
How does pulmonary stenosis affect the lungs?
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Heavy or rapid breathing
- Rapid heart rate
- Swelling in the feet, ankles, face, eyelids, and/or abdomen
What is the treatment for narrowing of the arteries?
What is the Treatment of Renal Artery Stenosis? Doctors try to relieve the narrowing in the artery and improve the blood flow to the kidney. The simplest way to do this is by placing a small balloon in the artery during an angiogram, and inflating it so that the narrowing is stretched up. This procedure is called angioplasty.
What are the treatments for mild pulmonary vascular congestion?
- Alcohol abuse or cocaine and other illegal drug use
- HIV/AIDS
- Thyroid disorders (having either too much or too little thyroid hormone in the body)
- Too much vitamin E
- Treatments for cancer, such as radiation and chemotherapy
What is the normal pulmonary artery systolic pressure?
Normal pulmonary artery systolic pressure at rest is 18 to 25 mm Hg, with a mean pulmonary pressure ranging from 12 to 16 mm Hg. This low pressure is due to the large cross-sectional area of the pulmonary circulation, which results in low resistance.
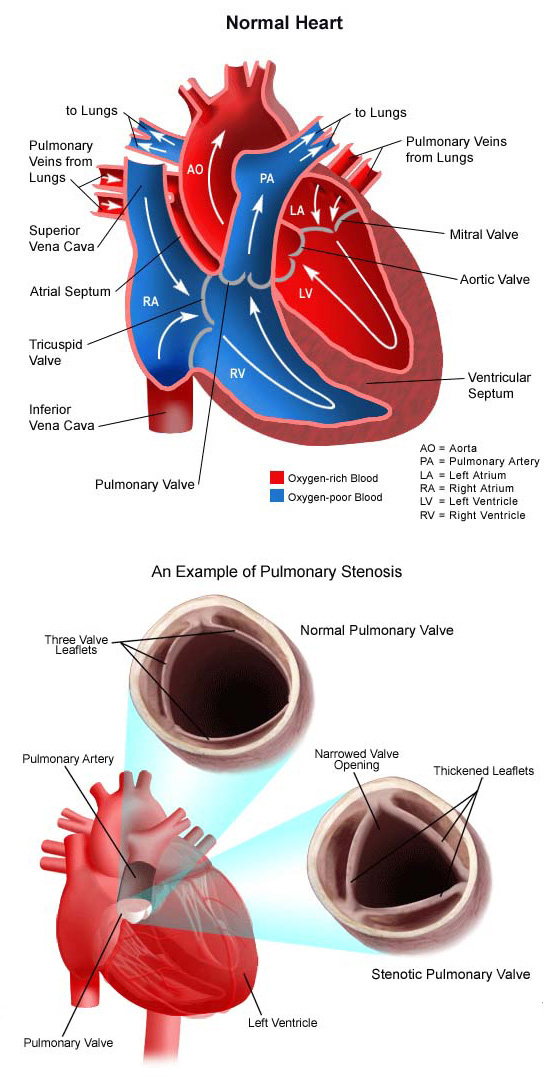
What is the cause of pulmonary stenosis?
Pulmonary valve stenosis is most often a congenital heart defect. The exact cause is unclear. The pulmonary valve doesn't develop properly as the baby is growing in the womb. The pulmonary valve is made of three thin pieces of tissue called flaps (cusps).
What happens when you have pulmonary stenosis?
In pulmonary stenosis (pul-muh-NAIR-ee stuh-NO-sis), the pulmonary valve is too small, too narrow, and can't open all the way. This causes the right ventricle to pump harder to send blood out to the lungs. Over time, this can cause thickening of the right ventricle and strain the heart.
Does pulmonary stenosis go away?
In children with mild degrees of pulmonary stenosis, it is common occurrence that the stenosis might improve over time. However, children with even mild pulmonary stenosis require lifelong follow-up as the pulmonary valve may become stiffer and therefore work less sometimes later on in adult life.
What are the symptoms of pulmonary valve stenosis?
When the valve narrowing (stenosis) is moderate to severe, the symptoms include:Abdominal distention.Bluish color to the skin (cyanosis) in some people.Poor appetite.Chest pain.Fainting.Fatigue.Poor weight gain or failure to thrive in infants with a severe blockage.Shortness of breath.More items...•
Can you live a normal life with pulmonary stenosis?
