
What is Cellular Respiration?
- The reactions involved in cellular respiration are catabolic reactions that involve the breakdown of larger organic molecules into smaller forms.
- The overall process of cellular respiration takes place in a number of steps that are specialized for the degradation of specific molecules.
- Cellular respiration is a basis of life that occurs in all living forms. ...
What are the four main steps of cellular respiration?
What are the four processes of respiration quizlet?
- Pulmonary ventilation/breathing. – inspiration (air in) & expiration (air out) in response to changes of O2 & CO2 in blood.
- External respiration. – exchange of O2, CO2 between alveoli/blood in the pulmonary capillaries.
- Transport of respiratory gases. …
- Internal respiration.
What pathway does cellular respiration begin with?
Cellular respiration begins with a pathway called GYLCOLYSIS, which takes place in the THYLAKOID of the cell. 8. At the end of glycolysis, about 90% percent of the chemical energy is locked in the bonds of the PYRUVIC ACID molecule. 9.
Where does the final stage of cellular respiration occur?
mitochondria. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. If oxygen is available, aerobic respiration will go forward. In eukaryotic cells, the pyruvate molecules produced at the end of glycolysis are transported into mitochondria, which are the sites of cellular respiration.
What is cellular respiration and how does it happen?
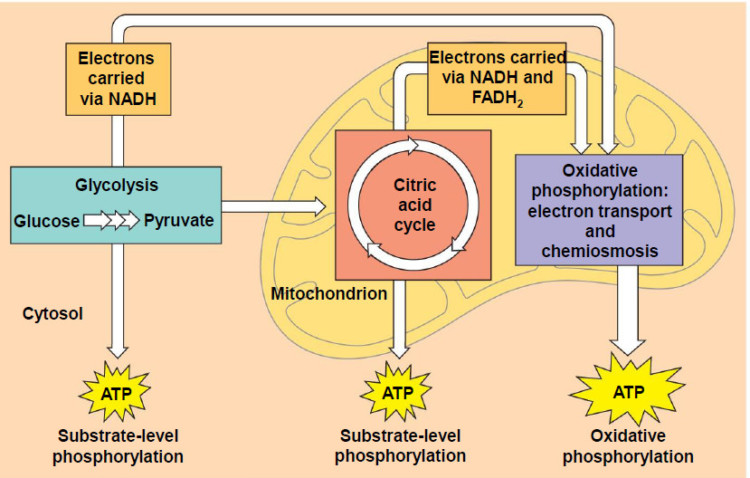
Cellular respiration is the process in which cells break down glucose, release the stored energy, and use it to make ATP. The process begins in the cytoplasm and is completed in a mitochondrion. Cellular respiration occurs in three stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and electron transport.
What is the process of cellular process?
Cellular processes, such as transcription, DNA replication, and DNA repair, are regulated by an intimate and self-reinforcing crosstalk and interdependence between histone-modifying complexes and other histone-modifying activities, such as acetylation, phosphorylation, and methylation.
What is respiration process in simple words?
“Respiration is defined as a metabolic process wherein, the living cells of an organism obtains energy (in the form of ATP) by taking in oxygen and liberating carbon dioxide from the oxidation of complex organic substances.”
What is cellular respiration in short words?
Listen to pronunciation. (sel RES-pih-RAY-shun) A chemical process in which oxygen is used to make energy from carbohydrates (sugars). Also called aerobic metabolism, aerobic respiration, and oxidative metabolism.
Why respiration is called cellular process?
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions occurring inside the cells to convert biochemical energy obtained from the food into a chemical compound called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions carried out for maintaining the living state of the cells in an organism.
What are the 4 processes of respiration?
There are four stages: glycolysis, the link reaction, the Krebs cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. During glycolysis, glucose molecules (six-carbon molecules) are split into two pyruvates (three-carbon molecules) during a sequence of enzyme-controlled reactions. This occurs in both aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
What are the 3 processes of respiration?
The reactions of cellular respiration can be grouped into three stages: glycolysis (stage 1), the Krebs cycle, also called the citric acid cycle (stage 2), and electron transport (stage 3).
What is an example of cellular respiration?
An example of cellular respiration in plants is the use of photoautotrophic processes to obtain the glucose needed for cellular respiration. This means that plants can use the light energy they acquire from the sun to yield glucose and oxygen.
What is a sentence for cellular respiration?
1. While breaking up sugars, the woman's body cells are creating energy through cellular respiration. 2. Cellular respiration is a process in which cells take apart food molecules and use their atoms as a source of energy.
Where do cellular respiration occur?
Cellular respiration is a process that occurs in the mitochondria of all organisms. In this process, both plants and animals break down simple sugars into carbon dioxide and water and release energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
What is ATP in cellular respiration?
