Key Takeaways
- Price elasticity of demand is a measurement of the change in consumption of a product in relation to a change in its price.
- A good is elastic if a price change causes a substantial change in demand or supply.
- A good is inelastic if a price change does not cause demand or supply to change very much.
Full Answer
Is the price of any good inelastic or elastic?
If demand for a good or service is relatively static even when the price changes, demand is said to be inelastic, and its coefficient of elasticity is less than 1.0. Examples of elastic goods include clothing or electronics, while inelastic goods are items like food and prescription drugs. Click to see full answer.
What does it mean if a cost is inelastic?
They’re two economic terms used to describe how sensitive a good or service is to price fluctuations. If the demand for a product or service is sensitive to price fluctuations, it is considered elastic. If the opposite is true, and a product or service is not very sensitive to price fluctuations, it is considered inelastic.
What is the difference between price elastic and inelastic demand?
The differences between elastic and inelastic demand can be drawn clearly on the following grounds:
- Elastic Demand is when a small change in the price of a good, cause a greater change in the quantity demanded. ...
- The elasticity of demand can be calculated as a ratio of percent change in the price of the commodity to the percent change in price, if the coefficient of elasticity ...
- When the demand is elastic, the curve is shallow. ...
What is the difference between elastic and inelastic goods?
• Goods, which are elastic, are usually goods which have easily replaceable substitutes, and goods, which are inelastic, are usually necessities or goods which are habit forming.
What is the difference between inelastic and elastic demand?
The difference between inelastic and elastic demand lies in how easily things can impact consumer habits. Try to visualize something that is elastic, like a rubber band, and something that is inelastic, like twine. You can stretch and change rubber band with little effort. The same is true of elastic demand in economics. A slight change in something like price or supply yields significant changes in demand.
What is inelastic demand?
Similar to elastic demand, inelastic demand also represents buying trends relative to price. If consumers tend to buy the same amount of a product even after significant changes in price, economists describe that product as having inelastic demand. This means that demand for this product does not stretch or change easily.
What is economic demand?
Demand is a feature of economics that refers to consumer willingness or desire to purchase a product or service. Predicting demand has many factors, including price, availability and exclusivity. Further variations occur between target markets with different behaviors and income levels.
How to calculate elastic demand?
Economists calculate elastic demand by dividing the percentage of change in the quantity of items sold by the percentage of change in price.
What is the demand ratio of elastic demand?
When these two percentages change at the same rate, the demand ratio is equal to 1%. Products with elastic demand are those whose demand ratio is equal to 1% or greater. For example, if the price of an item drops by 10% and demand for that product raises by 25%, then the demand ratio is greater than 1%.
When a monopoly produces a good or service, the item typically has an inelastic demand?
Market competition: When a monopoly produces a good or service, the item typically has an inelastic demand. If new a competitor appears on the market, then demand tends to become elastic.
What is demand in economics?
Demand is a feature of economics that refers to consumer willingness or desire to purchase a product or service. Predicting demand has many factors, including price, availability and exclusivity. Further variations occur between target markets with different behaviors and income levels.
What is price elasticity?
Price elasticity refers to how the quantity demanded or supplied of a good changes when its price changes. In other words, it measures how much people react to a change in the price of an item. Price elasticity of demand refers to how changes to price affect the quantity demanded of a good. Conversely, price elasticity of supply refers ...
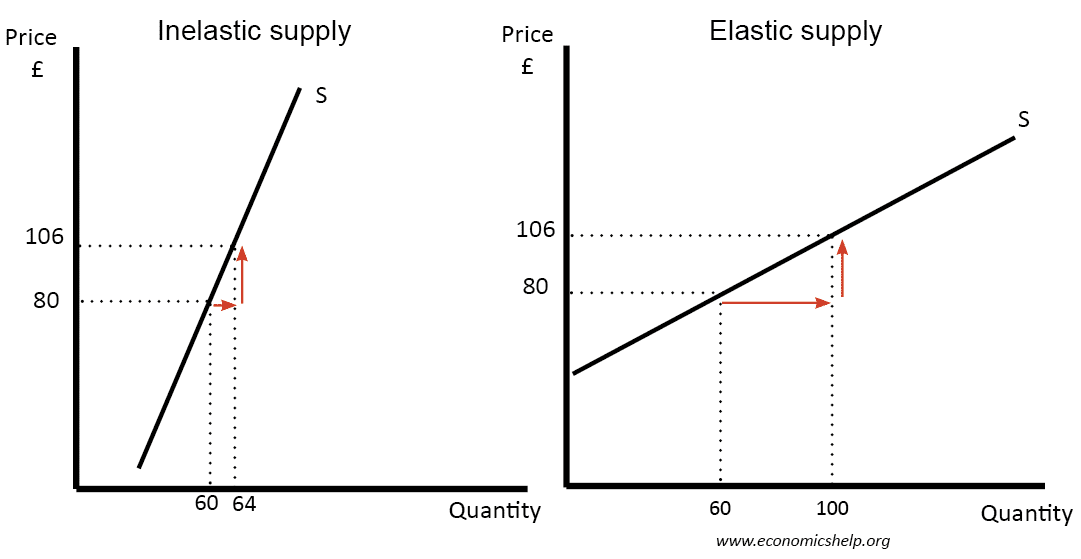
How does price elasticity of supply work?