They can lead normal lives. Mild pulmonary valve stenosis in childhood doesn't get worse after the first year of life. However, mild pulmonary stenosis in a young infant may move to more severe degrees that need follow-up. Children with moderate-to-severe degrees of pulmonary stenosis need treatment.
Is pulmonary valve stenosis life threatening?
To compensate, the heart has to work harder to pump enough blood through the valve, and to the body. Pulmonary stenosis can be mild, moderate, severe or life-threatening. This condition is also called pulmonic stenosis or pulmonary valve stenosis.
How do you fix pulmonary stenosis?
Several types of surgery can help fix congenital pulmonary stenosis. In some cases, the surgeon may do a valvectomy. That's when the surgeon removes the old pulmonary valve and replaces it with a new valve. The new valve may be artificial or from a cadaver donor.
Is exercise good for pulmonary stenosis?
Many children with pulmonary stenosis have a limited response to exercise. The limitation is related to the severity of the stenosis and it improves after relief of the obstruction. The exercise limitation appears to be more marked in adult patients than in children.
Is pulmonary stenosis a heart disease?
Pulmonary stenosis is a common form of congenital heart disease (CHD). It occurs in 7-10 percent of all CHD. What happens in pulmonary stenosis? When blood flow from your heart to your lungs is obstructed, the right ventricle has to work harder.
How is pulmonary stenosis diagnosed?
Tests to diagnose pulmonary valve stenosis may include: Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This quick and painless test records the electrical signals in the heart. Sticky patches (electrodes) are placed on the chest and sometimes the arms and legs.
How common is pulmonary stenosis?
What is pulmonary stenosis? Pulmonary stenosis is relatively common and accounts for about 10% of heart defects diagnosed during childhood. It can occur in children with otherwise normal hearts or along with other congenital heart defects such as atrial septal defect or Tetralogy of Fallot.
Can you live without your pulmonary valve?
Pulmonary valvectomy is an uncommon treatment for pulmonary stenosis and this is the longest documented survival of a patient without a pulmonic valve.
What happens when the pulmonary artery is blocked?
If the main pulmonary artery is completely blocked, the right ventricle (the chamber of the heart that pumps blood into the lungs) cannot get the blood into the lungs; this “right ventricular failure” then leads to death from PE. The age and health of the affected individual are also critical factors.
What are the symptoms of end stage pulmonary hypertension?
Pulmonary hypertension signs and symptoms include:Blue lips and skin (cyanosis)Chest pressure or pain.Dizziness or fainting spells (syncope)Fast pulse or pounding heartbeat (palpitations)Fatigue.Shortness of breath (dyspnea), initially while exercising and eventually while at rest.More items...•
Can you live without a pulmonary valve?
Pulmonary valvectomy is an uncommon treatment for pulmonary stenosis and this is the longest documented survival of a patient without a pulmonic valve.
What is pulmonary stenosis?
Pulmonary stenosis is a congenital (present at birth) defect that occurs due to abnormal development of the fetal heart during the first eight weeks of pregnancy.
Why is pulmonary stenosis a concern?
Mild pulmonary stenosis may not cause any symptoms. Problems can occur when pulmonary stenosis is moderate to severe. When this is the case, the right ventricle has to work harder to try to move blood through the tight pulmonary valve. Eventually, the right ventricle is no longer able to handle the extra workload, and it fails to pump forward efficiently. Pressure builds up in the right atrium, and then in the veins bringing blood back to the right side of the heart. Fluid retention and swelling may occur.
How is pulmonary stenosis diagnosed?
If a child’s doctor hears a heart murmur during a physical examination, the child will be referred to a pediatric cardiologist for a diagnosis. In this case, a heart murmur is simply a noise caused by the turbulence of blood flowing through the narrowed pulmonary valve. Symptoms your child exhibits will also help with the diagnosis.
What is the long-term outlook after pulmonary stenosis repair?
Your child’s cardiologist may recommend that antibiotics be given to prevent bacterial endocarditis for a period of time following surgery and always for all valve replacements. Occasionally, repeat interventional cath lab procedures may be necessary during infancy and childhood to stretch the valve open. Replacement of the pulmonary valve may be recommended later during adolescence or early adulthood to prevent complications such as enlargement of the right ventricle, heart failure, and arrhythmias (irregular or fast heartbeats).
