Hormones Prostaglandins
Prostaglandin
The prostaglandins are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derived enzymatically from the fatty acid arachid…
Why are prostaglandins known as local hormones?
- Prostaglandins are a subset of a larger family of substances called eicosanoids
- Other subgroups include thromboxanes, leukotrienes and lipoxins (just out of interest!)
- Eicosanoids are localised tissue hormones that seem to be the fundamental regulating molecules in most forms of life
- Prostaglandins are chemical mediators, or ‘local’ hormones. ...
Are prostaglandins good or bad?
Studies have shown the more prostaglandin inflammation you have, the worse your menstrual cramps can be, which is known as dysmenorrhea. What Do Prostaglandins Do? While all this menstrual cramp talk may make you think all prostaglandin functions are bad, they are actually very necessary and protective of your health.
What gland produces prostaglandins?
prostaglandin, any of a group of physiologically active substances having diverse hormonelike effects in animals. Prostaglandins were discovered in human semen in 1935 by the Swedish physiologist Ulf von Euler, who named them, thinking that they were secreted by the prostate gland.
What foods increase prostaglandins?
What trimester of pregnancy marks the return of the inflammatory response as well as prostaglandins?
- Bananas. …
- Sunflower Seeds. …
- Ginger. …
- Pineapple: remember that alcohol is contraindicated for cramps so stay away from the piña coladas!
What is the function of prostaglandin hormone?
Prostaglandins play a role in the following reproductive functions: 1) conception; 2) luteolysis; 3) menstruation; and 4) parturition. It has also been proposed that Prostaglandin A may be the natriuretic hormone, the circulating hormone which controls sodium reabsorption by the kidney.
What causes high prostaglandins during period?
The more estrogen-based foods you consume, the more likely your uterine lining becomes abnormally thick. As a result, when it begins to break down during the menstrual cycle, this process creates more prostaglandins, resulting in higher levels of pain.
What produces prostaglandin in the body?
Prostaglandins are synthesized in cells from arachidonic acid by cyclooxygenases (COX-1 and COX-2) and terminal prostaglandin synthases. COX-1 is responsible for baseline synthesis of prostaglandins, while COX-2 produces increased levels of prostaglandins in inflammatory responses.
What are prostaglandins effects?
Prostaglandins can have healing effects, especially in the stomach. They decrease stomach acid production while also stimulating the release of protective mucus in the GI tract. In addition, prostaglandins also influence blood clotting to prevent bleeding. They also help dissolve clots when a person is healing.
What foods are high in prostaglandins?
These foods contain arachidonic acids, which instigate the production of cramp-causing prostaglandins....FOODS:Bananas. ... Sunflower Seeds. ... Ginger. ... Pineapple: remember that alcohol is contraindicated for cramps so stay away from the piña coladas!
What foods reduce prostaglandins?
In contrast, omega-3 fatty acids can ease menstrual pain because of their ability to decrease prostaglandins, which promote cramps. Choose foods that are high in omega-3 fatty acids such as seeds, nuts, eggs, dark green vegetables and salmon.
Why do prostaglandins cause pain?
High concentrations of prostaglandins cause pain by direct action upon nerve endings. More typically, however, at low concentrations, they markedly increase sensitivity to pain. The pain threshold may be so altered that even normally painless stimuli may be painful.
Does prostaglandin increase with age?
Taken together, our results are consistent with the notion that the up-regulation of COX protein and mRNA levels with age is the main contributing factor in the age associated increase in prostaglandin E2.
How do you control prostaglandins?
To balance prostaglandin production, steps to take include: eating a high-fiber, anti-inflammatory diet; taking magnesium, zinc, omega-3s and bromelain; exercising and sleeping enough; treating estrogen dominance; treating food allergies; avoiding stimulants, alcohol and smoking.
Are prostaglandins good?
First discovered in semen, prostaglandins were later found in cells throughout the body, as well as in women's menstrual fluid. Prostaglandins affect reproductive processes and are also thought to play a major role in promoting and resolving inflammation in the body.
When do prostaglandins rise menstrual cycle?
Two prostaglandins in particular called, “PGF2α” and “PGE2”, cause the uterine muscle to contract (cramp). The amounts of these prostaglandins rise after ovulation and reach their peak during menstruation (16,17). The cramping caused by this prostaglandin helps trigger the period.
How do you get rid of prostaglandins?
Some women find that eating anti-inflammatory foods, like cherries, blueberries, squash, tomatoes, almonds, dark leafy greens, foods high in omega-3 fatty acids and bell peppers help. Drink chamomile tea. Chamomile is full of anti-inflammatory substances to help inhibit prostaglandins.
Can high levels of prostaglandins cause infertility?
Period cramps that are caused by the normal activity of prostaglandins are called primary dysmenorrhea. This type of painful period should not negatively impact your fertility.
Does endometriosis cause high prostaglandins?
The bad news is that women with endometriosis have been shown to produce an excess of a prostaglandin called PGE2, which causes inflammation, pain, and uterine contractions.
