
The product is the result of a multiplication problem. In 5 x 8 = 40...40 is the product. The quotient is the result of a division problem. In 30 divided by 5 equals 6...6 is the quotient.
What is difference between a product and a quotient?
- Insert your function into the first part of the formula. ...
- Replace the “f (x)” in the formula’s numerator. This part is easy, because you’re just copying the formula exactly as written in the question and pasting it in:
- Use algebra to simplify. In most cases, things will start to cancel out, making the formula a little less ugly.
What is the sum difference product and quotient?
The outcome of adding two or more numbers gives the sum. The outcome of subtracting the two numbers gives the difference. The outcome of multiplying the two or more numbers gives the product. The result of the division of one number by another is the quotient.
How does difference sum quotient and product alike?
SUM – The sum is the result of adding two or more numbers. DIFFERENCE – The difference of two numbers is the result of subtracting these two numbers. PRODUCT – The product of two or more numbers is the result of multiplying these numbers. QUOTIENT – The quotient of two numbers is the result of the division of these numbers.
What is the formula for product?
What is the Product Cost Formula?
- Examples of Product Cost Formula (With Excel Template) Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of Product Cost in a better manner. ...
- Explanation. ...
- Relevance and Uses of Product Cost Formula. ...
- Product Cost Formula Calculator. ...
How do you find product or quotient?
0:022:41How Do You Figure Out the Sign of a Product or Quotient? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWhen determining the sign of a product or quotient we first need to look at a simple situation. SoMoreWhen determining the sign of a product or quotient we first need to look at a simple situation. So let's look at a situation where we're only multiplying or dividing two numbers let's take five times
What is a product in math?
The term "product" refers to the result of one or more multiplications. For example, the mathematical statement would be read " times equals ," where is called the multiplier, the multiplicand and is their product.
What is quotient with example?
: the number obtained by dividing one number by another Dividing 10 by 5 gives a quotient of 2.
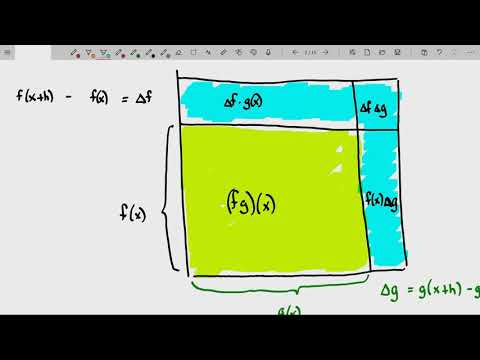
What is product rule and quotient rule?
The Product Rule in Words The Product Rule says that the derivative of a product of two functions is the first function times the derivative of the second function plus the second function times the derivative of the first function.
What is the quotient of an equation?
Quotient is the answer obtained when we divide one number by another. For example, if we divide the number 6 by 3, we get the result as 2, which is the quotient.
Does product mean multiply?
The product of two numbers is the result you get when you multiply them together.
What is the product of a number?
In Mathematics, the term “product” is the result of the multiplication operation. If the given numbers are multiplied together, we get the result called the product. For example, if two numbers 4 and 5 are multiplied, we get the result 20. Hence, we can say that 20 is the product of the numbers 4 and 5.
What is the quotient of 63 and 9?
The quotient (integer division) of 63/9 equals 7; the remainder (“left over”) is 0. 63 is the dividend, and 9 is the divisor.
What is the quotient of a number?
The result of dividing two numbers (the dividend by the divisor) is called the quotient.
What is product rule example?
We can apply the product rule to find the differentiation of the function of the form u(x)v(x). For example, for a function f(x) = x2 sin x, we can find the derivative as, f'(x) = sin x·2x + x2·cos x.
How do you solve the product rule?
2:1811:10Product Rule For Derivatives - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe derivative of f times g is equal to the derivative of the first part f prime times the secondMoreThe derivative of f times g is equal to the derivative of the first part f prime times the second part plus the first part times the derivative of the second.
What is the product rule in algebra?
The product rule states that if two factors raised to an exponent are being multiplied together, and they have the same base, we can add the exponents. In this example, x and x 3 are our two factors.
Must read
I'm Arbab Hassan Believer. I belong to Sargodha Pakistan. My qualification is B.sc double Math plus Stat. I work on SEO. I have splendid expertise on it. And I'm working on a lot of education, technical, and SEO tips sites.
Simple Definition of Derivative in Calculus
Derivative is the rate of change of a function f (x) with respect to any variable.
What is the Product and Quotient Rule with Example
if f and g are differentiable at x , then fg is also differentiable at x and [f (x)g (x)]’ = f’ (x) g (x) + f (x) g’
What is the product rule?
The product rule is In other words, the derivative of a product of two functions equals the derivative of the first times the second, plus the first times the derivative of the second. 3. One function divided by another. Select the third example, showing a quotient.
What is the derivative of sine?
The derivative of sine is cosine, the derivative of a line is a horizontal line, and the derivative of their sum is just the sum of these two (i.e., a cosine curve shifted up). 2. The product of the same functions. Select the second example from the drop down menu.
Introduction
Taking the derivatives of simple functions (i.e. polynomials) is easy using the power rule.
Exercise 2
Calculate the derivative of g ( x ) = 2 x sin x sec x . {\displaystyle g (x)=2x\sin x\sec x.}
The Product Rule
The first of the differentiation rules we discuss here is the product rule. Evidently, this is for differentiating products, that is, when two functions of the same variable are multiplied together. Hence, suppose that we want to differentiate a function that we can write as y = f ( x) g ( x). The derivative is given by:
The Quotient Rule
The second of the differentiation rules we discuss here is the quotient rule. As suggested, this is for differentiating quotients, that is, when one function of a given variable is divided by another function of the same variable. Hence, suppose that we want to differentiate a function that we can write as y = f ( x) g ( x).
The Chain Rule
The final differentiation rule we discuss here is the chain rule. Of course, this is for differentiating chains, also known as a function of a function or composite functions. This is when one function is applied on top of another (see more on composite functions ).
