
A pseudogestational sac, also known as a pseudosac or intra-cavitary fluid, is the concept that a small amount of intrauterine fluid in the setting of a positive pregnancy test and abdominal pain could be erroneously interpreted as a true gestational sac in ectopic pregnancy.
What is a pseudosac in pregnancy?
Pseudosac URL of Article A pseudogestationalsac, also known as a pseudosac or intra-cavitary fluid, is the concept that a small amount of intrauterine fluid in the setting of a positive pregnancy test and abdominal pain could be erroneously interpreted as a true gestational sac in ectopic pregnancy.
What is the difference between gestational sac and pseudogestational SAC?
A pseudogestational sac is a buildup of fluid within the uterus that mimics a gestational sac, giving the false appearance of pregnancy. With the use of modern ultrasound technology, the differentiation between the two should not be difficult. A pseudogestational sac is also known as intra-cavity fluid.
What is a pseudo-pseudogestational SAC?
A pseudogestational sac is a buildup of fluid within the uterus that mimics a gestational sac, giving the false appearance of a pregnancy. Pseudo means false and gestational implies pregnancy.
What does a sac-like structure in the uterus with a positive?
A sac-like structure in the uterus with a positive pregnancy test could represent an early gestational sac or a pseudogestational sac of ectopic pregnancy. Ectopic pregnancy potentially is life-threatening; therefore, making a timely diagnosis is critical.
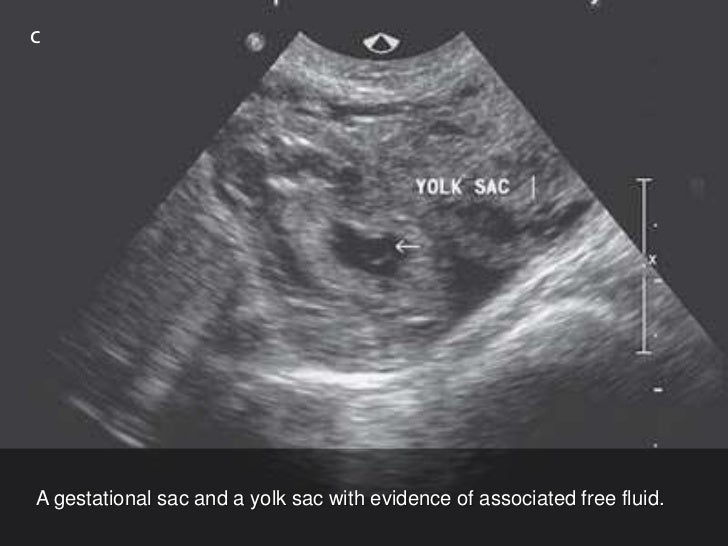
How common is Pseudogestational sac?
The pseudogestational sac sign is a well described entity in the literature in the setting of ectopic gestation, and represents a decidual reaction surrounding intrauterine fluid/hemorrhage without a yolk sac or fetal pole [3,5,8]. As many as 1 in 10 ectopic pregnancies present with a pseudogestational sac.
Does empty sac mean ectopic pregnancy?
“Ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed when the gestational sac with a live fetal pole or yolk sac is found outside an empty uterine cavity,” says Dr. Khalife. “Sometimes, diagnosis can be challenging if the ectopic pregnancy is in its early stage and the sac is not yet visible by ultrasound.”
What week of pregnancy is gestational sac?
The gestational sac is the first structure seen in pregnancy by ultrasound as early as 4.5 to 5 weeks of gestational age, but it is only 97.6% specific for the diagnosis of intrauterine pregnancy.
What is the difference between sac and gestational sac?
The yolk sac is inside the gestational sac, a large cavity of fluid inside the uterus that surrounds an embryo. The yolk sac attaches to the outside of the developing embryo. The yolk sac must be inside the gestational sac, and the gestational sac must be inside the uterus.
Can an empty sac turn into a baby?
Can a blighted ovum turn into a baby? No, an empty gestational sac will not turn into an embryo. The formation of the embryo occurs within two weeks of conception. By the time the gestational sac is formed, the cells should have already formed the embryo.
Is an empty sac at 6 weeks normal?
Often, seeing no yolk sac (or a yolk sac that is smaller than normal or otherwise misshapen) at 6 weeks can be a sign of miscarriage. Unfortunately, you'll most likely have to wait until a follow-up ultrasound to be sure.
How does gestational sac look like?
The gestational sac can be detected sonographically when it is 2 to 3 mm in diameter, which corresponds to a gestational age between 29 days and 31 days. The appearance of a normal early gestational sac is a small fluid collection surrounded completely by an echogenic rim of tissue.
What is the sac size for 6 weeks pregnant?