What is the role of prostaglandins in pregnancy?
forming platelets into a cluster or breaking them up. opening or closing up airways. contracting or relaxing smooth muscle in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. causing uterine contractions in pregnancy and when not pregnant. As you can see, prostaglandins play a variety of roles in the body.
How do prostaglandins affect the body?
Prostaglandins have significant effects, but they also have limitations. They usually have a short half-life, so they don’t last long in the body. For this reason, they can only affect cells that are close by. That’s why they’re present throughout the body to exert the following effects.
What are prostaglandins made of?
Prostaglandins are compounds in the body made of fats that have hormone-like effects. They’re interesting because they can have different effects depending on the receptors where they attach. Some known effects include uterine cramping and increased sensitivity to pain. Researchers have even created artificial prostaglandins for use in medication ...
How do prostaglandins help with bleeding?
In addition, prostaglandins also influence blood clotting to prevent bleeding. They also help dissolve clots when a person is healing.
What are the effects of prostaglandins?
They know prostaglandins can have a variety of inflammatory effects, including causing vasodilation, promoting fevers, and recruiting cells involved in allergic reactions. Doctors have also identified the prostaglandin type PGE2 as causing redness, swelling, and pain.
What are the health problems that can result from too many prostaglandins?
Complications. Too many or too few prostaglandins in the body can cause health complications. Known problems with too many prostaglandins include arthritis and menstrual cramping. Conditions that can result from too few prostaglandins include glaucoma and stomach ulcers.
Why are protaglandins unique?
Prostaglandins are unique compounds because they have hormone-like effects. That is, they influence reactions in the body when they’re present in certain tissues.
What is a prostaglandin?
prostaglandin, any of a group of physiologically active substances having diverse hormonelike effects in animals. Prostaglandins were discovered in human semen in 1935 by the Swedish physiologist Ulf von Euler, who named them, thinking that they were secreted by ...
How do prostaglandins work?
Most prostaglandins act locally; for instance, they are powerful locally acting vasodilators. Vasodilation occurs when the muscles in the walls of blood vessels relax so that the vessels dilate. This creates less resistance to blood flow and allows blood flow to increase and blood pressure to decrease. An important example of the vasodilatory action of prostaglandins is found in the kidneys, in which widespread vasodilation leads to an increase in the flow of blood to the kidneys and an increase in the excretion of sodium in the urine. Thromboxanes, on the other hand, are powerful vasoconstrictors that cause a decrease in blood flow and an increase in blood pressure.
How do thromboxanes and prostacyclins work?
Thromboxanes and prostacyclins play an important role in the formation of blood clots. The process of clot formation begins with an aggregation of blood platelets. This process is strongly stimulated by thromboxanes and inhibited by prostacyclin. Prostacyclin is synthesized in the walls of blood vessels and serves the physiological function of preventing needless clot formation. In contrast, thromboxanes are synthesized within platelets, and, in response to vessel injury, which causes platelets to adhere to one another and to the walls of blood vessels thromboxanes are released to promote clot formation. Platelet adherence is increased in arteries that are affected by the process of atherosclerosis. In affected vessels the platelets aggregate into a plaque called a thrombus along the interior surface of the vessel wall. A thrombus may partially or completely block (occlude) blood flow through a vessel or may break off from the vessel wall and travel through the bloodstream, at which point it is called an embolus. When an embolus becomes lodged in another vessel where it completely occludes blood flow, it causes an embolism. Thrombi and emboli are the most common causes of heart attack (myocardial infarction). Therapy with daily low doses of aspirin (an inhibitor of cyclooxygenase) has had some success as a preventive measure for people who are at high risk of heart attack.
What is the role of arachidonic acid in cell membranes?
In response to many different stimuli, including various hormonal, chemical, or physical agents, a chain of events is set in motion that results in prostaglandin formation and release.
What is the synthesis of prostaglandins?
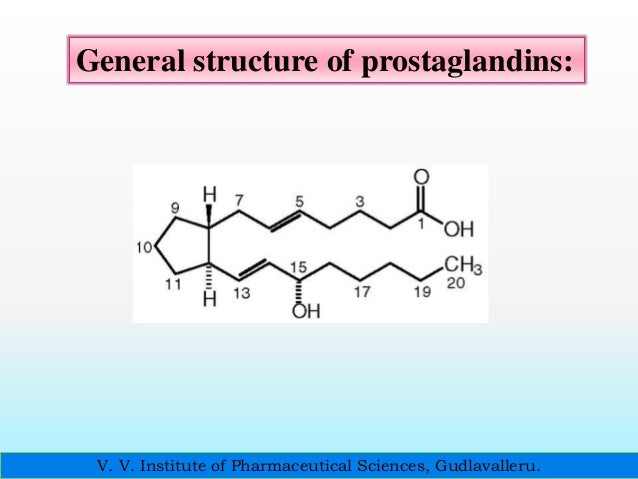
Synthesis of prostaglandins. The prostaglandins are made up of unsaturated fatty acids that contain a cyclopentane (5-carbon) ring and are derived from the 20-carbon, straight-chain, polyunsaturated fatty acid precursor arachidonic acid. Arachidonic acid is a key component of phospholipids, which are themselves integral components of cell membranes.