What is supravalvar pulmonary stenosis?
Supravalvar pulmonary stenosis. The pulmonary artery just above the pulmonary valve is narrowed.
What percentage of congenital heart defects are caused by pulmonary stenosis?
Pulmonary stenosis is a component of half of all complex congenital heart defects. Pulmonary stenosis accounts for 5 to 10 percent of all congenital heart defect cases.
How long does it take for a chest tube to bleed?
Bleeding may occur for several hours, or even a few days after surgery.
What is pulmonary stenosis?
When the heart squeezes, the right ventricle (the lower right chamber) pumps blood out into the pulmonary artery, which then takes blood to the lungs. The pulmonary valve (also known as the pulmonic valve) is located between the right ventricle and the main pulmonary artery. The pulmonary valve's job is to prevent blood from leaking back into the heart between beats.
How to diagnose pulmonary stenosis?
The Cardiac Center at CHOP typically diagnoses pulmonary stenosis after a primary care doctor detects a heart murmur and refers a child to us. To confirm a suspected diagnosis of pulmonary stenosis, some of all of these tests may be used: 1 Pulse oximetry: a painless way to monitor the amount of oxygen in the blood 2 Chest X-ray 3 Echocardiogram (also called an "echo" or ultrasound): sound waves are used to see the internal structure of the heart 4 Electrocardiogram (ECG): measures the electrical activity in the heart 5 Cardiac MRI: a three-dimensional picture of the heart arteries and veins 6 Cardiac catheterization : a thin tube is inserted into the heart through a vein and/or artery in either the leg or, in very young children, through the belly button
What is it called when you have a blockage in the pulmonary artery?
This condition is also called pulmonic stenosis or pulmonary valve stenosis. When the blockage is below the pulmonary valve, because of too much muscle (muscular bundles), this is called subpulmonic stenosis. Also, the stenosis can occur above the pulmonary valve, in the pulmonary artery itself; this is called supravalvar pulmonic stenosis.
How many sections are there in a pulmonary valve?
A normal pulmonary valve is made up of three thin sections. In pulmonary stenosis, two of the sections are stuck together or are too thick. There may also be fewer than three sections. As a result, the pulmonary valve is too narrow and the heart has to work harder to pump enough blood to the body. Pulmonary stenosis can be mild, moderate, severe ...
What is a heart murmur?
A heart murmur (an extra heart sound when a doctor listens to the child’s heart with a stethoscope)
Can pulmonic stenosis be treated with cardiac catheterization?
Subpulmonic and supravalvar pulmonic stenosis do not get better with cardiac catheterization, and will require surgery if the amount of blockage is moderate or severe. Surgery for subpulmonic stenosis involves cutting out the extra muscles below the valve.
Can pulmonary stenosis run in families?
Pulmonary stenosis can run in families, so be sure to tell your cardiologist if there is a history of a heart murmur in other close family members.
What is pulmonary valve stenosis?
Pulmonary valve stenosis – problems with the pulmonary valve (for example, development of less than three leaflets, leaflets that may be partially fused together, thick leaflets that do not open all the way) that make it more difficult for the valve leaflets to open and permit blood to flow from the right ventricle to the lungs
What causes pulmonary artery stenosis?
Other causes of pulmonary artery stenosis can include: other syndromes that affect the heart (such as rubella syndrome [ a group of heart and other health problems in an infant caused by rubella infection in the mother during pregnancy ] and Williams syndrome [a group of abnormalities affecting the heart and other organs]) and surgical procedures used to correct other heart defects (for example, pulmonary artery banding - a purposeful narrowing of the artery to reduce blood flow to the lungs).
How to narrow a narrowed artery?
This treatment method consists of moving a balloon dilation catheter into the narrowed area of the artery. The balloon is carefully inflated – first under low pressure and then under higher pressure – until the narrowed area is widened. The balloon is then deflated and removed. Although the narrowing is improved in a majority of patients following balloon dilation, overtime the artery can again become narrow in as many as 15% to 20% of cases, requiring further ballooning. Different types of balloons are currently being developed that will likely lead to better and longer-lasting results.
What is the absence of a pulmonary valve?