Price elasticity of supply (PES) works in the same way that PED does. Equations to calculate PES are the same (except that the quantity used is the quantity supplied instead of quantity demanded).
What is the PED of a good with perfectly inelastic demand?
A good with perfectly inelastic demand would have a PED of 0, where even huge changes in price would cause no change in demand.
What does unit elastic PES mean?
Unit elastic PES would mean that increases in the price will lead to proportionately equal increases in quantity supplied.
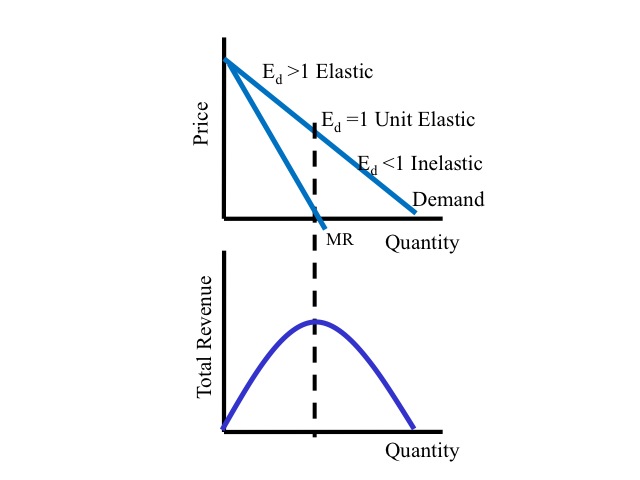
What is elastic demand?
Elastic demand occurs when changes in price cause a disproportionately large change in quantity demanded. For example, a good with elastic demand might see its price increase by 10%, but demand falls by 30% as a result.
Why is it not ideal to use the price elasticity formula?
Using this formula is not ideal because the direction of the change in price or quantity can affect the number calculated for price elasticity.
What would happen if demand was elastic?
A good with perfectly elastic demand would have a PED of infinity, where even minuscule changes in price would cause an infinitesimally large change in demand.
What Is Price Elasticity of Demand?
Price elasticity of demand is the ratio of the percentage change in quantity demanded of a product to the percentage change in price. Economists employ it to understand how supply and demand change when a product’s price changes.
What are some examples of inelastic products?
But the less discretionary a product is, the less its quantity demanded will fall. Inelastic examples include luxury items that people buy for their brand names. Addictive products are quite inelastic, as are required add-on products like ink-jet printer cartridges.
What Makes a Product Elastic?
If a price change for a product causes a substantial change in either its supply or demand , it is considered elastic. Generally, it means that there are acceptable substitutes for the product. Examples would be cookies, luxury automobiles, and coffee.
How to calculate elasticity of demand?
To calculate the elasticity of demand, consider this example: Suppose that the price of apples falls by 6% from $1.99 a bushel to $1.87 a bushel. In response, grocery shoppers increase their apple purchases by 20%. The elasticity of apples therefore is: 0.20/0.06 = 3.33, The demand for apples is quite elastic.
What is elastic product?
As a rule of thumb, if the quantity of a product demanded or purchased changes more than the price changes, the product is termed elastic. (For example, the price changes by +5%, but the demand falls by -10%).
What is the unitary price elasticity?
If the change in quantity purchased is the same as the price change (say, 10%/10% = 1) , the product is said to have unit (or unitary) price elasticity.
What is elastic demand?
If the quantity demanded of a product changes greatly in response to changes in its price, it is termed "elastic." That is, the demand point for the product is stretched far from its prior point. If the quantity purchased shows a small change after a change in its price, it is termed "inelastic." The quantity didn't stretch much from its prior point.
What is price elasticity?
Unless and otherwise specified, price elasticity is termed as the elasticity of demand, which is the degree of responsiveness of a product with respect to the change in price. It can be elastic or inelastic for a particular commodity.
What is the difference between elastic and inelastic demand?
The differences between elastic and inelastic demand can be drawn clearly on the following grounds: Elastic Demand is when a small change in the price of a good, cause a greater change in the quantity demanded. Inelastic demand means a change in the price of a good, will not have a significant effect on the quantity demanded.
Why do products with no or less close substitutes have an inelastic demand?
As compared to the products with a large number of substitutes, have an elastic demand because of the consumers switch to different substitute, if there is a small change in their prices.
What is elastic demand?
