
What are the characteristics of precipitation gravimetric analysis?
All precipitation gravimetric analysis share two important attributes. First, the precipitate must be of low solubility, of high purity, and of known composition if its mass is to accurately reflect the analyte’s mass. Second, the precipitate must be easy to separate from the reaction mixture.
What are the conditions for a precipitate to be considered precipitate?
In addition to having a low solubility, the precipitate must be free from impurities. Because precipitation usually occurs in a solution that is rich in dissolved solids, the initial precipitate is often impure. We must remove these impurities before determining the precipitate’s mass.
What is a precipitation reaction?
A precipitation reaction is a useful method for identifying inorganic and organic analytes. Because a qualitative analysis does not require quantitative measurements, the analytical signal is simply the observation that a precipitate has formed.
What are insoluble compounds in precipitation gravimetry?
In precipitation gravimetry an insoluble compound forms when we add a precipitating reagent, or precipitant, to a solution containing our analyte.
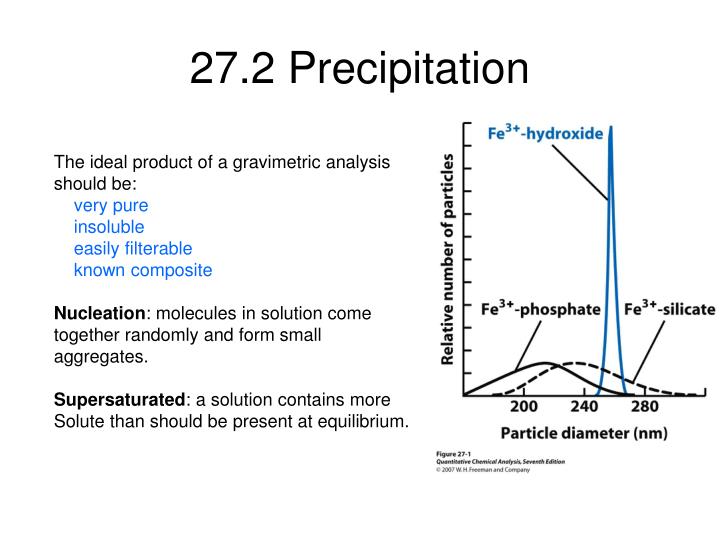
What is co precipitation and post precipitation with example?
An example for coprecipitation is the precipitation of silver ions with other ions during the silver chloride precipitation; an example for post precipitation is the formation of calcium oxalate after the precipitation of magnesium oxalate.
What is co precipitation in gravimetric analysis?
In gravimetric analysis, which consists on precipitating the analyte and measuring its mass to determine its concentration or purity, coprecipitation is a problem because undesired impurities often coprecipitate with the analyte, resulting in excess mass.
How can post precipitation be avoided?
The post precipitation can be avoided by using water-immiscible liquid. Explanation: Post precipitation is the kind of precipitation where the precipitation of the undesirable compound takes place after the formation of the precipitate of the desired compound.
What is precipitation gravimetry used for?
Precipitation gravimetry can be used to determine the mass of sodium sulfate in an aqueous solution. A good precipitating agent would be barium chloride, as the sulfate and barium ions would react to form the insoluble barium sulfate.
What is Post and co precipitation?
Coprecipitation is a kind of precipitation where soluble compounds in a solution are eliminated during the course of precipitation. Post precipitation is a kind of precipitation where the precipitation of the undesirable compound occurs after the formation of the precipitate of the desired compound.
What is the difference between precipitation and co precipitation method?
Precipitation is settling down of insoluble particles from a solution. Co-precipitation is a process in which normally soluble compounds are carried out of solution by a precipitate. In precipitation, normally insoluble compounds are precipitated. But in co-precipitation normally soluble compounds are precipitated.
Why is HCl added in gravimetric analysis?
HCl is added to prevent the precipitation of other anions such as phosphate, fluoride or carbonate (which the solution may contain) as their insoluble barium salts on the addition of BaCl2 solution.
What is the principle of gravimetry?
The principle of Gravimetric Analysis: The principle behind the gravimetric analysis is that the mass of an ion in a pure compound and can be determined. Later, used to find the mass percent of the same ion in a known quantity of an impure compound.
What is gravimetry in pharmaceutical analysis?
The gravimetric analysis technique measures a change in mass to determine the concentration of a substance or the mass of a substance. Analyses are also known as analyses because they involve chemical substances. A technique based on mass measurement can ascertain the amount of analyte (the element being analyzed).
What are the steps in precipitation gravimetry?
The steps required in gravimetric analysis, after the sample has been dissolved, can be summarized as follows: preparation of the solution, precipitation, digestion, filtration, Washing, drying or igniting, weighing and finally calculation.
How do you calculate gravimetry?
0:009:25Gravimetric Analysis Calculation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipRemember the HCL is not a reactant you heat it and then at the end you isolate this precipitate thatMoreRemember the HCL is not a reactant you heat it and then at the end you isolate this precipitate that is formed. Because of the reaction between the sulphate and barium which is the barium sulfate.
