Promoters and terminators are stretches of DNA upstream and downstream (respectively) of genes that control both the rate at which the gene is transcribed and the rate at which mRNA is degraded. As a result, both of these elements control net protein expression from a synthetic construct. Thus, it is highly important to discover and engineer promoters and terminators with desired characteristics.
What is the difference between promoter and Terminator?
is that promoter is one who promotes, particularly with respect to entertainment events or goods while terminator is one who finishes. One who promotes, particularly with respect to entertainment events or goods. (genetics) The section of DNA that controls the initiation of RNA transcription as a product of a gene.
What is the NOS terminator of a promoter?
Promoters serve as restricting destinations for RNA polymerase, the catalyst used to incorporate mRNA (that is later deciphered into protein).The NOS terminator is the terminator region of the gene for nopaline synthase. Nopaline is an opine, a food source for Agrobacteria made by plants (albeit using a gene transferred from the Agrobacteria).
What is the function of a promoter?
A promoter is a DNA sequence placed upstream of the transcription start site. This important DNA sequence is found in both eukaryotes and the prokaryotes; although the eukaryotic promoters may differ from the prokaryotic promoters.
What are the promoter sequences?
Promoter sequences are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryote. Promoter is the site for binding of RNA polymerase. They are highly conserved regions known as consensus sequences. The TATA box of eukaryotes and the Pribnow box and the -35 promoter of prokaryotes are the common promoters.
What is terminator in biology?
A sequence in DNA that signals termination of transcription to RNA Polymerase. This should not be confused with terminator codons that are the stopping signal for translation. Also known as: terminator, rho-independent termination site.
What is a promoter in biology?
A promoter, as related to genomics, is a region of DNA upstream of a gene where relevant proteins (such as RNA polymerase and transcription factors) bind to initiate transcription of that gene. The resulting transcription produces an RNA molecule (such as mRNA).
What are terminators in transcription?
In genetics, a transcription terminator is a section of nucleic acid sequence that marks the end of a gene or operon in genomic DNA during transcription.
What is the terminator region?
The terminator region, on the other hand, is the nucleotide sequence that determines the detachment of RNA polymerase from the DNA template strand, which occurs towards the end of the transcription process.
What is promoter and its function?
A promoter is a person or a group of people who come up with an idea of forming a profitable business venture. After the idea is conceived, the promoters make initial investigations to discover the plan's pros and cons. They also calculate working capital needs, estimated costs and potential income.
Is TATA box a promoter?
A TATA box is a DNA sequence that indicates where a genetic sequence can be read and decoded. It is a type of promoter sequence, which specifies to other molecules where transcription begins. Transcription is a process that produces an RNA molecule from a DNA sequence.
What is the role of the promoter terminator and mRNA in transcription?
Promoter: The startting site on a DNA strand for trnascription of RNA by the RNA polymerase. Terminator: The site on a DNA strand at which transcription ends. mRNA: The type of RNA molecule that directs the incorporation of amino acids into proteins.
How do you identify a terminator and a promoter?
The promoter is located towards the 5-end of the structural gene. It is a DNA sequence that provides a binding site for RNA polymerase. On the contrary, the terminator is located towards the 3-end of the coding strand and it usually defines the end of the process of transcription.
What is termination in translation?
Translation ends in a process called termination. Termination happens when a stop codon in the mRNA (UAA, UAG, or UGA) enters the A site. Stop codons are recognized by proteins called release factors, which fit neatly into the P site (though they aren't tRNAs).
How do terminators work?
Terminators can speak naturally, copy the voices of others, read and write human handwriting, and even sweat, smell, bleed, and age. Being machines, it is typically believed by humans that they are incapable of behavioral responses such as emotions.
Is a terminator A protein?
Using the ter protein and highly purified dnaB helicase, we show that the terminator protein is a DNA sequence-specific contra-helicase, i.e., the protein when bound to its recognition sequence (τ) strongly impedes the ATP-dependent unwinding of double-stranded DNA.
What are the two types of terminators?
