
Probability sampling vs Non-probability Sampling Methods
| Probability Sampling Methods | Non-probability Sampling Methods |
| Probability Sampling is a sampling techn ... | Non-probability sampling method is a tec ... |
| These are also known as Random sampling ... | These are also called non-random samplin ... |
| These are used for research which is con ... | These are used for research which is exp ... |
| These involve a long time to get the dat ... | These are easy ways to collect the data ... |
What are the types of non probability sampling?
Feb 25, 2022 · Non-probability sampling is a sampling technique where the odds of any member being selected for a sample cannot be calculated. In addition, probability sampling involves random selection, while non-probability sampling does not–it relies on the subjective judgement of the researcher.
What are some examples of non probability sampling?
Apr 10, 2022 · Probability sampling means that every member of the target population has a known chance of being included in the sample. In non-probability sampling, the sample is selected based on non-random criteria, and not every member of the population has a chance of being included.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of non probability sampling?
This type of research commonly known as quantitative research uses probability sampling techniques, also known as random or representative sampling (Alvi, 2016). Probability, a topic taught as part of the secondary mathematics syllabus, is synonym with keywords like random, fair, roll, dice, coins and probability spaces. The simplicity
What are the uses of non-probability sampling?
Jun 29, 2020 · Non-probability sampling is a sampling technique where the odds of any member being selected for a sample cannot be calculated. In addition, probability sampling involves random selection, while non-probability sampling does not–it relies on the subjective judgement of the researcher. Click to see full answer.
What is Probability sampling technique?
Definition: Probability sampling is defined as a sampling technique in which the researcher chooses samples from a larger population using a method based on the theory of probability. For a participant to be considered as a probability sample, he/she must be selected using a random selection.
What is non-probability sampling techniques?
Definition: Non-probability sampling is defined as a sampling technique in which the researcher selects samples based on the subjective judgment of the researcher rather than random selection.
What is the main difference between probability and non-probability?
Generally, nonprobability sampling is a bit rough, with a biased and subjective process. This sampling is used to generate a hypothesis. Conversely, probability sampling is more precise, objective and unbiased, which makes it a good fit for testing a hypothesis.Jul 22, 2019
What are the 4 types of probability sampling?
There are four types of probability sampling that you can use in systematic investigations namely: simple random sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and cluster sampling.Jan 25, 2022
What are sampling techniques?
Sampling is a technique of selecting individual members or a subset of the population to make statistical inferences from them and estimate characteristics of the whole population.
What is the difference between probability and non-probability sampling which is better and why?
The difference between nonprobability and probability sampling is that nonprobability sampling does not involve random selection and probability sampling does. In general, researchers prefer probabilistic or random sampling methods over nonprobabilistic ones, and consider them to be more accurate and rigorous.
What is meant by non-probability sampling?
What is non-probability sampling? Definition: Non-probability sampling is defined as a sampling technique in which the researcher selects samples based on the subjective judgment of the researcher rather than random selection. This sampling method depends heavily on the expertise of the researchers.
What does probability sampling mean?
Probability sampling refers to the selection of a sample from a population, when this selection is based on the principle of randomization, that is, random selection or chance. Probability sampling is more complex, more time-consuming and usually more costly than non-probability sampling.
What is an example of a probability sampling method?
Definition: Probability sampling is defined as a sampling technique in which the researcher chooses samples from a larger population using a method based on the theory of probability. For example, if you have a population of 100 people, every person would have odds of 1 in 100 for getting selected.
What is probability sampling?
This type of research commonly known as quantitative research uses probability sampling techniques, also known as random or representative sampling (Alvi, 2016). Probability, a topic taught as part of the secondary mathematics syllabus, is synonym with keywords like random, fair, roll, dice, coins and probability spaces. The simplicity with which it is presented at this level of compulsory education is the root of what probability sampling is. In fact, Karwa (2019) in a Youtube video, (2019, 03:15-05:21) refers to probability sampling as randomization implying that the targeted population sample has a known, equal, fair and a non-zero chance of being selected, (Brown, 2007; MeanThat, 2016), thus ensuring equity between prospective research participants. This fair chance is calculated in a very simple way, like the probability of getting an odd number on a dice. The formula for the basic probability draw is
What is the simplest sampling technique?
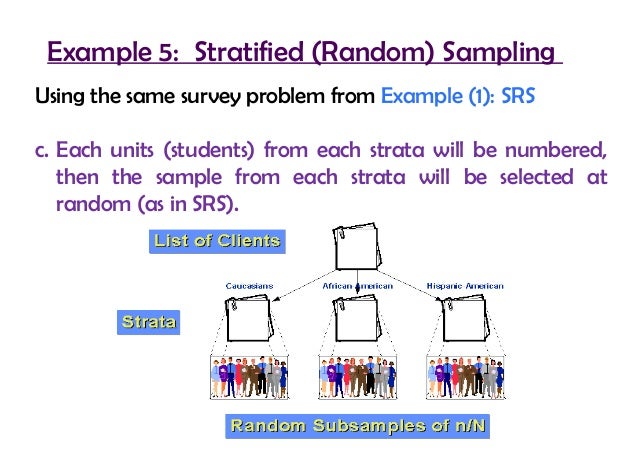
This section discusses each one of the sampling techniques identified in Table 1. The simplest method used is referred to as simple random sampling (SRS) which consists in giving a fair chance to every member within the sample frame because its draw is very straight forward (Kolb, 2011). The drawing procedures involves the placing of names or numbers in a container or using a more high-tech device to generate the list needed. Despite its fairness, validity and simplicity of analysis, (Acharya et al., 2013), the downsides of SRS are its cost, the need for a list of the whole population, which might not always be available or necessarily have the most recent one, the construction of a sample frame and high sampling errors thus leading to low precision (Ghauri & Grønhaug, 2005). Applying SRS in practice could look like the exemplar situation in Figure 1.
