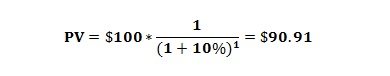
Present value
- Years' purchase. The traditional method of valuing future income streams as a present capital sum is to multiply the average expected annual cash-flow by a multiple, known as "years' purchase".
- Background. ...
- Interest rates. ...
- Calculation. ...
- Present value method of valuation. ...
- See also
- References. ...
- Further reading. ...
What is the formula for present value?
What is the formula for calculating the present value? The formula for calculating the present value is: Present Value = FV / (1+r) n . where, FV = Future value . r = Rate of return . n = Number of periods
What is present worth method?
straightforward. The present worth P is renamed PW of the alternative. The present worth method is quite popular in industry because all future costs and revenues are transformed to equivalent monetary units NOW; that is, all future cash flows are converted (discounted) to present amounts (e.g., dollars) at a specific rate of return, which is the MARR.
What is the rationale behind the net present value method?
What Is the Rationale Behind the Net Present Value Method?
- Definition and Rationale. NPV is a capital budgeting method for comparing the costs and benefits of proposed investments or projects.
- Absolute Decision Criteria. The NPV method provides straightforward criteria for choosing or rejecting investment projects. ...
- Time Value of Money. ...
- Budget Constraints. ...
What does present value mean?
Present value measures the effect of time on money. Present value is what a sum of money or a series of cash flows paid in the future is worth today at a rate of interest called the “discount” rate. Present value is used to plan for financial goals and to make investment decisions.

What is present value example?
Present value is the value right now of some amount of money in the future. For example, if you are promised $110 in one year, the present value is the current value of that $110 today.
How do you calculate present value?
The present value formula PV = FV/(1+i)^n states that present value is equal to the future value divided by the sum of 1 plus interest rate per period raised to the number of time periods.
What is the purpose of present value analysis?
In short, net present value analysis is an effective way to aggregate the cash flows associated with a business decision that are spread over a number of time periods, though some analysis may be required to accumulate all of the relevant cash flows.
What is present value method what are its advantages and disadvantages?
The advantages of the net present value includes the fact that it considers the time value of money and helps the management of the company in the better decision making whereas the disadvantages of the net present value includes the fact that it does not considers the hidden cost and cannot be used by the company for ...
What is the present value factor?
Present value factor, also known as present value interest factor (PVIF) is a factor that is used to calculate the present value of money to be received at some future point in time. In other words, this factor helps us to determine whether cash received now is worth more, or less than when it is received later.
How do you calculate present value by hand?
Calculating present value is called discounting. Discounting cash flows, like our $25,000, simply means that we take inflation and the fact that money can earn interest into account....Calculating Present Value Using the FormulaFV = the future value.i = interest rate.t = number of time periods.
What is PV in accounting?
Present value is the current worth of cash to be received in the future with one or more payments, which has been discounted at a market rate of interest.
Why is NPV the best method?
Net present value uses discounted cash flows in the analysis, which makes the net present value more precise than of any of the capital budgeting methods as it considers both the risk and time variables.
Which method is better NPV or IRR?
IRR is useful when comparing multiple projects against each other or in situations where it is difficult to determine a discount rate. NPV is better in situations where there are varying directions of cash flow over time or multiple discount rates.
Which is better NPV or payback?
NPV is the best single measure of profitability. Payback vs NPV ignores any benefits that occur after the payback period. It also does not measure total incomes. An implicit assumption in the use of payback period is that returns to the investment continue after payback period.
Which capital budgeting technique is best?
NPV Method is the most optimum method for capital budgeting. Reasons: Consider the cash flow during the entire product tenure and the risks of such cash flow through the cost of capital. It is consistent with maximizing the value to the company, which is not the case in the IRR and profitability index.
How do you calculate PV and FV?
Key TakeawaysThe present value formula is PV = FV/(1 + i) n where PV = present value, FV = future value, i = decimalized interest rate, and n = number of periods. ... The future value formula is FV = PV× (1 + i) n.
How do you calculate net present value example?
