
What does prediction mean in a scientific method?
Understanding Hypotheses and Predictions
- Research Questions. Descriptive research questions are based on observations made in previous research or in passing. ...
- Hypothesis. In simple terms, a hypothesis is the answer to your causal question. ...
- Prediction. On the other hand, a prediction is the outcome you would observe if your hypothesis were correct. ...
- A final note. ...
What are the 6 steps of the scientific method?
the six steps of the scientific method include: 1) asking a question about something you observe, 2) doing background research to learn what is already known about the topic, 3) constructing a hypothesis, 4) experimenting to test the hypothesis, 5) analyzing the data from the experiment and drawing conclusions, and 6) communicating the results to …
Can you prove God exist using the scientific method?
The scientific method can’t be used to measure or detect God for at least three reasons. 2. The first reason is due to the fact that God exists outside of space, and the scientific method is only able to measure things inside of our spatial universe. 3.
Can you prove anything using the scientific method?
it is impossible for the scientific method (SM) to prove that anything is true. Yes, this is well known. Varsha Verma said: So like mathematics, the scientific method builds knowledge on axioms which cannot be proven to be true. I would say that the scientific method builds knowledge on experimental evidence, not axioms.
What is the scientific method?
What is the purpose of performing an experiment?

What is an example of a prediction?
Predictions can be types of guesses, but they usually come directly from observations . For example, if a delivery driver comes to your house every day at 2 p.m. for four days in a row, you might predict that the driver will come the following day at the same time.
What is a prediction in science simple definition?
Therefore, by definition, a prediction is making a statement of what will happen in the future. In science, a prediction is what you expect to happen if your hypothesis is true. So, based on the hypothesis you've created, you can predict the outcome of the experiment.
Is hypothesis a prediction?
Hypothesis refers to the supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence, as a starting point for further investigation. On the other hand, prediction refers to a thing that is predicted or a forecast of something. Thus, this explains the main difference between hypothesis and prediction.
What is a scientific prediction called?
scientific hypothesis, an idea that proposes a tentative explanation about a phenomenon or a narrow set of phenomena observed in the natural world.
Why is scientific prediction important?
To give the advice, experts often would like to draw on the results of an experiment. But they don't always have relevant experimental evidence. Collecting expert predictions about research results could be a powerful new tool to help improve science - and the advice scientists give.
What makes a good prediction?
Predicting requires the reader to do two things: 1) use clues the author provides in the text, and 2) use what he/she knows from personal experience or knowledge (schema). When readers combine these two things, they can make relevant, logical predictions.
What comes first hypothesis or prediction?
A scientist creates a hypothesis prior to the experiment, where a prediction typically occurs following the results of the experiment and the determination of whether the hypothesis is true.
What is the difference between prediction and test?
A prediction is a possible answer to the question, and a test is what you take at the end of the semester in class. A prediction is usually a specific statement “if . . .then”, and the test is the actual experiment used to obtain data.
What is a prediction definition for kids?
Prediction is using evidence from a text to say what may happen next, what events may unfold or how a character may behave.
How do you explain prediction to a child?
Ask the child what they think will happen next, and make them point out clues in the image that support their prediction....Ask “what if” questions.“What if I put salt instead of sugar in your tea? ... “What if the sun didn't rise? ... “What if everything you touched turned into candy?More items...
What is the meaning of prediction for kids?
Kids Definition of prediction 1 : an act of predicting. 2 : something predicted : forecast a prediction that there would be an earthquake. Other Words from prediction. predictive \ -ˈdik-tiv \ adjective.
What is a prediction for kids?
A prediction is a statement that someone makes about what they think is going to happen. It is often very helpful to know what is going to happen to help prepare for these future events. Predictions are based on the idea that two beginning positions that are like each other will have similar results.
The 6 Scientific Method Steps and How to Use Them - PrepScholar
When you’re faced with a scientific problem, solving it can seem like an impossible prospect. There are so many possible explanations for everything we see and experience—how can you possibly make sense of them all?
7 Steps of the Scientific Method - Padlet
A scientific of procedure that has characterized natural science since the 17th century.
What Is the Scientific Method? 7 Steps To Test Conclusions
A career in science involves using various processes and methods to reach conclusions. If you plan to pursue a scientific career path, it is helpful to understand some key methods that you might use and encounter in your daily tasks.
The five steps of the scientific method | Actforlibraries.org
The scientific method is a five-step process used in scientific investigation. Sometimes the steps are combined or added to, but the five are the basic structure for any endeavor to answer a question objectively.
Why did Popper use the idea of falsification to draw a line instead of pseudo and proper science?
The latter demarcation was the primary concern of many logical empiricists. Popper used the idea of falsification to draw a line instead between pseudo and proper science. Science was science because its method involved subjecting theories to rigorous tests which offered a high probability of failing and thus refuting the theory.
