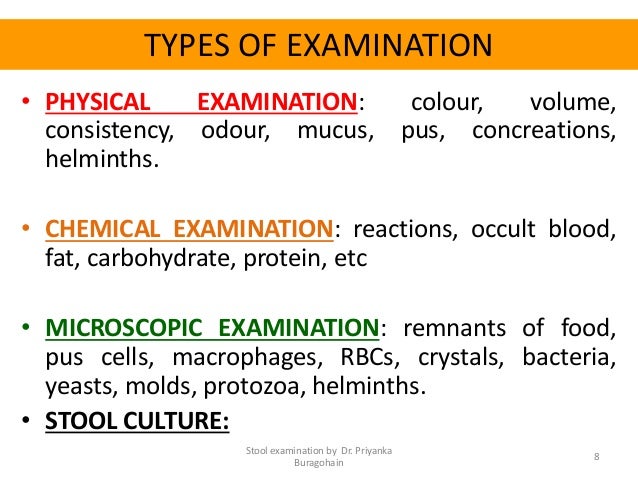
Common Causes
If there are more than 10 pus cells per each high power field it indicates infection. Sputum is referred to the secretions of lower respiratory tract (bronchi & lungs). Increased pus cells in sputum would mean that the infection is in lower repiratory tract.
Related Conditions
Pus in Sputum Associated with Disease-prone Bacteria in Bronchiectasis. Clinically, sputum purulence has been important in reflecting the intensity of inflammation and infection of the airways in these patients, and purulence is also usually associated with the presence of a pathogen.
What is the meaning of high pus cells in sputum?
As a general rule, sputum is dark green in the early stages of an infection and gradually lightens as the infection improves. It is the presence of an enzyme called myeloperoxidase that gives the sputum its green color, during an infection.
What does pus in sputum mean in bronchiectasis?
Sputum is a mixture of saliva and mucus that you cough up from your respiratory tract. It’s usually colored and thick in consistency, especially when you have an infection in your lungs. Plain saliva comes from your mouth and is usually clear.
What color is sputum in early stages of infection?
What is sputum made of?

What does pus cells in sputum mean?
Purulent sputum contains pus, composed of white blood cells, cellular debris, dead tissue, serous fluid, and viscous liquid (mucus). Purulent sputum is typically yellow or green. It is seen in cases of pneumonia, bronchiectasis, lung abscess, or an advanced stage of bronchitis.
How many pus cells are found in normal sputum?
The quality of sputum samples is determined by the minimum number of squamous epithelial cells and polymorphonuclear leukocytes per low power field. An acceptable specimen has more than 25 leukocytes and fewer than 10 epithelial cells per low power field.
What is pus cells?
Pus is a whitish-yellow, yellow, or brown-yellow protein-rich fluid called liquor puris that accumulates at the site of an infection. It consists of a buildup of dead, white blood cells that form when the body's immune system responds to the infection.
Does sputum mean infection?
Having green, yellow, or thickened phlegm does not always indicate the presence of an infection. And if there is an infection, the color of the phlegm does not determine whether a virus, bacterium, or pathogen has caused it. Simple allergies can also cause changes in the color of the mucus.
Can sputum test detect pneumonia?
A sputum test can diagnose: Bronchitis. Lung abscess. Pneumonia.
How do you read a sputum report?
Sputum CultureClear. This usually means no disease is present, but large amounts of clear sputum may be a sign of lung disease.White or gray. This may also be normal, but increased amounts may mean lung disease.Dark yellow or green. This often means a bacterial infection, such as pneumonia. ... Brown. ... Pink. ... Red.
What if pus cells are high?
Increased number of pus cells may reveal some destructive or healing process in the urinary tract, anywhere from kidney to the bladder. It usually is taken as indicative of an infection. Acute infections are most common cause of increased pus cells and get back to normal after couple of days of treatment.
Can pus cells be cured?
Pus is a common and normal byproduct of your body's natural response to infections. Minor infections, especially on the surface of your skin, usually heal on their own without treatment. More serious infections usually need medical treatment, such as a drainage tube or antibiotics.
What is pus cells normal range?