What is drying and ignition?
Drying and Ignition of Precipitate: Heating of precipitate below 250oC is referred as drying. The purpose of drying and ignition of precipitate is to obtain a compound of known and constant composition. During this drying, the water associated with the precipitate is also get remove.
What is the purpose of precipitation gravimetry?
Precipitation gravimetry is an analytical technique that uses a precipitation reaction to separate ions from a solution. The chemical that is added to cause the precipitation is called the precipitant or precipitating agent. The solid precipitate can be separated from the liquid components using filtration, and the mass of the solid can be used along with the balanced chemical equation to calculate the amount or concentration of ionic compounds in solution. Sometimes you might hear people referring to precipitation gravimetry simply as gravimetric analysis, which is a broader class of analytical techniques that includes precipitation gravimetry and volatilization gravimetry. If you want to read more about gravimetric analysis in general, see this article on gravimetric analysis and volatilization gravimetry.
How do we predict the products of a precipitation reaction?
You might remember that precipitation reactions are a type of double replacement reaction, which means we can predict the products by swapping the anions (or cations) of the reactants . We might check our solubility rules if necessary, and then balance the reaction. In this problem we are already given the identity of the precipitate, . That means we just have to identify the other product, , and make sure the overall reaction is balanced. The resulting balanced chemical equation is:
What happens if precipitate is not completely dry?
A higher mass of will result in calculating more moles of in Step , which will be converted into more moles of in our mixture. In the last step, we will end up calculating that the mass percent of is higher than it really is.
How to check for water in a sample?
Lab tip: If you have time, one way to check for water in the sample is to recheck the mass a few times during the end of the drying process to make sure the mass is not changing even if you dry it longer . This is called drying to constant mass, and while it does not guarantee that your sample is completely dry, it certainly helps! You can also try stirring up your sample during the drying process to break up clumps and increase surface area. Make sure you don't tear holes in the filter paper, though!
Can stoichiometry be used to analyze precipitation?
We now know how to use stoichiometry to analyze the results of a precipitation gravimetry experiment. If you are doing gravimetric analysis in lab, however, you might find that there are various factors than can affect the accuracy of your experimental results (and therefore also your calculations). Some common complications include:
Can we use the molecular weight of a precipitate to convert it to moles?
Since we are assuming that the mass of the precipitate is all , we can use the molecular weight of to convert the mass of precipitate to moles.
Does all of the precipitating agent react to form?
All of the has reacted to form . In terms of the stoichiometry, we need to make sure we add an excess of the precipitating agent so all of the from reacts.
What is precipitation gravimetry?
In precipitation gravimetry an insoluble compound forms when we add a precipitating reagent, or precipitant, to a solution containing our analyte. In most methods the precipitate is the product of a simple metathesis reaction between the analyte and the precipitant; however, any reaction generating a precipitate can potentially serve as a gravimetric method.
What are the attributes of precipitation gravimetric analysis?
All precipitation gravimetric analysis share two important attributes. First, the precipitate must be of low solubility, of high purity, and of known composition if its mass is to accurately reflect the analyte’s mass. Second, the precipitate must be easy to separate from the reaction mixture.
Why is the solubility-precipitation equilibrium dynamic?
During digestion, the dynamic nature of the solubility–precipitation equilibrium, in which the precipitate dissolves and reforms , ensures that the occlusion is reexposed to the supernatant solution. Because the rates of dissolution and reprecipitation are slow, there is less opportunity for forming new occlusions.
Why do we need to remove residual traces of supernatant?
Because the supernatant is rich with dissolved inert ions, we must remove any residual traces of supernatant to avoid a positive determinate error without incurring solubility losses. In many cases this simply involves the use of cold solvents or rinse solutions containing organic solvents such as ethanol. The pH of the rinse solution is critical if the precipitate contains an acidic or basic ion. When coagulation plays an important role in determining particle size, adding a volatile inert electrolyte to the rinse solution prevents the precipitate from reverting into smaller particles that might pass through the filter. This process of reverting to smaller particles is called peptization. The volatile electrolyte is removed when drying the precipitate.
How accurate is a precipitate?
To provide accurate results, a precipitate’s solubility must be minimal. The accuracy of a total analysis technique typically is better than ±0.1%, which means that the precipitate must account for at least 99.9% of the analyte. Extending this requirement to 99.99% ensures that the precipitate’s solubility does not limit the accuracy of a gravimetric analysis.
Why does size matter in precipitation?
Size matters when it comes to forming a precipitate. Larger particles are easier to filter, and, as noted earlier, a smaller surface area means there is less opportunity for surface adsorbates to form. By carefully controlling the reaction conditions we can significantly increase a precipitate’s average particle size.
Which table lists precipitants?
Any of the precipitants listed in Table 8.1, Table 8.3, and Table 8.4 can be used for a qualitative analysis.