How is a theory confirmed?
A theory is then confirmed by testing, where more facts are brought under the theory, called the Consilience of Inductions. Whewell felt that this was the method by which the true laws of nature could be discovered: clarification of fundamental concepts, clever invention of explanations, and careful testing.
What is the scientific method?
The study of scientific method is the attempt to discern the activities by which that success is achieved. Among the activities often identified as characteristic of science are systematic observation and experimentation, inductive and deductive reasoning, and the formation and testing of hypotheses and theories.
Why is the scientific method used in research?
Also within mainstream science, reference to the scientific method is used in arguments regarding the internal hierarchy of disciplines and domains. A frequently seen argument is that research based on the H-D method is superior to research based on induction from observations because in deductive inferences the conclusion follows necessarily from the premises. (See, e.g., Parascandola 1998 for an analysis of how this argument has been made to downgrade epidemiology compared to the laboratory sciences.) Similarly, based on an examination of the practices of major funding institutions such as the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Biomedical Sciences Research Practices (BBSRC) in the UK, O’Malley et al. (2009) have argued that funding agencies seem to have a tendency to adhere to the view that the primary activity of science is to test hypotheses, while descriptive and exploratory research is seen as merely preparatory activities that are valuable only insofar as they fuel hypothesis-driven research.
What is the turn to practice in science?
This “turn to practice” can be seen as the latest form of studies of methods in science, insofar as it represents an attempt at understanding scientific activity, but through accounts that are neither meant to be universal and unified, nor singular and narrowly descriptive. To some extent, different scientists at different times and places can be said to be using the same method even though, in practice, the details are different.
Why are computer methods subjected to tests of verification and validation?
Because computers can be used to automate measurements, quantifications, calculations , and statistical analyses where, for practical reasons, these operations cannot be otherwise carried out, many of the steps involved in reaching a conclusion on the basis of an experiment are now made inside a “black box”, without the direct involvement or awareness of a human. This has epistemological implications, regarding what we can know, and how we can know it. To have confidence in the results , computer methods are therefore subjected to tests of verification and validation.
How did quantum and relativistic revolutions affect physics?
The quantum and relativistic revolutions in physics in the early 20 th century had a profound effect on methodology. Conceptual foundations of both theories were taken to show the defeasibility of even the most seemingly secure intuitions about space, time and bodies. Certainty of knowledge about the natural world was therefore recognized as unattainable. Instead a renewed empiricism was sought which rendered science fallible but still rationally justifiable.
What is Scientific Method?
The Scientific method is a process with the help of which scientists try to investigate, verify, or construct an accurate and reliable version of any natural phenomena. They are done by creating an objective framework for the purpose of scientific inquiry and analyzing the results scientifically to come to a conclusion which either supports or contradicts the observation made at the beginning.
What is the first step in the scientific method?
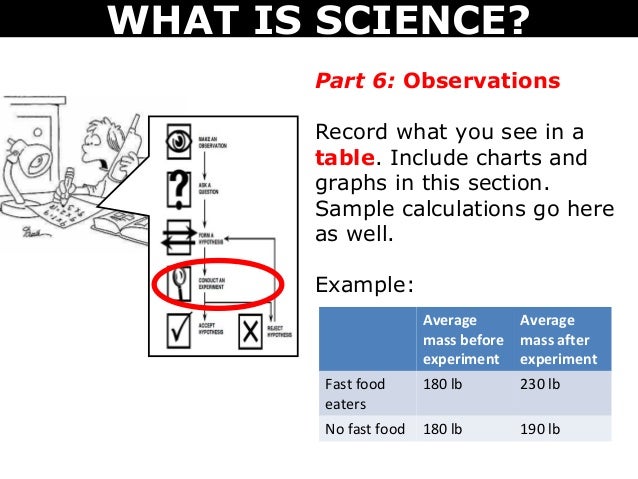
However, there is a generally accepted sequence of steps of scientific methods. Observation and formulation of a question: This is the first step of a scientific method. In order to start one, an observation has to be made into any observable aspect or phenomena of the universe and a question needs to be asked pertaining to that aspect.
How many bean plants are planted in the same pot?
Executing the hypothesis and collecting the data: Four bean plants are planted in identical pots using the same soil. Two are placed inside and the other two are placed outside. Parameters like the amount of exposure to sunlight, amount of water all are the same.
What happens if a hypothesis is not accepted?
If the data found in the analysis is consistent with the hypothesis, it is accepted. If not, then it is rejected or modified and analyzed again. It must be remembered that a hypothesis cannot be proved or disproved by doing one experiment.
How do scientists test a hypothesis?
Testing the hypothesis: After the hypothesis is made, it needs to be tested scientifically. Scientists do this by conducting experiments. The aim of these experiments is to determine whether the hypothesis agrees with or contradicts the observations made in the real world.