The normal range of pus cells in urine is 0-5/hpf , however up to 10 pus cells may be present without any definite infection.
What happens if sputum test is positive?
A sample of sputum is added to a substance that promotes the growth of bacteria. If no bacteria grow, the culture is negative. If bacteria grow, the culture is positive. If TB bacteria grow, then the person has tuberculosis.
What color sputum is pneumonia?
With pneumonia, you may cough up phlegm that is yellow, green, or sometimes bloody. Your symptoms will vary based on the type of pneumonia you have. Cough, fever, chills, and shortness of breath are common symptoms with all types of pneumonia.
What colour sputum is normal?
Clear sputum: Clear sputum is usually normal, although it may be increased in some lung diseases. White or gray sputum: White or grayish tinged sputum can also be normal, but may be present in increased amounts with some lung diseases or precede other color changes associated with other conditions.
What is the normal range of pus cells?
The normal range of pus cells in urine is 0-5/hpf , however up to 10 pus cells may be present without any definite infection.
What if pus cells are 6 8 HPF?
The normal range of pus cells in the urine is 0-5. Since the report suggests pus cells of 8-10 and bacteria is present, it is suggestive of urinary tract infection(UTI).
What if pus cells are 20/25 HPF?
I think you mean 20-25 pus cells/hpf (high power field of microscope), the usual term, and not %. Normal numbers of pus cells are up to 5 in males and may be up to 10 in females. The presence of pus cells in urine is also called pyuria, and is defined as >10 pus cells / microlitre of urine.
What is the meaning of pus cells 4 6 HPF?
Pyuria is significant if there are more than 4 pus cells/HPF in a centrifuged urine sample. Presence of pyuria in presence of lower urinary tract symptoms and positive nitrite accompanied by bacteria is highly suggestive of urinary tract infection.
Why is sputum produced?
Sputum is produced when a person’s lungs are diseased or damaged. Sputum is not saliva but the thick mucus – sometimes called phlegm – which is coughed up from the lungs. The body produces mucus to keep the thin, delicate tissues of the respiratory tract moist so that small particles of foreign matter that may pose a threat can be trapped ...
What is sputum in coughing?
Sputum is a type of mucus that may be expelled when coughing. There are many different reasons for the body to produce excess sputum. Below is a list of some of these causes, along with how the sputum may appear.
Why is my sputum yellow?
Some infections may cause sputum to be yellow, gray, or rusty colored.
What is the body's response to excess mucus?
Sometimes, such as when there is an infection in the lungs, an excess of mucus is produced. The body attempts to get rid of this excess by coughing it up as sputum.
When to take sputum samples for AFB?
A sputum sample will usually be collected first thing in the morning. Depending on the infection in question, up to three more samples may be taken on the following days.
Is sputum an indication of RTI?
When to see a doctor. Share on Pinterest. Sputum may be an indication of an RTI, which in some cases will require medical attention. Anyone who suspects they have TB should seek medical attention and get treatment. If someone thinks that they may have pneumonia, they should also speak to a doctor.
What causes a white frothy sputum in a child's cough?
Mucus production: The cause of white frothy sputum with cough is due to mucus production in the lungs, nose, and sinus. This is the way our immune system gets rid of un... Read More
Does cough and colds can be cause of sputum?
Sputum: Mucus production is normal. Excessive mucus production can be triggered by allergies, irritants and infections (viral, bacteria). Cough is frequently... Read More
What is the predominant inflammatory cell present in sputum?
The predominant inflammatory cell present in sputum is the neutrophil. Increased sputum eosinophilia is seen in asthmatic individuals compared with healthy subjects ( Fig. 16-3 ). Sputum eosinophilia in steroid-naïve asthmatic individuals is generally suggestive of a steroid-responsive process, and a marked reduction in eosinophil counts is typically observed after treatment with corticosteroids. Some studies have targeted sputum eosinophil levels to adjust inhaled corticosteroid dose with significant reductions in asthma exacerbations and improvement in lung functions. In these studies, patients without eosinophilia were able to reduce the dose of inhaled steroid without deterioration in lung function. 10,11
What is sputum production?