Pulmonary atresia – absence of a pulmonary valve, preventing blood from flowing from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery and onward to the lungs. Truncus arteriosus – the formation of only one combined artery instead of the normal two outlets from the heart, the aorta and pulmonary artery. Pulmonary valve stenosis – problems ...
What is the narrowing of the pulmonary artery?
Pulmonary artery stenosis is a narrowing (stenosis) that occurs in the pulmonary artery, a large artery that sends oxygen-poor blood into the lungs to be enriched with oxygen. The narrowing may occur in the main pulmonary artery and/or in the left or right pulmonary artery branches. This narrowing makes it difficult for blood to reach ...
What is patent ductus arteriosus?
Patent ductus arteriosus – an open passageway between the pulmonary artery and the aorta. Normally, this passageway closes on its own within a few hours of birth, but when it does not, surgery or an outpatient catheter-based procedure is needed to close the opening. Other causes of pulmonary artery stenosis can include: other syndromes ...
How is a stainless steel balloon expandable stent placed?
Stent placement is accomplished by positioning the stent across the narrowed segment of the artery. The stent is mounted on a balloon angioplasty catheter and covered with a sheath as it is moved into position. The sheath then is withdrawn off the stent-balloon angioplasty assembly and the balloon is inflated to its recommended pressure, expanding the stent and anchoring it in place.
What is pulmonary stenosis?
Pulmonary stenosis is relatively common and accounts for about 10% of heart defects diagnosed during childhood. It can occur in children with otherwise normal hearts or along with other congenital heart defects such as atrial septal defect or Tetralogy of Fallot.
What are the effects of this problem on my child's health?
The health effects of pulmonary stenosis are related to the severity of the narrowing and the presence of other heart defects. The severity of narrowing is measured as the pressure difference across the affected area. The higher the number, the greater degree of narrowing and the harder the right heart has to work to pump blood to the lungs.
How is this problem diagnosed?
Clinical features: Symptoms are related to the degree of narrowing and usually develop slowly over time. Possible symptoms include shortness of breath with exercise and low stamina. Critical pulmonary stenosis in the newborn can cause blueness of the lips (a condition called cyanosis) and/or congestive heart failure.
How is the problem treated?
Treatment options for pulmonary stenosis include open-heart surgery or balloon angioplasty. The primary indication for treatment is the degree of narrowing and treatment is timed to prevent damage to the right heart.
Clinics
Care and services for patients with this problem are provided in the Congenital Heart and Cardiovascular Surgery clinics at the University of Michigan Medical Center in Ann Arbor.
When does pulmonary stenosis occur?
Pulmonary stenosis occurs when the pulmonary valve does not form correctly. This happens in the first 8 weeks of fetal development. We don’t know exactly why. Most of the time it occurs by chance.
What is the most common type of pulmonary stenosis?
Pulmonary stenosis is classified according to location and severity of the defect. There are 3 types: Valvar pulmonary stenosis is the most common. In this, the pulmonary valve is dome-shaped and the opening is narrow. The leaflets are fused together.
What happens if the right ventricle is blocked?
This might cause arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), loss of energy and fluid retention. If the pressure in the right heart is high enough, unoxygenated or “blue” blood can cross over into the left atrium.
What is a leak in the pulmonary valve after surgery?
After surgery, there is the possibility of a leak developing in the pulmonary valve. This is called pulmonary insufficiency (PI). It means that blood being pumped from the right ventricle into the pulmonary artery leaks back into the right ventricle. When this happens, the right ventricle has to work harder.
What test is used to diagnose pulmonary stenosis?
If you develop any of the following symptoms, you should contact your adult congenital heart disease (ACHD) cardiologist for evaluation: The most common diagnostic test used to confirm pulmonary stenosis is an echocardiogram. Cardiac MRI is becoming more important.
What percentage of CHD is pulmonary stenosis?
Pulmonary stenosis is a common form of congenital heart disease (CHD). It occurs in 7-10 percent of all CHD. What happens in pulmonary stenosis?
What is it called when the muscle under the pulmonary valve is thickened?
When the muscle under the pulmonary valve is thickened, it is called subvalvar pulmonary stenosis. This is caused by additional muscle bundles in the right ventricle. Supravalvar stenosis occurs when there is narrowing in the pulmonary artery above the pulmonary valve. There can be one or more than one areas of narrowing.
