How do you calculate discrete probability distribution?
How do I calculate probabilities using a discrete probability distribution? First draw a table to represent the probability distribution. If it is given as a function then find each probability; If any probabilities are unknown then use algebra to represent them; Form an equation using Add together all the probabilities and make the sum equal ...
What are some examples of discrete random variables?
The following are examples of discrete random variables:
- The number of cars sold by a car dealer in one month
- The number of students who were protesting the tuition increase last semester
- The number of applicants who have applied for a vacant position at a company
- The number of typographical errors in a rough draft of a book
How do you calculate random variable?
To use our calculator, you must do the following:
- Define whether you need to calculate the probability or the limit of the random variable given a probability.
- Enter the data of the problem: Mean: It is the average value of the data set that conforms to the normal distribution. ...
- Once you have entered all the data, click on Solve.
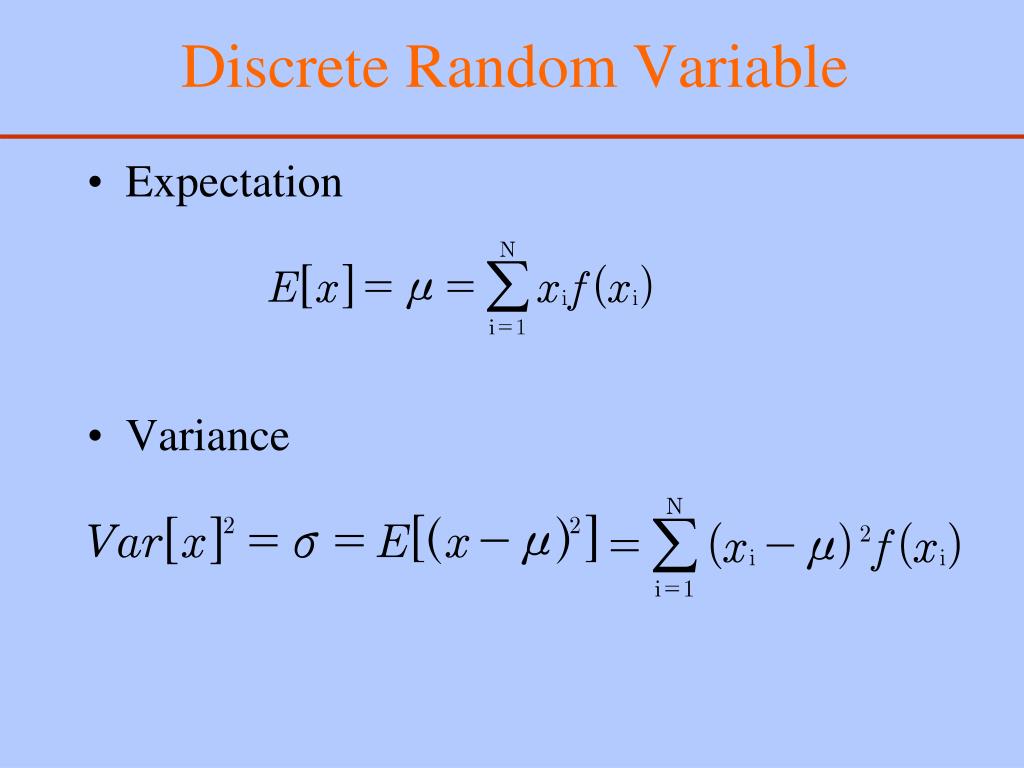
What is the mean of this discrete random variable?
The mean of a discrete random variable x is the average value that we would expect to get if the experiment is repeated a large number of times. The mean is denoted by μ and obtained using the formula μ = ΣxP (x) Another name for the mean of a discrete random variable is expected value.
What do you mean by probability distribution?
A probability distribution is a statistical function that describes all the possible values and probabilities for a random variable within a given range.
What is discrete probability distribution give an example?
A discrete probability distribution counts occurrences that have countable or finite outcomes. This is in contrast to a continuous distribution, where outcomes can fall anywhere on a continuum. Common examples of discrete distribution include the binomial, Poisson, and Bernoulli distributions.
How do you find the discrete probability distribution?
How To Find Discrete Probability Distribution?Step 1: Determine the sample space of the experiment. ... Step 2: Define a discrete random variable, X. ... Step 3: Identify the possible values that the variable can assume. ... Step 4: Calculate the probability associated with each outcome.More items...
What are the types of probability distribution explain with examples?
Probability distribution formulasDistributionType of formulaDiscrete uniformProbability mass functionPoissonProbability mass functionNormalProbability density functionContinuous uniformProbability density function2 more rows•Jun 9, 2022
When a probability function is used to describe a discrete probability distribution?