Sputum production is a common complaint in patients with inflammatory disorders of the airways, like asthma, cystic fibrosis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Clinically, sputum collection for evaluation of pulmonary infections is widely used. The routine use of sputum for analysis of inflammatory markers is limited by variability in methods for sample collection and processing. Sputum induction is accomplished by administration of either normal or hypertonic saline via nebulization. Subjects are typically treated with short-acting beta-agonists before sputum induction to reduce the chances for bronchoconstriction. Monitoring of pulmonary functions during sputum induction is also recommended, either with periodic spirometry or peak flow measurements. If the patient's oxygenation is marginal before initiation of the protocol, continuous monitoring with pulse oximetry should also be considered.
How long can expectorated sputum be stored?
Once expectorated sputum should be processed within 2 h. There is evidence that sputum can be stored for up to 9 h in a refrigerator at 4 o C or that sputum can be snap frozen for longer without affecting cell counts [9], although experience with these techniques is limited. The whole expectorate or selected sputum plugs can be processed. The latter approach has the advantage of producing better quality cytospins and more repeatable differential cell counts [10]. A common method used to process induced sputum is outlined in Box 42.2. The total cell count, cell viability and squamous cell contamination are assessed using a hemocytometer. Differential cell counts are determined by counting 400 leukocytes on an appropriately stained cytospin. Other biomarkers can also be measured in the sputum supernatant. Some of the molecular markers of airway inflammation that have been successfully measured in sputum are shown in Table 42.2.
How is sputum induction accomplished?
Sputum induction is accomplished by administration of either normal or hypertonic saline via nebulization. Subjects are typically treated with short-acting beta-agonists before sputum induction to reduce the chances for bronchoconstriction.
How is sputum used in proteomics?
Sputum can be used to study proteomics of the upper respiratory system. The collection of sputum is noninvasive and fairly straightforward, although, for proteomic studies, the protocol is slightly more rigorous than one that would be prescribed by a physician. It involves first washing out the mouth with water to remove any contaminants in the oral cavity. To induce expectoration, a sterile hypertonic saline aerosol is inhaled for a set period of time. After expelling saliva, the patients are then asked to cough at 2-min intervals, at which time the sputum is collected. The sample is then mixed with an equal volume of dithiothreitol to enhance cell dispersal from the surrounding mucus before it is centrifuged at 16,000×g for 5 min. Sputum samples can be stored at −70 °C before analysis. 77
What is a sputum gram?
Sputum Gram's stain and culture can be performed noninvasively and are inexpensive diagnostic tests. A sputum Gram's stain specimen is considered satisfactory for interpretation when the neutrophil count is >25 per low-power field and <10 epithelial cells. There is some controversy regarding how the results of a sputum Gram's stain should influence clinical practice. The ATS recommends that this test be used to broaden antibiotic therapy to treat unsuspected organisms not covered by the usual empiric regimen. Conversely, the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) guidelines suggest that empiric antimicrobial therapy be narrowed based on sputum Gram's stain findings. Keep in mind the diagnostic limitations of sputum Gram's stain and culture, including the inability to visualize atypical organisms, contamination by oral flora, and the difficulty encountered by some patients to provide adequate specimens.
When should expectorated sputum be collected?
Expectorated sputum specimen should be collected early in the morning on three occasions. The wide-mouthed, sterile, plastic container (wax free) with a tight fitting cap containing the sputum specimen should be immediately transported to the laboratory or held at 39.2°F (4°C) until processed.
What is a sputum smear microscopy?
Sputum smear microscopy is the initial step taken in laboratory sputum analysis. It is a fast and inexpensive technique, precisely, in resource-limited settings. Gram stain is used to differentiate bacteria into two broad groups (gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms). The Gram stain is the first staining technique performed in preliminary bacterial identification, which helps determine if there is an adequate amount of pathogens in the culture and make a definitive diagnosis. It is also crucial because it can address antibiotic therapy more specifically. With the Gram stain, the bacterial species are distinguished into gram-positive and gram-negative groups by the differences of cell walls' physical and chemical properties. Some bacteria have a thick peptidoglycan layer cell wall stained with crystal violet (gram-positive).
Why is sputum important in medicine?
