Explore
A demyelinating disease is any condition that results in damage to the protective covering (myelin sheath) that surrounds nerve fibers in your brain, optic nerves and spinal cord. When the myelin sheath is damaged, nerve impulses slow or even stop, causing neurological problems.
What is a demyelinating disease?
Secondary demyelination is the loss of myelin secondary to loss of axons. Axonal trophic factors sustain myelin. When the axon is severed or not sustained by its neuron of origin, the axon and then its myelin degenerates. This can happen secondary to infarcts, trauma, toxic, metabolic, or degenerative nervous system diseases.
What is secondary demyelination and what causes it?
Types of demyelination like MS, optic neuritis, and acute-disseminated encephalomyelitis are caused by inflammation in the brain and spinal cord. GBS involves inflammatory demyelination of peripheral nerves in other parts of the body.
What are the different types of demyelination?
The effects of demyelination can occur rapidly. In Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS), myelin may only be under attack for a few hours before symptoms appear. Not everyone is affected by demyelinating conditions in the same way. However, some demyelinating symptoms are very common.
How fast do the effects of demyelination occur?

What is primary and secondary demyelination?
Primary demyelinating diseases typically involve loss of myelin with relative sparing of axons. Secondary demyelinating disorders represent a spectrum of white matter disease characterized by damage to neurons or axons with the resultant breakdown of myelin.
What can cause demyelination in the brain?
Demyelination of the brain and spinal cord is often caused by inflammation due to autoimmune conditions or in response to viral infections. Multiple sclerosis (MS) causes demyelination in the brain, spine, and/or optic nerve.
What types of symptoms would you expect from a demyelinating disease?
Symptoms: The most common symptoms of demyelinating disorders are:Vision loss.Muscle weakness.Muscle stiffness.Muscle spasms.Changes in how well your bladder and bowels work.Sensory changes.
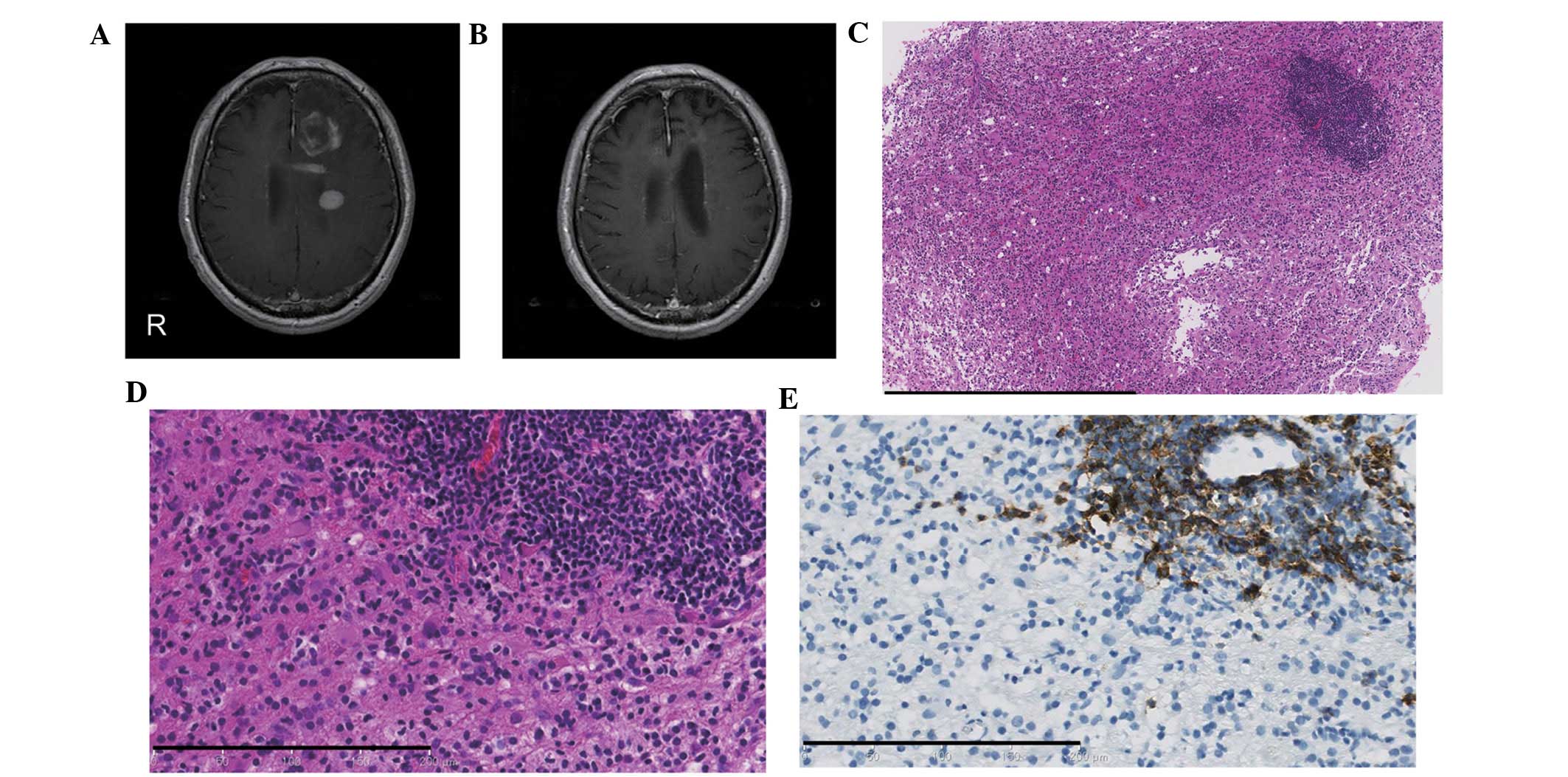
What does demyelination mean on MRI?
