distinct as it is a transient organ; it develops with the fetus throughout pregnancy and then is discharged with the fetus at the time of birth. The placenta is sometimes known as the "afterbirth" because it is discharged via the vagina after the fetus is delivered. The placenta is a transient circulatory organ found in mammals that connects the fetus to the mother's uterus during pregnancy. The placenta is found only in the case of mammals.
Why is the placenta important to the fetus?
Because the fetus is unable to feed, breathe, or expel waste while within the womb, the placenta essentially serves the role of numerous organ systems for the fetus.
How does the placenta form?
The placenta is formed from the outer layer of this blastocyst. This layer is followed by two layers: the overlying syncytiotrophoblast and the underlying cytotrophoblast. The placenta is covered by a multinucleated cell layer in the latter. It develops as a result of the differentiation and fusion of cytotrophoblast cells. The placenta's major job is to act as a barrier, and the syncytiotrophoblast plays that role. During pregnancy, the placenta expands. The supply of cells to the placenta by maternal blood is completed by the end of the first trimester.
What is the placenta called when the midgut extension of the splanchnopleure surrounding?
Yolk-Sac Placenta: When the midgut extension of the splanchnopleure surrounding the yolk merges with the extraembryonic somatopleure to make embryonic contact with the uterine wall, this is referred to as a Yolk-Sac Placenta. Mustelus is an example of the same.
When a fertilized egg termed a blastocyst implants in the maternal endometrium?
When a fertilized egg termed a blastocyst implants in the maternal endometrium, the placenta begins to form. The placenta is formed from the outer layer of this blastocyst.
Why are cats called placental mammals?
Ans. Various animals like cats, dogs, and humans are referred to as “placental mammals” because the placenta is an evolutionary adaption that all mammals share , but monotremes, marsupials, and non-mammals do not.
What connects the fetus to the placenta?
The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta, allowing materials to be transferred.
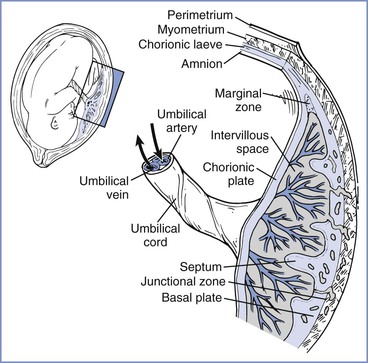
What is the structure of the placenta?
Structure: Placenta is a structure that establishes firm connection between the foetus and the mother. From the outer surface of the chorion a number of finger like projections known as chorionic villi grow into the tissue of the uterus. These villi penetrate the tissue of the uterine wall of the mother and form placenta.
What is the blood that passes through the placenta?
In the placenta, the foetal blood comes very close to the maternal blood, and this permits the exchange of materials between the two. Food (glucose, amino acids, lipids), water, mineral salts, vitamins, hormones, antibodies and oxygen pass from the maternal blood into the foetal blood, and foetal metabolic wastes, such as carbon dioxide, urea and warn pass into the maternal blood.
What is the signal for parturition?
The signals for parturition orginate from the fully developed foetus and the placenta which induce mild uterine contractions called foetal ejection reflex. Parturition is induced by a complex neuroendocrine mechanism. When time comes for the baby to be delivered, pituitary gland secretes adrenocortico tropic hormone (ACTH) which stimulates the adrenal glands to secrete steroids.
What hormone stimulates milk production?
The production and release of milk is called lactation (L. lactare = to suckle). Prolactin, a hormone of anterior pituitary stimulates lactation after parturition. High levels of estrogen act directly on mammary glands and can block the stimulation by prolactin. The mother produces thick, yellowish, high protein fluid called colostrum for 2-3 days after parturition.
Where does the blood of the foetus come from?
The blood of the foetus in the capillaries of the chorionic villi comes in close contact with the mother’s blood in the tissue between the villi, Inn they are always separated by a membrane, through which substances must diffuse or lie transported by some active, energy requiring process. The type of placenta in man is of described as deciduate ...
Which organ digests protein before passing them into foetal blood?
The trophoblast ol the placenta digest protein before passing them into foetal blood.
What is the term for the involuntary contractions of the uterus?
Before child birth, there is a long series of involuntary contractions of uterus called as “labour pains”. Umblical cord is a tube containing blood vessels which connect the abdomen of the developing embryo with the placenta of the mother. Its position in the baby is shown by navel.
What does the placenta do?
2 Placenta removes the waste from the fetus for processing by the mother's body, also helps in filteration of microbes that cold was infection.
Why is placenta important?
1 It allows gas exchange so that the fetus gets enough of oxygen and also helps it to get sufficient nuterition. 2 Placenta removes the waste from the fetus for processing by the mother's body, also helps in filteration of microbes that cold was infection. Answer verified by Toppr. Upvote (0)
What is the placenta?
The placenta is defined as an organ that develops during pregnancy in mammals. The placenta provides oxygen and nutrients to the growing fetus in the uterus of the mother.
How long is the placenta?
The placenta is disk-shaped and measures up to 22 cm in length. The placenta is also rich in blood vessels. The placenta is formed by chorion and the uterine tissue.
Where is the waste material excreted from the fetus?
The waste materials from the fetus is excreted through the placenta.