
How do you determine a dipole?
- The heightof the dipole above ground;
- The conductivityof the ground below;
- The dielectric constantof the ground below;
- The presence of buildings, trees, metal structures (tower) nearby.
What is the electric field due to a dipole?
Two equal and opposite charges separated by some distance constitute a dipole. The electric field strength due to a dipole, far away, is always proportional to the dipole moment and inversely proportional to the cube of the distance. Dipole moment is the product of the charge and distance between the two charges.
What is equation to calculate potential energy?
Formula. To calculate potential energy multiply the mass of the body (object) with the gravitational acceleration and the height from the surface of the Earth. The formula (equation) to calculate potential energy is [1]: E p = m · g · h (1) where: E p [J] – potential energy;
What is the formula Fo potential energy?
The formula for potential energy that is used depends on the type of energy that is stored. To calculate the potential energy of an object, the formula for potential energy (PE) is PE = mgh, where m stands for mass of the object in kilograms (kg), g is the gravitational field strength and h is the height of the object in meters (m).
Why is potential energy of a dipole negative?
If we rotate the dipole through a small angle do, the work done by the torque is dW=Ide =-pE sino de. The work is negative as the rotation de is opposite to the torque. The change in electric potential energy of the dipole is, therefore, dU=-dW=pE sino do.
What is the potential energy of the charge and dipole system?
Solution : `E = (1)/(4 pi epsilon_0) q/(a^2)` (Fig .
What is the potential energy of a dipole when it is parallel to a magnetic field?
Thus, potential energy is minimum when dipole is parallel to B.
Why is electric potential 0 in a dipole?
The potential energy is zero since for a dipole the potential energy is zero at its equatorial plane, and potential energy is nothing but potential × charge.
How do you find the electric potential of a dipole?
Electric Potential of a Dipole Electric dipole moment is represented by a vector p of magnitude 2qa and this vector points in direction from -q to +q. To find electric potential due to a dipole consider charge -q is placed at point P and charge +q is placed at point Q as shown below in the figure.
How do you find potential energy of a dipole in an electric field?
P.E=−pEcosθ=−p⋅E. This is negative when θ is acute and positive when θ is obtuse. You should verify that the product of p and E does have the dimensions of energy.
What is the potential energy of a dipole when it is perpendicular to magnetic field?
What is the potential energy of a dipole when it is perpendicular to a magnetic field? UPLOAD PHOTO AND GET THE ANSWER NOW! Solution : `P.E.=-MB cos theta=-MB cos 90^@=zero`.
What is minimum potential energy of a magnetic dipole in magnetic field?
zero
R: The minimum potential energy of magnetic dipole is zero.
What do you mean by potential energy of a magnet?
The potential energy of a magnet or magnetic moment in a magnetic field is defined as the mechanical work of the magnetic force (actually magnetic torque) on the re-alignment of the vector of the magnetic dipole moment and is equal to: while the energy stored in an inductor (of inductance ) when a current.
Where is zero potential in a dipole?
The locus of the point of zero potential of an electrical dipole is straight line drawn at the middle of the electric dipole.
Is potential on a dipole zero?
From the above equation, we can see that the potential energy of dipole placed in an external field is zero when the angle Ɵ is equal to 90° or when the dipole makes an angle of 90°.
Where is the electric potential 0?
The electric potential is zero at an infinite distance from the point charge. For two opposite charges of equal magnitude, the electric potential is zero in the middle since the electric field between both the charges will be equal and opposite. Was this answer helpful?
What is the potential energy of the charge?
The electric potential energy of any given charge or system of changes is termed as the total work done by an external agent in bringing the charge or the system of charges from infinity to the present configuration without undergoing any acceleration.
What is the potential energy of dipole with charge particles system as shown in Figure?
What is the potential energy of dipole with charge particles system as shown in (Fig. 3.96) ? . UPLOAD PHOTO AND GET THE ANSWER NOW! Solution : Potential energy of dipole will be zero because electric field due to point charges at dipole will cancel out.
What is relation between potential energy and dipole moment?
The highest potential energy is present in an electric dipole when the angle between the dipole moment and electric field is 180°.
What orientation of the dipole has the greatest electric potential energy?
The potential energy is lowest when the dipole is aligned with E and highest if it is anti-aligned. If the field is not uniform, then the magnitude of the electric force acting on the positive charge can be different from that acting on the negative charge, and there can be a net force acting on the dipole.
When is the potential energy of a dipole placed in an external field?
From the above equation, we can see that the potential energy of dipole placed in an external field is zero when the angle Ɵ is equal to 90° or when the dipole makes an angle of 90°.
When a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field, does the charge experience a force?
As we know that, when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field, both the charges as a whole do not experience any force, but it experiences a torque equal to τ which can be given as, This torque rotates the dipole unless it is placed parallel or anti-parallel to the field.