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is the source of energy for use and storage at the cellular level. The structure of ATP is a nucleoside triphosphate, consisting of a nitrogenous base (adenine), a ribose sugar, and three serially bonded phosphate groups.
What is the main product of respiration?
ATPThe main product of cellular respiration is ATP; waste products include carbon dioxide and water.
What is the purpose of respiration?
The main purpose of respiration is to provide oxygen to the cells at a rate adequate to satisfy their metabolic needs. This involves transport of oxygen from the lung to the tissues by means of the circulation of blood.
What is respiration Class 10 short answer?
Respiration is the process in which the cells of an organism obtain energy by combining oxygen and glucose, resulting in the release of carbon dioxide, water, and ATP (energy).
What is respiration 5th standard?
Respiration is the process that all living things go through to create the energy they need to live. This happens in the cells so it is also called cellular respiration. It usually involves exchanging two gases—oxygen and carbon dioxide. The cells take in oxygen and release carbon dioxide.
What is respiration with example?
Respiration is taking a breath or the act of breathing. An example of respiration is inhaling and exhaling air. Any similar process, in organisms that lack lungs, that exchanges gases with its environment. The process of inhaling and exhaling; breathing, breath.
What is respiration BYJU's?
Respiration is the process through which living organisms take in oxygen and give out carbon dioxide to release energy. So, naturally, respiration is a major and vital process of gas exchange. The transport of gases during respiration, both oxygen and carbon dioxide are carried out by the blood cells.
What is cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that uses glucose to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an organic compound the body can use for ene...
What is the purpose of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is used to generate usable ATP energy in order to support many other reactions in the body. ATP is particularly important for...
What are the main steps of cellular respiration?
There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis; the citric acid (TCA) or the Krebs cycle; and the electron transport chain, where o...
Where does cellular respiration take place?
Cellular respiration takes place in the cytoplasm and mitochondria of each cell of the body. Glycolysis occurs inside the cytoplasm, while the TCA...
What are the reactants of cellular respiration?
The reactants of cellular respiration vary at each stage, but initially, it requires an input of glucose, ATP, and NAD+. NAD+, a nicotinamide deriv...
What are the products of cellular respiration?
The final end products of cellular respiration are ATP and H2O. Glycolysis produces two pyruvate molecules, four ATPs (a net of two ATP), two NADH,...
What are the rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration?
There are three primary rate-determining enzymes in cellular respiration. These enzymes catalyze the rate-limiting steps, which are the slowest rea...
What diseases can affect cellular respiration?
Several diseases can affect cellular respiration. Since cellular respiration is so vital to bodily functions, many of these diseases severely affec...
What are the most important facts to know about cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions...
Which step of respiration is shared by all types of respiration?
Glycolysis is the only step which is shared by all types of respiration. In glycolysis, a sugar molecule such as glucose is split in half, generating two molecules of ATP.
What is the main product of cellular respiration?
The main product of any cellular respiration is the molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This molecule stores the energy released during respiration and allows the cell to transfer this energy to various parts of the cell. ATP is used by a number of cellular components as a source of energy.
How much ATP does aerobic respiration produce?
The process of aerobic respiration produces a huge amount of ATP from each molecule of sugar. In fact, each molecule of sugar digested by a plant or animal cell yields 36 molecules of ATP! By comparison, fermentation usually only produces 2-4 molecules of ATP.
How does aerobic respiration work?
Instead of directly reducing intermediates of the Krebs cycle, aerobic respiration uses oxygen as the final electron receptor. But first, the electrons and protons bound to electron carriers (such as NADH), are processed through the electron transport chain. This chain of proteins within the mitochondrial membrane uses the energy from these electrons to pump protons to one side of the membrane. This creates an electromotive force, which is utilized by the protein complex ATP synthase phosphorylate a large number of ATD molecules, creating ATP.
What is the process of converting sugars into energy?
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert sugars into energy. To create ATP and other forms of energy to power cellular reactions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy into a useable form.
Why is aerobic respiration so efficient?
Aerobic respiration is so efficient because oxygen is the most powerful electron acceptor found in nature. Oxygen “loves” electrons – and its love of electrons “pulls” them through the electron transport chain of the mitochondria.
Why is aerobic respiration important for eukaryotes?
Aerobic respiration is an extremely efficient process allows eukaryotes to have complicated life functions and active lifestyles. However, it also means that they require a constant supply of oxygen, or they will be unable to obtain energy to stay alive.
What is the process of cellular respiration?
cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation. (For longer treatments of various aspects of cellular respiration, see tricarboxylic acid cycle and metabolism .)
How does cellular respiration work?