Gestational Sac: Gestational age = 4 weeks plus (mean sac diameter in mm x days). This relies on the growth of the normal gestational sac of 1 mm per day after the 4th week of gestation....1st Trimester Ultrasound Scanning.Gestational Age (Weeks)Sac Size (mm)CRL (mm)566147278829156 more rows
When does the baby's heartbeat start?
A fetal heartbeat may first be detected by a vaginal ultrasound as early as 5 1/2 to 6 weeks after gestation. That's when a fetal pole, the first visible sign of a developing embryo, can sometimes be seen. But between 6 1/2 to 7 weeks after gestation, a heartbeat can be better assessed.
Is it possible to have a gestational sac and not be pregnant?
A blighted ovum is a pregnancy where a sac and placenta grow, but a baby does not. It is also called an 'anembryonic pregnancy' as there is no embryo (developing baby). Because a blighted ovum still makes hormones, it can show up as a positive pregnancy test.
Is it normal to only see a sac at 5 weeks?
In fact, at 5 weeks, you'll likely only see the yolk sac and the gestational sac — and many not even that. What you don't see may unnecessarily worry you, but it's perfectly normal.
At what HCG level can you see a sac?
Currently, a gestational sac is always seen when the HCG level is greater than 1800 mIU/ml.
Why is my sac empty during pregnancy?
A blighted ovum, also called an anembryonic pregnancy, occurs when an early embryo never develops or stops developing, is resorbed and leaves an empty gestational sac. The reason this occurs is often unknown, but it may be due to chromosomal abnormalities in the fertilized egg.
How soon can you see an ectopic pregnancy on ultrasound?
Levels of this hormone increase during pregnancy. This blood test may be repeated every few days until ultrasound testing can confirm or rule out an ectopic pregnancy — usually about five to six weeks after conception.
Is empty sac at 5 weeks normal?
In fact, at 5 weeks, you'll likely only see the yolk sac and the gestational sac — and many not even that. What you don't see may unnecessarily worry you, but it's perfectly normal.
How common is empty sac pregnancy?
How common is a blighted ovum? Blighted ovum is the most common cause of miscarriage. Experts estimate that blighted ovum accounts for about 50 percent of all miscarriages in the first trimester. About 15 percent of all pregnancies end in miscarriage before 13 weeks of pregnancy.
What is a pseudosac?
A pseudogestational sac, also known as a pseudosac or intra-cavitary fluid, is the concept that a small amount of intrauterine fluid in the setting of a positive pregnancy test and abdominal pain could be erroneously interpreted as a true gestational sac in ectopic pregnancy.
Where is ultrasound located?
generally irregularly-shaped with pointed edges and/or filled with debris, sometimes referred to as 'beaking'. centrally located in the endometrial cavity, rather than eccentrically located within the endometrium. displaces the anterior and posterior endometrial cavity surfaces. does not demonstrate a yolk sac.
Can a beta-hCG be detected on ultrasound?
The sign was originally reported before the use of transvaginal ultrasound imaging and caution should be exercised if considering diagnosing a pseudogestational sac with modern ultrasound equipment. In a woman with a positive beta-hCG, any intrauterine sac-like fluid collection seen on ultrasound is highly likely to be a gestational sac 6.
Where is the pseudosac located?
As opposed to a normal gestational sac, a pseudosac is typically located centrally and may fill the entire endometrial cavity and it also lacks the “double ring” sign. True gestational sacs will usually be slightly off-center and will have a detectable double decidual sign. True sacs also will eventually develop an internal yolk sac later followed by an embryo, but pseudosacs will have neither.
What is the pain of an ectopic pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy classically presents with steady unilateral lower abdominal pain and amenorrhea. If the ectopic ruptures and particularly if internal bleeding is significant, the abdominal pain may be generalized with abdominal distension and syncope or near syncope.
Is a pseudosac a normal pregnancy?
The sonogram shows a sac in the uterus but this is not a normal gestational sac or a normal pregnancy. The presence of a pseudosac rather than a true gestational sac means that the pregnancy is likely elsewhere, or ectopic. Pseudosacs occur in about 10% of ectopic pregnancies and can lead the ultrasound technician, the radiologist, or the treating provider astray if they are identified as a sign of a normal pregnancy and not seen for what they truly are-a potential red herring.
Can ectopic pregnancy cause pain in the lower abdomen?
Ectopic pregnancy classically presents with steady unilateral lower abdominal pain and amenorrhea. If the ectopic ruptures and particularly if internal bleeding is significant, the abdominal pain may be generalized with abdominal distension and syncope or near syncope. There are many atypical presentations, however, to be aware of. The pain may be crampy or midline similar to that of a threatened miscarriage and there may even be vaginal bleeding, though it is usually scant. In rare instances, pain may even be absent.
What Does an Empty Gestational Sac Mean?