Myelin is an insulating material. When it's worn away or damaged, nerves can deteriorate, causing problems in the brain and throughout the body. Damage to myelin around nerves is called demyelination.
Can demyelination be cured?
Treatment. There is no cure for demyelinating diseases, but disease-modifying therapies can alter the disease progression in some patients. Disease-modifying therapies can be used together with symptomatic treatment. The symptoms and progression of demyelinating diseases varies between patients.
Does demyelination mean MS?
Demyelination occurs when myelin, which is the protective coating of nerve cells, sustains damage. When this happens, neurological problems can occur. Demyelination can result from various medical conditions, including multiple sclerosis (MS).
What autoimmune diseases cause demyelination?
Demyelinating process may be the feature of nervous impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus, Behcet's disease (BD), Sjoegren's syndrome (SS), systemic sclerosis (SSc) or very rarely other systemic autoimmune diseases.
What drugs cause demyelination?
Two Common Drugs Promote Remyelination in Demyelinating Disease of Mice. Might miconazole and clobetasol have a role in managing multiple sclerosis? In multiple sclerosis (MS) and other demyelinating diseases, autoimmune attacks lead to demyelination.
Can a virus cause demyelination?
Viral infections cause a variety of demyelinating diseases in animals and humans. Demyelinating diseases are defined as disorders of the central or peripheral nervous system with destruction of myelin and relative preservation of axons.
Can demyelination cause headaches?
Headache is a rare presenting demyelinating feature in people who go on to develop multiple sclerosis (MS). It has been suggested that approximately 2% of MS patients present with headache. There has been a debate whether MS patient group are at higher risk of developing headaches.
Can white matter lesions in the brain be nothing?
Studies have found that white matter lesions appear in some degree on brain scans of most older adults but less often in younger people. White matter lesions are among the most common incidental findings—which means the lesions have no clinical significance—on brain scans of people of any age.
Why does demyelination occur?
Demyelination is often caused by inflammation that attacks and destroys myelin. Inflammation can occur in response to an infection, or it can attack the body as part of an autoimmune process. Toxins or infections can also harm myelin or may interfere with its production.
What is the diagnosis of demyelination?
Diagnosis. Treatment. Demyelination is loss of myelin, a type of fatty tissue that surrounds and protects nerves throughout the body. This condition causes neurological deficits, such as vision changes, weakness, altered sensation, and behavioral or cognitive (thinking) problems. Demyelination can affect areas of the brain, spinal cord, ...
What is the most common demyelinating disease?
MS : MS is the most common demyelinating disease. It is characterized by demyelination in the brain, spine, and/or optic nerve. There are several types of MS , and some are characterized by relapses and remissions, while others are characterized by a gradual decline .
What is peripheral neuropathy? What are some examples?
For example, peripheral neuropathy affects the hands and feet in what is often described as a “stocking glove” distribution. Demyelination affecting the lower spine or the spinal nerves causes sensory changes or weakness of the legs, and may also diminish bowel and bladder control.
How is MS diagnosed?
MS is diagnosed by physical examination, imaging studies, LP, and sometimes with evoked potential tests. MS usually starts between the ages of 20 and 40, and, while it is manageable, it is a lifelong illness with no definitive cure. 3
How does DMT work for MS?
Steroids and DMTs work by suppressing the immune system to prevent the inflammatory attack on the myelin. 7
Can copper deficiency cause demyelination?
Copper deficiency: Similar to B12 deficiency, low copper secondary to a prior history of gastric surgery, excessive intake of zinc, or malabsorption can affect the spinal cord and peripheral nerves. A deficiency is unlikely to cause demyelination, but it may contribute to demyelinating disease.
What does demyelination cause?
Demyelination can lead to pain, numbness, and other symptoms.
What is the most common demyelinating disease?
The most common type of demyelinating disease is MS. It happens when the immune system mistakenly attacks and damages myelin. The term multiple sclerosis means “many scars.”. Damage to myelin in the brain and spinal cord can result in hardened scars that can appear at different times and in different places.
What happens when myelin is damaged?
Demyelination occurs when myelin, which is the protective coating of nerve cells, experiences damage. When this happens, neurological problems can occur.
What is the cause of vision problems?
Neurological damage can result in vision problems. Neuromyelitis optica, or Devic’s disease, occurs when the immune system attacks and destroys myelin, resulting in: optic neuritis. pain, weakness, or both in the spine and limbs. bladder and bowel problems.
What is a DMT for MS?
Current guidelines recommend that doctors prescribe one of these disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) from the earliest possible stage when it appears to be most effective. A DMT for MS will reduce the activity of the immune system.
Is demyelinating disease a cure?
There are currently no cures available for demyelinating diseases, but treatment can help people manage symptoms.
What is demyelination?
Demyelination is where the myelin sheath surrounding the axons of the nerve cells becomes damaged or worn away.
Symptoms
The symptoms that are experienced by demyelination depend on the condition and where in the nervous system the demyelination has occurred.
Causes of demyelination
Demyelination occurs when there is a loss of myelin. When there is a deficiency or a sudden decrease in myelin, the nerves may not be able to function at all, resulting in the neurological problems associated with demyelination.
Diagnosis
Demyelinating conditions can be diagnosed through using different methods. However, sometimes the signs and symptoms can be confusing, and it may take a long time to determine the type and cause of demyelination.
Treatment
The treatment options for demyelination depends on the conditions and the severity of symptoms. Currently, there are no treatments that effectively restore or rebuild myelin, but usually myelin will often regenerate on its own.
Treatment for symptoms
Since people with demyelinating conditions often experience a lot of different symptoms, these symptoms can be targeted in treatment to help make the condition more bearable.
