What does PRF stand for in ultrasound?
Pulse repetition frequency (PRF) indicates the number of ultrasound pulses emitted by the transducer over a designated period of time. It is typically measured as cycles per second or hertz (Hz). In medical ultrasound the typically used range of PRF varies between 1 and 10 kHz 1.
What is medium Doppler PRF?
Medium PRF is used with Pulse-Doppler radar, which is required for look-down/shoot-down capability in military systems. Doppler radar return is generally not ambiguous until velocity exceeds the speed of sound. A technique called ambiguity resolution is required to identify true range and speed.
What is PRF (pulses per second)?
"Pulses per second" redirects here. It is not to be confused with Pulse-per-second signal. The pulse repetition frequency ( PRF) is the number of pulses of a repeating signal in a specific time unit, normally measured in pulses per second.
What is PRF in radar?
A radar system uses a radio frequency electromagnetic signal reflected from a target to determine information about that target. PRF is required for radar operation. This is the rate at which transmitter pulses are sent into air or space.

What is the PRF in ultrasound?
Pulse repetition frequency (PRF) indicates the number of ultrasound pulses emitted by the transducer over a designated period of time. It is typically measured as cycles per second or hertz (Hz).
Is PRF the same as frequency?
In radar, a radio signal of a particular carrier frequency is turned on and off; the term "frequency" refers to the carrier, while the PRF refers to the number of switches. Both are measured in terms of cycle per second, or hertz. The PRF is normally much lower than the frequency.
What does high PRF mean?
A high PRF can be used to determine Doppler frequency and therefore relative velocity for all targets. It can also be used when a moving object of interest is obscured by a stationary mass, such as the ground or a mountain, in the radar return.
How do you increase PRF on ultrasound?
Decreasing the pulse repetition period (PRP) to increase the PRF and the Nyquist limit. Applying a low-frequency transducer to create a small Doppler shift for blood flow velocity.
What does PRF stand for?
PRFAcronymDefinitionPRFPoint Response FunctionPRFPublic Relations FirmPRFPersonnel Resources File (US DoD)PRFProject Request Form60 more rows
How do you calculate PRF?
PRT is also equal to the sum, PRT = PW+RT. PRF = pulse repetition frequency. PRF has units of time-1 and is commonly expressed in Hz (1 Hz = 1/s) or as pulses per second (pps). PRF is the number of pulses transmitted per second and is equal to the inverse of PRT.
What is the significance of pulse repetition frequency?
Pulse Repetition Frequency (PRF) is the number of pulses of a repeating signal in a specified unit of time. The unit of time is usually one second. The PRF tells us how many pulses of a signal are repeated in one second. This term is particularly associated with radar applications.
What is the normal range of pulse repetition rates?
The pulse repetition rate (frequency) can vary between a single shot to 300 kHz, but the common workable range is 15–200 kHz.
What is PRF pulse width?
The number of pulses transmitted in one second is called the "frequency", and is most often referred to as the "PRF" (pulse repetition frequency). The "duty ratio" (often called the Duty Cycle) is the ratio of the pulse width (PW) to the pulse repetition frequency (PRF), and is given by...
What is the difference between pulsed wave and continuous wave Doppler?
Pulsed-Wave Doppler. Thus, pulsed-wave Doppler has signal aliasing at high frequencies but has depth acuity, whereas continuous-wave Doppler has no signal aliasing but does have depth ambiguity.
What is the main limitation of pulsed wave Doppler?
However, PW Doppler has a major drawback: it cannot correctly depict higher velocities (usually above 1.5 - 1.7m/sec). To understand the reasons we have to first address aliasing phenomena. Aliasing is best explained by the analogy of a clock.
What is the difference between PW and CW Doppler?
CW Doppler measures all blood flow velocities along the cursor line. This is in contrast to PW Doppler which measures flow at a specific point within the heart using a sample volume box. Thus CW can measure multiple different blood flows within different cardiac chambers throughout the cardiac cycle.
How is PRF related to frequency shift?