What happens to gravimetric accuracy as the methods of gravimetric analysis are more and more investigated?
As the methods of gravimetric analysis are more and more investigated, the conditions securing accuracy become more define d; points of doubt are cleared up and the science becomes more exact.
What does the student have to do to ascertain the completeness of precipitation?
The student must bring all his chemical knowledge to bear in ascertaining the completeness of precipitation, and must always apply tests to check, the operation, that is, to ascertain whether too little or too much of the precipitant has been added.
Why should the habit of drowning the analysis with large doses of precipitant be carefully avoided?
The habit of drowning the analysis with large doses of precipitant must be carefully avoided, not because, as the student sometimes thinks, the authorities grudge him materials, but because such a practice leads to very uncertain results.
Can precipitate be thrown down?
Frequently, though not always, precipitates thrown down in hot to boiling solutions, with the gradual addition of the precipitating solution, aided by continual stirring, produce the best results.
Is silver precipitated by H2S?
Silver, for instance, is precipitated as the chloride AgCl, copper as the sulphide by H2S, iron as the hydroxide by NH4HO, and so on. He will also find that some methods are introduced which are either not used or are of minor importance in qualitative work.
Is precipitating reagent always added?
The precipitating reagent should always be added, unless otherwise specified, in the liquid form, or where a gas is the precipitating agent, it should be passed through the liquid, and in this case again heat frequently aids precipitation .
What are the attributes of precipitation?
All precipitation gravimetric analyses share two important attributes. First, the precipitate must be of low solubility, of high purity, and of known composition if its mass is to reflect accurately the analyte’s mass. Second, it must be easy to separate the precipitate from the reaction mixture.
How accurate is a precipitate?
To provide an accurate result, a precipitate’s solubility must be minimal. The accuracy of a total analysis technique typically is better than ±0.1%, which means the precipitate must account for at least 99.9% of the analyte. Extending this requirement to 99.99% ensures the precipitate’s solubility will not limit the accuracy of a gravimetric analysis.
Why do we need to remove residual traces of supernatant?
Because the supernatant is rich with dissolved inert ions, we must remove residual traces of supernatant without incurring loss of analyte due to solubility. In many cases this simply involves the use of cold solvents or rinse solutions that contain organic solvents such as ethanol. The pH of the rinse solution is critical if the precipitate contains an acidic or a basic ion. When coagulation plays an important role in determining particle size, adding a volatile inert electrolyte to the rinse solution prevents the precipitate from reverting into smaller particles that might pass through the filter. This process of reverting to smaller particles is called peptization. The volatile electrolyte is removed when drying the precipitate.
Why is silver not a selective precipitant?
For example, silver is not a selective precipitant for chloride because it also forms precipitates with bromide and with iodide. Interferents often are a serious problem and must be considered if accurate results are to be obtained.
Why is precipitation impure?
Because precipitation usually occurs in a solution that is rich in dissolved solids, the initial precipitate often is impure. To avoid a determinate error, we must remove these impurities before we determine the precipitate’s mass.
Why does size matter in precipitation?
By controlling the reaction conditions we can significantly increase a precipitate’s average particle size.
Is precipitation gravimetry time intensive?
Precipitation gravimetry is time intensive and rarely practical if you have a large number of samples to analyze; however, because much of the time invested in precipitation gravimetry does not require an analyst’s immediate supervision, it is a practical alternative when working with only a few samples. Equipment needs are few—beakers, filtering devices, ovens or burners, and balances—inexpensive, routinely available in most laboratories, and easy to maintain.
What happens to precipitate after drying?
After drying, the precipitate frequently has to be ignited, that is, heated to a dull or a bright red heat, either in the air or in a current of some gas such as hydrogen, carbon dioxide, coal gas, or oxygen.
How to wash a precipitate?
WASHING THE PRECIPITATE: A precipitate may be washed directly on the filter, or it may be washed partly by decantation and partly on the filter. If by decantation, the precipitate is allowed to settle, and the supernatant liquid is poured on the filter. Wash water is added to the precipitate, and after settling, the decantation is repeated a few times, and finally the precipitate is transferred to the paper or Gooch crucible.
How to remove precipitate from glass beaker?
Particles of precipitate adhering to a beaker may be removed by rubbing with a piece of rubber tubing on the end of a glass rod.
What temperature should a precipitate be in a water oven?
The actual temperature of the precipitate in the water oven rarely, if ever, reaches 100° C. under normal conditions; and when instructed to dry a precipitate in the water oven at 100° C., it will be sufficient to heat the water to the boiling point and transfer the precipitate to the oven. If specially desired, the boiling point ...
What happens after precipitate is separated from solution?
After the precipitate has been separated from the solution, it has in some cases to be dried and then weighed; in others, it has to be dried and ignited before weighing. The operations of drying and ignition and the necessary apparatus will now be described.
When is the washing water added to the Gooch method?
When the Gooch method is used, the washing water is added before the crucible is drained, a little liquid being kept above the filter till the final wash, when the crucible is drained.