When we use a probability function to describe a discrete probability distribution we call it a probability mass function (commonly abbreviated as pmf).
Which of the following is a discrete probability distribution?
Discrete probability distribution includes binomial distribution, which means finite set of values and poisson distribution, which means infinite set of values.
What is discrete and example?
Let's define it: Discrete data is a count that involves integers. Only a limited number of values is possible. The discrete values cannot be subdivided into parts. For example, the number of children in a school is discrete data.
What are the real life examples of discrete probability distribution?
Introduction Statistical discrete processes – for example, the number of accidents per driver, the number of insects per leaf in an orchard, the number of thunderstorms per year, the number of earthquakes per year, the number of patients visit emergency room in a certain hospital per day - often occur in real life.
What is meant by discrete data give example?
Discrete data is information that can only take certain values. These values don't have to be whole numbers (a child might have a shoe size of 3.5 or a company may make a profit of £3456.25 for example) but they are fixed values – a child cannot have a shoe size of 3.72!
What is meant by discrete distribution?
What is Discrete Distribution? A discrete distribution is a distribution of data in statistics that has discrete values. Discrete values are countable, finite, non-negative integers, such as 1, 10, 15, etc.
What is the function of a discrete random variable?
Given a discrete random variable, X, its probability distribution function, f(x), is a function that allows us to calculate the probability that X = x.#N#In other words, f(x) is a probability calculator with which we can calculate the probability of each possible outcome (value) of X .
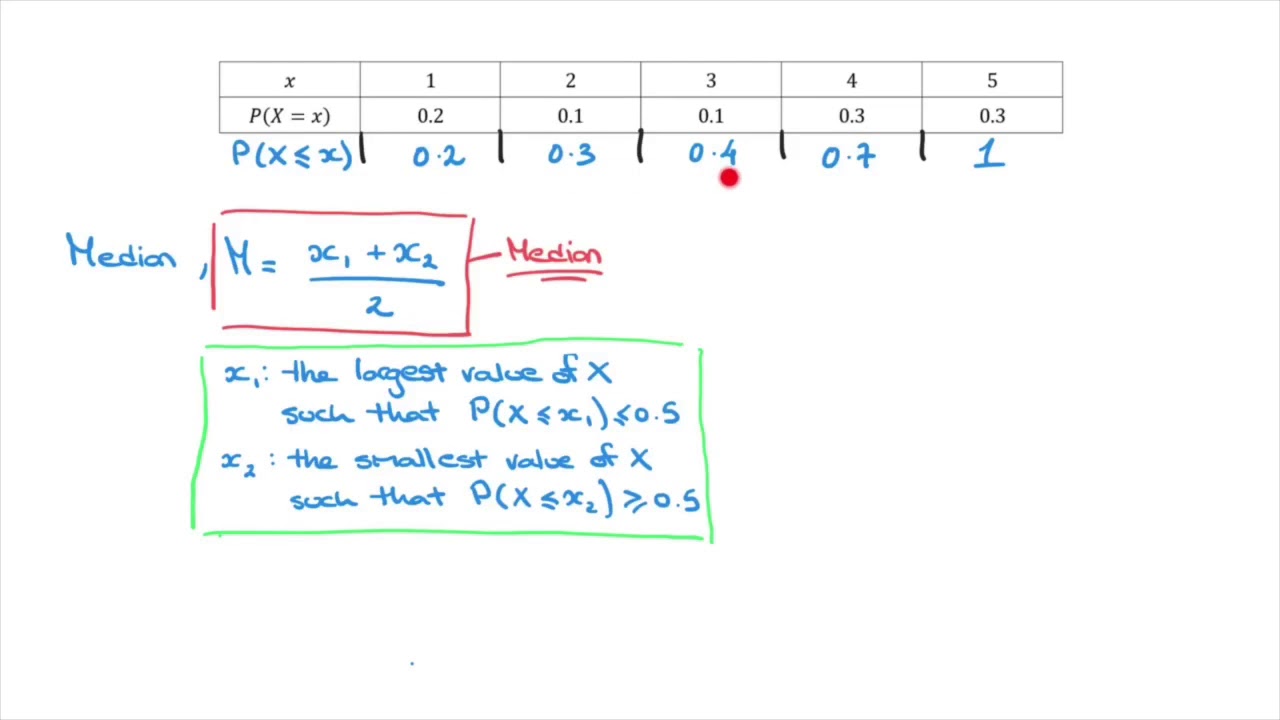
What is the probability of picking a ball with 2 on it?
