Primer annealing is a critical step in polymerase The DNA polymerases are enzymes that create DNA molecules by assembling nucleotides, the building blocks of DNA. These enzymes are essential to DNA replication and usually work in pairs to create two identical DNA strands from a single original DNA molecule. During this proces… The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technology in molecular biology used to amplify a single copy or a few copies of a piece of DNA across several orders of magnitude, generating thousands to millions of copies of a particular DNA sequence.DNA polymerase
Polymerase chain reaction
Full Answer
What is annealing of primers in PCR?
Annealing of primers. The PCR uses two primers, each complementary to opposite strands of the region of DNA, which have been denatured by heating. They cannot "anneal" to the strand of DNA at temperature 95 degrees centigrade, so the test tube is cooled to 45 - 60 degrees C. The temperature of this step depends on the melting temperature...
What is the annealing temperature of primers?
The annealing temperature depends on the length of the primers, GC content and specificity. And of course, on the melting temperature! “At a temperature, half of the template unwind is our melting temperature, so technically at that temperature, our primer can’t bind to the target. We have to set the temperature below it.”
What is annealing?
What is Annealing? A Complete Process Guide - TWI What is Annealing? A Complete Process Guide Annealing is a heat treatment process that changes the physical and sometimes also the chemical properties of a material to increase ductility and reduce the hardness to make it more workable.
What is spherification annealing?
The heat treatment process is obtained by slow cooling after thermal insulation. It is mainly used to obtain spherical pearlite tissues for the hypereutectic steel to eliminate internal stress, reduce the hardness and improve machinability. Spherification annealing is a kind of incomplete annealing.
What is the meaning of primer annealing?
Primer annealing is a critical step in polymerase chain reaction or PCR. In this step, the primers bind to flanking sequences of the target DNA for amplification.
Why is primer annealing important in PCR?
Primers in PCR reaction should have similar melting temperatures so that they anneal to and dissociate from complementary DNA sequences at approximately the same temperature, which allows the synchronous extension of both single-stranded DNA molecules in each cycle.
Why do we anneal primers?
The annealing step (30 sec to 1 min, at temperatures 45–60 °C), is required so that the primers bind to the complementary sequence on each of the DNA single strands. The primers are designed such that they bracket the target of interest and the region of sequence that lies between them is referred to as the amplicon.
How are primers annealed in PCR?
The PCR uses two primers, each complementary to opposite strands of the region of DNA, which have been denatured by heating. They cannot "anneal" to the strand of DNA at temperature 95 degrees centigrade, so the test tube is cooled to 45 - 60 degrees C.
What is annealing and why is it done?
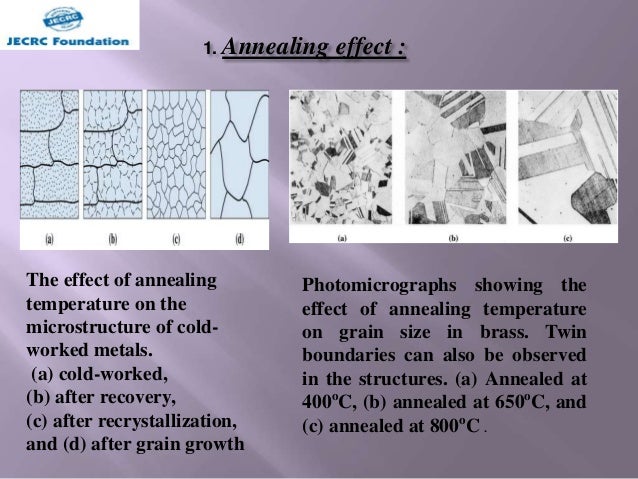
Annealing is a heat treatment process used to reduce hardness, increase ductility and help eliminate internal stresses. Recyrstallisation annealing is applied to cold-worked metal to obtain nucleation and growth of new grains without phase change.
What are the 3 main steps of PCR?
PCR is based on three simple steps required for any DNA synthesis reaction: (1) denaturation of the template into single strands; (2) annealing of primers to each original strand for new strand synthesis; and (3) extension of the new DNA strands from the primers.
How do you do annealing process?
In the case of ferrous metals, such as steel, annealing is performed by heating the material (generally until glowing) for a while and then slowly letting it cool to room temperature in still air. Copper, silver and brass can be either cooled slowly in air, or quickly by quenching in water.
What is the annealing temperature for primer?
Primer sets with a range of annealing temperatures were used to amplify 12 targets in human genomic DNA with a 60°C annealing temperature using Platinum SuperFi II DNA Polymerase.
What happens if annealing temperature is too high?
