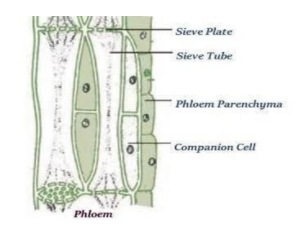
Phloem is the structure that transports nutrients from the leaves down to the roots. The primary phloem is new growth located in the stems and roots while the secondary phloem is created after primary growth ends and is found in the vascular cambium
Vascular cambium
The vascular cambium is the main growth tissue in the stems and roots of many plants, specifically in dicots such as buttercups and oak trees, gymnosperms such as pine trees, as well as in certain vascular plants. It produces secondary xylem inwards, towards the pith, and secondary p…
What are the main components of phloem?
The components of phloem are:
- (1). Sieve elements
- (2). Companion cells
- (3). Phloem parenchyma
- (4). Phloem fibres and Sclereids. Ø In some plants, in addition to the above mentioned cell types, the phloem also have internal secretary tissues such as Laticifers (Hevea) and resin ...
- (1). Sieve elements. Ø Sieve elements are the fundamental cell type in the phloem. ...
- (2). Sieve tubes. ...
What does the secondary phloem eventually become in trees?
…cambium eventually arises in the secondary phloem situated just behind the old cork cambium. That portion of the secondary phloem that forms between the new cork cambium and the old one becomes crushed and displaced externally as well. This process is repeated often each growing season. Read More; trees
Why is there secondary phloem between periderm?
Secondary Phloem Helps with sugar transport This and Periderm make up the bark. Secondary plant body Tissues produced by the vascular cambium and four cambium, which thicken the stems and roots of woody plants. Sapwood The soft outer layers of a recently formed wood between the heartwood and the bark, containing the vascular tissue.
What is primary phloem?
The primary phloem is the vascular tissue that takes the responsibility of transporting and distributing various organic nutrients. This vascular tissue also functions as a pathway for signaling molecules and has an important structural function inside the plant body. The phloem tissue in the plants is typically made up of the sclerenchyma ...

What is primary phloem and secondary phloem?
Primary phloem is produced from the apical meristem, which is a primary meristematic tissue, whereas secondary phloem is produced by vascular cambium, which is a secondary or lateral meristem. Phloem fibres or bast fibres are generally absent in primary phloem but present in secondary phloem.
What is primary phloem?
The primary phloem is a type of phloem that forms from the procambium during the primary growth. The primary growth is responsible for the growth in length in plants. The procambium is a meristematic tissue that enables the primary growth of a plant.
What is secondary phloem?
Formed by more than one cell type, the secondary phloem is considered a complex tissue composed of conducting cells (sieve elements), parenchyma (axial and radial) and generally sclerenchyma (fibres and/or sclereids).
Whats the difference between primary and secondary xylem and phloem?
The main difference between primary xylem and secondary xylem is that primary xylem is formed by the primary growth of the procambium whereas secondary xylem is formed by the secondary growth of the vascular cambium.
Where is secondary phloem?
The secondary phloem is located in the stems and roots. It forms inner to the primary phloem. A radial system of phloem rays occurs in the secondary phloem.
What are the 3 types of phloem?
Types of phloem The different elements of phloem include sieve tubes, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres.
What are the two types of phloem cells?
The phloem is a complex tissue and is formed typically by three cell types, the sieve elements, the parenchyma cells, and the sclerenchyma cells (Figure 2a–d).
What are the 4 types of phloem cells?
Answer. In angiosperms it possesses four components of phloem. They are sieve tubes, phloem parenchyma, phloem fibres and companion cells.
What is the secondary xylem called?
The inner non-functional secondary xylem is called heartwood, the outer functional secondary xylem, sapwood.
What is the difference between primary and secondary system?
Primary sources can be described as those sources that are closest to the origin of the information. They contain raw information and thus, must be interpreted by researchers. Secondary sources are closely related to primary sources and often interpret them.
What is the difference between primary and secondary tissues?
Definition. Primary meristem refers to a type of meristem involved in the primary growth and thus gives rise to the primary tissues of the plant while secondary meristem refers to a type of meristem involved in the secondary growth and thus gives rise to the secondary tissues of the plant.
What is the function of secondary xylem and phloem?
The secondary xylem provides additional structural support and additional water conduction tissue in shrubs and trees. The secondary phloem replaces the primary phloem. Similarly, as the trunk of a woody plant gets larger, the dermal tissue need to be expanded and replaced.
What is primary phloem and primary xylem?
Primary xylem and phloem are arranged in vascular bundles that run the length of the plant from roots to leaves. The ground tissues, which comprise the remaining plant matter, include various support, storage, and photosynthetic tissues.
What produces primary phloem?
Primary phloem is formed by the apical meristems (zones of new cell production) of root and shoot tips; it may be either protophloem, the cells of which are matured before elongation (during growth) of the area in which it lies, or metaphloem, the cells of…
What is primary and secondary xylem?
Primary xylem is derived from the primary meristem, i.e. procambium. It is of two types, namely protoxylem and metaxylem. Protoxylem develops first and then metaxylem. Secondary xylem is derived from lateral meristem, i.e. vascular cambium during secondary growth, e.g. in the dicot stem during secondary growth.
What is a primary plant?
The primary plant body is mainly composed of primary tissues. Apical meristem and the intercalary meristems are called the primary meristems as they contribute to the formation of a primary plant body.
What is the phloem in plants?
As with the xylem, the phloem is a conductive tissue responsible for transporting beneficial substances for the plant organism. The origin of the word phloem, as well as its meaning comes from the Greek word “phloios”, which translates as “bark”. From this word the famous botanist Karl Wilhem von Nageli coined the term phloem to define one of the main conductive tissues of vascular plants in 1873.
What is the function of a phloem?
Hence, its main function is to transport and distribute the sap produced throughout the plant for its management, absorption and storage. Phloem, also called bast or sieve tissue , is made up of plant cells without nuclei capable of forming walls through which nutrients can be conducted.
What is the difference between a phloem and a xylem?
Finally, the phloem is made up of a series of cells that make up a soft cell wall, while the xylem is made up of lignified cell walls.
How does a phloem transport system work?
The phloem transport system works bi-directionally, transporting nutrients throughout the plant. In the case of xylem, this is unidirectional.
What is the process of a plant being transported to a meristem?
This process carried out by the phloem is also known as translocation. This occurs when the sugars that have accumulated during the development of the plant are transported to the so-called meristems, which are another type of plant tissue in charge of developing new cells to increase and improve the development of the plant. This process usually occurs especially during spring, which is the time of year when the plants are most active.
Which tissue is responsible for the process of converting sap into sap?
The phloem is the order to transport the processed sap, which is the result after the photosynthesis process carried out by the plant, while the xylem is the conductive tissue that transports the raw sap for its transformation into processed sap.