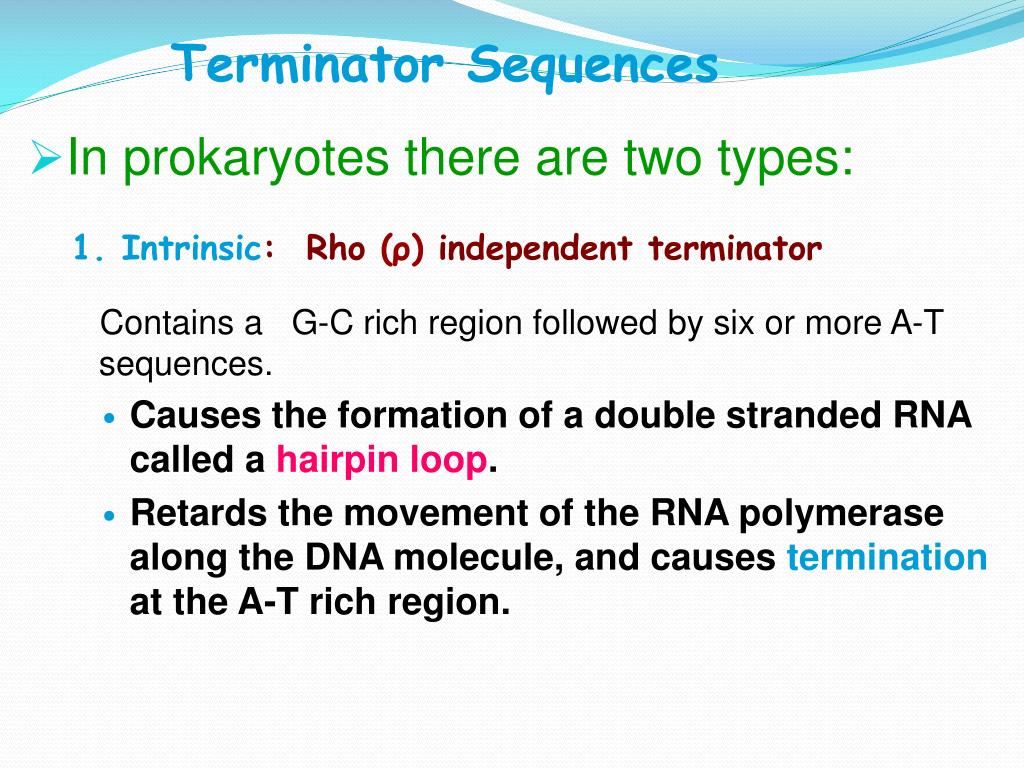
Terminators are genetic parts that usually occur at the end of a gene or operon and cause transcription to stop. In prokaryotes, terminators usually fall into two categories (1) rho-independent terminators and (2) rho-dependent terminators.
As nouns the difference between promoter and terminator
is that promoter is one who promotes, particularly with respect to entertainment events or goods while terminator is one who finishes.
English
One who promotes, particularly with respect to entertainment events or goods.
What is the function of a promoter?
A promoter is a sequence of DNA needed to turn a gene on or off. The process of transcription is initiated at the promoter. Usually found near the beginning of a gene, the promoter has a binding site for the enzyme used to make a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule.
Where is the promoter located?
The promoter region is the sequence typically referred to that's right upstream or right next to where a gene is about to be transcribed. It's the region where certain regulatory elements will bind; these are proteins that will bind to help RNA get transcribed. Now, "promoter", the term "promoter", can actually be a little bit of a nebulous term because it's not very exact. There are specific sequences that are generally found within a promoter region, but sometimes people refer to even extended promoter region that might include sequences that are farther upstream of the gene that might help enhance or repress the particular gene that's about to be transcribed in certain cell types. In general, if you think of the promoter as that piece of DNA that's just upstream of the transcription start site of a gene, that's pretty much what we refer to as promoters.
Is the promoter region nebulous?
Now, "promoter", the term "promoter", can actually be a little bit of a nebulous term because it's not very exact. There are specific sequences that are generally found within a promoter region, but sometimes people refer to even extended promoter region that might include sequences that are farther upstream of the gene ...