An elastic demand is one in which a slight change in the price will lead to drastic change in the demand for the product. It differs from an inelastic demand in the sense that a change in price may have no or little effect on the demand of consumers.
How to find the elasticity of demand?
The elasticity of demand can be calculated as a ratio of percent change in the price of the commodity to the percent change in price, if the coefficient of elasticity of demand is greater than, equal to 1, then the demand is elastic, but if it’s less than one the demand is said to be inelastic.
Why is demand inelastic?
The demand is said to be inelastic when the demand for the given product or service does not change in response to the fluctuations in price. Such a demand is not much sensitive to price.
When the demand for the given product is inelastic, what happens?
When the demand for the given product is inelastic then no matter what the price is, people will not stop buying it. In the same way, if the price falls, there will not be much change in the quantity demanded by consumers.
What is price elasticity?
Price elasticity is a measure of how consumers react to the prices of products and services. Normally demand declines when prices rise, but depending on the product/service and the market, how consumers react to a price change can vary. There are two types price elasticities:
What determines price elasticity?
Several factors determine price elasticity. For example, if there are no substitute products, demand tends to be inelastic. In such cases, suppliers have some power over price.
What is the measure of price elasticity of demand?
Price elasticity of demand: also known as PED or E d, is a measure in economics to show how demand responds to a change in the price of a product or service.
What is the elasticity of a PED?
The PED is -1 (minus one) Price elasticity may vary from minus one to plus one. Most products and services range from minus one to zero. Giffen or Veblen goods, on the other hand, range from zero to plus one.
Why is diet coke elastic?
Demand for one can of diet coke is elastic because there are other cheap alternatives available.
What is the difference between product C and product A?
In this image, demand for products A and B changes to a greater extent than alterations in price. Products D, E, and F have smaller demand changes than alterations in price. With product C, demand and prices change by the same proportion. Product A is a non-essential good (such as a weekend in a spa), product F is an essential good (such as milk or bread), while product C might be a Coke (people would turn to Pepsi if Coke’s price rose).
What is income elasticity of demand?
Income elasticity of demand measures how demand for a product or service changes when people’s incomes change.
What is inelastic demand?
Inelastic demand is when a buyer’s demand for a product does not change as much as its change in price. When price increases by 20% and demand decreases by only 1%, demand is said to be inelastic. This situation typically occurs with everyday household products and services. Products and Services A product is a tangible item ...
What are the two types of inelastic demand curves?
Demand Curve. There are two types of inelastic demand curves: 1. Perfectly inelastic demand. 2. Inelastic demand. An example of the two types of curves are shown below: Note: Perfectly inelastic demand is when a change in prices does not change the quantity of demand at all.
How many types of elasticity of demand are there?
There are five types of elasticity of demand:
How to draw a demand curve?
Using data from the example calculation, a demand curve is drawn by placing the price on the Y-axis and demand on the X-axis. The line drawn from the example data results in an inelastic demand curve.
What does "inelastic" mean in economics?
Inelastic means that a 1 percent change in the price of a good or service has less than a 1 percent change in the quantity demanded or supplied.
What Is Inelastic?
Inelastic is an economic term referring to the static quantity of a good or service when its price changes. Inelastic means that when the price goes up, consumers’ buying habits stay about the same, and when the price goes down, consumers’ buying habits also remain unchanged.
What is elastic demand?
By way of contrast, an elastic good or service is one for which a 1 percent price change causes more than a 1 percent change in the quantity demanded or supplied. Most goods and services are elastic because they are not unique and have substitutes. If the price of a plane ticket increases, fewer people will fly. A good would need to have numerous substitutes to experience perfectly elastic demand. A perfectly elastic demand curve is depicted as a horizontal line because any change in price causes an infinite change in quantity demanded.
What are some examples of inelastic goods?
Perfectly Inelastic Goods. There are no examples of perfectly inelastic goods. If there were, that means producers and suppliers would be able to charge whatever they felt like and consumers would still need to buy them. The only thing close to a perfectly inelastic good would be air and water, which no one controls.
How does inelasticity affect a seller?
The inelasticity of a good or service plays a significant role in determining a seller's output. For instance, if a smartphone producer knows that lowering the price of its newest product by 5 percent will result in a 10 percent increase in sales, the decision to lower prices could be profitable. However, if lowering smartphone prices by 5 percent only results in a 3 percent increase in sales, then it is unlikely that the decision would be profitable.
Why are goods and services elastic?
Most goods and services are elastic because they are not unique and have substitutes. If the price of a plane ticket increases, fewer people will fly. A good would need to have numerous substitutes to experience perfectly elastic demand.
Why is the demand curve a vertical line?
The demand curve for a perfectly inelastic good is depicted as a vertical line in graphical presentations because the quantity demanded is the same at any price. Supply could be perfectly inelastic in the case of a unique good such as a work of art. No matter how much consumers are willing to pay for it, there can never be more than one original version of it.