The sputum is examined grossly and microscopically to aid medical diagnosis. The sputum contains various cells and molecular compounds such as soluble lipids and proteins. Its analysis is crucial in medicine. The sputum analysis involves an analytical approach to investigate the cellular and acellular components expelled from the patient's upper respiratory tract. This procedure is essential in the evaluation and management of lower respiratory infections or other longstanding health conditions.[1] Clinically, sputum molecular biomarkers or gene sequencing of the microorganisms have increased medicine accuracy and represent a milestone in the current evaluations of the algorithms running for precision medicine.
Why is it important to collect a sputum sample?
Collecting a good quality sputum sample is the first step for getting an , the pathogens identified from sputum culture do not always originate from lower respiratory tract infections because they may be part of contaminant sites or preexisting in the oral flora. Thus, standard microbiological procedures for organisms' isolation and identification are critical for the sputum quality assessment (QA).
Why do we do sputum culture?
Clinical diagnostic sputum tests aim to detect the causes of lower respiratory tract infections and some other diseases. It also provides an efficacious tool for monitoring the effectiveness of clinical treatment. Sputum culture is the most common test needed to be performed when the patient has pneumonia. It is used to identify the bacteria or fungi causing the airways or lung infection.
How is sputum induction used?
Sputum inductionis a procedure used to collect adequate lower respiratory secretions from patients who have trouble producing sputum to aid the diagnosis of TB. In particular, patients with suspicion of miliary tuberculosis and/or tuberculous pleural effusion are often targeted using this adjuvant procedure. In such settings, the patient inhales nebulized hypertonic saline solution to liquefy airway secretions. This solution stimulates the patient coughing and promotes expectoration of airway secretions. The medical professionals prepare a 20 ml 3% hypertonic saline solution and inject it into the nebulizer cup filled with water. Similar to the non-adjuvant procedure, the patients are always required to wash their mouth thoroughly.
What is the fluid that is secreted by the airways?
Mucus is the fluid secreted by the airways (also known as bronchial and windpipes) and lungs. In the setting of an infection or a longstanding health condition, the term of phlegm is also used. The mixture of saliva and mucus specifically coughed up from the respiratory tract, often either following an infection or an irritation of the mucosa, is precisely labeled "sputum." The term phlegm arises from the Greek word "ϕλ?γμ?" which in the ancient books of medicine was used to label humor caused by heat.
How to identify a suspected organism?
To identify a suspected organism, at first, the bacteria will be inoculated in a series of differential media. Then use different indicators to observe the specific end products of metabolism inside of the medium.
What is a sputum gram?
A sputum Gram’s stain is a laboratory test that allows your doctor to diagnose a bacterial infection in your respiratory tract. They may order it if you have symptoms of a respiratory infection that might be caused by bacteria. It’s the most common preliminary test beyond a chest X-ray for pneumonia and other respiratory infections, ...
What does it mean when a sputum test shows a Gram positive?
If the test results from your sputum Gram’s stain are abnormal, it means that bacteria and white blood cells have been detected. The bacteria found will be Gram-positive or Gram-negative. Common Gram-positive bacteria detected by the test include: Staphylococcus. Streptococcus.
What does it mean when you have a normal sputum test?
A normal test result means that few white blood cells and no bacteria have been found in your sputum sample, and your symptoms may be due to other causes.
How long can you keep sputum in the refrigerator?
You can refrigerate it for up to 24 hours if needed, but you shouldn’t freeze it or store it at room temperature. If you can’t cough up enough sputum, try breathing steam in from boiling water, or take a hot steamy shower. The sputum sample must come from deep inside your lungs for the test to be accurate.
What to do if you can't cough up enough sputum?
If you still can’t cough up enough sputum, your doctor will likely do a bronchoscopy to collect sputum directly from your lungs.
Why do you get a sputum stain?
Your doctor may order a sputum Gram’s stain to help identify the cause of pneumonia. This is an infection that can affect your lower respiratory tract. It’s often caused by microorganisms, like bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
What is the stain used to analyze sputum?
At the laboratory, a technician will analyze your sputum sample using a sputum Gram’s stain.