Why are exemplars used in sampling?
In the attempt to make the complex simple for beginning researchers, exemplars for each sampling techniques were used to facilitate the student’s understanding of each. Furthermore, in not limiting each technique to the what it consists in, as it has included the how, the when and the why, it is hoped that a better-informed decision can be made on the sample most suited for a particular study. The debate on the benefits and limitations of the probability and non-probability sampling techniques emphasised the point that both methods are equally valid if they fit the purpose for which they are being used. In accepting such parity of esteem, researchers can increase the robustness of their studies when making the best use of both worlds.
When to use non-probability samples?
Non-probability samples are often used during the exploratory stage of a research project, and in qualitative research, which is more subjective than quantitative research, but are also used for research with specific target populations in mind, such as farmers that grow maize. SUGGESTED What are Research Panels?
What is probability sampling?
Probability sampling is the most common form of sampling for public opinion studies, election polling, and other studies in which results will be applied to a wider population. This is the case whether or not the wider population is very large, such as the population of an entire country, or small, such as young females living in a specific town. ...
What are the two methods of sampling?
There are two main methods of sampling: Probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In probability sampling, respondents are randomly selected to take part in a survey or other mode of research. For a sample to qualify as a probability sample, each person in a population must have an equal chance of being selected for a study, ...
Why is sample important in research?
A research sample is those who partake in any given study, and enables researchers to conduct studies of large populations without needing to reach every single person within a population. Sample source, sample size, and how the sample was selected all have an effect on the reliability and validity of a study’s results – that is, how much those reading the results can trust that they will continue to produce the same results over time , and that they represent the wider population being studied .
Is non probability sampling more effective than probability sampling?
Generally speaking, non-probability sampling can be a more cost-effective and faster approach than probability sampling, but this depends on a number of variables including the target population being studied. Certain types of non-probability sa mpling can also introduce bias into the sample and results. For general population studies intended ...
What is probability sampling?
Probability sampling. Definition: Any method of sampling that uses random selection. You have a complete population that you can choose from here. Since all persons (or “units”) have an equal chance of being selected for your survey, you can randomly select participants without missing entire portions of your audience.
What is sampling error?
Definition: A method of sampling that is arbitrary, or not random. This method is used when there isn’t a full population list available. People are not selected randomly, therefore you cannot know the size and effect of sampling error (missed persons, unequal representation, etc.).
Can you use probability based sample?
In a perfect world you could always use a probability-based sample, but in reality, you have to consider the other factors affecting your results (availability, cost, time, what you want to say about results). It is also possible to use both different types for the same project.
What is non probability sampling?
Non-probability sampling is a sampling method in which not all members of the population have an equal chance of participating in the study, unlike probability sampling. Each member of the population has a known chance of being selected.
Why is non-probability sampling important?
Non-probability sampling is most useful for exploratory studies like a pilot survey (deploying a survey to a smaller sample compared to pre-determined sample size). Researchers use this method in studies where it is impossible to draw random probability sampling due to time or cost considerations.
Why is non probability sampling more cost effective than probability sampling?
Getting responses using non-probability sampling is faster and more cost-effective than probability sampling because the sample is known to the researcher. The respondents respond quickly as compared to people randomly selected as they have a high motivation level to participate. Select your respondents.
What is judgmental sampling?
Judgmental or Purposive sampling: In the judgmental samplingmethod, researchers select the samples based purely on the researcher’s knowledge and credibility. In other words, researchers choose only those people who they deem fit to participate in the research study. Judgmental or purposive sampling is not a scientific method of sampling, ...
Why do statisticians use non probability sampling?
Although statisticians prefer probability sampling because it yields data in the form of numbers, however, if done correctly, it can produce similar if not the same quality of results.
Why do researchers use snowball sampling?
Researchers use this technique when the sample size is small and not easily available. This sampling system works like the referral program. Once the researchers find suitable subjects, he asks them for assistance to seek similar subjects to form a considerably good size sample.
Why do we use convenience sampling?
Convenience sampling is a non-probability sampling technique where samples are selected from the population only because they are conveniently available to the researcher. Researchers choose these samples just because they are easy to recruit, and the researcher did not consider selecting a sample that represents the entire population.#N#Ideally, in research, it is good to test a sample that represents the population. But, in some research, the population is too large to examine and consider the entire population. It is one of the reasons why researchers rely on convenience sampling, which is the most common non-probability sampling method, because of its speed, cost-effectiveness, and ease of availability of the sample.

What Is Probability Sampling?
- Probability sampling is a type of sampling that ensures each subject of a study has the same likelihood of being selected. The goal of probability sampling is to get a sample that is representative of the greater population in order to generalize the results of the study to a larger …
Methods For Probability Sampling
- Probability sampling is more likely to produce objective, unbiased data. Here are some probability sampling methods for you to consider implementing into your current research processes:
Methods For Non-Probability Sampling
- Non-probability sampling can be useful when seeking ideas or gathering public opinions about a topic. Some methods for non-probability sampling include:
Probability Sampling vs. Non-Probability Sampling
- While you can use probability sampling and non-probability sampling when conducting a study, it's important to understand how these two categories differ. Some of their key differences include: 1. Use in qualitative or quantitative research:Researchers often use probability sampling in quantitative research because it is more statistically accurate and non-probability sampling in q…