Annealing temperature was too high If the annealing temperature is too high, primers are unable to bind to the template. The rule of thumb is to use an annealing temperature that is 5°C lower than the Tm of the primer.
What are the 4 steps of PCR?
The PCR process has 4 steps:collection, preparation, amplification, and post PCR clean-up. The PCR machine steps happen in the amplification step. It begins with a segment of a DNA sample placed in a suitable tube along with the reagents and chemicals listed above.
Why buffer is used in PCR?
PCR is carried out in a buffer that provides a suitable chemical environment for activity of DNA polymerase. The buffer pH is usually between 8.0 and 9.5 and is often stabilized by Tris-HCl. For Taq DNA polymerase, a common component in the buffer is potassium ion (K+) from KCl, which promotes primer annealing.
What is good annealing temperature for PCR?
The annealing temperature of a standard PCR protocol is either 55°C [2, 3] or 60°C [4]. The chosen temperature depends on the strand-melting temperature of the primers and the desired specificity. For greater stringency higher temperatures are recommended [2].
Why are primers important in PCR?
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) Because DNA polymerase can add a nucleotide only onto a preexisting 3'-OH group, it needs a primer to which it can add the first nucleotide. This requirement makes it possible to delineate a specific region of template sequence that the researcher wants to amplify.
What does annealing mean in PCR?
In PCR, a DNA sample is heated up to denature the two strands. These single strands are used as templates to replicate the DNA. Then the sample's cooled slightly so small pieces of DNA, called primers, can bind or anneal to the template strands. These primers will set the borders for the DNA to be copied.
What happens if annealing temperature is too low in PCR?
If the annealing temperature is too low, primers may bind nonspecifically to the template. The rule of thumb is to use an annealing temperature that is 5°C lower than the Tm of the primer.
How does annealing temperature affect PCR?
As the PCR annealing temperature is increased, the stringency of primer annealing is also increased leading to more specific and reproducible amplification.
What is annealing?
The process of heating a metal or alloy to an appropriate temperature for a certain period of time and then slowly cooling (generally with the furnace cooling) is called annealing.
What is the essence of annealing?
The essence of annealing is the transformation of the pearlite after heating the steel to austenitizing. After annealing, the tissue is close to that after equilibrium.
What is the best way to shorten the annealing time?
In order to shorten the annealing time, isothermal annealing can be used.
Why is isothermal annealing not recommended?
However, it is not suitable for large section steel parts and large batch furnace materials, because isothermal annealing is not easy to achieve the isothermal temperature of the internal or batch workpiece.
What is spherification annealing?
Spherification annealing is a kind of incomplete annealing.
What is the temperature of diffusion annealing?
The diffusion annealing temperature is very high, usually for 100 ~ 200 ℃ above Ac3 or Accm, the concrete temperature depends on the degree of segregation and the steel grade.
When hypereutectoid steel heated to above Accm austenitic state and slow cooling?
When hypereutectoid steel heated to above Accm austenitic state and slow cooling annealing , Fe3CⅡ precipitated in mesh along the grain boundary, the strength, hardness, plasticity and toughness of steel are significantly reduced, which leave a hidden danger to the final heat treatment.
What is annealing DNA?
Annealing Definition. The hydrogen bonds are based on attraction between opposite charges. This means the two strands of DNA aren't physically connected to each other. Instead, the nitrogenous base pairs, the rungs of the ladder, have an electrostatic attraction.
What is the annealing step of PCR?
These primers will set the borders for the DNA to be copied. This part of PCR is actually called the annealing step. After the primers bind, the temperature is increased slightly so the rest of the nucleotides are filled in. For PCR, this process is repeated many times over to make many copies of , or amplify, the DNA.
Why is DNA used in PCR?
This allows the strands to remain annealed until the scientist can take the samples out of the machine. The DNA produced via PCR can be used in laboratory settings for performing research. Scientists can also use the DNA to teach bacteria to make proteins for us to use, such as insulin.
What is the chemical bond that anneals DNA?
These are all paired together with a chemical bond called a hydrogen bond. Annealing describes the two strands being joined together, and denaturation describes them being split apart. Because it's known that these actions depend on temperature, scientists have figured out how to denature and anneal DNA to copy it through heating in a process called polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
What is the process of DNA separating?
Because this looks like a zipper unzipping, we call the process ''unzipping''. More scientifically, the process of DNA strands separating is called denaturation, because it's no longer in its natural state. Heat can disrupt the DNA's hydrogen bonds and lead to denaturation. Because heat is involved, this process of turning double-stranded DNA into single strands is sometimes referred to as ''DNA melting.''
Why does DNA melt?