How much do prostaglandins affect blood pressure?
Prostaglandins are very potent; for example, in humans some affect blood pressure at concentrations as low as 0.1 microgram per kilogram of body weight. The structural differences between prostaglandins account for their different biological activities.
What enzyme catalyzes the release of arachidonic acid from phospholipid molecules?
These stimuli, either directly or indirectly, result in the activation of an enzyme called phospholipase A 2. This enzyme catalyzes the release of arachidonic acid from phospholipid molecules. Depending on the type of stimulus and the enzymes present, arachidonic acid may diverge down one of several possible pathways.
What Are Prostaglandins?
Prostaglandins are hormone-like substances with diverse roles in the body, principally the acute immune reaction and inflammation [ 1 ].
What are the functions of prostaglandins?
Prostaglandins are powerful hormone-like substances that have diverse functions in the human body, most notably controlling the immune response and inflammation . Both high and low levels play roles in different chronic disorders, so it’s essential to keep them in check.
What is the role of prostaglandins in the kidney?
Increases the feeling of pain [ 1] increases cell uptake of calcium [ 1] important for fertility/reproductive cycle in women [ 1] involved in kidney function [ 1] Prostaglandins are made from a fatty acid called arachidonic acid.
How do protaglandins affect the body?
Prostaglandins only affect the cells they are made by and the cells in the surrounding area. They have diverse effects on the body, including: 1 increasing/decreasing inflammation, and contributing to the signs of acute inflammation, such as redness, heat, swelling, and pain 2 constricting or dilating blood vessels 3 inducing labor 4 increasing the production of mucus
How many patients have higher PGD2 levels?
Higher PGD2 levels were found in 17 patients with kidney failure compared to 34 patients with healthy kidney function. Levels of an enzyme needed to make PGD2 (PGD synthase) were 35 times higher in kidney failure patients [ 56 ].
Where is PGE2 found?
High levels of PGE2 and PGI2 are found in the gut, which protects the stomach and small intestine from damage [ 12, 13 ].
How many types of prostaglandins are there?
While the body produces many types of prostaglandins, there are four primary types:
What are some examples of prostaglandins?
Some examples of prostaglandins are prostaglandin B, E, A, and F while some examples of hormones include estrogen, testosterone, insulin, auxin, and gibberellin.
Which type of prostaglandin activates the formation of blood clots?
Thromboxane is the type of prostaglandin which activates the formation of blood clot. Induction of the labor. Prostaglandins like PGE2 are responsible for the uterine contractions, which induce labor. Prostaglandins have functions in other systems including the gastrointestinal tract, kidney, and bronchi.
What are the two types of regulatory molecules in the body?
Prostaglandins and hormones are two types of regulatory molecules in the body. Prostaglandins are lipid molecules, which act as hormones while hormones are either proteins, peptides or steroids.
What are hormones? What are their functions?
What are Hormones. Hormones are the main type of regulatory molecules in the body produced by the endocrine glands. They are secreted to the bloodstream and transported to the effector organs through the blood. They can be either proteins, peptides or steroids. Some amino acid derivatives act as hormones as well.
Where do hormones occur in the body?
Steroid hormones can diffuse into the cell; hence, their receptors occur inside the cell. On the other hand, the receptors for the protein or peptide hormones occur on the cell membrane. Some plant hormones act on the site of production while others are transported to the site of action through the sap.
Is prostaglandin a lipid?
Moreover, prostaglandins are lipid molecules while proteins can be either proteins, peptides or steroids.
What Are Prostaglandins?
Prostaglandins are lipid compounds, called eicosanoids, that have hormone-like effects in humans and other mammals. What are some of the functions of prostaglandins? Two of the most important are regulating inflammation and contracting the uterus in females in order to allow for birth and menstruation.
What are the functions of prostaglandins?
Prostaglandins function: Major functions of prostaglandins include: ( 1) Promoting inflammation in tissue that has been damaged or infected, in order to encourage healing. Regulating functions of the female reproductive system, including ovulation, menstruation and the induction of labor. Promoting blood clotting.
How does prostaglandin work?
During an inflammatory response, both the level and the types of prostaglandin production change dramatically. Prostaglandin production is normally low in tissues that are not inflamed, but levels increases during an acute inflammatory response. When prostaglandins increase, this helps with recruitment of leukocytes and the infiltration of immune cells.
What triggers prostaglandin production?
What triggers prostaglandin production? The body makes more prostaglandins in response to injury, infection, disease or other stressors. This ultimately causes symptoms associated with inflammation, including: redness, swelling, pain, fever, cramping and tenderness. ( 2)
Why are protaglandins important?
Prostaglandins are important for overcoming a number of health conditions because they help to control processes that release inflammatory compounds, help regulate blood flow and play a role in the formation of blood clots.
How many prostaglandins are produced in the human body?
There are four bioactive prostaglandins produced in the body human body, including:
Why do protaglandins cause fever?
They also increase pain and can cause a fever, which are normal reactions to injury, infection or illnesses. Prostaglandins are produced via a chemical reaction that first takes place due to the effects of an enzyme called cyclooxygenase (cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2).