What is pulmonary stenosis?
A stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of an area in the body.
What causes pulmonar stenosis?
Pulmonary stenosis is usually caused by abnormal development of the heart during the first few months of pregnancy. This heart defect usually occurs at random and the exact cause is unknown. Pulmonary stenosis is not anyone’s fault.
What are the symptoms of pulmonary stenosis?
Infants and children often do not have any symptoms because the defect is mild. In some cases, your child may have a heart murmur.
Appointments and Referrals
Request an appointment or second opinion, refer a patient, find a doctor or view test results with MGHfC's secure online services.
What causes a baby to have pulmonary stenosis?
In most cases, the cause isn't known. It's a common type of heart defect. Babies born to mothers who had rubella (German measles) during pregnancy were more likely to develop pulmonary stenosis along with deafness and patent ductus arteriosus. Some patients can have other heart defects along with PS.
What is a thickened or fused heart valve?
A thickened or fused heart valve that does not fully open. The pulmonary valve allows blood to flow out of the heart, into the pulmonary artery and then to the lungs.
How to relieve obstruction in cardiac catheter?
In most children the obstruction can be relieved during cardiac catheterization by balloon valvuloplasty. In this procedure, a special tool, a catheter containing a balloon, is placed across the pulmonary valve. The balloon is inflated for a short time to stretch open the valve. Some children may need surgery.
Do you need antibiotics for pulmonary valve replacement?
Children who have had pulmonary valve replacement will need to receive antibiotics before certain dental procedures. See the section on Endocarditis for more information. Congenital Heart Defect ID sheet.
Can pulmonary valves be made normal?
The pulmonary valve can be treated to improve the obstruction and leak, but the valve can't be made normal. Treatment is needed when the pressure in the right ventricle is high (even though there may be no symptoms). In most children the obstruction can be relieved during cardiac catheterization by balloon valvuloplasty.
What is pulmonary stenosis in children?
Pulmonary stenosis is a birth defect of the heart (congenital). It can happen when the pulmonary valve doesn't develop as it should during the first 8 weeks of pregnancy. The pulmonary valve connects the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery. It normally has 3 flaps (leaflets) that work like a one-way door. This means they allow blood to flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery, but not backward from the pulmonary artery to the right ventricle.
What are the symptoms of pulmonary stenosis in a child?
Some children with pulmonary stenosis do not have symptoms. The more severe the stenosis, the more likely the child is to have symptoms. The most common symptoms may include:
How is pulmonary stenosis diagnosed in a child?
The healthcare provider will ask about your child symptoms and health history. He or she will give your child a physical exam. The provider will listen to your child's heart and lungs with a stethoscope. The provider may hear an abnormal heart sound (heart murmur). He or she may also find other signs or symptoms. The provider may refer your child to a pediatric cardiologist. This is a doctor with special training to treat heart problems in children.
What are the possible complications of pulmonary stenosis in a child?
In time, the right ventricle becomes enlarged and is no longer able to handle the extra work. It fails to pump well (heart failure). Another complication can be an abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia).
How can I help my child live with pulmonary stenosis?
The outlook for children with pulmonary stenosis is usually excellent. For a period of time, your child's cardiologist may recommend your child take antibiotics to prevent infection of the heart lining and valves (bacterial endocarditis). Your child may need to take them before medical and dental procedures.
What is the function of the pulmonary valve?
The pulmonary valve connects the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery. It normally has 3 flaps (leaflets) that work like a one-way door. This means they allow blood to flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery, but not backward from the pulmonary artery to the right ventricle.
Which stenosis makes it hard for the blood to flow from the right ventricle to the lungs?
Pulmonary stenosis makes it hard for the blood to flow from the right ventricle to the lungs.
What Is Pulmonary Stenosis?
- Pulmonary valve stenosis signs and symptoms vary, depending on how much blood flow is blocked. Some people with mild pulmonary stenosis don't have symptoms. Those with more-severe pulmonary stenosis may first notice symptoms while exercising. Pulmonary valve stenos…
What Are The Effects of This Problem on My Child's Health?
How Is This Problem Diagnosed?
How Is The Problem Treated?
Clinics