What is the terminator of a gene?
In genetics, a transcription terminator is a section of nucleic acid sequence that marks the end of a gene or operon in genom ic DNA during transcription. This sequence mediates transcriptional termination by providing signals in the newly synthesized transcript RNA that trigger processes which release the transcript RNA from ...
What is the terminator sequence of mRNA?
The terminator sequence in DNA contains a 20 basepair GC-rich region of dyad symmetry followed by a short poly-A tract or "A stretch" which is transcribed to form the terminating hairpin and a 7–9 nucleotide "U tract" respectively. The mechanism of termination is hypothesized to occur through a combination of direct promotion of dissociation through allosteric effects of hairpin binding interactions with the RNA polymerase and "competitive kinetics". The hairpin formation causes RNA polymerase stalling and destabilization, leading to a greater likelihood that dissociation of the complex will occur at that location due to increased time spent paused at that site and reduced stability of the complex. Additionally, the elongation protein factor NusA interacts with the RNA polymerase and the hairpin structure to stimulate transcriptional termination.
Where are rho dependent terminators found?
Rho-dependent terminators are found in bacteria and phages. The Rho-dependent terminator occurs downstream of translational stop codons and consists of an unstructured, cytosine-rich sequence on the mRNA known as a Rho utilization site ( rut) for which a consensus sequence has not been identified, and a downstream transcription stop point ( tsp ).
What is the mechanism of prokaryotic transcriptional termination?
In Rho-independent termination, a terminating hairpin forms on the nascent mRNA interacting with the NusA protein to stimulate release of the transcript from the RNA polymerase complex (top). In Rho-dependent termination, the Rho protein binds at the upstream rut site, translocates down the mRNA, and interacts with the RNA polymerase complex to stimulate release of the transcript.
What is the difference between the promoter and the operator?
The key difference between the promoter and the operator is based on the type of molecule that binds to the respective DNA sequence. RNA polymerase binds to the promoter, whereas regulatory molecules of the operon system bind to the operator.
Where is the promoter located?
A promoter is a DNA sequence placed upstream of the transcription start site. This important DNA sequence is found in both eukaryotes and the prokaryotes; although the eukaryotic promoters may differ from the prokaryotic promoters. Promoters are the DNA regions in which RNA polymerase binds to during the transcription process.
What is the role of promoters in RNA?
Promoters are the DNA regions in which RNA polymerase binds to during the transcription process. It is the main enzyme involved in producing the single-stranded RNA (mRNA, tRNA, rRNA) from a DNA template. Depending on the type of RNA, the RNA polymerase will differ.
What are the promoters and operators of RNA?
Promoter and Operator are important DNA sequences that are involved in the transcription process and in transcription regulation. Promoter sequences are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryote. Promoter is the site for binding of RNA polymerase. They are highly conserved regions known as consensus sequences. The TATA box of eukaryotes and the Pribnow box and the -35 promoter of prokaryotes are the common promoters. Operators are only present in prokaryotes, where they control the gene expression by binding the repressor and inhibiting transcription of the downstream genes (lac operon concept), or bind to the activator and induce transcription ( trp operon concept). This is the difference between promoter and operator.
What is an operator in a prokaryotic cell?
Operators are the sites in which the regulatory molecule binds into an operon model. Promoters are found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Operators are found only in prokaryotes. Promoter facilitates the binding of the RNA polymerase and transcription factors (only in eukaryotes) to the gene for gene transcription.
Which factor is involved in recognizing the promoter and in the assembly of the enzyme on the promoter?
In prokaryotes, the mechanism is much simpler as they do not contain any transcription factors. Instead, the sigma factor of RNA polymerase is involved in recognizing the promoter and in the assembly of the enzyme on the promoter.
What is the binding factor of RNA polymerase to the tata box?
The binding of RNA polymerase to the TATA box is facilitated by the binding transcription factors. This transcription factors, make confirmation changes in the promoter sequence and increase its affinity for RNA polymerase to bind.