A yolk sac, which indicates a viable pregnancy, is usually seen within the gestational sac by 35 days gestation. 8 One of the more common types of miscarriages—known as an anembryonic pregnancy, empty sac, or blighted ovum—happens when a gestational sac does not contain an embryo. In other words, an embryo failed to develop. 9
Why is my gestational sac not showing up on my scan?
If a gestational sac is not seen on a follow-up scan, or if your hCG levels indicate one should be seen, it can be a sign of a miscarriage or ectopic pregnancy.
What If My Doctor Sees an Empty Gestational Sac?
If your doctor discovers an empty gestational sac on an ultrasound, they may confirm that your pregnancy is nonviable— in other words, that the pregnancy will not result in the birth of a baby as it is not progressing normally.
What is an early transvaginal ultrasound?
Early transvaginal ultrasounds are a relatively easy way to follow a pregnancy early on. Paired with your hCG levels, ultrasounds can give you and your doctor an idea about how your pregnancy is progressing. The gestational sac is the first structure your doctor will look for with an early ultrasound.
What is the first sign of pregnancy?
One of the first signs of pregnancy on an ultrasound is the gestational sac, which encloses the developing baby and contains amniotic fluid. The gestational sac is found in the uterus. On the ultrasound image, it appears as a white rim around a clear center.
What is the next positive sign of pregnancy?
After the sac becomes visible, the next positive sign of pregnancy is a yolk sac that develops within it. 1 The yolk sac provides nutrition to the developing embryo until the placenta takes over. It's an important indicator of pregnancy health.
What is the next proof of pregnancy?
After a home pregnancy test has turned positive and a blood test measuring levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) have confirmed pregnancy, the next proof of pregnancy requires an ultrasound. When you have your first ultrasound your doctor may talk about the presence or absence of the gestational sac.
What happens during pseudopregnancy?
Pseudopregnancy occurs in many small mammalian species, in both nonmated or in those which are mated but do not conceive. As a consequence, the subsequent luteal phase, although not supporting a pregnancy, does stimulate mammary development, as well as hyperplasia of the endometrium. As the luteal phase ends, the progesterone concentrations decline and prolactin concentrations increase, resulting in behavioural changes and sometimes lactation. Excessively long luteal phases may be seen in some pseudopregnant laboratory rodents. Treatment is not always necessary because pseudopregnancy is a normal occurrence, and once the corpora lutea regress, either normal cyclicity returns or the animal becomes anoestrus or progresses to oestrus. If the animal is lactating, then treatment is warranted, and cabergoline can be used to good effect. If repeated pseudopregnancy occurs, then the animal should either be mated or spayed.
What is pseudopregnancy in dogs?
Pseudopregnancy is an exaggerated form of a normal physiologic process. Every nonovariectomized female dog has a prolonged luteal phase of estrus, and this phase is called covert pseudopregnancy or physiologic pseudopregnancy. Some dogs, especially of the toy breeds, develop an exaggerated reaction. The mechanism is poorly understood, but prolactin or its receptors play a role. The presence of progesterone is necessary for the tissue changes to occur. Overtly pseudopregnant dogs either have an increased concentration of prolactin or have increased sensitivity to prolactin. This prolactin milieu can occur with a more rapid than usual decline in progesterone when dogs are spayed during diestrus. Hyperprolactinemia that occurs in response to visual stimuli of the presence of surrogate neonates results in the mammary development, lactation, maternal behavior, and other clinically apparent changes of pseudopregnancy. Uterine changes in pseudopregnancy can include the formation of structures that resemble placental sites (now called localized endometrial hyperplasia of pseudopregnancy or pseudoplacentation endometrial hyperplasia) and mucometra; obviously there are no fetuses.
What happens to prolactin at the end of diestrus?
The abrupt decline in serum progesterone at the end of diestrus stimulates release of prolactin from the anterior pituitary, with subsequent mothering behavior and lactation.
How long does pseudopregnancy last in rabbits?
Pseudopregnancy (pseudocyesis, false pregnancy) can occur in rabbits, even in pet does kept singly. Pseudopregnancy typically lasts 16 to 17 days and may be followed by hair pulling and nesting behavior.64 The corpus luteum secretes progesterone, causing uterine and mammary development. 60 Mammary development is most pronounced in the first 10 days of false pregnancy, after which mammary involution typically follows by day 16. 60,64 The condition resolves spontaneously but may recur or may lead to hydrometra or pyometra. Pseudopregnancy strongly depresses fertility, and its cause is still unknown. 79 A lower kindling rate was found in group-housed does with one buck versus those housed in a one-to-one ratio, with pseudopregnancies found in 23% of the does in the group-housing system against 0% in the control does housed individually. 69 Ovariohysterectomy is the treatment of choice and ideally would be performed once the mammary tissue had involuted. Hormonal therapy with either progestins or androgens is of unproved effectiveness and should be considered only in rare cases where pseudopregnancy is protracted or refractory.