PRF is the Doppler sampling frequency of the transducer and is reported in kilo Hertz (KHz). The frequency with which these pulses are emitted determines the maximum Doppler shifts obtainable. The maximum Doppler shift frequency that can be sampled without aliasing is PRF/2, called the Nyquist limit [14].
What is the frequency of a pulse?
Pulse frequency is the number of cycles produced across the gap in 1 s. The higher the frequency, finer is the surface finish that can be obtained. With an increase of number of cycles per second, the length of the on-time decreases.
What is the relationship between frame rate and PRF?
True. PRF is the number of pulses created per second. In this example, it is the lines per image multiplied by frame rate. When the frame rate is 30 Hz, how long does it take to create a frame?
What is the maximum pulse rate frequency?
What Is Maximum Heart Rate? Your maximum heart rate is, on average, the highest your pulse can get. One way to get a rough estimate of your predicted maximum is to subtract your age from the number 220. For example, a 40-year-old's predicted maximum heart rate is about 180 beats per minute.
What is PRF in radar?
Typical values for a marine radar are 1000–3000 pps. The pulse repetition interval (PRI) is the time interval between pulses. It should be noted that PRF and PRI effectively refer to the same feature and are simply related by the expression PRF=1/PRI.
How does low PRF affect radar?
A very low PRF would result in appreciable rotation of the antenna before the next pulse, in the limit leaving azimuthal gaps where no targets could be detected. To also help reduce the possibility of such effects, the pulse length is chosen to be suitably short to limit the effective energy being radiated in order that excessive power does not exacerbate the situation (see also Section 2.3.3.3 ). This is all a bit of a compromise, but by experience suitable PRFs and pulse lengths are readily determined that give adequate performance. Even so, second trace echo effects are not an uncommon experience to the user, especially from very large targets, for example wind turbines located at distances rather longer than the user-set maximum displayed range (see also Section 3.9.6 ).
What is Doppler flowmetry used for?
Doppler flowmetry is also used for extracorporeal flow measurements, as in blood flow determination in vascular shunts (e.g., carotid shunt) and in cardiopulmonary bypass procedures.
What is the main ultrasound reflector in the circulatory system?
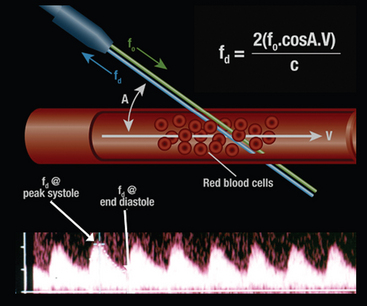
Red blood cells are the main ultrasound reflectors in the circulatory system. When transmitted beams reach blood cells that are moving away from transmitter ( Figure 7.10A ), ultrasound beams reflected back to the receptor transducer having lower frequency than the transmitted. The resultant Doppler shift, in this case, positive, brings information about flow direction and is proportional to the flow velocity. When the flow approaches the transducer ( Figure 7.10B ), the frequency of the reflected ultrasound beam is bigger than the transmitted frequency (negative Doppler shift).
What is the Doppler shift?
The change in frequency, which is also termed the Doppler shift, provides information about the object’s speed and direction of motion. Doppler shift flow transducer measures blood flow in a noninvasively transcutaneous way. The transducer is positioned over the skin, near the vessel whose flow is to be measured.
How many transducers does a Doppler shift use?
The Doppler shift can be obtained with continuous wave (CW Doppler) and pulsed wave (PW Doppler) ultrasound. CW Doppler needs two transducers: one continuously transmits the ultrasound beam, while the other continuously receives the reflected beams. PW Doppler can use only one transducer, which alternately emits and receives ultrasound beams to Doppler shift achievement ( Figure 7.11A ).
What is Doppler echocardiography?
Doppler echocardiography is a method for detecting the direction and velocity of moving blood within the heart. This technique is used for detection of cardiac insufficiency due to valves malfunctioning and stenosis, as well as a large number of other abnormal flows.
Why is PRF important in ultrasound?