Discover how cellular respiration transforms your food into energy usable by your cells. Cellular respiration releases stored energy in glucose molecules and converts it into a form of energy that can be used by cells. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. See all videos for this article. Cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen ...
How many NAD molecules are in the TCA cycle?
The products of a single turn of the TCA cycle consist of three NAD + molecules, which are reduced (through the process of adding hydrogen, H +) to the same number of NADH molecules, and one FAD molecule, which is similarly reduced to a single FADH 2 molecule. These molecules go on to fuel the third stage of cellular respiration, ...
What is the process of cellular respiration in which glucose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water?
(For longer treatments of various aspects of cellular respiration, see tricarboxylic acid cycle and metabolism .) During the process of glycolysis in cellular respiration, glucose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water.
What is the process of glycolysis?
Glycolysis (which is also known as the glycolytic pathway or the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway) is a sequence of 10 chemical reactions taking place in most cells that breaks down a glucose molecule into two pyruvate (pyruvic acid) molecules. Energy released during the breakdown of glucose and other organic fuel molecules from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins during glycolysis is captured and stored in ATP. In addition, the compound nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD +) is converted to NADH during this step ( see below ). Pyruvate molecules produced during glycolysis then enter the mitochondria, where they are each converted into a compound known as acetyl coenzyme A, which then enters the TCA cycle. (Some sources consider the conversion of pyruvate into acetyl coenzyme A as a distinct step, called pyruvate oxidation or the transition reaction, in the process of cellular respiration.)
What is the process by which food molecules are metabolized to obtain chemical?
algae: Cellular respiration. Cellular respiration in algae, as in all organisms, is the process by which food molecules are metabolized to obtain chemical...
What are the three main metabolic processes?
The overall process, however, can be distilled into three main metabolic stages or steps: glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation ...
Where does aerobic respiration take place?
While most aerobic respiration (with oxygen) takes place in the cell's mitochondria, and anaerobic respiration (without oxygen) takes place within the cell's cytoplasm. Loading PDF ... (adenosine triphosphate) chemical found in most living cells and used for energy.
What is the process by which food, in the form of sugar (glucose), is transformed into energy within?
Cellular Respiration. Cellular respiration is the process by which food, in the form of sugar (glucose), is transformed into energy within cells. Grades.
What is the definition of fermentation?
Adjective. relating to organisms whose cells have a nuceleus. fermentation. Noun. natural or artificial process of changing a food's sugars into alcohols. glycolysis. Noun. breakdown of a carbohydrate (such as glucose) using enzymes, resulting in the release of energy. habitat.
What is the definition of ATP?
Adjective. living, active, or occurring in the presence of free oxygen. anaerobic. Adjective. living, active, or occurring in the absence of free oxygen. ATP. Noun. (adenosine triphosphate) chemical found in most living cells and used for energy. cellular respiration.
What are the organelles of plants?
Some of the major organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, the endoplasmic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus. Plant cells also include chloroplasts, which are responsible for photosynthesis. Use these classroom resources to examine how cells function with your students. View Collection.
What Is Cellular Respiration?
Cellular respiration is the process that cells use to make energy and is biochemically different from the process of breathing, also known as respiration. Cellular respiration takes place within cells, in the cytoplasm and the mitochondria. All cells need energy, so all cells do cellular respiration, including both plant and animal cells.
How is ATP formed in cellular respiration?
ATP is formed in all three steps of cellular respiration. During glycolysis two ATP are formed for one glucose molecule.
What are the two types of anaerobic respiration?
There are two main types of anaerobic respiration, lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation. In lactic acid fermentation pyruvate is converted to lactic acid, no ATP is formed and NAD+ is regenerated.
Why do cells not go through the Krebs cycle?
In anaerobic respiration, cells go through glycolysis but do not proceed through the Krebs cycle because they do not have oxygen to act as a final acceptor in oxidative phosphorylation. Instead, after glycolysis, cells shift to either lactic acid fermentation or alcoholic fermentation to regenerate the electron carrier NAD+. This entire process occurs in the cytoplasm, unlike aerobic respiration which occurs both in the cytoplasm and the mitochondria.
What is pyruvate converted to?
In alcoholic fermentation pyruvate is converted to acetaldehyde, then ethanol. Like in lactic acid fermentation, no ATP is formed but NAD+ is regenerated to be used in glycolysis.
How is carbon dioxide removed from the body?
Carbon dioxide is toxic and must be removed from the body through exhalation. There are three steps to aerobic cellular respiration or cellular respiration that uses oxygen: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation.
What is the acetyl-coa cycle?
The acetyl-CoA enters the Krebs cycle. During the Krebs cycle more electron carriers, both NADH and FADH2, are generated as well as a small amount of ATP. Acetyl-CoA is regenerated and the cycle continues.