Heat can disrupt the DNA's hydrogen bonds and lead to denaturation. Because heat is involved, this process of turning double-stranded DNA into single strands is sometimes referred to as ''DNA melting.''. However, the strands can't stay separated. They have to rejoin once all the new pieces have been made.
What are some challenges in the annealing step of PCR?
The recommended melting temperature of PCR primers is usually in the range of 55°C to 70°C and within 5°C of each other. Because of the differences in sequence, length, and composition of the primers, it is often difficult to have similar melting temperatures (T m s) between the two. In that case, the primer with the higher T m could bind to unintended targets, while the primer with the lower T m would have difficulty binding at an annealing temperature chosen for these primers ( Figure 1 ). This can drastically reduce the yield and specificity of PCR and even cause PCR to fail.
How can I overcome challenges associated with PCR annealing?
To help simplify and save time in PCR, we (Thermo Fisher Scientific) have developed novel Invitrogen Platinum DNA polymerases with reaction buffers that allow a universal annealing temperature of 60°C. Their buffers are designed with an isostabilizing component, which increases the stability of primer-template duplexes during the annealing step ( Figure 3 ).
How to enable PCR success with maximum yield and specificity?
To enable PCR success with maximal yield and specificity, the annealing temperature of each primer set and its target should be optimized ( Figure 2 ). This optimization process can be long and tedious, especially when amplifying multiple DNA targets using different primer sets.
What is the isostabilizing component of PCR?
Primer binding in Platinum PCR products with the universal annealing buffer. The isostabilizing component enables specific binding of the primers to the DNA template , even when their melting temperatures differ from the 60°C annealing temperature.
What temperature is optimal for PCR?
The annealing temperature was optimized in a gradient thermal cycler by increasing the temperature in 2-degree steps. The optimal annealing temperature in this case was 56°C.
Can I try the universal annealing in my PCR?
Our latest Platinum DNA polymerases are designed for a universal annealing temperature of 60°C. Request a sample (where available) to try them for free in your experiments. These products can help you save time and simplify PCR protocols by:
Why is annealing done?
Annealing is often done after the material has undergone a hardening or cold working process to prevent brittleness from failing or to make it more malleable for subsequent operations.
What is annealing in chemistry?
Annealing is a heat treatment process that changes the physical and sometimes also the chemical properties of a material to increase ductility and reduce the hardness to make it more workable.
What are the disadvantages of annealing?
Disadvantages of Annealing. The main disadvantage of annealing is that it can be a time consuming process, depending on which materials are being annealed. Materials with high temperature requirements can take a long time to cool sufficiently, especially if they naturally cool in an annealing furnace.
What are the benefits of annealing?
The main benefits of annealing are how the process improves the workability of a material, increases toughness, decreases hardness, and increases the ductility and machinability of a metal.
Why do metals need to be annealed?
In addition, some metals are annealed to increase their electrical conductivity.
What materials can be used in an annealing process?
Examples are many types of steel and cast iron. Some types of aluminum, copper, brass and other materials can also respond to an annealing process.
Why is hot rolled steel shaped?
Hot rolled steel is also shaped and shaped by heating it above the recrystallization temperature.
What Is Annealing and Why Is It Done?
Annealing is the process of heat treatment that modifies the microstructure of a material to change its electrical or electrical properties. In steels, annealing is used to reduces hardness, increase ductility, & help eliminate internal stress. Annealing is a traditional term and may indicate subcritical, intermediate, or complete annealing in the classification of environments.
Why is annealing important?
The main reason for annealing is to reduce the hardness of a material. In addition, it is also used to relieve the internal stress of the material, restore ductility for additional support of the material, and increase the machinability of the material. Annealing improves the formability of the material. Hard, weak materials can be difficult to curve or press without cracking the material.
How Does an Annealing Furnace Work?
An annealing furnaces work by heating materials above the recrystallization temperature and then cooling the material after holding it at a suitable temperature for a suitable length of time . The material crystallizes again once the healing process causes the atomic motion to be redistributed and dislocations in the workpiece to be erased. Annealing work in three-stage – the recovery stage, recrystallization stage, and grain growth stage. These tasks are as follows:
What is isothermal annealing?
Isothermal annealing is the controller cooling annealing method applied to steel and some non-ferrous alloy such as titanium alloy. In terms of steel, it is slowly heated to temperatures slightly above Ac3 hypo eutectoid steel or slightly above Ac1 eutectoid steel and hyper eutectoid steel.
What temperature does recrystallization annealing take?
The recrystallization annealing process involves heating the steel slowly to 30 °C ~ 50 °C above AC3 eutectic steel or AC1 eutectoid steel or hypereutectoid steel, preserving for a suitable time, and then slowly – cooling down slowly.
What happens when an alloy is annealed?