What determines the energy of a dipole in an electric field?
The energy of a dipole in an electric field depends on the orientation of the dipole relative to the field.
What is the true electric potential at a dipole's center due to the dipole?
The true electric potential at a dipole’s center due to the dipole is zero.
What happens when a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field?
When you have a dipole placed in a uniform electric field, it experiences some torque which tends to rotate the dipole. If you want to rotate the dipole further, you will need to do some work, the work done is called Potential energy of the dipole and is represented by U.
When the dipole is aligned perpendicular to the field, what is the potential energy?
That means that when the dipole is aligned perpendicular to the field the potential energy is zero. When it is aligned opposite to the field you have to store energy = dipole moment times the field, and if it is aligned
When is potential energy 0?
According to this the potential energy is - pE when the dipole is aligned with the field direction, 0 when it is rotated perpendicular to the field and + pE when it's direction is opposite to that of the field. Recall that the potential energy is always considered relative to a reference.
When we do some work, we rotate the dipole by an additional angle?
When we do some work we rotate the dipole by an additional angle say d θ. Due to this work the dipole gets inclined to the uniform electric field from an angle θ 1 to θ 2
When the field and dipole moment are pointed the same way, what is the result?
Changes that store energy are taken to be positive and those that release energy as negative (well, except in come conventions in thermodynamics, never mind). So when the field and dipole moment are pointed the same way ( p → ⋅ E → is positive) we want a negative result, and when they are pointed the other way p → ⋅ E → is negative then we want a positive result.
What is an electric dipole?
An electric dipole is a pair of charges having equal magnitudes but opposite sign separated at a distance , say d. When such a dipole is placed in a uniform electric field, the electric field exerts force on the dipole which then rotates the dipole in clockwise or anticlockwise direction. Here we discuss the electric field and potential energy of an electric dipole.
How to find the direction of the electric field?
The unit vector ^j j ^ gives the direction to the electric field vector which is along y-axis. If E1y E 1 y is the y-component of E1 E 1 and E2y E 2 y is the y-component of E2 E 2, then you know that E1 = E1y E 1 = E 1 y and E2 = E2y E 2 = E 2 y (there is no x-component of electric field at the point p p ). The net electric field which is →E = →E y E → = E → y (the subscript y-represents the y-component) at the point p p is
What is the y component of an electric field?
The y-component of electric field due to the electric dipole is a zero vector, that is the y-component of one charge is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the y-component of another charge. The y-component of →E 1 E → 1 due to positive charge is Esinθ^j E sin. .
Is the net electric field negative?
As you can see from the above expression of the net electric field that the electric field is proportional to 1 y3 1 y 3 instead of 1 y2 1 y 2. The above expression of net electric field tells us that the net electric field is along negative y-direction in our case shown in Figure 2. If you consider only the magnitude of the net electric field, it is
What is dipole in electrical field?
A dipole is a pair of opposite charges with equal magnitudes separated by a distance, d. Where is the permittivity of free space. The electric potential is a scalar field whose gradient becomes the electrostatic vector field. Since it is a scalar field, it is easy to find the potential due to a system of charges.
What is electric potential?
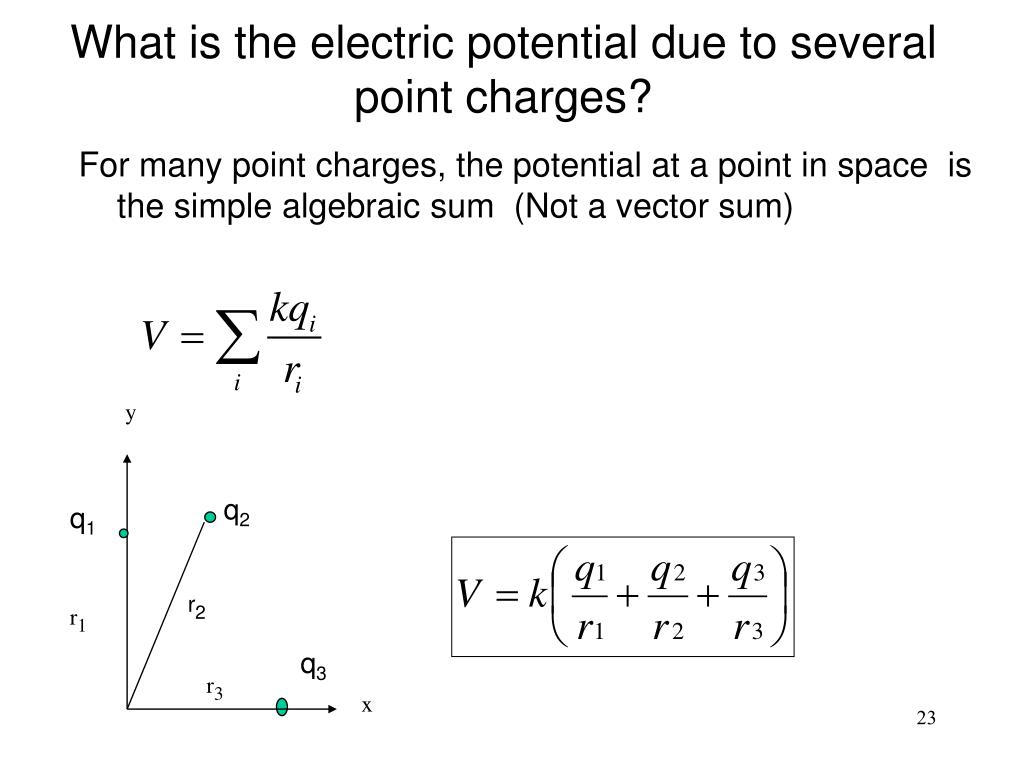
The electric potential is a scalar field whose gradient becomes the electrostatic vector field. Since it is a scalar field, it is easy to find the potential due to a system of charges. It is the summation of the electric potentials at a point due to individual charges.