How to treat pseudocysis in dogs?
Many owners want the unusual behaviors to stop, but until the dog's bodily response to the hormone changes runs its course, the best treatment is no treatment. Progestins will stop the behaviors of pseudocyesis by putting the dog back into “pregnancy.” The down side to this treatment is that each time it ends, the signs of pseudocyesis return in 10% to 15% of these dogs. 3 An ovariohysterectomy within 3 months after estrus can also result in a sharp drop in progesterone and signs of pseudocyesis, including lactation, by 4 days postsurgery. 101 A hysterectomy alone can prolong luteal activity, because there is no longer a uterine feedback mechanism. 151 It is suggested that this surgery be postponed at least 3 months past estrus, 3 or until signs of pseudocyesis end, whichever is longest. Dogs that show external signs of pseudocyesis develop pyometra less often than those that do not. 60
How many does pseudopregnancy occur in?
Pseudopregnancy can occur in 20% of does group-housed compared with single-housed does.
What is a pseudodocyesis?
Pseudocyesis or false pregnancy represents a hysterical conversion reaction in a woman who either desperately wishes to conceive, or is extremely fearful of becoming pregnant. The woman develops amenorrhea, progressive abdominal distension, morning sickness, sensations of fetal activity, breast engorgement with a prominent venous pattern, and, at times, galactorrhea [166–169]. Hyperprolactinemia is present in the majority of women, and may be of pathophysiologic significance, in that its luteotropic activity may be the cause of the persistent corpus luteum found in these individuals. In addition, LH levels may be elevated which may also account for maintenance of the corpus luteum [166]. When confronted with the diagnosis, some women experience a rapid decrease in abdominal girth, which was due to gaseous distension of the intestine, cessation of galactorrhea and resumption of menses. This syndrome, along with anorexia nervosa and the environmental deprivation syndrome, illustrate the profound influence that the cerebral cortex has on the hypothalamus.
Overview
A yolk sac is a structure that develops inside your uterus during early pregnancy. It provides an embryo with nourishment (food). It helps circulate gasses between you and the embryo. The yolk sac also produces cells that turn into important structures, such as the umbilical cord, blood cells and reproductive organs.
Function
The yolk sac has many essential jobs in fetal development before the placenta and organs develop. The yolk sac:
Anatomy
The yolk sac is inside the gestational sac, a large cavity of fluid inside the uterus that surrounds an embryo. The yolk sac attaches to the outside of the developing embryo. The yolk sac must be inside the gestational sac, and the gestational sac must be inside the uterus. Otherwise, this can indicate the pregnancy has failed or will fail.
Conditions and Disorders
If your healthcare provider can’t see the yolk sac, it might indicate the pregnancy is not viable. That means the pregnancy won’t result in a birth. But it also can mean that the estimated gestational age is wrong.
Why do women have false pregnancy?
Some researchers have suggested that poverty, a lack of education, childhood sexual abuse, or relationship problems might play a role in triggering false pregnancy.
How to tell if a woman is pregnant with a false baby?
To determine whether a woman is experiencing a false pregnancy, the doctor will usually evaluate their symptoms, perform a pelvic exam and abdominal ultrasound -- the same tests used to feel and visualize the unborn baby during a normal pregnancy. In a case of false pregnancy, no baby will be seen on the ultrasound, and there won't be any heartbeat.
How long does pseudocyesis last?
Women with pseudocyesis have many of the same symptoms as those who are actually pregnant, including: These symptoms can last for just a few weeks, for nine months, or even for several years.
How long does a false pregnancy last?
Nausea and vomiting. Weight gain. These symptoms can last for just a few weeks, for nine months, or even for several years. A very small percentage of patients with false pregnancy will arrive at the doctor's office or hospital with what feels like labor pains. Continued.
What is it called when you believe you are pregnant?
False pregnancy, clinically termed pseudocyesis, is the belief that you are expecting a baby when you are not really carrying a child.
Can a false pregnancy be detected on an ultrasound?
In a case of false pregnancy, no baby will be seen on the ultrasound, and there won't be any heartbeat. Sometimes, however, the doctor will find some of the physical changes that occur during pregnancy, such as an enlarged uterus and softened cervix. Urine pregnancy tests will always be negative in these cases, ...
Can pseudocyesis cause weight gain?
People with pseudocyesis have many, if not all, symptoms of pregnancy -- with the exception of an actual fetus. Some men experience a related phenomenon known as couvade, or sympathetic pregnancy. They will develop many of the same symptoms as their pregnant partners, including weight gain, nausea, and backache.