The temperature below the solidification temperature of the alloy was preserved for a long time and then gradually cooled. Homogenization annealing results in a solid diffusion of elements in the alloy to reduce chemical composition inhomogeneity separation, primarily to reduce chemical composition inhomogeneity intragranular segregation or dendrite segregation within the grain size.
What is homogenization annealing?
Homogenization annealing, also known as diffusions annealing, is an annealings method for ingots or castings of steel & non-ferrous alloys such as tin bronze, silicon bronze, white copper, magnesium alloys and etc. The ingots or casting is heated to a high degree.
How to calculate annealing temperature?from geneticeducation.co.in
For calculating the exact annealing, we need to first calculate the melting temperature of primers. The equation for it is:
What are some challenges in the annealing step of PCR?from thermofisher.com
The recommended melting temperature of PCR primers is usually in the range of 55°C to 70°C and within 5°C of each other. Because of the differences in sequence, length, and composition of the primers, it is often difficult to have similar melting temperatures (T m s) between the two. In that case, the primer with the higher T m could bind to unintended targets, while the primer with the lower T m would have difficulty binding at an annealing temperature chosen for these primers ( Figure 1 ). This can drastically reduce the yield and specificity of PCR and even cause PCR to fail.
What happens when you set a PCR at a lower annealing temperature?from geneticeducation.co.in
When we set PCR at a lower annealing temperature it gives relaxation to primers. Sometimes, it’s like a free ticket for primers to bind at any position in the genome. It anneals at any place and gives an amplification band or many bands.
What temperature does taq polymerase react with?from pressbooks.umn.edu
As mentioned above the taq polymerase is active at temperatures around 70°C (158°F), so the reaction is heated from 55-65°C to 70°C to allow activation of the taq polymerase.
How to enable PCR success with maximum yield and specificity?from thermofisher.com
To enable PCR success with maximal yield and specificity, the annealing temperature of each primer set and its target should be optimized ( Figure 2 ). This optimization process can be long and tedious, especially when amplifying multiple DNA targets using different primer sets.
What happens when primers bind at a higher temperature?from geneticeducation.co.in
We will get fewer amplicons. In most cases, a higher annealing temperature leads to ‘no amplification’ .
What temperature is optimal for PCR?from thermofisher.com
The annealing temperature was optimized in a gradient thermal cycler by increasing the temperature in 2-degree steps. The optimal annealing temperature in this case was 56°C.
How to calculate annealing temperature?
For calculating the exact annealing, we need to first calculate the melting temperature of primers. The equation for it is:
What is a primer-dimer?
Primer-dimer is yet another in which primers bind to each other and synthesize smaller PCR amplicons. Those are fragments observed between 50 to 100bp regions, however, are dimers.
What happens when you set a PCR at a lower annealing temperature?
When we set PCR at a lower annealing temperature it gives relaxation to primers. Sometimes, it’s like a free ticket for primers to bind at any position in the genome. It anneals at any place and gives an amplification band or many bands.
What temperature does a PCR primer bind to?
The annealing temperature is the temperature at which the PCR primers bind to the complementary template region, usually is between 50ºC to 68ºC.
What happens when primers bind at a higher temperature?
We will get fewer amplicons. In most cases, a higher annealing temperature leads to ‘no amplification’ .
How long does primer binding take?
Besides, setting the temperature for primer binding, the time duration for the step is indeed important. The ideal time for the step is 30 to 60 sec.
How many temperature variations are there in PCR?
In summary, we have to put 3 to 4 temperature variations in the PCR to check the best one. Meaning, we can’t rely on a single temperature.
Primers
Primers A primer is a short sequence of nucleotides that provides the starting point for the DNA polymerase ( taq) to attach to. These primers are used to flank the region of the DNA that we want to be copied. These primers bind to the complementary strand of the DNA template.
Template DNA
This is the stand of DNA the taq polymerase is going to use for amplification
Denaturation
In vitro, we cannot replicate all of the biological intricacies that occur in the nucleus of a cell, however, we do know that under extreme heat, that the double helix will break apart. Therefore, the first step of the PCR reaction is to subject the DNA to extreme heat (95°C/ 203°F) to break apart the two strands forming the template DNA.
Annealing
Now that we have successfully denatured the DNA, the temperature is too high for the primers to attach the DNA template so the reaction is cooled down to temperatures between 55-65°C (131-149°F).
Primer extension
Once the primers have attached to the DNA template we are now ready for the taq polymerase to attach and begin adding nucleotides to create a new double-stranded piece of DNA. As mentioned above the taq polymerase is active at temperatures around 70°C (158°F), so the reaction is heated from 55-65°C to 70°C to allow activation of the taq polymerase.