What is the confidence in the hypothesis?
The confidence in the hypothesis increases or decreases based on the result of the experiments. Analysis and Conclusion: This step involves the use of proper mathematical and other scientific procedures to determine the results of the experiment. Based on the analysis, the future course of action can be determined.
What is the difference between hypothesis and prediction?
HYPOTHESIS is the answer you think you'll find. PREDICTION is your specific belief about the scientific idea: If my hypothesis is true, then I predict we will discover this. EXPERIMENT is the tool that you invent to answer the question, and. CONCLUSION is the answer that the experiment gives.
What happens if your experiment isn't designed well?
You may not even get any definitive answer at all! The Scientific Method is a logical and rational order of steps by which scientists come to conclusions about the world around them.
What is the next stage of the scientific method?
The next stage of the Scientific Method is known as the "hypothesis.". This word basically means "a possible solution to a problem, based on knowledge and research.". The hypothesis is a simple statement that defines what you think the outcome of your experiment will be. All of the first stage of the Scientific Method -- the observation, ...
Why is it important to do an experiment?
It is absolutely necessary to design a science fair experiment that will accurately test your hypothesis. The experiment is the most important part of the scientific method. It's the logical process that lets scientists learn about the world.
Why is the scientific method important?
The Scientific Method helps to organize thoughts and procedures so that scientists can be confident in the answers they find. OBSERVATION is first step, so that you know how you want to go about your research. HYPOTHESIS is the answer you think you'll find.
Why is science fair not a failure?
Remember, a science fair experiment isn't a failure simply because does not agree with your hypothesis. No one will take points off if your prediction wasn't accurate. Many important scientific discoveries were made as a result of experiments gone wrong!
Why is it important to use as many sources as you can find?
For this stage of the Scientific Method, it's important to use as many sources as you can find. The more information you have on your science fair topic, the better the design of your experiment is going to be, and the better your science fair project is going to be overall.
What is the scientific method?
The scientific method is a specific approach to induction reasoning. With induction, you generalize from a set of effects or observations to produce laws or rules. Deduction is the opposite, you would start from a rule to deduce an effect. The ancient Greeks discussed induction widely, and this discussion was continued by Arab Alchemists and many medieval European philosophers. The scientific method refines the process of induction so that it could more consistently produce valuable new knowledge. This page only briefly summarizes the scientific method.
What is the purpose of performing an experiment?
Perform an experiment or experiments to ensure that results predicted based on hypothesis are achieved in the experiments.
Overview and Organizing Themes
- This entry could have been given the title Scientific Methods and goneon to fill volumes, or it could have been extremely short, consistingof a brief summary rejection of the idea that there is any such thingas a unique Scientific Method at all. Both unhappy prospects are dueto the fact that scientific activity varies so much acrossdisciplines, tim...
Historical Review: Aristotle to Mill
- Attempting a history of scientific method compounds the vast scope ofthe topic. This section briefly surveys the background to modernmethodological debates. What can be called the classical view goesback to antiquity, and represents a point of departure for later divergences.[1] We begin with a point made by Laudan (1968) in his historical surveyof scientific method: To se…
Logic of Method and Critical Responses
- The quantum and relativistic revolutions in physics in the early20thcentury had a profound effect on methodology.Conceptual foundations of both theories were taken to show thedefeasibility of even the most seemingly secure intuitions aboutspace, time and bodies. Certainty of knowledge about the natural worldwas therefore recognized as unattainable. Instead a renewed empiricism…
Statistical Methods For Hypothesis Testing
- Despite the many difficulties that philosophers encountered in tryingto providing a clear methodology of conformation (or refutation),still important progress has been made on understanding howobservation can provide evidence for a given theory. Work instatistics has been crucial for understanding how theories can betested empirically, and in recent decades a h…
Method in Practice
- Attention to scientific practice, as we have seen, is not itself new.However, the turn to practice in the philosophy of science of late canbe seen as a correction to the pessimism with respect to method inphilosophy of science in later parts of the 20thcentury,and as an attempted reconciliation between sociological andrationalist explanations of scientific knowledge. Much of t…
Discourse on Scientific Method
- Despite philosophical disagreements, the idea of thescientific method still figures prominently in contemporary discourseon many different topics, both within science and in society at large.Often, reference to scientific method is used in ways that conveyeither the legend of a single, universal method characteristic of allscience, or grants to a particular method or set of methods privilegea…
Conclusion
- The question of the source of the success of science has been at thecore of philosophy since the beginning of modern science. If viewed asa matter of epistemology more generally, scientific method is a partof the entire history of philosophy. Over that time, science andwhatever methods its practitioners may employ have changeddramatically. Today, many philosophers have taken u…