It is calculated by taking the difference between the present value of cash inflows and present value of cash outflows over a period of time. As the name suggests, net present value is nothing but net off of the present value of cash inflows and outflows by discounting the flows at a specified rate.
How do you find the present value factor on a calculator?
0:142:10How to Calculate Present value factor, factoring and constant on ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo let's start so here is the trick. For. Example you want to calculate. The factor for 10%. ForMoreSo let's start so here is the trick. For. Example you want to calculate. The factor for 10%. For let's say 3 to 4 years.
How do you calculate present value of cash flows?
PV = C / (1 + r) nC = Future cash flow.r = Discount rate.n = Number of periods.
Example 1 – Cash Inflow Project
The management of Fine Electronics Company is considering to purchase an equipment to be attached with the main manufacturing machine. The equipmen...
Example 2 – Cost Reduction Project
Smart Manufacturing Company is planning to reduce its labor costs by automating a critical task that is currently performed manually. The automatio...
Net Present Value Method – Uneven Cash Flow
Notice that the projects in the above examples generate equal cash inflow in all the periods (the cost saving in example 2 has been treated as cash...
Choosing Among Several Alternative Investment Proposals
Sometime a company may have limited funds but several alternative proposals. In such circumstances, if each alternative requires the same amount of...
Advantages and Disadvantages
The basic advantage of net present value method is that it considers the time value of money. The disadvantage is that it is more complex than othe...
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the net present value method?
Advantages and Disadvantages: The basic advantage of net present value method is that it considers the time value of money. The disadvantage is that it is more complex than other methods that do not consider present value of cash flows.
What is net present value?
Net present value is the difference between the present value of cash inflows and the present value of cash outflows that occur as a result of undertaking an investment project. It may be positive, zero or negative. These three possibilities of net present value are briefly explained below:
What happens if the present value of cash inflow is less than the present value of cash outflow?
If present value of cash inflow is less than present value of cash outflow, the net present value is said to be negative and the investment proposal is rejected.
What is the cash generated by a project?
The cash generated by a project is immediately reinvested to generate a return at a rate that is equal to the discount rate used in present value analysis.
Why is a project attractive?
The project seems attractive because its net present value is positive.
What is the purpose of investing in assets?
Investments in assets are usually made with the intention to generate revenue or reduce costs in future. The reduction in cost is considered equivalent to increase in revenues and should, therefore, be treated as cash inflow in capital budgeting computations.
Which proposal has the highest net present value?
Proposal X has the highest net present value but is not the most desirable investment. The present value indexes show proposal Y as the most desirable investment because it promises to generate 1.07 present value for each dollar invested, which is the highest among three alternatives.
What is the present value of an annuity?
The present value of an annuity is the value of all the payments received over a period of time in the future in today’s dollars, at a certain discount rate.
What is the present value of a lump sum in the future?
Think of the present value of a lump sum in the future as the money you would need to invest today at a rate of interest that would accumulate to the desired amount in the future. In the example above, the amount of money you need to invest today that will accumulate to $1,020 a year in the future at 2% is $1,000.
What is the present value factor of 4% for two years?
Present value factor at 4% for two years = .925 (see first table above)
What is future value?
We can also measure future value. Future value is what a sum of money invested today will be worth over time, at a specified rate of interest.
What is present value?
Present Value (PV) is today’s value of money you expect from future income and is calculated as the sum of future investment returns discounted at a specified level of rate of return expectation.
When is present value calculated?
Since the present value is calculated at the beginning of the period while making investment decisions , it includes some assumptions regarding inflation and the rate of returns on investment, which should be realistic and proper analysis; a comparison of various investment options is necessary to find the right plan to invest.
Why is present value important?
Present value calculation helps in making many investment decisions for the business as well as individuals; although the exact value cannot be calculated because of changing interest rates on many investments and inflationary effects , this calculation still helps in estimating individuals’ money worth in terms of his future expectation.
Why is PV calculation important?
Important for analysis: For every business, it is important to understand future cash inflow or outflow from business; PV calculation turns necessary when you expect a certain level of future cash flow.
What is future cash flow?
Future cash flow resulting after a certain period on today’s investments is known as Future value. When. It focuses on value at the beginning of a period. Future Value focuses on Value at the end of the period. Rate.