The probability of picking a ball with 2 on it equals to the probability of X being equal to 2, that's P ( X = 2). So the probability of picking a ball numbered 4 is 16 40 .
What is discrete variable?
A discrete variable is a variable that can "only" take-on certain numbers on the number line. We usually refer to discrete variables with capital letters: X, Y, Z, …. A typical example would be a variable that can only be an integer, or a variable that can only by a positive whole number. Discrete variables can either take-on an infinite number ...
What are the possible outcomes of a single dice roll?
When we roll a single dice, the possible outcomes are: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 The probability of each of these outcomes is 1 6.#N#If we define the discrete variable X as:
How many numbers are in a bag?
A bag contains several balls numbered either: 2, 4 or 6 with only one number on each ball. A simple experiment consists of picking a ball, at random, out of the bag and looking at the number written on the ball. Defining the discrete random variable X as:
What is a game of chance?
A game of chance consists of picking, at random, a ball from a bag. Each ball is numbered either 2, 4 or 6. The discrete random variable is defined as:
What to do if playback doesn't begin?
If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device.
Discrete Probability Distribution Definition
Discrete Probability Distribution Example
Discrete Probability Distribution PMF
Discrete Probability Distribution CDF
Discrete Probability Distribution Mean
- The meanof a discrete probability distribution gives the weighted average of all possible values of the discrete random variable. It is also known as the expected value. The formula for the mean of a discrete random variable is given as follows: E[X] = ∑x P(X = x)
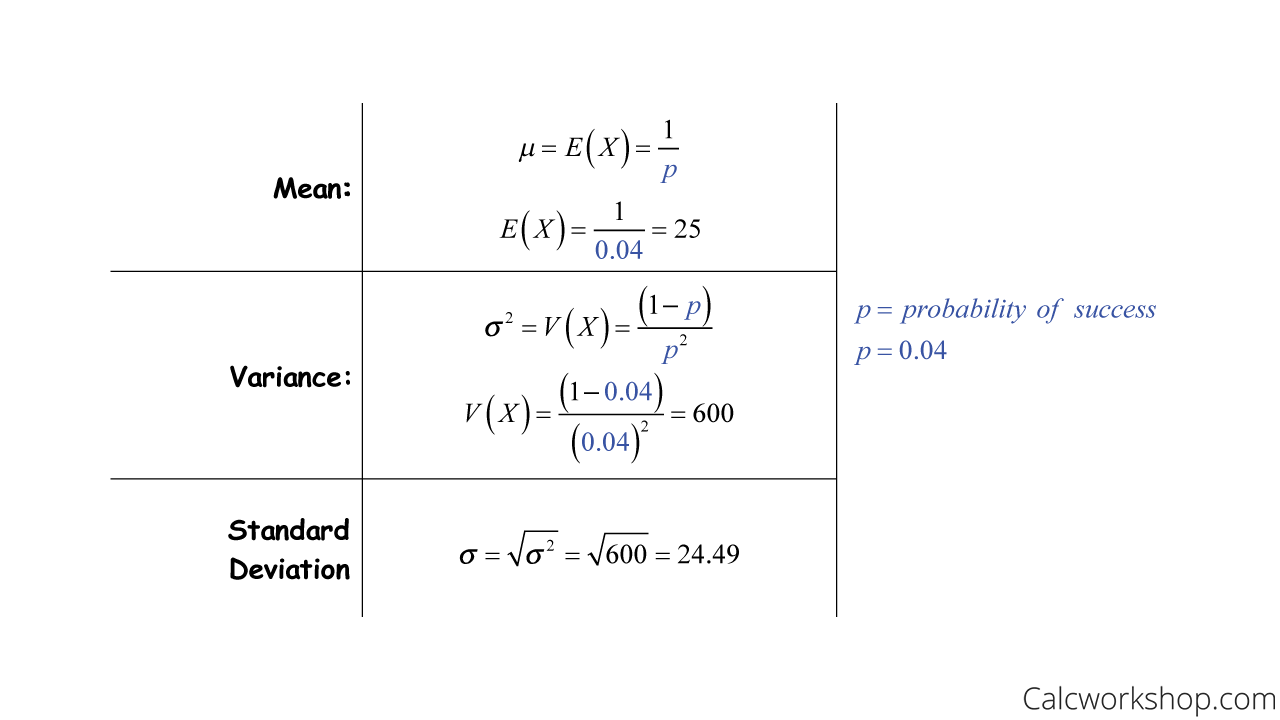
Discrete Probability Distribution Variance