How to find the overall dipole of a molecule?
If we imagined the Carbon Dioxide molecule centered at 0 in the XY coordinate plane, the molecule's overall dipole would be given by the following equation: ( 0) = 0.
What is dipole-dipole interaction?
Dipole-Dipole Interactions. Dipole-Dipole interactions result when two dipolar molecules interact with each other through space. When this occurs, the partially negative portion of one of the polar molecules is attracted to the partially positive portion of the second polar molecule.
Why does the V of a dipole go to zero?
It would seem, based on the above discussion, that in a system composed of a large number of dipolar molecules randomly interacting with one another, V should go to zero because the molecules adopt all possible orientations. Thus the negative potential energy of two molecular dipoles participating in a favorable interaction would be cancelled out by the positive energy of two molecular dipoles participating in a high potential energy interaction. Contrary to our assumption, in bulk systems, it is more probable for dipolar molecules to interact in such a way as to minimize their potential energy (i.e., dipoles form less energetic, more probable configurations in accordance with the Boltzmann's Distribution ). For instance, the partially positive area of a molecular dipole being held next to the partially positive area of a second molecular dipole is a high potential energy configuration and few molecules in the system will have sufficient energy to adopt it at room temperature. Generally, the higher potential energy configurations are only able to be populated at elevated temperatures. Therefore, the interactions of dipoles in a bulk Solution are not random, and instead adopt more probable, lower energy configurations. The following equation takes this into account:
Why do atoms have dipoles?
Molecular dipoles occur due to the unequal sharing of electrons between atoms in a molecule. Those atoms that are more electronegative pull the bonded electrons closer to themselves. The buildup of electron density around an atom or discreet region of a molecule can result in a molecular dipole in which one side of the molecule possesses a partially negative charge and the other side a partially positive charge. Molecules with dipoles that are not canceled by their molecular geometry are said to be polar.
What happens to the molecules as the temperature of the system increases?
As the temperature of the system increases, more molecules have sufficient energy to occupy the less favorable configurations. The higher, less favorable, configurations are those that give less favorable interactions between the dipoles (i.e., higher potential energy configurations). Example 5.
How do dipole interactions affect living organisms?
The biggest impact dipole interactions have on living organisms is seen with protein folding. Every process of protein formation, from the binding of individual amino acids to secondary structures to tertiary structures and even the formation of quaternary structures is dependent on dipole-dipole interactions.
What law allows charged atoms to interact with each other?
It is important to remember that due to the second law of thermodynamics, the amount of work done by an object can never exceed (and is often considerably less) than the objects potential energy. On a subatomic level, charged atoms have an electric potential which allows them to interact with each other.
Magnitude and Direction of An Electric Dipole Moment
Importance of Electric Dipoles
- Molecules whose centre of positive charge and centre of negative charge coincide are called non-polar molecules as they lack polarity due to zero dipole moment. Methane and carbon dioxide are a few examples of non-polar molecules with zero dipole moment. On the other hand, molecules having a permanent dipole moment are called polar molecules. The concept of an electric dipol…
Electric Potential Energy of An Electric Dipole in A Uniform Field
- Electric Dipole in an External Electric Field Let’s consider a dipole consisting of two equal and opposite charges +q and -q, separated by a distance d in a uniform electric field of field intensity E. The force experienced by individual charges is +qE and -qE. In the case of electric dipoles, instead of experiencing any force individually, they ex...
Summary
- An electric dipole consists of two charges with an equal magnitude but in opposite directions. It is important for these two charges not to coincide so that they form polar molecules which have various significant applications in the field of chemistry and physics. The potential energy of an electric dipole placed in a uniform external electric field is the amount of work done in bringing …