What is PV calculation?
Fundamental concept: To calculate the value of various investments like bonds, stocks, bank deposits, insurance, and pension funds, you need PV calculations. Time-value of money: level of interest rate, inflation, and periods helps in making on investment return you expect in the future from your investment.
Is interest rate considered when calculating future value?
Only the interest rate is considered while calculating future value. It is important to make the decision today regarding a particular investment. Future Value provides a number which will receive in the future, which does not affect decision making today. It is required to get a certain future value.
What are the two functions of net present value?
Excel offers two functions for calculating net present value: NPV and XNPV. The two functions use the same math formula shown above but save an analyst the time for calculating it in long form.
What does negative net present value mean?
If the net present value of a project or investment, is negative it means the expected rate of return that will be earned on it is less than the discount rate (required rate of return or hurdle rate#N#Hurdle Rate Definition A hurdle rate, which is also known as minimum acceptable rate of return (MARR), is the minimum required rate of return or target rate that investors are expecting to receive on an investment. The rate is determined by assessing the cost of capital, risks involved, current opportunities in business expansion, rates of return for similar investments, and other factors#N#). This doesn’t necessarily mean the project will “lose money.” It may very well generate accounting profit (net income), but since the rate of return generated is less than the discount rate, it is considered to destroy value. If the NPV is positive, it creates value.
Why Are Cash Flows Discounted?
The cash flows in net present value analysis are discounted for two main reasons, (1) to adjust for the risk of an investment opportunity, and (2) to account for the time value of money (TVM).
What is the NPV of a security?
For example, if a security offers a series of cash flows with an NPV of $50,000 and an investor pays exactly $50,000 for it, then the investor’s NPV is $0. It means they will earn whatever the discount rate is on the security. Ideally, an investor would pay less than $50,000 and therefore earn an IRR that’s greater than the discount rate.
What is NPV analysis?
NPV analysis is a form of intrinsic valuation and is used extensively across finance. and accounting for determining the value of a business, investment security, capital project, new venture, cost reduction program, and anything that involves cash flow.
What is XNPV function?
The XNPV function =XNPV () allows for specific dates to be applied to each cash flow so they can be at irregular intervals. The function can be very useful as cash flows are often unevenly spaced out, and this enhanced level of precision is required.
What is terminal value?
Finally, a terminal value is used to value the company beyond the forecast period, and all cash flows are discounted back to the present at the firm’s weighted average cost of capital. To learn more, check out CFI’s free detailed financial modeling course.
What Is Net Present Value (NPV)?
Net present value (NPV) is the difference between the present value of cash inflows and the present value of cash outflows over a period of time. NPV is used in capital budgeting and investment planning to analyze the profitability of a projected investment or project. NPV is the result of calculations used to find today’s value of a future stream of payments.
What is NPV analysis?
1 One important drawback of NPV analysis is that it makes assumptions about future events that may not be reliable.
What Is the Difference Between NPV and IRR?
NPV and IRR are closely related concepts, in that the IRR of an investment is the discount rate that would cause that investment to have an NPV of zero. Another way of thinking about this is that NPV and IRR are trying to answer two separate but related questions. For NPV, the question is, “What is the total amount of money I will make if I proceed with this investment, after taking into account the time value of money?” For IRR, the question is, “If I proceed with this investment, what would be the equivalent annual rate of return that I would receive?”
Why Are Future Cash Flows Discounted?
NPV uses discounted cash flows due to the time value of money (TMV). The time value of money is the concept that money you have now is worth more than the identical sum in the future due to its potential earning capacity through investment and other factors such as inflation expectations. The rate used to account for time, or the discount rate, will depend on the type of analysis undertaken. Individuals should use the opportunity cost of putting their money to work elsewhere as an appropriate discount rate—simply put, it’s the rate of return the investor could earn in the marketplace on an investment of comparable size and risk.
What is NPV in investing?
NPV seeks to determine the present value of an investment's future cash flows above the investment's initial cost. The discount rate element of the NPV formula discounts the future cash flows to the present-day value. If subtracting the initial cost of the investment from the sum of the cash flows in the present day is positive, then the investment is worthwhile. 2
What is NPV in finance?