This is explained by the fact that each ultrasound pulse generates a snapshot of blood flow. The greater the number of snapshots per unit of time, the more accurate the description of blood flow. This is illustrated in Figure 3, which depicts a clock observed 5, 3 and 2 times during one cycle. As shown in Figure 3A, it is possible to determine with certainty the direction of the rotation with 5 observations per cycle. Using 3 observations per cycle, it is not possible to determine the direction of the rotation. With 2 observations per cycle, it appears that there is no rotation. This example illustrates the significance of high pulse repetition frequency in order to obtain accurate assessments of blood flow and myocardial movement.
How is PRF important?
The importance of high PRF is explained mathematically by Nyquist’s theorem (Harry Nyquist), which demonstrates that a wave must be sampled ( i.e recorded) at least twice per cycle in order to be reliably measured. For pulsed wave Doppler, this implies that PRF must be at least twice the Doppler shift.
What is the maximum velocity that can be determined by Doppler shift?
Thus, the maximum velocity that can be determined is half the PRF and this limit is called the Nyquist limit.
What is the advantage of pulsed wave doppler?
The major advantage of pulsed wave Doppler is the ability to specify where (along the Doppler line) to measure velocities. This is possible because the pulsed wave Doppler sends and analyses sound waves sequentially. The ultrasound machine is programmed to ignore all signals, except those reflected from a certain depth.
How is pulse frequency determined?
The number of ultrasound pulses sent per second is called pulse repetition frequency (PRF). PRF is determined by the speed of sound and the distance it must travel. Since the speed of sound in the human body is constant (1540 m/s), the PRF only depends on the distance the sound waves must travel. The longer the distance, the more time required for sound waves to travel back and forth, which results in lower pulse repetition frequency (fewer ultrasound pulses can be sent per second).
What is a PW Doppler?
The pulsed wave Doppler (PW Doppler) sends short pulses of ultrasound and analyzes reflected sound waves between the pulses. This is accomplished by using the same piezoelectric crystals to send and analyze sound waves. The crystals alternate rapidly between sending and analyzing ultrasound. Therefore, emitted sound waves can be associated with reflected sound waves, making it possible to determine the distance of the reflector ( i.e the structure reflecting the sound wave).
Why is pulsed wave doppler important?
This is the main advantage of pulsed wave Doppler, namely its ability to determine the location of the measured velocities. However, the pulsed wave Doppler requires time to analyze reflected sound waves. This is due to the fact that the same piezoelectric elements are used to send and analyze sound waves. This reduces the maximum velocity that can ...
What is PRF in radar?
The term is used within a number of technical disciplines, notably radar . In radar, a radio signal of a particular carrier frequency is turned on and off; the term "frequency" refers to the carrier, while the PRF refers to the number of switches. Both are measured in terms of cycle per second, or hertz.
What is PRF in physics?
PRF is usually associated with pulse spacing, which is the distance that the pulse travels before the next pulse occurs.
What is the reciprocal of PRF?
The reciprocal of PRF (or PRR) is called the pulse repetition time ( PRT ), pulse repetition interval ( PRI ), or inter-pulse period ( IPP ), which is the elapsed time from the beginning of one pulse to the beginning of the next pulse. The IPP term is normally used when referring to the quantity of PRT periods to be processed digitally.
How many pulses per second is a Type 7 radar?
For instance, a typical World War II radar like the Type 7 GCI radar had a basic carrier frequency of 209 MHz (209 million cycles per second) and a PRF of 300 or 500 pulses per second. A related measure is the pulse width, the amount of time the transmitter is turned on during each pulse.
How does radar determine range?
A radar system determines range through the time delay between pulse transmission and reception by the relation:
What is pulse repetition frequency?
Pulse repetition frequency (PRF) is the number of times a pulsed activity occurs every second.
What is medium PRF?
Medium PRF is used with Pulse-Doppler radar, which is required for look-down/shoot-down capability in military systems . Doppler radar return is generally not ambiguous until velocity exceeds the speed of sound.
