What are the characteristics of psammomatous calcifications?
Psammomatous calcifications: round with concentric laminations (onion-like appearance) Psammomatous calcifications in the absence of a serous neoplasm should prompt additional sampling to rule out a neoplastic process; their presence should be mentioned in the report if a serous tumor cannot be identified
What is extensive psammomatous calcification of the uterus and cervix?
Extensive psammomatous calcification of the uterus and cervix associated with a uterine serous carcinoma This report describes a uterine serous carcinoma with bilateral ovarian metastasis, which was associated with widespread extensive psammomatous calcification of the uterine leiomyomata, the myometrium, and the cervical stroma.
When should psamommatous calcifications be included in the report?
Psammomatous calcifications in the absence of a serous neoplasm should prompt additional sampling to rule out a neoplastic process; their presence should be mentioned in the report if a serous tumor cannot be identified Benign ovary with surface adhesions and focal stromal psamommatous calcifications (see comment)
What is the pathophysiology of psammoma bodies?
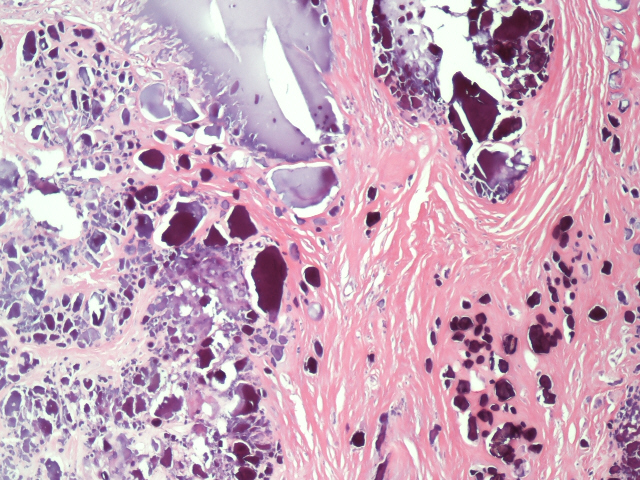
Psammoma bodies are round microscopic calcific collections. It is a form of dystrophic calcification. Necrotic cells form the focus for surrounding calcific deposition.
What is a calcification?
Calcification: A Disregarded or Ignored Issue in the Gynecologic Tumor Microenvironments
Why does calcification occur?
One theory is that calcification occurs due to degeneration of the tumor cells; another theory is that calcification occurs in response to secretions from cells in the tumor microenvironment.
Is ovarian cancer a psammomatous tumor?
In ovarian cancer, calc ification is predominantly psammomatous and largely occurs in serous papillary ovarian tumors.
Is calcification a degenerative change?
In uterine fibroids, cal cification occurs as a degenerative change and is predictive of a good prognosis. As for endometrial cancer and cervical cancer, calcification rarely occurs in these cancers. The mechanism of calcification in the gynecologic tumor microenvironments is not currently clear. One theory is that calcification occurs due ...
What is a psammoma body?
Psammoma bodies. Psammoma bodies are round microscopic calcific collections. It is a form of dystrophic calcification. Necrotic cells form the focus for surrounding calcific deposition. They have a lamellated concentric calcified structure, sometimes large enough to be seen on CT.
What are the different types of psammoma bodies?
Psammoma bodies are found in a diverse group of tumors which include: papillary thyroid carcinoma. papillary serous carcinoma of the endometrium 2. melanotic schwannoma (psammomatous variety) 3. meningioma. mesothelioma. serous cystadenocarcinoma of the ovary. adenocarcinoma of lung 1.
What is a psammomatous meningioma?
Psammomatous meningioma is a histologic subtype of meningioma usually presented as a heavily calcified intracranial or spinal mass lesion. The meningothelial and psammomatous types are the most common involving the spine.
What is the ratio of meningiomas?
Meningiomas are more common in women, with a ratio of 2:1 intracranially and 4:1 in the spine. This histologic subtype is particularly more common to arise from thoracic spine.
Is there a difference in clinical presentation among the different histologic subtypes of meningiom?
There is no relevant difference in clinical presentation among the various histologic subtypes of meningioma.
Can meningiomas be seen as plain films?
Plain films no longer have a role in the diagnosis or management of meningiomas. Historically, if visible, this subtype may be seen as a calcification along the neuroaxis.
Can a tumor be resectioned?
Surgical treatment could provide a partial or complete resection of a tumor, and the overall prognosis will depend in large part on the entirety of resection.
Why do doctors recommend risk factor reduction?
When a person has calcium deposits along the coronary arteries, doctors will recommend risk factor reduction. This is because people with artery calcification have a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases.
What causes calcification of the pericardium?
One of the main causes of pericardial calcification is pericarditis. This refers to inflammation within the pericardium, of which the cause is often unknown.
What is the best treatment for pericardial calcification?
If this is the case, anti-inflammatories such as colchicine, corticosteroids, or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) therapy may help.
What to do if a radiologist finds calcifications?
If a radiologist finds breast calcifications when reading a person’s mammogram, their course of action will be to compare this imaging with any prior mammogram (s). If necessary, they may perform additional testing to determine the origins and cause of the calcification. This could involve magnification mammography, ultrasound imaging, an MRI scan, or a biopsy.
Why do people not know they have calcification?
People may not know they have calcification because it does not always cause any symptoms. Some types of calcification are irreversible, but depending on the type, there may be ways to reduce pain and lower the risk of complications. Last medically reviewed on January 27, 2020. Biology / Biochemistry.
Why does my kidney calcify?
Kidney calcification can develop due to vitamin D therapy, primary hyperparathyroidism, or sarcoidosis, among other things. Treatment will depend and focus on the cause.
How to treat brain calcification?
Some treatment options for dystonia include: physical therapy. speech and voice therapy. relaxation and stress management.
Why is it important to identify psammomatous calcifications?
Identifying psammomatous calcifications is important; their presence in an otherwise normal ovarian specimen should raise the possibility of an underlying serous neoplasm and prompt additional sampling and correlation with intraoperative findings
What is a calcification of the ovaries?
Ovarian calcifications are commonly found in the context of a mass (mature teratoma, mucinous cystadenoma, serous neoplasia) but also in grossly normal ovaries (mostly within corpora albicantia) Often identified by radiologists on ultrasound or other pelvic imaging modalities.
What is the effect of impaired metabolism on the pH of the body?
Impaired metabolism elevates the pH and induces intracellular precipitation of calcium salts within epithelial cells or hystiocytes
Do you need to report psammomatous calcifications?
Nonpsammomatous calcifications and psammomatous calcifications within a serous neoplasm do not need to be reported
Is a calcification of the ovary considered a biopsy?
By itself, ovarian calcification is not an indication for biopsy or oophorectomy; pathologic evaluation of calcifications is usually seen in the setting of a mass or in prophylactic oophorectomies. Calcifications are divided into psammomatous (psammoma bodies) and nonpsammomatous.
What is a psammoma body?
Psammoma body. Micrograph of psammoma body in the centre of the field in a meningioma of brain. H&E stain. A psammoma body is a round collection of calcium , seen microscopically. The term is derived from the Greek word ψάμμος ( psámmos ), meaning " sand ".
What is the appearance of a psammoma body?
Psammoma bodies usually have a laminar appearance, are circular, acellular and basophilic.