NPV is used in capital budgeting and investment planning to analyze the profitability of a projected investment or project. NPV is the result of calculations used to find today’s value of a future stream of payments. It accounts for the time value of money and can be used to compare similar investment alternatives.
Why is IRR considered inferior to NPV?
Although the IRR is useful, it is usually considered inferior to NPV because it makes too many assumptions about reinvestment risk and capital allocation.
What is the net present value of a project?
Net present value (NPV) is a method used to determine the current value of all future cash flows generated by a project, including the initial capital investment. It is widely used in capital budgeting to establish which projects are likely to turn the greatest profit.
What does NPV mean in investment?
If the NPV of a project or investment is positive, it means that the discounted present value of all future cash flows related to that project or investment will be positive, and therefore attractive.
What is NPV in capital budgeting?
NPV is used in capital budgeting to compare projects based on their expected rates of return, required investment, and anticipated revenue over time. Typically, projects with the highest NPV are pursued. For example, consider two potential projects for company ABC:
Present Value
Present Value, or PV, is defined as the value in the present of a sum of money, in contrast to a different value it will have in the future due to it being invested and compound at a certain rate.
Net Present Value
A popular concept in finance is the idea of net present value, more commonly known as NPV. It is important to make the distinction between PV and NPV; while the former is usually associated with learning broad financial concepts and financial calculators, the latter generally has more practical uses in everyday life.
The Time Value of Money
PV (along with FV, I/Y, N, and PMT) is an important element in the time value of money, which forms the backbone of finance. There can be no such things as mortgages, auto loans, or credit cards without PV.
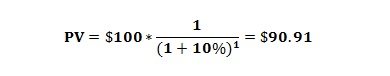
Understanding Present Value
- Present value is the concept that states an amount of money today is worth more than that same amount in the future. In other words, money received in the future is not worth as much as an equal amount received today. Receiving $1,000 today is worth more than $1,000 five years from …
Inflation and Purchasing Power
- Inflationis the process in which prices of goods and services rise over time. If you receive money today, you can buy goods at today's prices. Presumably, inflation will cause the price of goods to rise in the future, which would lower the purchasing power of your money. Money not spent today could be expected to lose value in the future by some implied annual rate, which could be inflati…
Discount Rate For Finding Present Value
- The discount rate is the investment rate of return that is applied to the present value calculation. In other words, the discount rate would be the forgone rate of return if an investor chose to accept an amount in the future versus the same amount today. The discount rate that is chosen for the present value calculation is highly subjective because it's the expected rate of return you'd recei…
PV Formula and Calculation
- Present Value=FV(1+r)nwhere:FV=Future Valuer=Rate of returnn=Number of periods\begin{alig…
Future Value vs. Present Value
- A comparison of present value with future value(FV) best illustrates the principle of the time value of money and the need for charging or paying additional risk-based interest rates. Simply put, the money today is worth more than the same money tomorrow because of the passage of time. Future value can relate to the future cash inflows from investing today's money, or the future pay…
Criticism of Present Value
- As stated earlier, calculating present value involves making an assumption that a rate of return could be earned on the funds over the time period. In the discussion above, we looked at one investment over the course of one year. However, if a company is deciding to go ahead with a series of projects that has a different rate of return for each year and each project, the present v…
Example of Present Value
- Let's say you have the choice of being paid $2,000 today earning 3% annually or $2,200 one year from now. Which is the best option? 1. Using the present value formula, the calculation is $2,200 / (1 +. 03)1= $2135.92 2. PV = $2,135.92, or the minimum amount that you would need to be paid today to have $2,200 one year from now. In other words, if you were paid $2,000 today and bas…
Definitions and Examples of Present Value
Types of Present Value
- Present Value of a Lump Sum
Think of the present value of a lump sumin the future as the money you would need to invest today at a rate of interest that would accumulate to the desired amount in the future. In the example above, the amount of money you need to invest today that will accumulate to $1,020 a … - Present Value of an Annuity
An annuityis a series of equal payments received for a fixed period of time. For example, lottery winners often have the option to receive their prize money in equal payments over 20 years. The present value of an annuity is the value of all the payments received over a period of time in the …
How Present Value Works
- The easiest way to calculate present value is to use one of the many free calculators on the internet, or a financial calculator app like the HP12C Financial Calculator, available on Google Play and in the Apple App Store. Most spreadsheet programs have present-value functions as well.
Present Value vs. Future Value
- We can also measure future value. Future value is what a sum of money invested today will be worth over time, at a specified rate of interest. As discussed earlier, $1,000 deposited in a savings account at a 2% annual interest rate has a future value of $1,020 at the end of one year. Let's look at what happens at the end of two years: That $1,000 deposit becomes $1,040.40. The extra ch…
How to Find Present Value?
Examples of Present Value
- Example #1
Mr. X wants $10,000 after three years. The interest rate available on a specific investment, which he is interested in, is 4% per annum. How much he should invest today to receive the desired amount. Solution Given, 1. Future Value = $10,000 2. Interest = 4% per annum 3. Period = 3 ye… - Example #2
Mr. A has $100,000 in hand from his savings; he wants $200,000 after ten years. He has three options, i.e., either. 1. Bank deposit at a rate of 4% per annum compounded quarterlyCompounded QuarterlyThe compounding quarterly formula depicts the total interest an …
Importance
- Important for analysis:For every business, it is important to understand future cash inflow or outflow from business; PV calculation becomes necessary when you expect a certain level of future cash...
- Fundamental concept: To calculate the value of various investments like bonds, stocks, bank deposits, insurance, and pension fundsPension FundsA pension fund refers to any plan or sc…
- Important for analysis:For every business, it is important to understand future cash inflow or outflow from business; PV calculation becomes necessary when you expect a certain level of future cash...
- Fundamental concept: To calculate the value of various investments like bonds, stocks, bank deposits, insurance, and pension fundsPension FundsA pension fund refers to any plan or scheme set up by...
- Time-value of money:level of interest rate, inflation, and periods helps in making an investment return you expect in the future from your investment. What is the current value of future worth that...
- Inflation effect:They make sure that the inflation effect on money is calculated over time by co…
Benefits
- Investment Decision:This method helps in making investment decisions since it calculates the current value of future cash flows in investment. If the investor does not have enough to invest from wh...
- Purchasing Power:Money worth today is more than the money worth tomorrow, which means a value of $100 today might not be equal to $100 after a year because inflation reduces the val…
- Investment Decision:This method helps in making investment decisions since it calculates the current value of future cash flows in investment. If the investor does not have enough to invest from wh...
- Purchasing Power:Money worth today is more than the money worth tomorrow, which means a value of $100 today might not be equal to $100 after a year because inflation reduces the value of money. Pre...
- Discount Rate: The rate of return on investment is called a discount rate. In other words, a combination of the time value of moneyTime Value Of MoneyThe Time Value of Money (TVM) principle states...
Limitation
- No guaranteed expected return: We calculate the PV by assuming interest rate over investment, but in reality, many investments cannot guarantee the rate of returns according to expectation, e.g., i...
- Inflation vs. Interest:If the inflation rate is higher than the interest rate on investments, then investment becomes worthless. Suppose the value of money you hold today is higher than to…
- No guaranteed expected return: We calculate the PV by assuming interest rate over investment, but in reality, many investments cannot guarantee the rate of returns according to expectation, e.g., i...
- Inflation vs. Interest:If the inflation rate is higher than the interest rate on investments, then investment becomes worthless. Suppose the value of money you hold today is higher than tomorrow pe...
Conclusion
- Present value calculation helps make many investment decisions for the business and individuals; However, the exact value cannot be calculated because of changing interest rates on many investments and inflationary effects; this calculation still helps in estimating individuals’ money worth in terms of their future expectations. Since the present value is calculated at the beginnin…
Recommended Articles
- This has been a guide to Present Value and its definition. Here we discuss how to find present value along with examples, benefits, limitations, and differences from future value. You can learn more about financing from the following articles – 1. How to Calculate Pension? 2. Present Value vs Future Value 3. Time Value of Money Formula 4. Present Value of an Annuity